Java IO流
1.字符流
1.1为什么会出现字符流【理解】
-
字符流的介绍
由于字节流操作中文不是特别的方便,所以Java就提供字符流
字符流 = 字节流 + 编码表
-
中文的字节存储方式
用字节流复制文本文件时,文本文件也会有中文,但是没有问题,原因是最终底层操作会自动进行字节拼接成中文,如何识别是中文的呢?
汉字在存储的时候,无论选择哪种编码存储,第一个字节都是负数
1.2编码表【理解】
-
什么是字符集
是一个系统支持的所有字符的集合,包括各国家文字、标点符号、图形符号、数字等
l计算机要准确的存储和识别各种字符集符号,就需要进行字符编码,一套字符集必然至少有一套字符编码。常见字符集有ASCII字符集、GBXXX字符集、Unicode字符集等
-
常见的字符集
-
ASCII字符集:
lASCII:是基于拉丁字母的一套电脑编码系统,用于显示现代英语,主要包括控制字符(回车键、退格、换行键等)和可显示字符(英文大小写字符、阿拉伯数字和西文符号)
基本的ASCII字符集,使用7位表示一个字符,共128字符。ASCII的扩展字符集使用8位表示一个字符,共256字符,方便支持欧洲常用字符。是一个系统支持的所有字符的集合,包括各国家文字、标点符号、图形符号、数字等
-
GBXXX字符集:
GBK:最常用的中文码表。是在GB2312标准基础上的扩展规范,使用了双字节编码方案,共收录了21003个汉字,完全兼容GB2312标准,同时支持繁体汉字以及日韩汉字等
-
Unicode字符集:
UTF-8编码:可以用来表示Unicode标准中任意字符,它是电子邮件、网页及其他存储或传送文字的应用 中,优先采用的编码。互联网工程工作小组(IETF)要求所有互联网协议都必须支持UTF-8编码。它使用一至四个字节为每个字符编码
编码规则:
128个US-ASCII字符,只需一个字节编码
拉丁文等字符,需要二个字节编码
大部分常用字(含中文),使用三个字节编码
其他极少使用的Unicode辅助字符,使用四字节编码
-
1.3字符串中的编码解码问题【应用】
-
相关方法
方法名 说明 byte[] getBytes() 使用平台的默认字符集将该 String编码为一系列字节 byte[] getBytes(String charsetName) 使用指定的字符集将该 String编码为一系列字节 String(byte[] bytes) 使用平台的默认字符集解码指定的字节数组来创建字符串 String(byte[] bytes, String charsetName) 通过指定的字符集解码指定的字节数组来创建字符串 -
代码演示
public class StringDemo { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { ? ? ? ?//定义一个字符串 ? ? ? ?String s = "中国"; ? ? ? ? ?//byte[] bys = s.getBytes(); //[-28, -72, -83, -27, -101, -67] ? ? ? ?//byte[] bys = s.getBytes("UTF-8"); //[-28, -72, -83, -27, -101, -67] ? ? ? ?byte[] bys = s.getBytes("GBK"); //[-42, -48, -71, -6] ? ? ? ?System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bys)); ? ? ? ? ?//String ss = new String(bys); ? ? ? ?//String ss = new String(bys,"UTF-8"); ? ? ? ?String ss = new String(bys,"GBK"); ? ? ? ?System.out.println(ss); ? } }
1.4字符流写数据【应用】
-
介绍
Writer: 用于写入字符流的抽象父类
FileWriter: 用于写入字符流的常用子类
-
构造方法
方法名 说明 FileWriter(File file) 根据给定的 File 对象构造一个 FileWriter 对象 FileWriter(File file, boolean append) 根据给定的 File 对象构造一个 FileWriter 对象 FileWriter(String fileName) 根据给定的文件名构造一个 FileWriter 对象 FileWriter(String fileName, boolean append) 根据给定的文件名以及指示是否附加写入数据的 boolean 值来构造 FileWriter 对象
-
成员方法
方法名 说明 void write(int c) 写一个字符 void write(char[] cbuf) 写入一个字符数组 void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) 写入字符数组的一部分 void write(String str) 写一个字符串 void write(String str, int off, int len) 写一个字符串的一部分 -
刷新和关闭的方法
方法名 说明 flush() 刷新流,之后还可以继续写数据 close() 关闭流,释放资源,但是在关闭之前会先刷新流。一旦关闭,就不能再写数据 -
代码演示
