Python - 深夜数据结构与算法之 LRUCache
目录
一.引言
LRU 即 Least Recently Used 意为最近使用,它是一种局部 Cache 的缓存方法,用于存储最近使用的元素,随着 Cache 中元素的增加,LRU Cache 会逐步挪去结尾的近期未使用的元素。
二.LRU Cache 简介
1.实现特性

LRU Cache 一般由两个要素决定,大小与替换策略。
- 大小 即 Cache 的容量,如果 Cache 非常大,像内存一样,那我们直接一直存就可以了?
- 替换 由于 Cache 一般不会无限制的增加,所以达到容量时,就需要根据策略进行替换删除元素
其实现一般通过 HashMap + Double LinkedList 即 Map + 双端链表实现。
2.工作流程
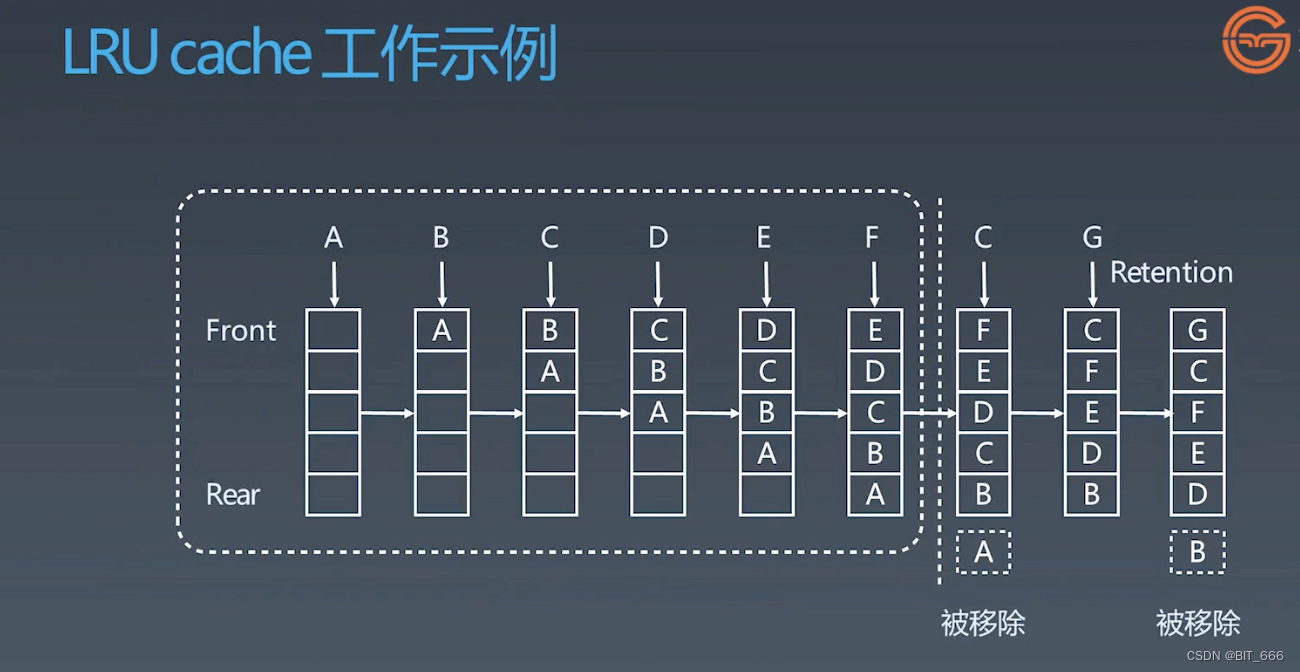
假设 Cache 的容量为 5,前面 A-E 正常记录 Cache 缓存,而当 F 插入时,根据 LRU 即最近最少使用的原则,排在最早且未被再次使用的 A 会被移出 Cache,而当 C 再次插入时,其会从 -2 的索引提到最前方,此时不涉及元素出链表,只是修改其顺序,后面以此类推。
除了 LRU 外,还有 LFU 其全称为 Least Frequently Used 代表最近使用频次最小,此时需要维护 Cache 内每个元素的使用频次,这里我们介绍 LRU,所以 LFU 就简单带过一下。完整的替换算法大家有兴趣可以 🪜 看一下 Wiki:?Cache_replacement_policies。
三.LRU Cache 实战
实现:?https://leetcode.cn/problems/lru-cache/description/

◆ 题目分析
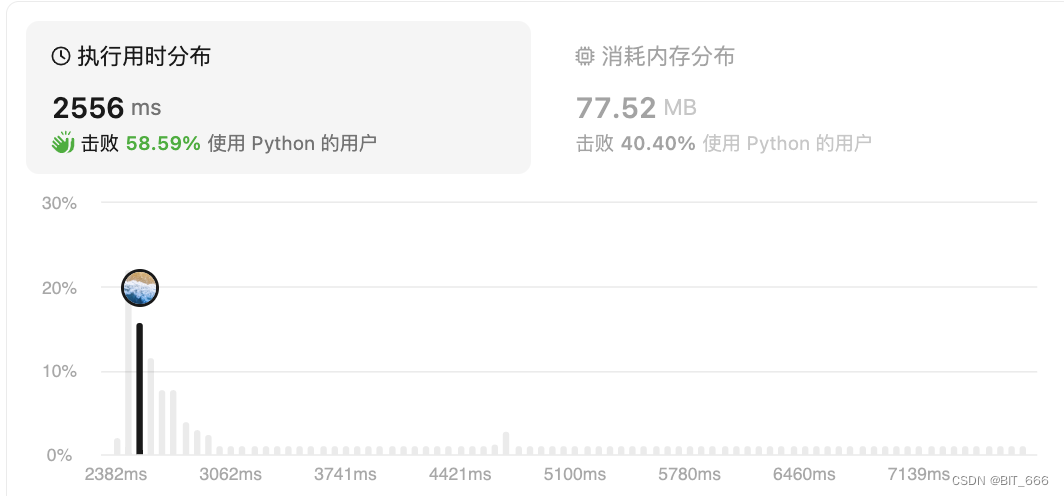
实现容量为 Capacity 的 LRU Cache,基于前面的简介,下面我们分别使用 Python 库函数和手动双端队列实现。
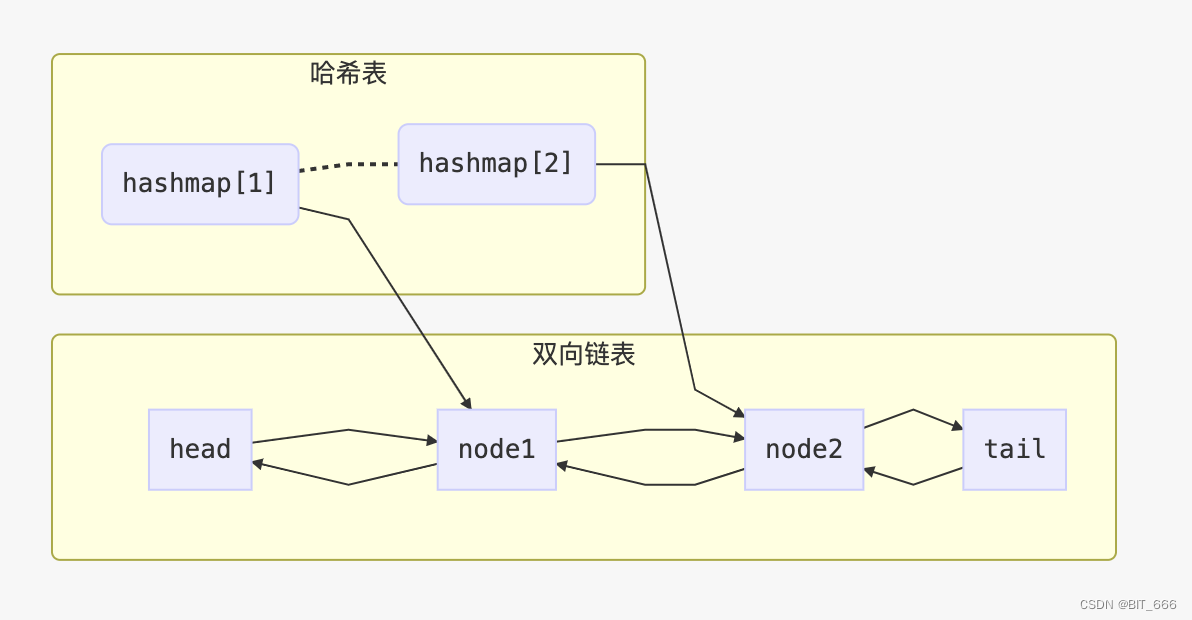
1.HashMap + ListNode
class ListNode:
# 双向链表
def __init__(self, key=None, value=None):
self.key = key
self.value = value
self.pre = None
self.next = None
class LRUCache(object):
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.capacity = capacity
