mpi 计算 pi 的示例程序 MPI_Bcast MPI_Reduce
发布时间:2023年12月31日
1,原理
从 0.0 到 1.0 对 4.0/(1.0+x*x) 进行定积分,便得到了pi 的解析值;
2,代码
//pi_reduce.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <mpi.h>
double f(double);
double f(double x)
{
return (4.0/(1.0+x*x));
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int done =0, n, myid, numprocs, i;
double PI25DT = 3.141592653589793238462643;// a more accurate PI
double mypi, pi, h, sum, x;
double startwtime = 0.0, endwtime;
int namelen;
char processor_name[MPI_MAX_PROCESSOR_NAME];//[256] openmpi-4.x
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);//& & mutiple processes below:
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &numprocs);// total number of processes
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &myid);// which process I am
MPI_Get_processor_name(processor_name, &namelen);// host name and its lenth
fprintf(stdout, "Process %d of %d on %s\n", myid, numprocs, processor_name);
n = 0;
if(myid == 0)
{
fprintf(stdout, "Please give N=\n");
fflush(stdout);
scanf("%d",&n);
fprintf(stdout, "n = %d\n", n);
//n= 1000000;
startwtime = MPI_Wtime();
}
//MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);//
MPI_Bcast(&n, 1, MPI_INT, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);// broadcast n to others
//MPI_Bcast在默认情况下是阻塞调用,它会等待所有进程完成归约操作后才会继续执行。你可以使用非阻塞版本的MPI_Ireduce来进行非阻塞调用
h = 1.0/(double)n;
sum = 0.0;
for(i=myid+1; i<=n; i+=numprocs)// each process would calculate several area of rectangles
{
// n proces, N rectangle
// proc 1-st: 1, n+1, 2n+1, ..., N1; N1 is as big as possible, and N1<=N;
// proc 2-nd: 2, n+2, 2n+2, ..., N2; N2 is as big as possible, and N2<=N;
// ...
// proc n-th: n, n+n, 2n+n, ..., Nn; Nn is as big as possible, and Nn<=N;
x = h *((double)i - 0.5);// x of this time
sum += f(x);
fprintf(stdout, "Process %d of %d on %s, n=%d, mypi=%.6f, x=%7.3f, h=%7.3f, sum=%7.3f\n", myid, numprocs, processor_name, n, mypi, x, h, sum);
}
