1.15 递归
目录
1.两数相加
给你两个?非空?的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照?逆序?的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储?一位?数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0?开头。
示例 1:
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] 输出:[7,0,8] 解释:342 + 465 = 807.
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0] 输出:[0]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9] 输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
提示:
- 每个链表中的节点数在范围?
[1, 100]?内 0 <= Node.val <= 9- 题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
分析:思路很好想,但是写起来超级麻烦,写了好久,可以细品一下
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
main()
{
node *head1=new node;
node *head2=new node;
node *head3=new node;
int x,len1=0,len2=0;
node *q=new node;
q=head1;
cin>>x;
if(x==0)
{
node *p=new node;
p->data=x;
q->next=p;
p->next=NULL;
q=q->next;
len1++;
}
else
{
while(x)
{
node *p=new node;
p->data=x;
q->next=p;
p->next=NULL;
q=q->next;
len1++;
cin>>x;
}
}
// q=head1->next;
// while(q)
// {
// cout<<q->data<<" ";
// q=q->next;
// }
q=head2;
cin>>x;
if(x==0)
{
node *p=new node;
p->data=x;
q->next=p;
p->next=NULL;
q=q->next;
len2++;
}
else
{
while(x)
{
node *p=new node;
p->data=x;
q->next=p;
p->next=NULL;
q=q->next;
len2++;
cin>>x;
}
}
cout<<"##################"<<endl;
cout<<len1<<" "<<len2<<endl;
// q=head2->next;
// while(q)
// {
// cout<<q->data<<" ";
// q=q->next;
// }
if(len1>len2)
{
q=head2;
while(q->next)
{
q=q->next;
// cout<<q->data<<" ";
}
while(len1>len2)
{
node *p=new node;
p->data=0;
q->next=p;
p->next=NULL;
q=q->next;
len2++;
}
}
if(len1<len2)
{
q=head1;
while(q->next)
{
q=q->next;
// cout<<q->data<<" ";
}
while(len1<len2)
{
node *p=new node;
p->data=0;
q->next=p;
p->next=NULL;
q=q->next;
len1++;
}
}
// cout<<"=========="<<endl;
int carry=0;
node *p=new node;
node *a=new node;
node *r=new node;
p=head1->next;
q=head2->next;
a=head3;
// cout<<p<<" "<<q<<endl;
while(q)
{
// cout<<"---------"<<endl;
node *r=new node;
a->next=r;
r->next=NULL;
x=p->data+q->data+carry;