self.hashmap = {}
# 新建 head/tail 节点
self.head = ListNode()
self.tail = ListNode()
# 初始化
self.head.next = self.tail
self.tail.pre = self.head
# get put 都可能需要把元素一到末尾,所以添加辅助方法
def move_node_to_end(self, key):
# 获取当前节点
node = self.hashmap[key]
# Pre -> Node -> Next => Pre <-> Next
node.pre.next = node.next
node.next.pre = node.pre
# pre -> tail => pre <-> node <-> tail
node.pre = self.tail.pre
node.next = self.tail
self.tail.pre.next = node
self.tail.pre = node
def get(self, key):
"""
:type key: int
:rtype: int
"""
# 在链表就移到末尾
if key in self.hashmap:
self.move_node_to_end(key)
res = self.hashmap.get(key, -1)
if res == -1:
return res
else:
return res.value
def put(self, key, value):
"""
:type key: int
:type value: int
:rtype: None
"""
if key in self.hashmap:
# 无需添加元素,但是需要更新 value 并移动
self.hashmap[key].value = value
self.move_node_to_end(key)
else:
cur_capacity = len(self.hashmap)
if cur_capacity == self.capacity:
self.hashmap.pop(self.head.next.key)
# 更新前面的元素前后指针
self.head.next = self.head.next.next
self.head.next.pre = self.head
# 容量支持插入新元素
new = ListNode(key, value)
self.hashmap[key] = new
new.pre = self.tail.pre