fflush(stdout);
mypi = h * sum;
//fprintf(stdout, "Process %d of %d on %s, n=%d, mypi=%.16f\n", myid, numprocs, processor_name, n, mypi);
//fflush(stdout);
//int MPI_Reduce(void* sendbuf, void* recvbuf, int count, PI_Datatype datatype, MPI_Op op, int root, MPI_Comm comm)
MPI_Reduce(&mypi, &pi, 1, MPI_DOUBLE, MPI_SUM, 0, MPI_COMM_WORLD);
//MPI_Reduce在默认情况下是阻塞调用,它会等待所有进程完成归约操作后才会继续执行。你可以使用非阻塞版本的MPI_Ireduce来进行非阻塞调用
//MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
if(myid == 0)
{
endwtime = MPI_Wtime();
printf("wall clock time = %f\n", endwtime -startwtime);
printf("pi is approximately %.16f, Error is %.16f\n", pi, fabs(pi - PI25DT));
fflush(stdout);
}
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
3,编译
#FORT := ../local/bin/mpif77
FORT := gfortran
LD_F_FLAGS := -lgfortran -L../local/lib/ -lmpi_mpifh
EXE := pi_red
CC := ../local/bin/mpicxx
all: $(EXE)
pi_red: pi_reduce.c
../local/bin/mpicc $< -o $@
jacobi: jacobi.f
$(FORT) $< -o $@ $(LD_F_FLAGS) -I../local/include
the_jacobi: the_jacobi.cpp
$(CC) $< -o $@
run_jacobi: jacobi
../local/bin/mpirun -np 4 ./jacobi
pi_reduce: pi_reduce.c
../local/bin/mpicc $< -o $@
run_pi_reduce: pi_reduce
../local/bin/mpirun -np 18 ./pi_reduce
#gcc max_name_openmpi.c -o max.out -I ../local/include/ -L ../local/lib -lmpi
#gfortran hello_ompi.f -I../local/include/ -L../local/lib/ -lmpi_mpifh -lgfortran
即:
../local/bin/mpicc? pi_reduce.c? -o? pi_red
4,运行
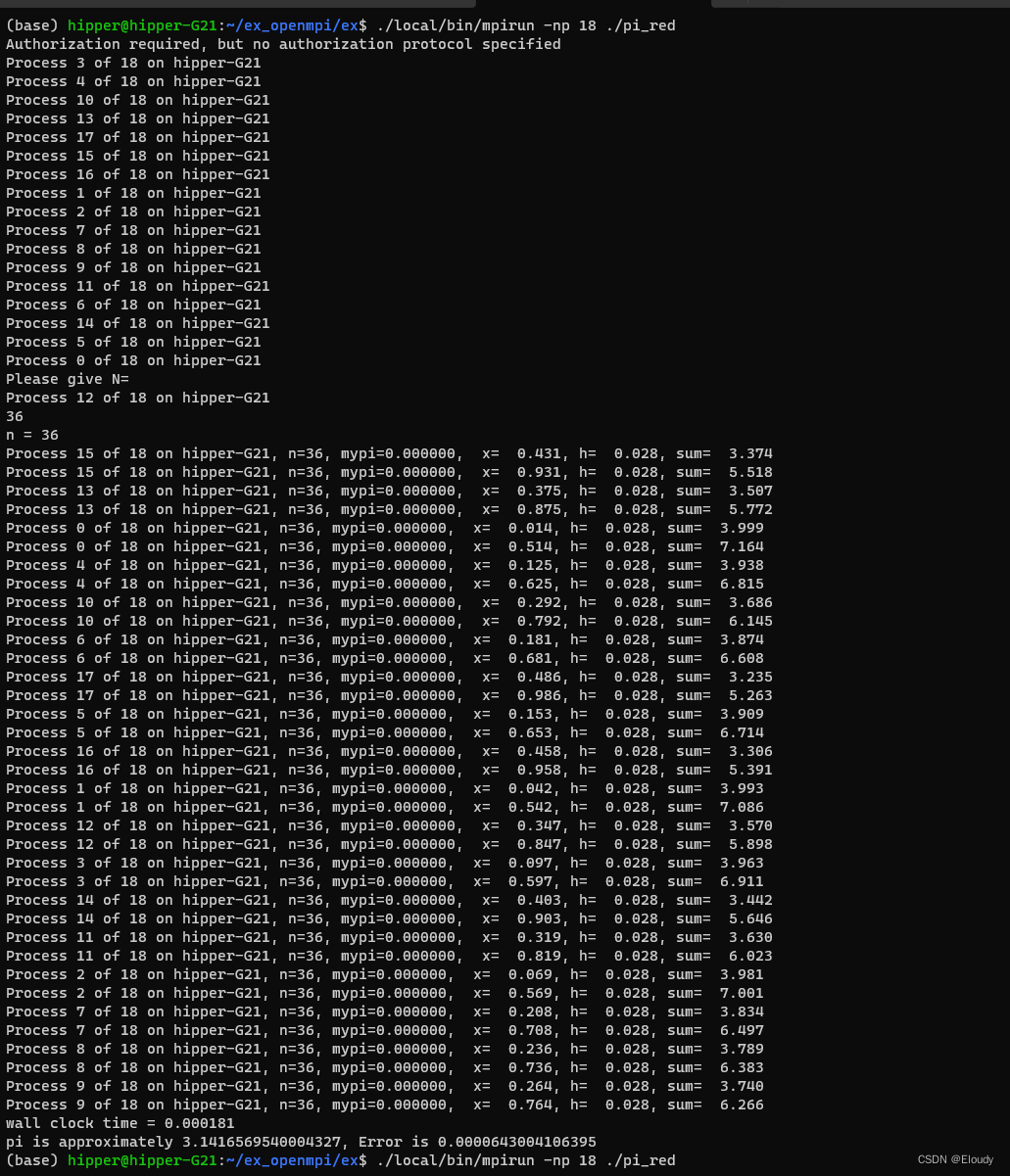
由于cpu是18个物理核心,所以使用了 18:
./local/bin/mpirun -np 18 ./pi_red需要输入n的值,这里输入了36,再大一些的任意整数都可以,理论上讲,越大越精确。
效果:
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/eloudy/article/details/135317114
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- router4j--SpringCloud动态路由利器
- TypeScript前端学习(三)
- AutoSAR(基础入门篇)4.4-Autosar_BSW的Memory功能
- Mysql主从同步和mysqldump备份
- 书生·浦语大模型实战营作业(二)
- Java 异常及处理|Error、Throwable、Exception
- 将TI的电量计Linux驱动从4.4内核移植到5.10
- HTML--CSS--盒子模型
- 【FPGA】篮球比赛计分器
- C++-友元-string字符串类