public class OutputStreamWriterDemo { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ? ? ? ?FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("myCharStream\\a.txt"); ? ? ? ? ?//void write(int c):写一个字符 // ? ? ? fw.write(97); // ? ? ? fw.write(98); // ? ? ? fw.write(99); ? ? ? ? ?//void writ(char[] cbuf):写入一个字符数组 ? ? ? ?char[] chs = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'}; // ? ? ? fw.write(chs); ? ? ? ? ?//void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len):写入字符数组的一部分 // ? ? ? fw.write(chs, 0, chs.length); // ? ? ? fw.write(chs, 1, 3); ? ? ? ? ?//void write(String str):写一个字符串 // ? ? ? fw.write("abcde"); ? ? ? ? ?//void write(String str, int off, int len):写一个字符串的一部分 // ? ? ? fw.write("abcde", 0, "abcde".length()); ? ? ? ?fw.write("abcde", 1, 3); ? ? ? ? ?//释放资源 ? ? ? ?fw.close(); ? } }
1.5字符流读数据【应用】
-
介绍
Reader: 用于读取字符流的抽象父类
FileReader: 用于读取字符流的常用子类
-
构造方法
方法名 说明 FileReader(File file) 在给定从中读取数据的 File 的情况下创建一个新 FileReader FileReader(String fileName) 在给定从中读取数据的文件名的情况下创建一个新 FileReader
-
成员方法
方法名 说明 int read() 一次读一个字符数据 int read(char[] cbuf) 一次读一个字符数组数据 -
代码演示
public class InputStreamReaderDemo { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ? ? ? ? ?FileReader fr = new FileReader("myCharStream\\b.txt"); ? ? ? ? ?//int read():一次读一个字符数据 // ? ? ? int ch; // ? ? ? while ((ch=fr.read())!=-1) { // ? ? ? ? ? System.out.print((char)ch); // ? ? ? } ? ? ? ? ?//int read(char[] cbuf):一次读一个字符数组数据 ? ? ? ?char[] chs = new char[1024]; ? ? ? ?int len; ? ? ? ?while ((len = fr.read(chs)) != -1) { ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.print(new String(chs, 0, len)); ? ? ? } ? ? ? ? ?//释放资源 ? ? ? ?fr.close(); ? } }
1.6字符流用户注册案例【应用】
-
案例需求
将键盘录入的用户名和密码保存到本地实现永久化存储
-
实现步骤
-
获取用户输入的用户名和密码
-
将用户输入的用户名和密码写入到本地文件中
-
关流,释放资源
-
-
代码实现
public class CharStreamDemo8 { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ? ? ? ?//需求: 将键盘录入的用户名和密码保存到本地实现永久化存储 ? ? ? ?//要求:用户名独占一行,密码独占一行 ? ? ? ? ?//分析: ? ? ? ?//1,实现键盘录入,把用户名和密码录入进来 ? ? ? ?Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); ? ? ? ?System.out.println("请录入用户名"); ? ? ? ?String username = sc.next(); ? ? ? ?System.out.println("请录入密码"); ? ? ? ?String password = sc.next(); ? ? ? ? ?//2.分别把用户名和密码写到本地文件。 ? ? ? ?FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("charstream\\a.txt"); ? ? ? ?//将用户名和密码写到文件中 ? ? ? ?fw.write(username); ? ? ? ?//表示写出一个回车换行符 windows \r\n MacOS \r Linux \n ? ? ? ?fw.write("\r\n"); ? ? ? ?fw.write(password); ? ? ? ?//刷新流 ? ? ? ?fw.flush(); ? ? ? ?//3.关流,释放资源 ? ? ? ?fw.close(); ? } }
1.7字符缓冲流【应用】
-
字符缓冲流介绍
-
BufferedWriter:将文本写入字符输出流,缓冲字符,以提供单个字符,数组和字符串的高效写入,可以指定缓冲区大小,或者可以接受默认大小。默认值足够大,可用于大多数用途
-
