邻值查找(链表、set、map)
题目
给定一个长度为?n?的序列?A,A?中的数各不相同。
对于?A?中的每一个数?Ai,求:min1≤j<i|Ai?Aj|
以及令上式取到最小值的?j(记为?Pi)。若最小值点不唯一,则选择使?Aj?较小的那个。
输入格式
第一行输入整数?n,代表序列长度。
第二行输入?n?个整数A1…An,代表序列的具体数值,数值之间用空格隔开。
输出格式
输出共?n?1行,每行输出两个整数,数值之间用空格隔开。
分别表示当?i?取?2~n时,对应的 |Ai?Aj| 最小值和?Pi 的值,其中 1 ≤ j < i。?
数据范围
n≤10^5,|Ai|≤10^9
样例
输入样例
3
1 5 3
输出样例
4 1
2 1题目思路
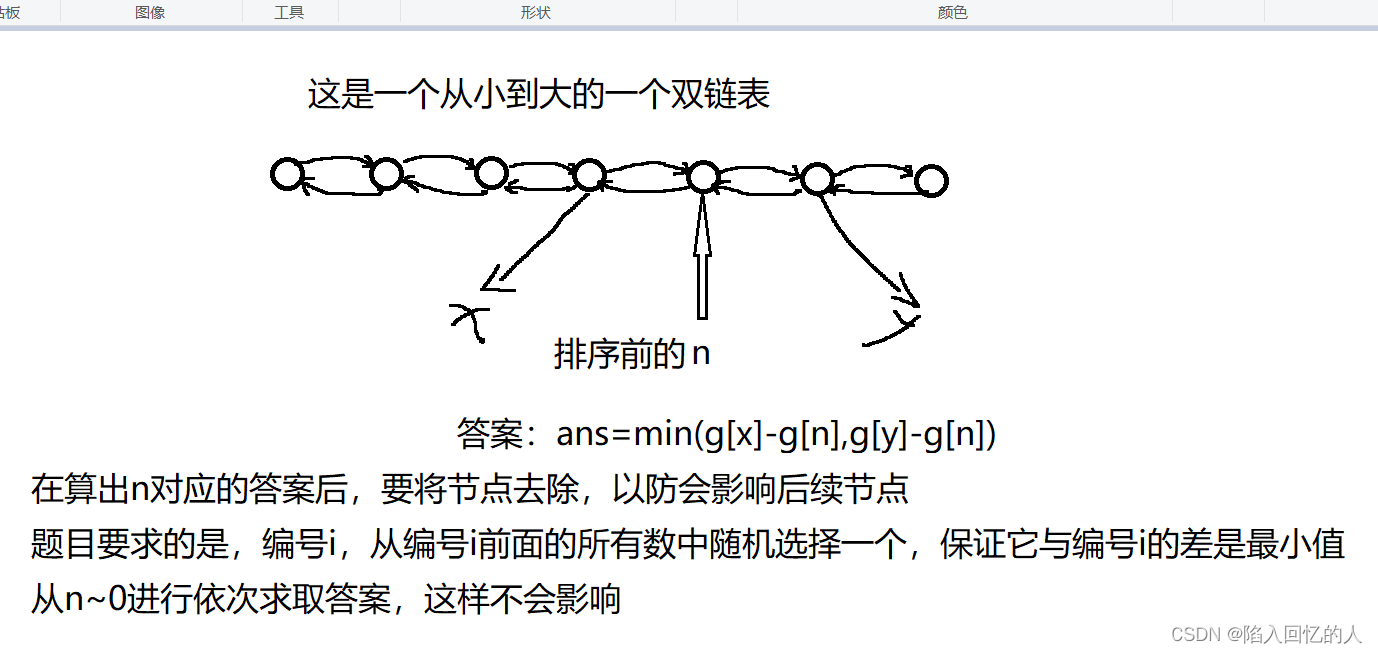
? ? ? ? 这个题目,如果看起来是比较简单的,但是,如果你使用暴力枚举的话,会TLE(超时),我们看一下,如果使用暴力枚举的话,它的时间复杂度为O(n^2),即两重for循环;那么它规模是1e10,在一秒中跑不完,所以会TLE。题目意思就是:从前i-1个数中选择一个,但要确保它与Ai的差为最小值即可。(当有多个时,会选择编号较小的那个)
? ? ? ? 方法一
? ? ? ? 使用双链表的形式去优化,这样时间复杂度会降到O(nlogn),主要是需要用到sort排序,不过双链表的实现形式比较浮在,代码比较长,我这里使用数组模拟双链表,这样简化了代码,是代码长度变短。
? ? ? ? 方法二
? ? ? ? 该方法就比较简单,直接使用c++中的set或者map,是因为set和map中自带了函数去查找:
? ? ? ? 1、能够查询大于x的最小的数(upper_bound():能够查询大于x的最小的数)
? ? ? ? 2、能够查询小于x的最大的数(lower_bound():能够查询大于等于x的最小的数)——使用lower_bound()函数查找到它自己,在进行‘--’操作就可以得到小于x的最大的数,当然,也可以使用find(),进行同样操作,也可以得到想要的结果;
源代码?
? ? ? ? 方法一
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1e5+10;
int l[N],r[N],p[N];
int n;
PII w[N],ans[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
scanf("%d", &w[i].first);
w[i].second=i;
}
sort(w+1,w+n+1);
//构造双链表
//处理边界问题
//如样例:1e9 -1e9 1e9 -1e9会出现答案为2e9 0,这样不是我们希望的
//所以1e9+10 -1e9 1e9 -1e9-10这样答案为2e9 1
w[0].first=1e9+10,w[n+1].first=-1e9-10;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
l[i]=i-1,r[i]=i+1;
//记录排序后n点在哪里
p[w[i].second]=i;
}
for(int i=n;i>1;i--){
int j=p[i],left=l[j],right=r[j];
int a=abs(w[j].first-w[left].first);
int b=abs(w[right].first-w[j].first);
if(a<=b){
ans[i]={a,w[left].second};
}else{
ans[i]={b,w[right].second};
}
//删除i节点
r[left]=right,l[right]=left;
}
for (int i=2;i<=n;i++) printf("%d %d\n",ans[i].first,ans[i].second);
return 0;
}
? ? ? ? 方法二?
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> A(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> A[i];
}
set<pair<int, int>> s; // 使用 pair 存储数值和下标
s.insert({A[0], 1});
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
s.insert({A[i], i+1}); // 存储数值和下标
auto it1 = s.find({A[i],i+1});
//auto it1 = s.lower_bound({A[i],i+1});
auto it2 = s.upper_bound({A[i],i+1});
int ans1=2e9+10,ans2=2e9+10;
if(it1!=s.begin()){
it1--;
ans1=abs(A[i]-it1->first);
}
if(it2!=s.end()){
ans2=abs(A[i]-it2->first);
}
if(ans1<=ans2){
cout << ans1 << ' ' << it1->second << endl;
}else{
cout << ans2 << ' ' << it2->second << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
?
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 掺铒光纤放大器(EDFA)如何有利于波分复用系统?
- Redis面试题13
- 报名倒计时 | Atlassian 社区日·上海站:与澳大利亚商务领事一起探索澳大利亚的创新力量
- JVM-透彻掌握Parallel垃圾回收器的使用方法
- Charles macOS Apple Silicon
- 字符串函数的模拟实现(部分字符串函数)
- android 自定义键盘长按弹窗
- Linux上如何一键安装软件?yum源是什么?Linux如何配置yum源?
- 【计算机毕业设计】SSM二手交易网站
- RPC原理介绍与使用(@RpcServiceAnnotation)