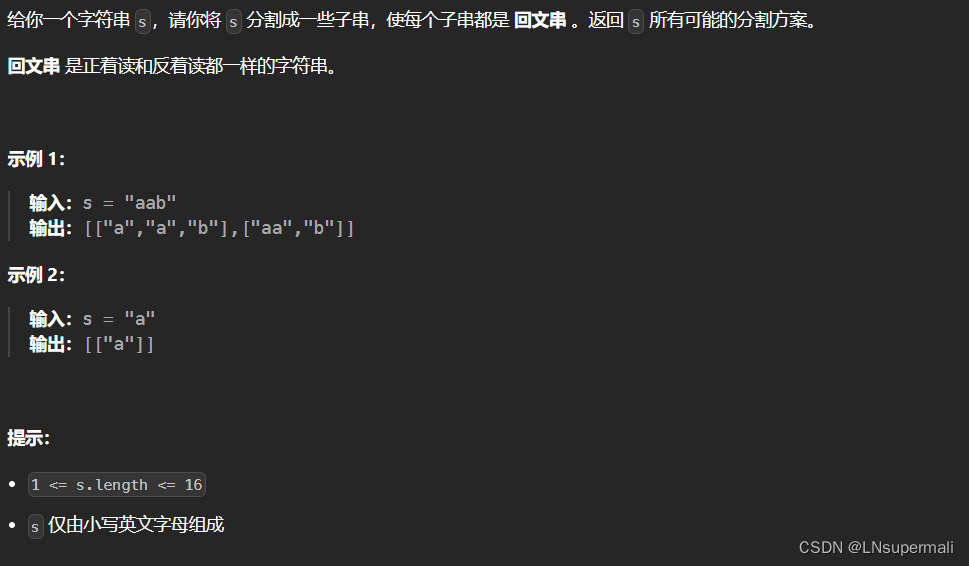
力扣131. 分割回文串(java 回溯法)
Problem: 131. 分割回文串
题目描述
思路
题目要求我们给出所有的回文子字符串,而涉及到穷举我们可以利用回溯来解决,另外我们也可以发现问题中涉及到元素存在重复但不可复用的特性,因此我们可以类似于利用回溯求解组合问题的套路求解,具体的:
我们以字符串中的每一个字符作为决策阶段,在回溯调用的过程中,每次进行回文判断,若判断当前决策路径上的子字符串为回文字符串,则将其添加到决策路径,并最终当决策阶段等于字符串的长度时将决策路径添加到结果集合中
解题方法
1.定义二维结果集result,决策路径path
2.编写判断回文字符串函数
3.编写调用回溯函数,初始决策阶段为03.1 若当前的决策路径等于字符串的长度,则将当前的决策路径添加到结果集result中并返回
3.2 for循环,令循环初始位置i等于当前的决策阶段(假设为k),并判断,若i到k位置的子字符串为回文串则将其添加到当前的决策路径,并开始下一阶段的递归调用,最后恢复当前决策路径的状态
复杂度
时间复杂度:
最坏时间复杂度: O ( n × 2 n ) O(n \times 2^n) O(n×2n)
空间复杂度:
递归开辟的栈空间 O ( 2 n ) O(2^n) O(2n)
Code
class Solution {
//Result list
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
//Decision Path
List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* Gets all return substrings
*
* @param s Given string
* @return List<List < String>>
*/
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
backtrack(s, 0);
return result;
}
/**
* Get all backtrace substrings using backtrace
*
* @param s Given string
* @param k Decision stage
*/
public void backtrack(String s, int k) {
//End condition
if (k == s.length()) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int end = k; end < s.length(); ++end) {
//
if (isPalindrome(s, k, end)) {
path.add(s.substring(k, end + 1));
backtrack(s, end + 1);
//Recover the current Decision Path
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
/**
* Determines whether a string is a palindrome string
*
* @param s Given string
* @param start The start position of given string
* @param end The end position of given string
* @return boolean
*/
private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int start, int end) {
while (start < end) {
if (s.charAt(start) != s.charAt(end)) {
return false;
}
start++;
end--;
}
return true;
}
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 一文搞懂SiLM824x系列SiLM8243BBCL-DG 双通道死区可编程隔离驱动 主要特性与应用 让技术变得更有价值
- 【C++PCL】点云处理基于法向量夹角的欧式聚类分割
- Java se的语言特征之多态
- 【鸿蒙开发】第八章 ArkTS语言UI范式-基础语法(二)
- 操作系统——I/O控制器
- PMP培训机构哪家好?
- 虾皮入驻需要营业执照吗
- 文章解读与仿真程序复现思路——电网技术EI\CSCD\北大核心《含共享储能的数据中心微网群分布式优化调度》
- Java和SpringBoot学习路线图
- 少儿编程 中国电子学会图形化编程2022年9月等级考试Scratch二级真题解析(选择题、判断题)