BufferedReader:从字符输入流读取文本,缓冲字符,以提供字符,数组和行的高效读取,可以指定缓冲区大小,或者可以使用默认大小。 默认值足够大,可用于大多数用途
-
-
构造方法
方法名 说明 BufferedWriter(Writer out) 创建字符缓冲输出流对象 BufferedReader(Reader in) 创建字符缓冲输入流对象 -
代码演示
public class BufferedStreamDemo01 { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ? ? ? ?//BufferedWriter(Writer out) ? ? ? ?BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?FileWriter("myCharStream\\bw.txt")); ? ? ? ?bw.write("hello\r\n"); ? ? ? ?bw.write("world\r\n"); ? ? ? ?bw.close(); ? ? ? ? ?//BufferedReader(Reader in) ? ? ? ?BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? FileReader("myCharStream\\bw.txt")); ? ? ? ? ?//一次读取一个字符数据 // ? ? ? int ch; // ? ? ? while ((ch=br.read())!=-1) { // ? ? ? ? ? System.out.print((char)ch); // ? ? ? } ? ? ? ? ?//一次读取一个字符数组数据 ? ? ? ?char[] chs = new char[1024]; ? ? ? ?int len; ? ? ? ?while ((len=br.read(chs))!=-1) { ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.print(new String(chs,0,len)); ? ? ? } ? ? ? ? ?br.close(); ? } }
1.8字符缓冲流特有功能【应用】
-
方法介绍
BufferedWriter:
方法名 说明 void newLine() 写一行行分隔符,行分隔符字符串由系统属性定义 BufferedReader:
方法名 说明 String readLine() 读一行文字。 结果包含行的内容的字符串,不包括任何行终止字符如果流的结尾已经到达,则为null -
代码演示
public class BufferedStreamDemo02 { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ? ? ? ? ?//创建字符缓冲输出流 ? ? ? ?BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?FileWriter("myCharStream\\bw.txt")); ? ? ? ? ?//写数据 ? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { ? ? ? ? ? ?bw.write("hello" + i); ? ? ? ? ? ?//bw.write("\r\n"); ? ? ? ? ? ?bw.newLine(); ? ? ? ? ? ?bw.flush(); ? ? ? } ? ? ? ? ?//释放资源 ? ? ? ?bw.close(); ? ? ? ? ?//创建字符缓冲输入流 ? ? ? ?BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?FileReader("myCharStream\\bw.txt")); ? ? ? ? ?String line; ? ? ? ?while ((line=br.readLine())!=null) { ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println(line); ? ? ? } ? ? ? ? ?br.close(); ? } }
1.9字符缓冲流操作文件中数据排序案例【应用】
-
案例需求
使用字符缓冲流读取文件中的数据,排序后再次写到本地文件
-
实现步骤
-
将文件中的数据读取到程序中
-
对读取到的数据进行处理
-
将处理后的数据添加到集合中
-
对集合中的数据进行排序
-
将排序后的集合中的数据写入到文件中
-
-
代码实现
public class CharStreamDemo14 { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ? ? ? ?//需求:读取文件中的数据,排序后再次写到本地文件 ? ? ? ?//分析: ? ? ? ?//1.要把文件中的数据读取进来。 ? ? ? ?BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("charstream\\sort.txt")); ? ? ? ?//输出流一定不能写在这里,因为会清空文件中的内容 ? ? ? ?//BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("charstream\\sort.txt")); ? ? ? ? ?String line = br.readLine(); ? ? ? ?System.out.println("读取到的数据为" + line); ? ? ? ?br.close(); ? ? ? ? ?//2.