手把手入门MO | 如何使用 Flink 将批量数据写入 MatrixOne
1 概述
Apache Flink 是一个强大的框架和分布式处理引擎,专注于进行有状态计算,适用于处理无边界和有边界的数据流。Flink 能够在各种常见集群环境中高效运行,并以内存速度执行计算,支持处理任意规模的数据。
2 应用场景
事件驱动型应用
- 事件驱动型应用通常具备状态,并且它们从一个或多个事件流中提取数据,根据到达的事件触发计算、状态更新或执行其他外部动作。典型的事件驱动型应用包括反欺诈系统、异常检测、基于规则的报警系统和业务流程监控。
数据分析应用
- 数据分析任务的主要目标是从原始数据中提取有价值的信息和指标。Flink 支持流式和批量分析应用,适用于各种场景,例如电信网络质量监控、移动应用中的产品更新和实验评估分析、消费者技术领域的实时数据即席分析以及大规模图分析。
数据管道应用
- 提取 - 转换 - 加载(ETL)是在不同存储系统之间进行数据转换和迁移的常见方法。数据管道和 ETL 作业有相似之处,都可以进行数据转换和处理,然后将数据从一个存储系统移动到另一个存储系统。不同之处在于数据管道以持续流模式运行,而不是周期性触发。典型的数据管道应用包括电子商务中的实时查询索引构建和持续 ETL。
本篇文档将介绍两种示例,一种是实现将存量数据写入到 MatrixOne,另一种是使用计算引擎 Flink 将流式数据写入到 MatrixOne 数据库。
3 前期准备
硬件环境
本次实践对于机器的硬件要求如下:

软件环境
本次实践需要安装部署以下软件环境:
- 已完成单机部署 MatrixOne。
- 下载安装 lntelliJ IDEA(2022.2.1 or later version)。
- 根据你的系统环境选择 JDK 8+ version 版本进行下载安装。
- 下载并安装 Kafka,推荐版本为 2.13 - 3.5.0。
- 下载并安装 Flink,推荐版本为 1.17.0。
- 下载并安装 MySQL,推荐版本为 8.0.33。
4 示例一
从 MySQL 迁移数据至 MatrixOne
步骤一:初始化项目
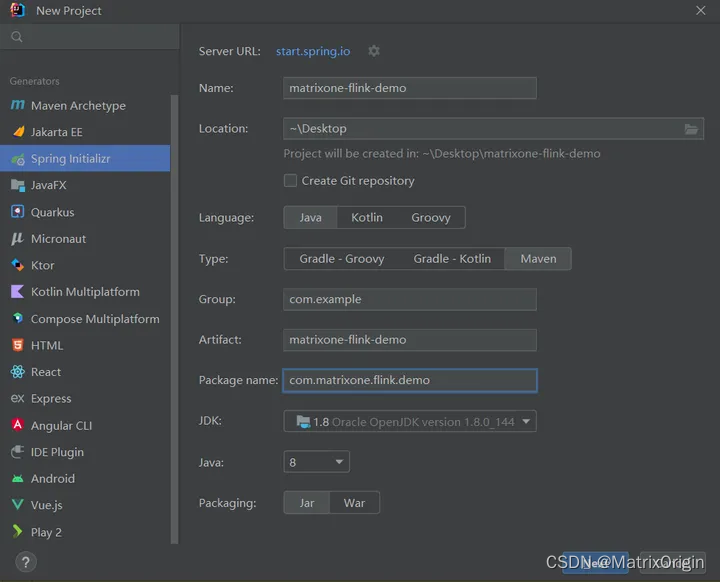
1. 启动 IDEA,点击?File > New > Project,选择?Spring Initializer,并填写以下配置参数:
- Name:mo-spark-demo
- Location:~\Desktop
- Language:Java
- Type:Maven
- Group:com.example
- Artiface:matrixone-flink-demo
- Package name:com.matrixone.flink.demo
- JDK 1.8
2. 添加项目依赖,在项目根目录下的 pom.xml 内容编辑如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.matrixone.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>matrixone-flink-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<scala.binary.version>2.12</scala.binary.version>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<flink.version>1.17.0</flink.version>
<scope.mode>compile</scope.mode>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Flink Dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-hive_2.12</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-java</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-streaming-java</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-clients</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-table-api-java-bridge</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-table-planner_2.12</artifactId>
<version>${flink.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JDBC相关依赖包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>1.15.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.33</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Kafka相关依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka_2.13</artifactId>
<version>3.5.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-connector-kafka</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0-1.17</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JSON -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.fastjson2</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson2</artifactId>
<version>2.0.34</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
<configuration>
<source>${java.version}</source>
<target>${java.version}</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
<configuration>
<descriptorRefs>
<descriptor>jar-with-dependencies</descriptor>
</descriptorRefs>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>make-assembly</id>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>single</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
步骤二:读取 MatrixOne 数据
使用 MySQL 客户端连接 MatrixOne 后,创建演示所需的数据库以及数据表。
1. 在 MatrixOne 中创建数据库、数据表,并导入数据:
CREATE DATABASE test;
USE test;
CREATE TABLE `person` (`id` INT DEFAULT NULL, `name` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL, `birthday` DATE DEFAULT NULL);
