python解决android版数美滑块验证码,30分钟快速解决
发布时间:2024年01月05日
话不多说点我【+qq】
先看滑块 右滑拼图 我们用opencv就可以了,要想提高识别率,就取对接图片打码平台

![]()
opencv代码,注释借鉴于网络
import cv2
import numpy as np
from io import BytesIO
def get_distance3(fg_resp, bg_resp):
"""计算滑动距离"""
# 1. 将背景图、滑块图的二进制响应体转为BytesIO对象
bg = BytesIO(bg_resp)
fg = BytesIO(fg_resp)
# 2. 使用imdecode进行图像解码,转成OpenCV中的Mat对象
target = cv2.imdecode(np.asarray(bytearray(fg.read()), dtype=np.uint8), 0)
template = cv2.imdecode(np.asarray(bytearray(bg.read()), dtype=np.uint8), 0)
# 3. 使用matchTemplate方法进行模板匹配,返回背景图中与滑块的位置匹配值数组
result = cv2.matchTemplate(target, template, cv2.TM_CCORR_NORMED)
# 4. 使用numpy中的unravel_index函数获取result中位置匹配值最大的索引位置,既是滑动的距离
_, distance = np.unravel_index(result.argmax(), result.shape)
return distance默认图片是600*300
所以计算出来的距离需要做操作(距离/600*391)
为什么是391? 因为我的手机设备把原图600*300的图缩放成391*195
你需要根据你的手机设备进行修改
网上去找一个生成鼠标轨迹的代码,直接用
def get_random_tracks(distance):
"""生成轨迹"""
tracks = []
y = 0
v = 0
t = 1
current = 0
mid = distance * 3 / 4
exceed = 80
z = t
tracks.append([0, 0, 1])
while current < (distance + exceed):
if current < mid / 2:
a = 15
elif current < mid:
a = 20
else:
a = -30
a /= 2
v0 = v
s = v0 * t + 0.5 * a * (t * t)
current += int(s)
v = v0 + a * t
y += random.randint(-5, 5)
z += 100 + random.randint(0, 10)
tracks.append([min(current, (distance + exceed)), y, z])
while exceed > 0:
exceed -= random.randint(0, 5)
y += random.randint(-5, 5)
z += 100 + random.randint(0, 10)
tracks.append([min(current, (distance + exceed)), y, z])
return tracks
解密的是des的 ,随便找个des加密代码就行
提交参数
(end_time-start_time,对应密钥)
(x/391,对应密钥)
(鼠标轨迹数组,对应密钥)
加密提交就行
结果,opencv成功概率还行 10个7次都过了
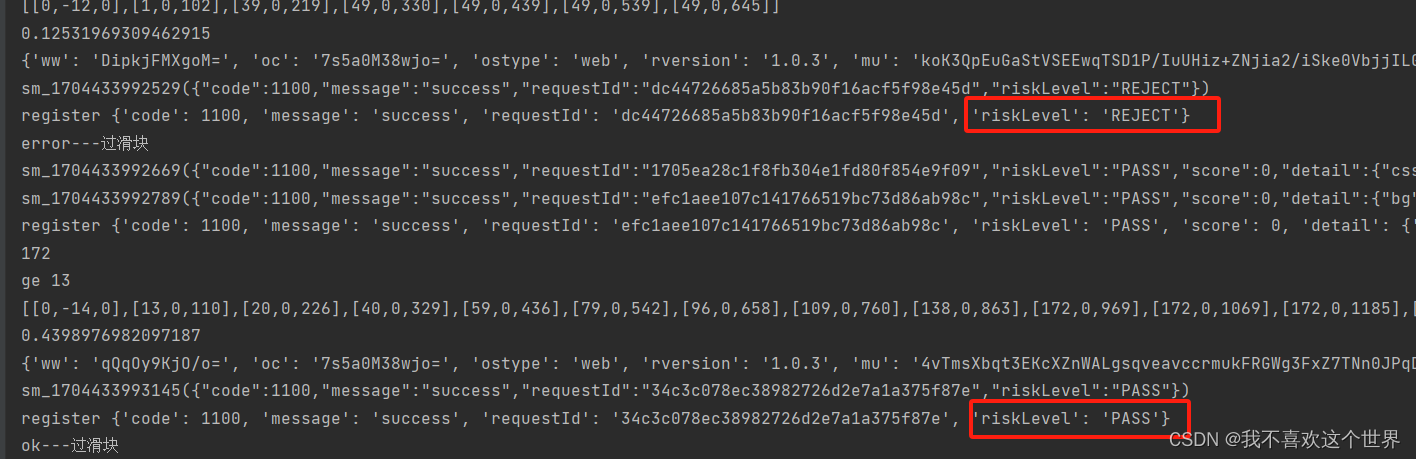
因为写多了不让发布
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_38124502/article/details/135407974
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- springboot(ssm小学生身体素质测评管理系统 学生体测平台Java系统
- 微型5G网关如何满足智能巡检机器人应用
- 真的干不过,00后整顿职场已经给我卷麻了,想离职了...
- 2024年超声波清洗机哪些比较值得入手?实用性强的超声波清洗机推荐
- 虚幻商城 蓝图汇总
- 得帆信息连续两年荣获“最佳企业级低代码”称号
- VSCode配置运行C语言项目
- 超详细解释奇异值分解(SVD)【附例题和分析】
- 【Python】tensor格式数据转为图像,并保存图像详解和示例
- 全视通-医院智能视讯系统 病房视讯系统解决方案 智能医院对讲系统信息发布系统