按照空格进行切割 ? ? ? ?String[] split = line.split(" ");//9 1 2 5 3 10 4 6 7 8 ? ? ? ?//3.把字符串类型的数组变成int类型 ? ? ? ?int [] arr = new int[split.length]; ? ? ? ?//遍历split数组,可以进行类型转换。 ? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < split.length; i++) { ? ? ? ? ? ?String smallStr = split[i]; ? ? ? ? ? ?//类型转换 ? ? ? ? ? ?int number = Integer.parseInt(smallStr); ? ? ? ? ? ?//把转换后的结果存入到arr中 ? ? ? ? ? ?arr[i] = number; ? ? ? } ? ? ? ?//4.排序 ? ? ? ?Arrays.sort(arr); ? ? ? ?System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); ? ? ? ? ?//5.把排序之后结果写回到本地 1 2 3 4... ? ? ? ?BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("charstream\\sort.txt")); ? ? ? ?//写出 ? ? ? ?for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { ? ? ? ? ? ?bw.write(arr[i] + " "); ? ? ? ? ? ?bw.flush(); ? ? ? } ? ? ? ?//释放资源 ? ? ? ?bw.close(); ? ? } }
1.10IO流小结【理解】
-
IO流小结
-
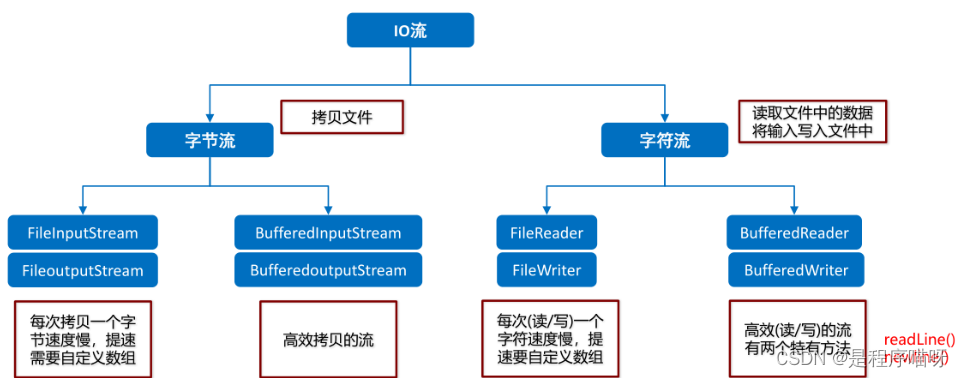
2.转换流
2.1字符流中和编码解码问题相关的两个类【理解】
-
InputStreamReader:是从字节流到字符流的桥梁,父类是Reader
它读取字节,并使用指定的编码将其解码为字符
它使用的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以被明确指定,或者可以接受平台的默认字符集
-
OutputStreamWriter:是从字符流到字节流的桥梁,父类是Writer
是从字符流到字节流的桥梁,使用指定的编码将写入的字符编码为字节
它使用的字符集可以由名称指定,也可以被明确指定,或者可以接受平台的默认字符集
2.2转换流读写数据【应用】
-
构造方法
方法名 说明 InputStreamReader(InputStream in) 使用默认字符编码创建InputStreamReader对象 InputStreamReader(InputStream in,String chatset) 使用指定的字符编码创建InputStreamReader对象 OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out) 使用默认字符编码创建OutputStreamWriter对象 OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out,String charset) 使用指定的字符编码创建OutputStreamWriter对象 -
代码演示
public class ConversionStreamDemo { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ? ? ? ?//OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? FileOutputStream("myCharStream\\osw.txt")); ? ? ? ?OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?FileOutputStream("myCharStream\\osw.txt"),"GBK"); ? ? ? ?osw.write("中国"); ? ? ? ?osw.close(); ? ? ? ? ?//InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? FileInputStream("myCharStream\\osw.txt")); ? ? ? ?InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? FileInputStream("myCharStream\\osw.txt"),"GBK"); ? ? ? ?//一次读取一个字符数据 ? ? ? ?int ch; ? ? ? ?while ((ch=isr.read())!=-1) { ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.print((char)ch); ? ? ? } ? ? ? ?isr.close(); ? } }
3.对象操作流
3.1对象序列化流【应用】
-
对象序列化介绍
-
对象序列化:就是将对象保存到磁盘中,或者在网络中传输对象
-
这种机制就是使用一个字节序列表示一个对象,该字节序列包含:对象的类型、对象的数据和对象中存储的属性等信息
-
字节序列写到文件之后,相当于文件中持久保存了一个对象的信息
-
反之,该字节序列还可以从文件中读取回来,重构对象,对它进行反序列化
-