INSERT INTO test.person (id, name, birthday) VALUES(1, 'zhangsan', '2023-07-09'),(2, 'lisi', '2023-07-08'),(3, 'wangwu', '2023-07-12');2. 在 IDEA 中创建 MoRead.java 类,以使用 Flink 读取 MatrixOne 数据:
package com.matrixone.flink.demo;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.MapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.BasicTypeInfo;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.ExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.operators.DataSource;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.operators.MapOperator;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.typeutils.RowTypeInfo;
import org.apache.flink.connector.jdbc.JdbcInputFormat;
import org.apache.flink.types.Row;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
/**
* @author MatrixOne
* @description
*/
public class MoRead {
private static String srcHost = "192.168.146.10";
private static Integer srcPort = 6001;
private static String srcUserName = "root";
private static String srcPassword = "111";
private static String srcDataBase = "test";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ExecutionEnvironment environment = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
// 设置并行度
environment.setParallelism(1);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
// 设置查询的字段类型
RowTypeInfo rowTypeInfo = new RowTypeInfo(
new BasicTypeInfo[]{
BasicTypeInfo.INT_TYPE_INFO,
BasicTypeInfo.STRING_TYPE_INFO,
BasicTypeInfo.DATE_TYPE_INFO
},
new String[]{
"id",
"name",
"birthday"
}
);
DataSource<Row> dataSource = environment.createInput(JdbcInputFormat.buildJdbcInputFormat()
.setDrivername("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver")
.setDBUrl("jdbc:mysql://" + srcHost + ":" + srcPort + "/" + srcDataBase)
.setUsername(srcUserName)
.setPassword(srcPassword)
.setQuery("select * from person")
.setRowTypeInfo(rowTypeInfo)
.finish());
// 将 Wed Jul 12 00:00:00 CST 2023 日期格式转换为 2023-07-12
MapOperator<Row, Row> mapOperator = dataSource.map((MapFunction<Row, Row>) row -> {
row.setField("birthday", sdf.format(row.getField("birthday")));
return row;
});
mapOperator.print();
}
}步骤三:将 MySQL 数据写入 MatrixOne
现在可以开始使用 Flink 将 MySQL 数据迁移到 MatrixOne。
1. 准备 MySQL 数据:
在 node3 上,使用 Mysql 客户端连接本地 Mysql,创建所需数据库、数据表、并插入数据:
mysql -h127.0.0.1 -P3306 -uroot -proot
mysql> CREATE DATABASE motest;
mysql> USE motest;
mysql> CREATE TABLE `person` (`id` int DEFAULT NULL, `name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `birthday` date DEFAULT NULL);
mysql> INSERT INTO motest.person (id, name, birthday) VALUES(2, 'lisi', '2023-07-09'),(3, 'wangwu', '2023-07-13'),(4, 'zhaoliu', '2023-08-08');2. 清空 MatrixOne 表数据:
在 node3 上,使用 MySQL 客户端连接 node1 的 MatrixOne。由于本示例继续使用前面读取 MatrixOne 数据的示例中的 test 数据库,因此我们需要首先清空 person 表的数据。
-- 在 node3 上,使用 Mysql 客户端连接 node1 的 MatrixOne
mysql -h192.168.146.10 -P6001 -uroot -p111
mysql> TRUNCATE TABLE test.person;3. 在 IDEA 中编写代码:
创建 Person.java 和 Mysql2Mo.java 类,使用 Flink 读取 MySQL 数据,执行简单的 ETL 操作(将 Row 转换为 Person 对象),最终将数据写入 MatrixOne 中。
package com.matrixone.flink.demo.entity;
import java.util.Date;
public class Person {
private int id;
private String name;
private Date birthday;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
}package com.matrixone.flink.demo;
import com.matrixone.flink.demo.entity.Person;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.MapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.BasicTypeInfo;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.typeutils.RowTypeInfo;
import org.apache.flink.connector.jdbc.*;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSink;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.types.Row;