// cout<<p->data<<" "<<q->data<<" "<<carry<<" "<<x<<endl;
r->data=x%10;
carry=x/10;
p=p->next;
q=q->next;
a=a->next;
cout<<r->data<<" "<<endl;
}
if(carry==1) cout<<carry;
}
2.两两交换链表中的节点
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1] 输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围?
[0, 100]?内 0 <= Node.val <= 100
分析:第一次想到的是可以给一个标记,后来发现根本用不上,只要一次后移两个节点,再单独处理空和只剩一个节点的情况即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
main()
{
int x;
node *head=new node;
head->next=NULL;
node *q=new node;
q=head;
while(cin>>x)
{
node *p=new node;
p->data=x;
q->next=p;
p->next=NULL;
q=q->next;
}
// q=head->next;
// while(q)
// {
// cout<<q->data<<" ";
// q=q->next;
// }
// cout<<"##################"<<endl;
node *p=new node;
p=head->next;
if(p) q=p->next;
while(p&&q)
{
// cout<<p->data<<" "<<q->data<<endl;
swap(p->data,q->data);
// cout<<p->data<<" "<<q->data<<endl;
p=q->next;
if(p) q=p->next;
}
// cout<<"##################";
q=head->next;
while(q)
{
cout<<q->data<<" ";
q=q->next;
}
}
后来发现是必须是交换节点不能直接交换节点里的数据,然后又去分析了一下

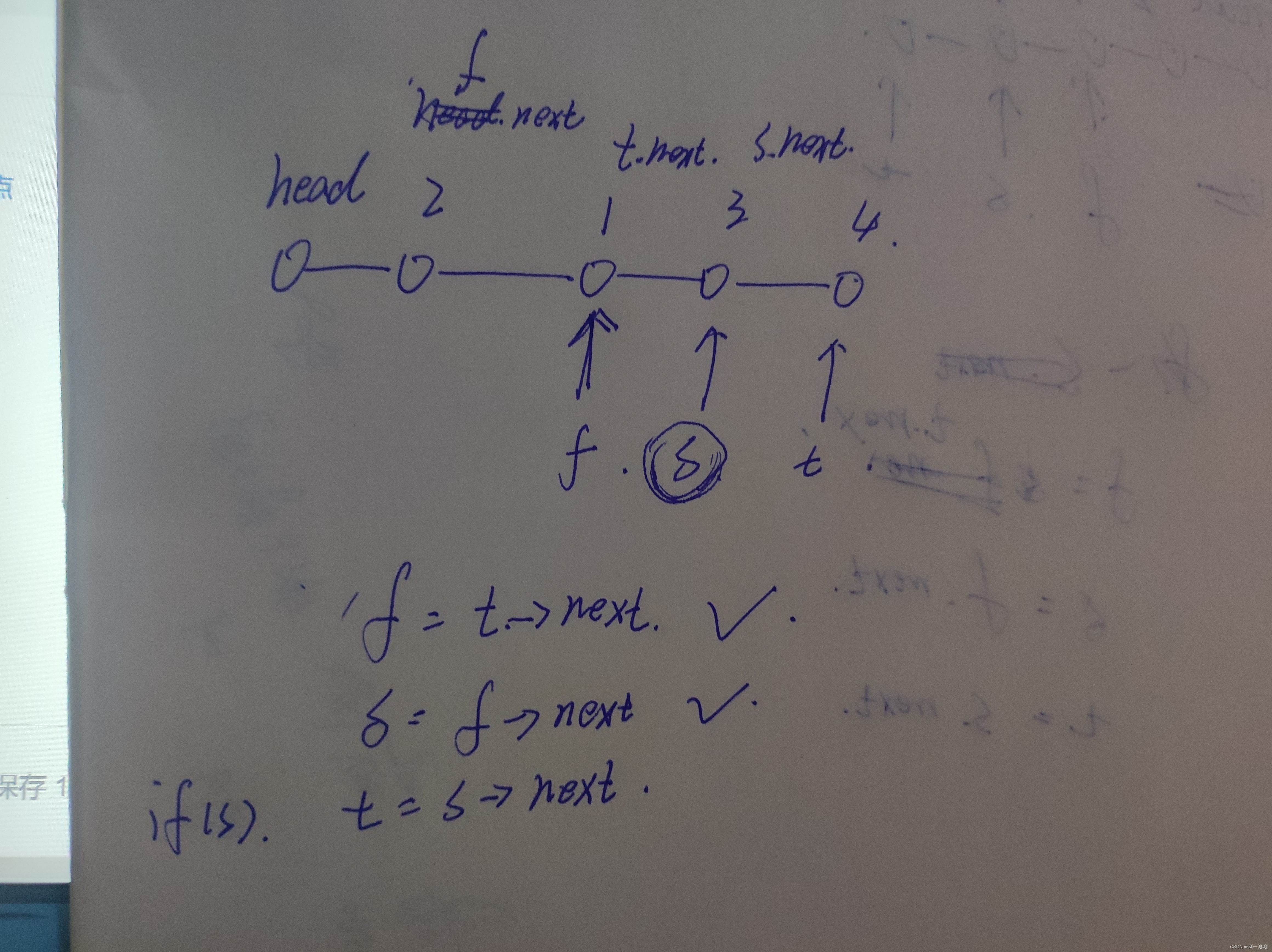
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
main()
{
int x;
node *head=new node;
head->next=NULL;
node *q=new node;
q=head;
while(cin>>x)
{
node *p=new node;
p->data=x;
q->next=p;
p->next=NULL;
q=q->next;
}
// q=head->next;
// while(q)
// {
// cout<<q->data<<" ";
// q=q->next;
// }
// cout<<"##################"<<endl;
node *f=new node;
node *s=new node;
node *t=new node;
f=head;
s=f->next;
if(s) t=s->next;
while(s&&t)
{
// cout<<p->data<<" "<<q->data<<endl;
f->next=t;
s->next=t->next;
t->next=s;
// cout<<p->data<<" "<<q->data<<endl;
f=t->next;
s=f->next;
if(s) t=s->next;
}
// cout<<"##################";
q=head->next;
while(q)
{
cout<<q->data<<" ";
q=q->next;
}
}
3.pow(x,?n)
实现?pow(x,?n)?,即计算?x?的整数?n?次幂函数(即,xn?)。
示例 1:
输入:x = 2.00000, n = 10 输出:1024.00000
示例 2:
输入:x = 2.10000, n = 3 输出:9.26100
示例 3:
输入:x = 2.00000, n = -2 输出:0.25000 解释:2-2 = 1/22 = 1/4 = 0.25
提示:
-100.0 < x < 100.0-231 <= n <= 231-1n?是一个整数- 要么?