-
对象序列化流: ObjectOutputStream
-
将Java对象的原始数据类型和图形写入OutputStream。 可以使用ObjectInputStream读取(重构)对象。 可以通过使用流的文件来实现对象的持久存储。 如果流是网络套接字流,则可以在另一个主机上或另一个进程中重构对象
-
-
构造方法
方法名 说明 ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out) 创建一个写入指定的OutputStream的ObjectOutputStream -
序列化对象的方法
方法名 说明 void writeObject(Object obj) 将指定的对象写入ObjectOutputStream -
示例代码
学生类
public class Student implements Serializable { ? ?private String name; ? ?private int age; ? ? ?public Student() { ? } ? ? ?public Student(String name, int age) { ? ? ? ?this.name = name; ? ? ? ?this.age = age; ? } ? ? ?public String getName() { ? ? ? ?return name; ? } ? ? ?public void setName(String name) { ? ? ? ?this.name = name; ? } ? ? ?public int getAge() { ? ? ? ?return age; ? } ? ? ?public void setAge(int age) { ? ? ? ?this.age = age; ? } ? ? ?@Override ? ?public String toString() { ? ? ? ?return "Student{" + ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?"name='" + name + '\'' + ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?", age=" + age + ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?'}'; ? } }测试类
public class ObjectOutputStreamDemo { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ? ? ? ?//ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out):创建一个写入指定的OutputStream的ObjectOutputStream ? ? ? ?ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("myOtherStream\\oos.txt")); ? ? ? ? ?//创建对象 ? ? ? ?Student s = new Student("佟丽娅",30); ? ? ? ? ?//void writeObject(Object obj):将指定的对象写入ObjectOutputStream ? ? ? ?oos.writeObject(s); ? ? ? ? ?//释放资源 ? ? ? ?oos.close(); ? } } -
注意事项
-
一个对象要想被序列化,该对象所属的类必须必须实现Serializable 接口
-
Serializable是一个标记接口,实现该接口,不需要重写任何方法
-
3.2对象反序列化流【应用】
-
对象反序列化流: ObjectInputStream
-
ObjectInputStream反序列化先前使用ObjectOutputStream编写的原始数据和对象
-
-
构造方法
方法名 说明 ObjectInputStream(InputStream in) 创建从指定的InputStream读取的ObjectInputStream -
反序列化对象的方法
方法名 说明 Object readObject() 从ObjectInputStream读取一个对象 -
示例代码
public class ObjectInputStreamDemo { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { ? ? ? ?//ObjectInputStream(InputStream in):创建从指定的InputStream读取的ObjectInputStream ? ? ? ?ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("myOtherStream\\oos.txt")); ? ? ? ? ?//Object readObject():从ObjectInputStream读取一个对象 ? ? ? ?Object obj = ois.readObject(); ? ? ? ? ?Student s = (Student) obj; ? ? ? ?System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge()); ? ? ? ? ?ois.close(); ? } }
3.3serialVersionUID&transient【应用】
-
serialVersionUID
-
用对象序列化流序列化了一个对象后,假如我们修改了对象所属的类文件,读取数据会不会出问题呢?