import java.sql.Date;
/**
* @author MatrixOne
* @description
*/
public class Mysql2Mo {
private static String srcHost = "127.0.0.1";
private static Integer srcPort = 3306;
private static String srcUserName = "root";
private static String srcPassword = "root";
private static String srcDataBase = "motest";
private static String destHost = "192.168.146.10";
private static Integer destPort = 6001;
private static String destUserName = "root";
private static String destPassword = "111";
private static String destDataBase = "test";
private static String destTable = "person";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment environment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
//设置并行度
environment.setParallelism(1);
//设置查询的字段类型
RowTypeInfo rowTypeInfo = new RowTypeInfo(
new BasicTypeInfo[]{
BasicTypeInfo.INT_TYPE_INFO,
BasicTypeInfo.STRING_TYPE_INFO,
BasicTypeInfo.DATE_TYPE_INFO
},
new String[]{
"id",
"name",
"birthday"
}
);
//添加 srouce
DataStreamSource<Row> dataSource = environment.createInput(JdbcInputFormat.buildJdbcInputFormat()
.setDrivername("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver")
.setDBUrl("jdbc:mysql://" + srcHost + ":" + srcPort + "/" + srcDataBase)
.setUsername(srcUserName)
.setPassword(srcPassword)
.setQuery("select * from person")
.setRowTypeInfo(rowTypeInfo)
.finish());
//进行 ETL
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Person> mapOperator = dataSource.map((MapFunction<Row, Person>) row -> {
Person person = new Person();
person.setId((Integer) row.getField("id"));
person.setName((String) row.getField("name"));
person.setBirthday((java.util.Date)row.getField("birthday"));
return person;
});
//设置 matrixone sink 信息
mapOperator.addSink(
JdbcSink.sink(
"insert into " + destTable + " values(?,?,?)",
(ps, t) -> {
ps.setInt(1, t.getId());
ps.setString(2, t.getName());
ps.setDate(3, new Date(t.getBirthday().getTime()));
},
new JdbcConnectionOptions.JdbcConnectionOptionsBuilder()
.withDriverName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver")
.withUrl("jdbc:mysql://" + destHost + ":" + destPort + "/" + destDataBase)
.withUsername(destUserName)
.withPassword(destPassword)
.build()
)
);
environment.execute();
}
}步骤四:查看执行结果
在 MatrixOne 中执行如下 SQL 查看执行结果:
mysql> select * from test.person;
+------+---------+------------+
| id | name | birthday |
+------+---------+------------+
| 2 | lisi | 2023-07-09 |
| 3 | wangwu | 2023-07-13 |
| 4 | zhaoliu | 2023-08-08 |
+------+---------+------------+
3 rows in set (0.01 sec)5 示例二
将 Kafka 数据写入 MatrixOne
步骤一:启动 Kafka 服务
Kafka 集群协调和元数据管理可以通过 KRaft 或 ZooKeeper 来实现。在这里,我们将使用 Kafka 3.5.0 版本,无需依赖独立的 ZooKeeper 软件,而是使用 Kafka 自带的?KRaft?来进行元数据管理。请按照以下步骤配置配置文件,该文件位于 Kafka 软件根目录下的 config/kraft/server.properties。
配置文件内容如下:
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#
# This configuration file is intended for use in KRaft mode, where
# Apache ZooKeeper is not present. See config/kraft/README.md for details.
#
############################# Server Basics #############################
# The role of this server. Setting this puts us in KRaft mode
process.roles=broker,controller
# The node id associated with this instance's roles
node.id=1
# The connect string for the controller quorum
controller.quorum.voters=1@192.168.146.12:9093
############################# Socket Server Settings #############################
# The address the socket server listens on.
# Combined nodes (i.e. those with `process.roles=broker,controller`) must list the controller listener here at a minimum.
