二叉树..
发布时间:2023年12月21日
前中后序非递归实现通用代码:
LinkedList<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode curr = root; // 代表当前节点
TreeNode pop = null; // 最近一次弹栈的元素
while (curr != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (curr != null) {
colorPrintln("前: " + curr.val, 31);
stack.push(curr); // 压入栈,为了记住回来的路
curr = curr.left;
} else {
TreeNode peek = stack.peek();
// 右子树可以不处理, 对中序来说, 要在右子树处理之前打印
if (peek.right == null) {
colorPrintln("中: " + peek.val, 36);
pop = stack.pop();
colorPrintln("后: " + pop.val, 34);
}
// 右子树处理完成, 对中序来说, 无需打印
else if (peek.right == pop) {
pop = stack.pop();
colorPrintln("后: " + pop.val, 34);
}
// 右子树待处理, 对中序来说, 要在右子树处理之前打印
else {
colorPrintln("中: " + peek.val, 36);
curr = peek.right;
}
}
}
public static void colorPrintln(String origin, int color) {
System.out.printf("\033[%dm%s\033[0m%n", color, origin);
}
1. 对称二叉树-力扣 101 题
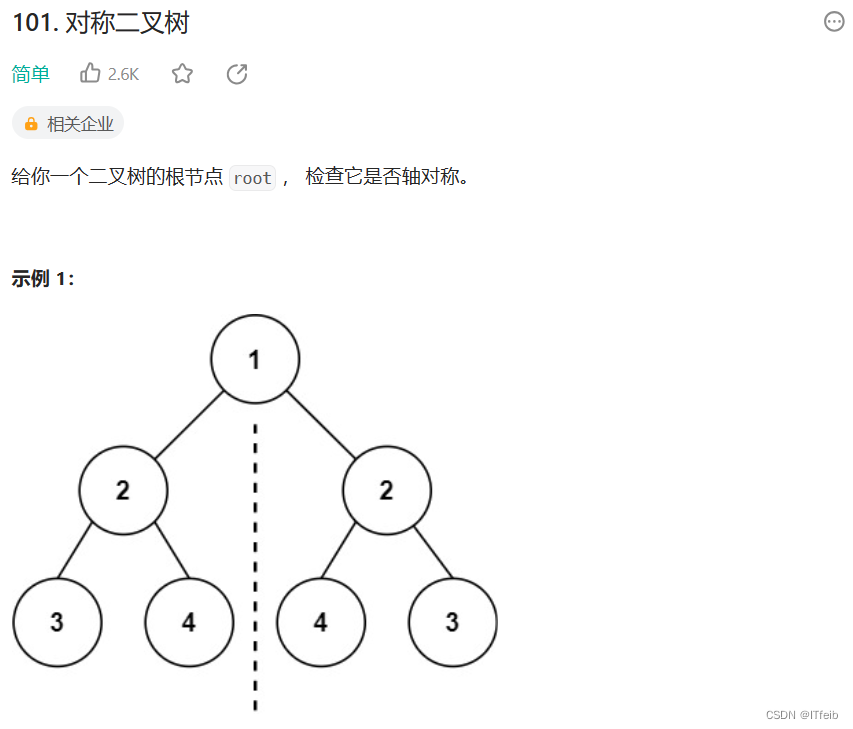
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return check(root.left, root.right);
}
public boolean check(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
// 若同时为 null
if (left == null && right == null) {
return true;
}
// 若有一个为 null (有上一轮筛选,另一个肯定不为 null)
if (left == null || right == null) {
return false;
}
if (left.val != right.val) {
return false;
}
return check(left.left, right.right) && check(left.right, right.left);
}
2. 二叉树最大深度-力扣 104 题
思路:左右根
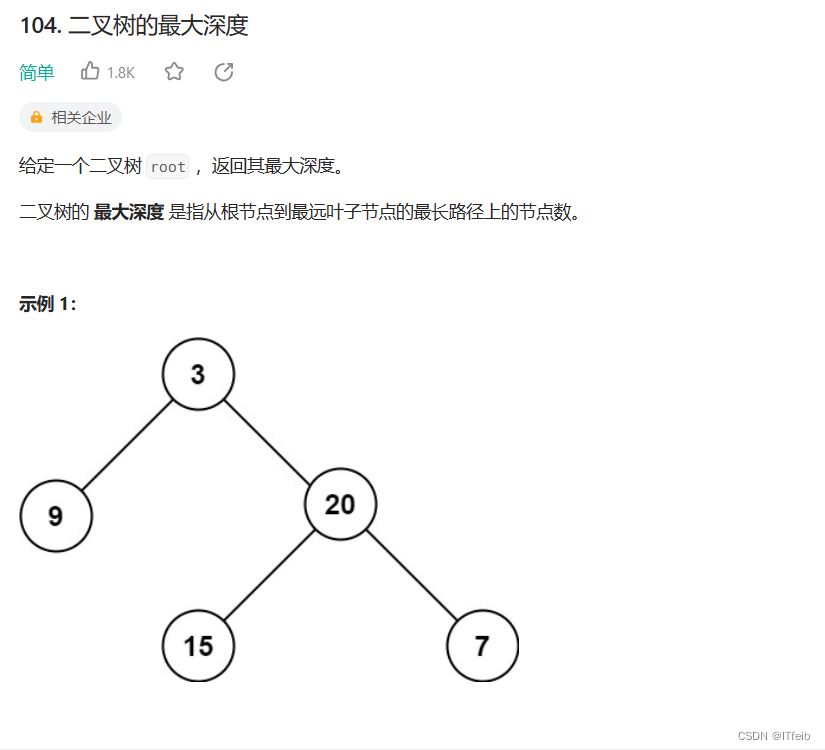
public int maxDepth(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return 0; // 非力扣题目改为返回 -1
}
int d1 = maxDepth(node.left);
int d2 = maxDepth(node.right);
return Integer.max(d1, d2) + 1;
}
非递归实现:思路:使用非递归后序遍历, 栈的最大高度即为最大深度
/*
思路:
1. 使用非递归后序遍历, 栈的最大高度即为最大深度
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode curr = root;
LinkedList<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();
int max = 0;
TreeNode pop = null;
while (curr != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (curr != null) {
stack.push(curr);
int size = stack.size();
if (size > max) {
max = size;
}
curr = curr.left;
} else {
TreeNode peek = stack.peek();
if(peek.right == null || peek.right == pop) {
pop = stack.pop();
} else {
curr = peek.right;
}
}
}
return max;
}
实现方式三:层序遍历:思路:使用层序遍历, 层数即最大深度
/*
思路:
1. 使用层序遍历, 层数即最大深度
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int level = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
level++;
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return level;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_51240148/article/details/135118927
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【数组】-Lc169-求众数(摩尔投票相抵消法)
- 【SD】loopback 回送
- [ Tool ] celery分布式任务框架基本使用
- OD Linux发行版本
- Windows下默认关闭数字键盘
- 衡兰芷若成绝响,人间不见周海媚(4k修复基于PaddleGan)
- 构建高效网络爬虫:代理IP池的建立与维护方法
- Java学校教务管理系统源码带微信小程序
- 机器学习笔记(二)使用paddlepaddle,再探波士顿房价预测
- 法大大推出“签约减碳”年度账单,引领低碳办公新风潮