-
会出问题,会抛出InvalidClassException异常
-
-
如果出问题了,如何解决呢?
-
重新序列化
-
给对象所属的类加一个serialVersionUID
-
private static final long serialVersionUID = 42L;
-
-
-
-
transient
-
如果一个对象中的某个成员变量的值不想被序列化,又该如何实现呢?
-
给该成员变量加transient关键字修饰,该关键字标记的成员变量不参与序列化过程
-
-
-
示例代码
学生类
public class Student implements Serializable { ? ?private static final long serialVersionUID = 42L; ? ?private String name; // ? private int age; ? ?private transient int age; ? ? ?public Student() { ? } ? ? ?public Student(String name, int age) { ? ? ? ?this.name = name; ? ? ? ?this.age = age; ? } ? ? ?public String getName() { ? ? ? ?return name; ? } ? ? ?public void setName(String name) { ? ? ? ?this.name = name; ? } ? ? ?public int getAge() { ? ? ? ?return age; ? } ? ? ?public void setAge(int age) { ? ? ? ?this.age = age; ? } ? // ? @Override // ? public String toString() { // ? ? ? return "Student{" + // ? ? ? ? ? ? ? "name='" + name + '\'' + // ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ", age=" + age + // ? ? ? ? ? ? ? '}'; // ? } }测试类
public class ObjectStreamDemo { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { // ? ? ? write(); ? ? ? ?read(); ? } ? ? ?//反序列化 ? ?private static void read() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { ? ? ? ?ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("myOtherStream\\oos.txt")); ? ? ? ?Object obj = ois.readObject(); ? ? ? ?Student s = (Student) obj; ? ? ? ?System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge()); ? ? ? ?ois.close(); ? } ? ? ?//序列化 ? ?private static void write() throws IOException { ? ? ? ?ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("myOtherStream\\oos.txt")); ? ? ? ?Student s = new Student("佟丽娅", 30); ? ? ? ?oos.writeObject(s); ? ? ? ?oos.close(); ? } }
3.4对象操作流练习【应用】
-
案例需求
创建多个学生类对象写到文件中,再次读取到内存中
-
实现步骤
-
创建序列化流对象
-
创建多个学生对象
-
将学生对象添加到集合中
-
将集合对象序列化到文件中
-
创建反序列化流对象
-
将文件中的对象数据,读取到内存中
-
-
代码实现
学生类
public class Student implements Serializable{ ? ? ? ?private static final long serialVersionUID = 2L; ? ? ?private String name; ? ?private int age; ? ? ?public Student() { ? } ? ? ?public Student(String name, int age) { ? ? ? ?this.name = name; ? ? ? ?this.age = age; ? } ? ? ?public String getName() { ? ? ? ?return name; ? } ? ? ?public void setName(String name) { ? ? ? ?this.name = name; ? } ? ? ?public int getAge() { ? ? ? ?return age; ? } ? ? ?public void setAge(int age) { ? ? ? ?this.age = age; ? } }测试类
public class Demo03 { ? ?/** ? ? * read(): ? ? * ? ? 读取到文件末尾返回值是 -1 ? ? * readLine(): ? ? * ? ? 读取到文件的末尾返回值 null ? ? * readObject(): ? ? * ? ? 读取到文件的末尾 直接抛出异常 ? ? * 如果要序列化的对象有多个,不建议直接将多个对象序列化到文件中,因为反序列化时容易出异常 ? ? * ? ? 建议: 将要序列化的多个对象存储到集合中,然后将集合序列化到文件中 ? ? */ ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ? ? ? ?/*// 序列化 ? ? ? ?//1.创建序列化流对象 ? ? ? ?ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("myCode\\oos.txt")); ? ? ? ?ArrayList<Student> arrayList = new ArrayList<>(); ? ? ? ?