# If the broker listener is not defined, the default listener will use a host name that is equal to the value of java.net.InetAddress.getCanonicalHostName(),
# with PLAINTEXT listener name, and port 9092.
# FORMAT:
# listeners = listener_name://host_name:port
# EXAMPLE:
# listeners = PLAINTEXT://your.host.name:9092
#listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092,CONTROLLER://:9093
listeners=PLAINTEXT://192.168.146.12:9092,CONTROLLER://192.168.146.12:9093
# Name of listener used for communication between brokers.
inter.broker.listener.name=PLAINTEXT
# Listener name, hostname and port the broker will advertise to clients.
# If not set, it uses the value for "listeners".
#advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://localhost:9092
# A comma-separated list of the names of the listeners used by the controller.
# If no explicit mapping set in `listener.security.protocol.map`, default will be using PLAINTEXT protocol
# This is required if running in KRaft mode.
controller.listener.names=CONTROLLER
# Maps listener names to security protocols, the default is for them to be the same. See the config documentation for more details
listener.security.protocol.map=CONTROLLER:PLAINTEXT,PLAINTEXT:PLAINTEXT,SSL:SSL,SASL_PLAINTEXT:SASL_PLAINTEXT,SASL_SSL:SASL_SSL
# The number of threads that the server uses for receiving requests from the network and sending responses to the network
num.network.threads=3
# The number of threads that the server uses for processing requests, which may include disk I/O
num.io.threads=8
# The send buffer (SO_SNDBUF) used by the socket server
socket.send.buffer.bytes=102400
# The receive buffer (SO_RCVBUF) used by the socket server
socket.receive.buffer.bytes=102400
# The maximum size of a request that the socket server will accept (protection against OOM)
socket.request.max.bytes=104857600
############################# Log Basics #############################
# A comma separated list of directories under which to store log files
log.dirs=/home/software/kafka_2.13-3.5.0/kraft-combined-logs
# The default number of log partitions per topic. More partitions allow greater
# parallelism for consumption, but this will also result in more files across
# the brokers.
num.partitions=1
# The number of threads per data directory to be used for log recovery at startup and flushing at shutdown.
# This value is recommended to be increased for installations with data dirs located in RAID array.
num.recovery.threads.per.data.dir=1
############################# Internal Topic Settings #############################
# The replication factor for the group metadata internal topics "__consumer_offsets" and "__transaction_state"
# For anything other than development testing, a value greater than 1 is recommended to ensure availability such as 3.
offsets.topic.replication.factor=1
transaction.state.log.replication.factor=1
transaction.state.log.min.isr=1
############################# Log Flush Policy #############################
# Messages are immediately written to the filesystem but by default we only fsync() to sync
# the OS cache lazily. The following configurations control the flush of data to disk.
# There are a few important trade-offs here:
# 1. Durability: Unflushed data may be lost if you are not using replication.
# 2. Latency: Very large flush intervals may lead to latency spikes when the flush does occur as there will be a lot of data to flush.
# 3. Throughput: The flush is generally the most expensive operation, and a small flush interval may lead to excessive seeks.
