单列集合Collection常用api
发布时间:2023年12月30日
集合体系结构

Collection
Collection是单列集合的祖宗接口,它的功能是全部单列集合都可以继承使用的。
public static void main(String[] args) {
//TODO Collection类 所有集合的接口
/*
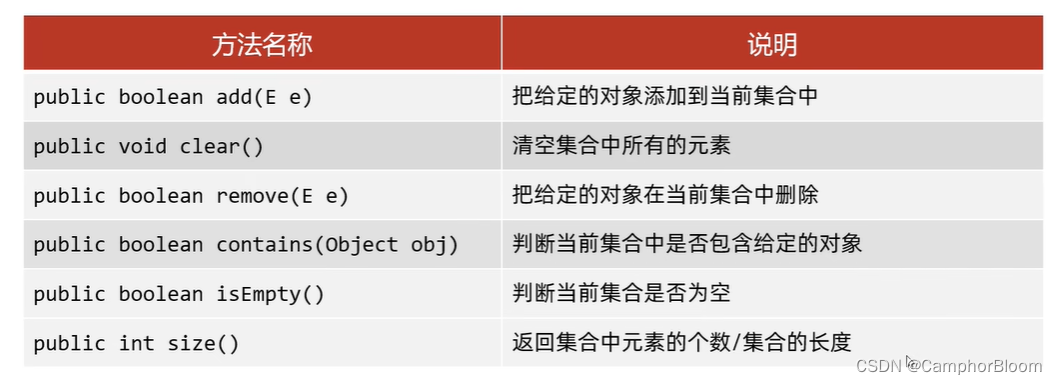
public boolean add(E e) 添加
public void clear() 清空
public boolean remove(E e) 删除
public boolean contains(Object obj) 判断是否包含
public boolean isEmpty() 判断是否为空
public int size() 集合长度
注意点:
Collection是一个接口,我们不能直接创建他的对象。
所以,只能创建他实现类的对象。
实现类:ArrayList
*/
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();
//1.添加元素
//细节1:如果我们要往List系列集合中添加数据,那么方法永远返回true,因为List系列的是允许元素重复的。
//细节2:如果我们要往Set系列集合中添加数据,如果当前要添加元素不存在,方法返回true,表示添加成功。
//如果当前要添加的元素已经存在,方法返回false,表示添加失败。
//因为Set系列的集合不允许重复。
coll.add("aaa");
coll.add("bbb");
coll.add("ccc");
System.out.println(coll);
//2.清空
//coll.clear();
//3.删除
//细节1:因为Collection里面定义的是共性的方法,所以此时不能通过索引进行删除。只能通过元素的对象进行删除。
//细节2:方法会有一个布尔类型的返回值,删除成功返回true,删除失败返回false
//如果要删除的元素不存在,就会删除失败。
System.out.println(coll.remove("aaa"));
//不存在
System.out.println(coll.remove("abc"));
System.out.println(coll);
//4.判断元素是否包含
//细节:底层是依赖equals方法进行判断是否存在的。
//所以,如果集合中存储的是自定义对象,也想通过contains方法来判断是否包含,那么在javabean类中,一定要重写equals方法。
boolean result1 = coll.contains("bbb");
System.out.println(result1);
//5.判断集合是否为空
boolean result2 = coll.isEmpty();
System.out.println(result2);//false
//6.获取集合的长度
coll.add("ddd");
int size = coll.size();
System.out.println(size);//3
}public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建集合的对象
Collection<Student> coll = new ArrayList<>();
//2.创建三个学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("zhangsan",23);
Student s2 = new Student("lisi",24);
Student s3 = new Student("wangwu",25);
//3.把学生对象添加到集合当中
coll.add(s1);
coll.add(s2);
coll.add(s3);
//4.判断集合中某一个学生对象是否包含
Student s4 = new Student("zhangsan",23);
//因为contains方法在底层依赖equals方法判断对象是否一致的。
//如果存的是自定义对象,没有重写equals方法,那么默认使用Object类中的equals方法进行判断,而Object类中equals方法,依赖地址值进行判断。
//需求:如果同姓名和同年龄,就认为是同一个学生。
//所以,需要在自定义的Javabean类中,重写equals方法就可以了。
System.out.println(coll.contains(s4));
}
}
class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//alt+insert快速生成 equals方法
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
//地址值相等直接返回true
if (this == o) return true;
//o为null或者 getClass不等于o直接返回false
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
//判断
return age == student.age && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
public String toString() {
return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}tips:查看Collection contains方法实现:
选中contains,右键选择Go To——》Implementation,找到相应的实现类(如ArrayList)。
可见底层是通过equals去判断是否包含的,源码:

文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45719444/article/details/135303637
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Epson打印机连接wifi
- 掼蛋功能之识别性格篇
- 谷歌大裁员,3 万员工面临被 AI 取代;网易、暴雪疑似「复合」!丨 RTE 开发者日报 Vol.113
- 消息队列学习笔记
- 网页在不同Android机表现有差异时需要排查页面样式是否针对主题模式作配置
- Spring学习 基于注解的AOP控制事务
- vue3中pinia的使用及持久化(详细解释)
- 【笔记】Helm-3 主题-11 基于角色的访问控制
- 外贸网站建站费用要多少?海洋建站的成本?
- 开源大模型应用开发