//2.创建多个学生对象 ? ? ? ?Student s = new Student("佟丽娅",30); ? ? ? ?Student s01 = new Student("佟丽娅",30); ? ? ? ?//3.将学生对象添加到集合中 ? ? ? ?arrayList.add(s); ? ? ? ?arrayList.add(s01); ? ? ? ?//4.将集合对象序列化到文件中 ? ? ? ?oos.writeObject(arrayList); ? ? ? ?oos.close();*/ ? ? ? ? ?// 反序列化 ? ? //5.创建反序列化流对象 ? ? ? ?ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("myCode\\oos.txt")); ? ? //6.将文件中的对象数据,读取到内存中 ? ? ? ?Object obj = ois.readObject(); ? ? ? ?ArrayList<Student> arrayList = (ArrayList<Student>)obj; ? ? ? ?ois.close(); ? ? ? ?for (Student s : arrayList) { ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println(s.getName() + "," + s.getAge()); ? ? ? } ? } }
4.Properties集合
4.1Properties作为Map集合的使用【应用】
-
Properties介绍
-
是一个Map体系的集合类
-
Properties可以保存到流中或从流中加载
-
属性列表中的每个键及其对应的值都是一个字符串
-
-
Properties基本使用
public class PropertiesDemo01 { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) { ? ? ? ?//创建集合对象 // ? ? ? Properties<String,String> prop = new Properties<String,String>(); //错误 ? ? ? ?Properties prop = new Properties(); ? ? ? ? ?//存储元素 ? ? ? ?prop.put("itheima001", "佟丽娅"); ? ? ? ?prop.put("itheima002", "赵丽颖"); ? ? ? ?prop.put("itheima003", "刘诗诗"); ? ? ? ? ?//遍历集合 ? ? ? ?Set<Object> keySet = prop.keySet(); ? ? ? ?for (Object key : keySet) { ? ? ? ? ? ?Object value = prop.get(key); ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println(key + "," + value); ? ? ? } ? } }
4.2Properties作为Map集合的特有方法【应用】
-
特有方法
方法名 说明 Object setProperty(String key, String value) 设置集合的键和值,都是String类型,底层调用 Hashtable方法 put String getProperty(String key) 使用此属性列表中指定的键搜索属性 Set<String> stringPropertyNames() 从该属性列表中返回一个不可修改的键集,其中键及其对应的值是字符串 -
示例代码
public class PropertiesDemo02 { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) { ? ? ? ?//创建集合对象 ? ? ? ?Properties prop = new Properties(); ? ? ? ? ?//Object setProperty(String key, String value):设置集合的键和值,都是String类型 ? ? ? ?prop.setProperty("itheima001", "佟丽娅"); ? ? ? ?prop.setProperty("itheima002", "赵丽颖"); ? ? ? ?prop.setProperty("itheima003", "刘诗诗"); ? ? ? ? ?//String getProperty(String key):使用此属性列表中指定的键搜索属性 // ? ? ? System.out.println(prop.getProperty("itheima001")); // ? ? ? System.out.println(prop.getProperty("itheima0011")); ? // ? ? ? System.out.println(prop); ? ? ? ? ?//Set<String> stringPropertyNames():从该属性列表中返回一个不可修改的键集,其中键及其对应的值是字符串 ? ? ? ?Set<String> names = prop.stringPropertyNames(); ? ? ? ?for (String key : names) { // ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println(key); ? ? ? ? ? ?String value = prop.getProperty(key); ? ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println(key + "," + value); ? ? ? } ? } }
4.3Properties和IO流相结合的方法【应用】
-
和IO流结合的方法
方法名 说明 void load(Reader reader) 从输入字符流读取属性列表(键和元素对) void store(Writer writer, String comments) 将此属性列表(键和元素对)写入此 Properties表中,以适合使用 load(Reader)方法的格式写入输出字符流 -