# The settings below allow one to configure the flush policy to flush data after a period of time or
# every N messages (or both). This can be done globally and overridden on a per-topic basis.
# The number of messages to accept before forcing a flush of data to disk
#log.flush.interval.messages=10000
# The maximum amount of time a message can sit in a log before we force a flush
#log.flush.interval.ms=1000
############################# Log Retention Policy #############################
# The following configurations control the disposal of log segments. The policy can
# be set to delete segments after a period of time, or after a given size has accumulated.
# A segment will be deleted whenever *either* of these criteria are met. Deletion always happens
# from the end of the log.
# The minimum age of a log file to be eligible for deletion due to age
log.retention.hours=72
# A size-based retention policy for logs. Segments are pruned from the log unless the remaining
# segments drop below log.retention.bytes. Functions independently of log.retention.hours.
#log.retention.bytes=1073741824
# The maximum size of a log segment file. When this size is reached a new log segment will be created.
log.segment.bytes=1073741824
# The interval at which log segments are checked to see if they can be deleted according
# to the retention policies
log.retention.check.interval.ms=300000文件配置完成后,执行如下命令,启动 Kafka 服务:
#生成集群ID
$ KAFKA_CLUSTER_ID="$(bin/kafka-storage.sh random-uuid)"
#设置日志目录格式
$ bin/kafka-storage.sh format -t $KAFKA_CLUSTER_ID -c config/kraft/server.properties
#启动Kafka服务
$ bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/kraft/server.properties步骤二:创建 Kafka 主题
为了使 Flink 能够从中读取数据并写入到 MatrixOne,我们需要首先创建一个名为 "matrixone" 的 Kafka 主题。在下面的命令中,使用 --bootstrap-server 参数指定 Kafka 服务的监听地址为 192.168.146.12:9092:
$ bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --topic matrixone --bootstrap-server 192.168.146.12:9092步骤三:读取 MatrixOne 数据
在连接到 MatrixOne 数据库之后,需要执行以下操作以创建所需的数据库和数据表:
1. 在 MatrixOne 中创建数据库和数据表,并导入数据:
CREATE TABLE `users` (
`id` INT DEFAULT NULL,
`name` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` INT DEFAULT NULL
)2. 在 IDEA 集成开发环境中编写代码:
在 IDEA 中,创建两个类:User.java 和 Kafka2Mo.java。这些类用于使用 Flink 从 Kafka 读取数据,并将数据写入 MatrixOne 数据库中。
package com.matrixone.flink.demo.entity;
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
package com.matrixone.flink.demo;
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;
import com.matrixone.flink.demo.entity.User;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.eventtime.WatermarkStrategy;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.serialization.AbstractDeserializationSchema;
import org.apache.flink.connector.jdbc.JdbcExecutionOptions;
import org.apache.flink.connector.jdbc.JdbcSink;
import org.apache.flink.connector.jdbc.JdbcStatementBuilder;
import org.apache.flink.connector.jdbc.internal.options.JdbcConnectorOptions;
import org.apache.flink.connector.kafka.source.KafkaSource;
import org.apache.flink.connector.kafka.source.enumerator.initializer.OffsetsInitializer;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStreamSource;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.OffsetResetStrategy;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/**
* @author MatrixOne
* @desc
*/
public class Kafka2Mo {
private static String srcServer = "192.168.146.12:9092";
private static String srcTopic = "matrixone";
private static String consumerGroup = "matrixone_group";
private static String destHost = "192.168.146.10";