new.next = self.tail
self.tail.pre.next = new
self.tail.pre = new
# Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = LRUCache(capacity)
# param_1 = obj.get(key)
# obj.put(key,value)代码比较长,但是都是基础的双端链表增删节点的操作,大家可以画示意图查看,更加直观。
2.OrderedDict
class LRUCache(collections.OrderedDict):
def __init__(self, capacity: int):
super().__init__()
self.capacity = capacity
def get(self, key: int) -> int:
if key not in self:
return -1
self.move_to_end(key)
return self[key]
def put(self, key: int, value: int) -> None:
if key in self:
self.move_to_end(key)
self[key] = value
if len(self) > self.capacity:
self.popitem(last=False)
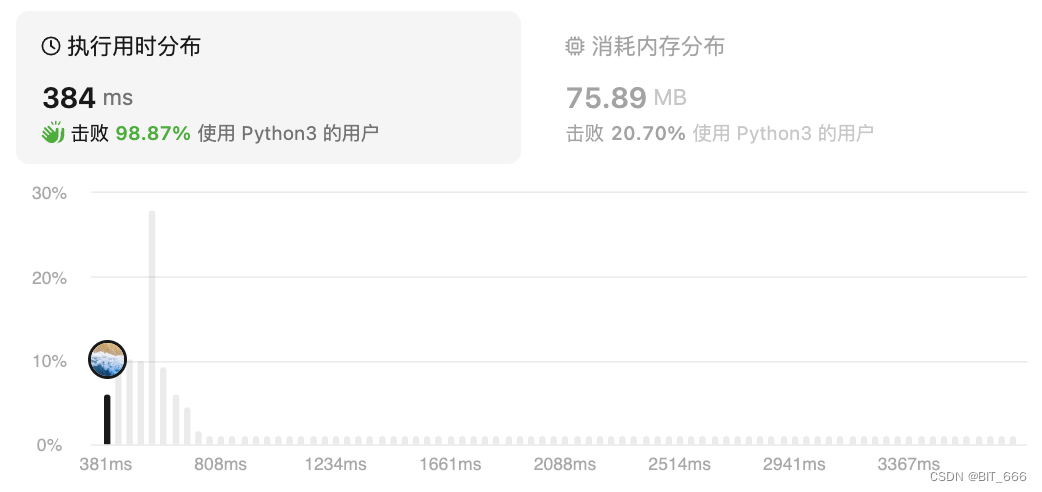
Collections 的 OrderedDict 默认包含了上面的功能,如果是在工作中可以这么调用。?
四.总结
上面介绍了 Python 中 LRU Cache 的特性与简单实现,在大数据场景下,除了 LRU Cache 外,还有基于 Time、Freq 等多元的 Cache 方案,我们可以直接调用 Google 的?guava 库,快速上手相关 Cache,提高元素搜索访问的效率。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 文件模块常用api
- 亚马逊CPC认证
- 网工工具:xshell、SecureCRT平替软件
- Ansys Lumerical | 采用一维光栅的出瞳扩展器的优化
- AtCoder ABC周赛2023 1/14 (Sun) D题题解
- 【小沐学Unity3d】3ds Max 减面工具汇总
- C语言操作符相关练习题
- 实操版!《企业数字化能力提升手册》
- 多线程(看这一篇就够了,超详细,满满的干货)
- Python入门-实战练习-基于组合数据类型