x?不为零,要么?n > 0?。 -104 <= xn <= 104
分析:之前写过一个求幂取余的方法,但是没用递归,打算再试一下
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
double mypow(double a,int b)
{
double half,rest;
if(b==0) return 1;
if(b==1) return a;
if(b==-1) return 1/a;
half=mypow(a,b/2);
if(b%2==0) rest=1;
else rest=a;
return half*half*rest;
}
main()
{
double a;
int b;
cin>>a>>b;
//printf("%.6f",mypow(a,b));
cout<<fixed<<setprecision(6)<<mypow(a,b);
}
4.消除游戏
列表?arr?由在范围?[1, n]?中的所有整数组成,并按严格递增排序。请你对?arr?应用下述算法:
- 从左到右,删除第一个数字,然后每隔一个数字删除一个,直到到达列表末尾。
- 重复上面的步骤,但这次是从右到左。也就是,删除最右侧的数字,然后剩下的数字每隔一个删除一个。
- 不断重复这两步,从左到右和从右到左交替进行,直到只剩下一个数字。
给你整数?n?,返回?arr?最后剩下的数字。
示例 1:
输入:n = 9 输出:6 解释: arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] arr = [2, 4, 6, 8] arr = [2, 6] arr = [6]
示例 2:
输入:n = 1 输出:1
提示:
1 <= n <= 109
分析:刚开始想到的是很像约瑟夫环,后来发现行不通,原因是这个题是从第一个数开始删除的,但是约瑟夫环不是,就得重新想办法了
分析:模仿约瑟夫环,我们只需要知道最后留下来的是几就好,从左往右删时,头部肯定需要换掉的,从右往左删时,如果剩余的总数是偶数,那么头部就不需要换,如果是奇数,那就需要换掉,换成它本身加上步长,所以要定义的变量就有总数num,步长step和头部head
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int num;
int ys(bool left,int n,int step,int head)
{
cout<<head<<" "<<step<<" "<<n<<endl;
if(n==1) return head;
if(left || n%2==1)
{
head=head+step;
}
n=n>>1;
step=step<<1;
left=!left;
return ys(left,n,step,head);
}
main()
{
int step=1,head=1;
bool left=true;
cin>>num;
cout<<ys(left,num,step,head);
}
5.字符串解码
给定一个经过编码的字符串,返回它解码后的字符串。
编码规则为:?k[encoded_string],表示其中方括号内部的?encoded_string?正好重复?k?次。注意?k?保证为正整数。
你可以认为输入字符串总是有效的;输入字符串中没有额外的空格,且输入的方括号总是符合格式要求的。
此外,你可以认为原始数据不包含数字,所有的数字只表示重复的次数?k?,例如不会出现像?3a?或?2[4]?的输入。
示例 1:
输入:s = "3[a]2[bc]" 输出:"aaabcbc"
示例 2:
输入:s = "3[a2[c]]" 输出:"accaccacc"
示例 3:
输入:s = "2[abc]3[cd]ef" 输出:"abcabccdcdcdef"
示例 4:
输入:s = "abc3[cd]xyz" 输出:"abccdcdcdxyz"
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 30s?由小写英文字母、数字和方括号?'[]'?组成s?保证是一个?有效?的输入。s?中所有整数的取值范围为?[1, 300]?
?分析:字符串解码很明显是要用栈来写的,很想不通为什么这个题要用递归写,也不知道该怎么用递归来写,在网上看了下他们的递归,是在s[i]为‘['时递归,直到s[i]为']'时返回res
在网上看了下他们的递归. - 力扣(LeetCode)? ? ? ? ??
?在这里它用了一个istringstream iss(s);搜了一下确实有点看不懂,明天要找时间看一下了
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
main()
{
int x,i;
string s;
getline(cin,s);
stack<int> k;
stack<string> ch;
int multi=0;
string res="";
for(i=0; i<s.size(); i++)
{
if(s[i]>='0'&&s[i]<='9')
multi=multi*10+s[i]-'0';
else if(s[i]=='[')
{
k.push(multi);
ch.push(res);
multi=0;
res="";
}
else if(s[i]==']')
{
string tmp=res;
for(int j=0; j<k.top()-1; j++)
{
tmp+=res;
}
res=ch.top()+tmp;
k.pop();
ch.pop();
}
else
{
res=res+s[i];
}
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 绝地求生:PUBG门派活动兑换奖励补充公告
- 深入理解 Hadoop (四)HDFS源码剖析
- 第一章-Mathematical Models in Mechanics(按照Edexcel课本顺序讲解,没有编辑完)
- 明明随机数
- 【索引的数据结构】第1章节:B+Tree存储结构
- 低代码开发平台支持复杂的业务逻辑和API对接吗
- Dubbo秘密传递:让你的代码行云流水
- 为什么SSL证书的身份验证是重要的?
- mybatis的二级缓存使用以及禁用
- JavaScript中将png或jpg图片生成base64格式的封装函数