private static Integer destPort = 6001;
private static String destUserName = "root";
private static String destPassword = "111";
private static String destDataBase = "test";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//初始化环境
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
//设置并行度
env.setParallelism(1);
//设置 kafka source 信息
KafkaSource<User> source = KafkaSource.<User>builder()
//Kafka 服务
.setBootstrapServers(srcServer)
//消息主题
.setTopics(srcTopic)
//消费组
.setGroupId(consumerGroup)
//偏移量 当没有提交偏移量则从最开始开始消费
.setStartingOffsets(OffsetsInitializer.committedOffsets(OffsetResetStrategy.LATEST))
//自定义解析消息内容
.setValueOnlyDeserializer(new AbstractDeserializationSchema<User>() {
@Override
public User deserialize(byte[] message) {
return JSON.parseObject(new String(message, StandardCharsets.UTF_8), User.class);
}
})
.build();
DataStreamSource<User> kafkaSource = env.fromSource(source, WatermarkStrategy.noWatermarks(), "kafka_maxtixone");
//kafkaSource.print();
//设置 matrixone sink 信息
kafkaSource.addSink(JdbcSink.sink(
"insert into users (id,name,age) values(?,?,?)",
(JdbcStatementBuilder<User>) (preparedStatement, user) -> {
preparedStatement.setInt(1, user.getId());
preparedStatement.setString(2, user.getName());
preparedStatement.setInt(3, user.getAge());
},
JdbcExecutionOptions.builder()
//默认值 5000
.withBatchSize(1000)
//默认值为 0
.withBatchIntervalMs(200)
//最大尝试次数
.withMaxRetries(5)
.build(),
JdbcConnectorOptions.builder()
.setDBUrl("jdbc:mysql://"+destHost+":"+destPort+"/"+destDataBase)
.setUsername(destUserName)
.setPassword(destPassword)
.setDriverName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver")
.build()
));
env.execute();
}
}代码编写完成后,你可以运行 Flink 任务,即在 IDEA 中选择 Kafka2Mo.java 文件,然后执行 Kafka2Mo.Main()。
步骤四:生成数据
使用 Kafka 提供的命令行生产者工具,您可以向 Kafka 的 "matrixone" 主题中添加数据。在下面的命令中,使用 --topic 参数指定要添加到的主题,而 --bootstrap-server 参数指定了 Kafka 服务的监听地址。
bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --topic matrixone --bootstrap-server 192.168.146.12:9092执行上述命令后,您将在控制台上等待输入消息内容。只需直接输入消息值 (value),每行表示一条消息(以换行符分隔),如下所示:
{"id": 10, "name": "xiaowang", "age": 22}
{"id": 20, "name": "xiaozhang", "age": 24}
{"id": 30, "name": "xiaogao", "age": 18}
{"id": 40, "name": "xiaowu", "age": 20}
{"id": 50, "name": "xiaoli", "age": 42} ?
?
步骤五:查看执行结果
在 MatrixOne 中执行如下 SQL 查询结果:
mysql> select * from test.users;
+------+-----------+------+
| id | name | age |
+------+-----------+------+
| 10 | xiaowang | 22 |
| 20 | xiaozhang | 24 |
| 30 | xiaogao | 18 |
| 40 | xiaowu | 20 |
| 50 | xiaoli | 42 |
+------+-----------+------+
5 rows in set (0.01 sec)关于MatrixOne
MatrixOne 是一款基于云原生技术,可同时在公有云和私有云部署的多模数据库。该产品使用存算分离、读写分离、冷热分离的原创技术架构,能够在一套存储和计算系统下同时支持事务、分析、流、时序和向量等多种负载,并能够实时、按需的隔离或共享存储和计算资源。 云原生数据库MatrixOne能够帮助用户大幅简化日益复杂的IT架构,提供极简、极灵活、高性价比和高性能的数据服务。
MatrixOne企业版和MatrixOne云服务自发布以来,已经在互联网、金融、能源、制造、教育、医疗等多个行业得到应用。得益于其独特的架构设计,用户可以降低多达70%的硬件和运维成本,增加3-5倍的开发效率,同时更加灵活的响应市场需求变化和更加高效的抓住创新机会。在相同硬件投入时,MatrixOne可获得数倍以上的性能提升。
MatrixOne秉持开源开放、生态共建的理念,核心代码全部开源,全面兼容MySQL协议,并与合作伙伴打造了多个端到端解决方案,大幅降低用户的迁移
关键词:超融合数据库、多模数据库、云原生数据库、国产数据库。
MatrixOrigin 官网:新一代超融合异构开源数据库-矩阵起源(深圳)信息科技有限公司 MatrixOne
Github 仓库:GitHub - matrixorigin/matrixone: Hyperconverged cloud-edge native database
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- SpringBoot中使用@Async实现异步调用
- 柯桥专业会计学校之相关财税知识,2023年新版增值税税率表
- SpringBoot-开启Actuator监控
- Network 灰鸽宝典【目录】
- 打造清晰的日志管理策略:如何在 NestJS 中集成 winston 高级日志系统
- 排序算法-冒泡排序
- linux安装java8
- 【Spring】AOP的AspectJ开发
- 目标检测YOLO实战应用案例100讲-基于深度学习的实时车道线与目标检测多任务实现(中)
- go获取文件md5后接着读取file对象EOF的问题记录