第1章 线性回归
发布时间:2024年01月06日
一、基本概念
1、线性模型

2、线性模型可以看成:单层的神经网络

输入维度:d
输出维度:1
每个箭头代表权重
一个输入层,一个输出层
单层神经网络:带权重的层为1(将权重和输入层放在一起)
3、LOSS
y:真实值
y^:估计值
平方损失:
4、训练数据
n个样本
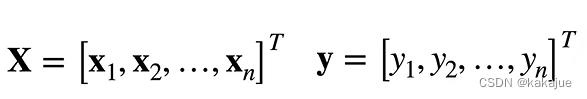
5、损失学习
训练损失
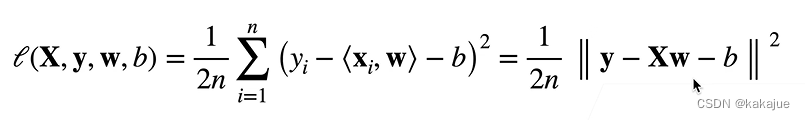
最小化损失来学习参数
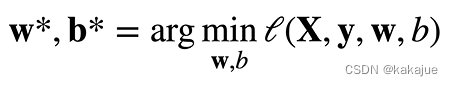
6、显示解

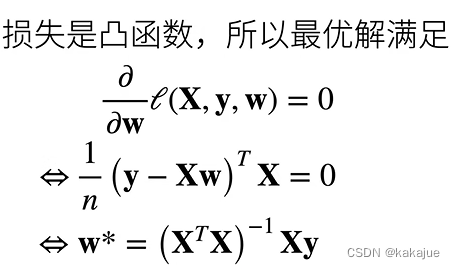
7、总结

二、优化方法
1、梯度下降


2、学习率
不能太大也不能太小
3、小批量 随机梯度下降

4、批量大小
不能太大也不能太小
5、总结

三、代码实现
1、从头开始实现
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #plt.show()
import random
import torch
from d2l import torch as d2l
# 随机生成数据集
# 权重w = 2, -3.4
# 偏差 b = -4.2
def synthetic_data(w, b, num_examples): #@save
""" y=Xw+b+噪声 """
# 均值为0,方差为1的随机数;n个样本,列数=w
X = torch.normal(0, 1, (num_examples, len(w)))
y = torch.matmul(X, w) + b
# 再加一个随机噪音
y += torch.normal(0, 0.01, y.shape)
# x和y做成一个列向量返回
return X, y.reshape((-1, 1))
# 生成训练样本
true_w = torch.tensor([2, -3.4])
true_b = 4.2
features, labels = synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, 1000)
print('features:', features[0],'\nlabel:', labels[0])
d2l.set_figsize()
d2l.plt.scatter(features[:, (1)].detach().numpy(), labels.detach().numpy(), 1)
plt.show()
def data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
num_examples = len(features)
indices = list(range(num_examples))
# 这些样本是随机读取的,没有特定的顺序
random.shuffle(indices)
for i in range(0, num_examples, batch_size):
batch_indices = torch.tensor(
indices[i: min(i + batch_size, num_examples)])
yield features[batch_indices], labels[batch_indices]
batch_size = 10
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
print(X, '\n', y)
break
# true_w = torch.tensor([2, -3.4])
# true_b = 4.2
# 初始化模型参数
w = torch.normal(0, 0.01, size=(2,1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
# 定义模型
def linreg(X, w, b): #@save
"""线性回归模型"""
return torch.matmul(X, w) + b
# 定义损失函数
def linreg(X, w, b): #@save
"""线性回归模型"""
return torch.matmul(X, w) + b
# 定义优化函数
def sgd(params, lr, batch_size): #@save
"""小批量随机梯度下降"""
with torch.no_grad():
for param in params:
param -= lr * param.grad / batch_size
param.grad.zero_()
def squared_loss(a, b):
y = (a - b) ** 2
y /= 2
return y
# 训练
lr = 0.03
num_epochs = 3
net = linreg
loss = squared_loss
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
l = loss(net(X, w, b), y) # X和y的小批量损失
# 因为l形状是(batch_size,1),而不是一个标量。l中的所有元素被加到一起,
# 并以此计算关于[w,b]的梯度
l.sum().backward()
sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size) # 使用参数的梯度更新参数
with torch.no_grad():
train_l = loss(net(features, w, b), labels)
print(f'epoch {epoch + 1}, loss {float(train_l.mean()):f}')
print(f'w的估计误差: {true_w - w.reshape(true_w.shape)}')
print(f'b的估计误差: {true_b - b}')2、简洁实现
# 1.生成数据集
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch.utils import data
from d2l import torch as d2l
true_w = torch.tensor([2, -3.4])
true_b = 4.2
features, labels = d2l.synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, 1000)
# 2.读取数据集
def load_array(data_arrays, batch_size, is_train=True): #@save
"""构造一个PyTorch数据迭代器"""
dataset = data.TensorDataset(*data_arrays)
return data.DataLoader(dataset, batch_size, shuffle=is_train)
batch_size = 10
data_iter = load_array((features, labels), batch_size)
print(next(iter(data_iter)))
# 3.定义模型
# nn是神经网络的缩写
from torch import nn
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(2, 1))
# 4.初始化模型参数
net[0].weight.data.normal_(0, 0.01)
net[0].bias.data.fill_(0)
# 5.定义损失函数
loss = nn.MSELoss()
# 6. 定义优化算法
trainer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.03)
# 7. 训练
num_epochs = 3
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in data_iter:
l = loss(net(X) ,y)
trainer.zero_grad()
l.backward()
trainer.step()
l = loss(net(features), labels)
print(f'epoch {epoch + 1}, loss {l:f}')
w = net[0].weight.data
print('w的估计误差:', true_w - w.reshape(true_w.shape))
b = net[0].bias.data
print('b的估计误差:', true_b - b)
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/fanwenjue/article/details/135422278
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 使用VS2015在win7 x64上编译调试FFmpeg(附源码和虚拟机下载)
- Fortinet【SD-WAN】& 阿里云企业网CEN混合组网解决方案,计算巢一键交付
- 详解IP安全:IPSec协议簇 | AH协议 | ESP协议 | IKE协议_ipsec esp
- LeetCode_1_简单_两数之和
- 小白向攻略简单易懂,怎么用DomoAI将手机里面的视频转换成丝滑流畅高帧数的动画
- 忆阻器芯片STELLAR权重更新算法(清华大学吴华强课题组)
- Python pip换国内源
- [Redis] Redisson实现分布式锁
- 插件分享 Chrome浏览器实现外语翻译自由
- mac安装mysql和docker