示例代码
public class PropertiesDemo03 { ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ? ? ? ?//把集合中的数据保存到文件 // ? ? ? myStore(); ? ? ? ? ?//把文件中的数据加载到集合 ? ? ? ?myLoad(); ? ? } ? ? ?private static void myLoad() throws IOException { ? ? ? ?Properties prop = new Properties(); ? ? ? ? ?//void load(Reader reader): ? ? ? ?FileReader fr = new FileReader("myOtherStream\\fw.txt"); ? ? ? ?prop.load(fr); ? ? ? ?fr.close(); ? ? ? ? ?System.out.println(prop); ? } ? ? ?private static void myStore() throws IOException { ? ? ? ?Properties prop = new Properties(); ? ? ? ? ?prop.setProperty("itheima001","佟丽娅"); ? ? ? ?prop.setProperty("itheima002","赵丽颖"); ? ? ? ?prop.setProperty("itheima003","刘诗诗"); ? ? ? ? ?//void store(Writer writer, String comments): ? ? ? ?FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("myOtherStream\\fw.txt"); ? ? ? ?prop.store(fw,null); ? ? ? ?fw.close(); ? } }
4.4Properties集合练习【应用】
-
案例需求
在Properties文件中手动写上姓名和年龄,读取到集合中,将该数据封装成学生对象,写到本地文件
-
实现步骤
-
创建Properties集合,将本地文件中的数据加载到集合中
-
获取集合中的键值对数据,封装到学生对象中
-
创建序列化流对象,将学生对象序列化到本地文件中
-
-
代码实现
学生类
public class Student implements Serializable { ? ?private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; ? ? ?private String name; ? ?private int age; ? ? ?public Student() { ? } ? ? ?public Student(String name, int age) { ? ? ? ?this.name = name; ? ? ? ?this.age = age; ? } ? ? ?public String getName() { ? ? ? ?return name; ? } ? ? ?public void setName(String name) { ? ? ? ?this.name = name; ? } ? ? ?public int getAge() { ? ? ? ?return age; ? } ? ? ?public void setAge(int age) { ? ? ? ?this.age = age; ? } ? ? ?@Override ? ?public String toString() { ? ? ? ?return "Student{" + ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?"name='" + name + '\'' + ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?", age=" + age + ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?'}'; ? } }测试类
public class Test { ? ? ?public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ? ? //1.创建Properties集合,将本地文件中的数据加载到集合中 ? ? ? ?Properties prop = new Properties(); ? ? ? ?FileReader fr = new FileReader("prop.properties"); ? ? ? ?prop.load(fr); ? ? ? ?fr.close(); //2.获取集合中的键值对数据,封装到学生对象中 ? ? ? ?String name = prop.getProperty("name"); ? ? ? ?int age = Integer.parseInt(prop.getProperty("age")); ? ? ? ?Student s = new Student(name,age); //3.创建序列化流对象,将学生对象序列化到本地文件中 ? ? ? ?ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("a.txt")); ? ? ? ?oos.writeObject(s); ? ? ? ?oos.close(); ? } }
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【MySQL】数据库之MMM高可用
- 基于java,springboot的房屋租赁系统的设计与实现
- 电脑录屏快捷键大全,助你成为录屏高手
- JVM面试系列-01
- Java程序员真的还有未来吗?如何备战2024春招?并狂拿大厂offer?
- 使用Vue3开发学生管理系统模板1
- 没啥特长又想搞钱的进:2024副业小项目推荐
- Spring高手之路-Spring事务的传播机制(行为、特性)
- Java 开源扫雷游戏 JMine 发布新版 3.0 及介绍视频
- 02. VBA从入门到精通——基础语法