博弈类问题
发布时间:2024年01月12日
?巴什博弈(Bash Game)


String bashGame2(int n, int m) {
return n % (m + 1) != 0 ? "先手" : "后手";
}
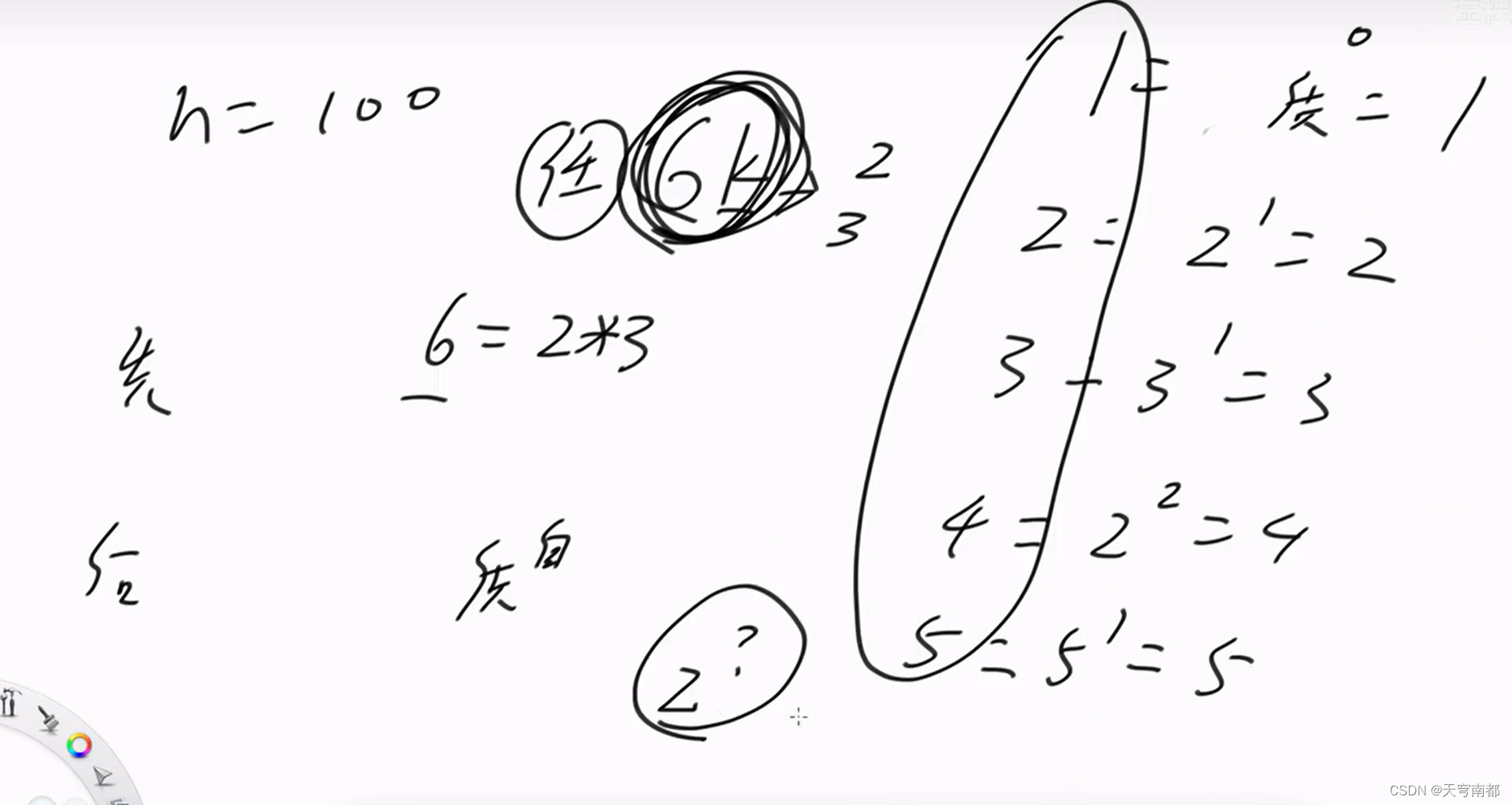
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
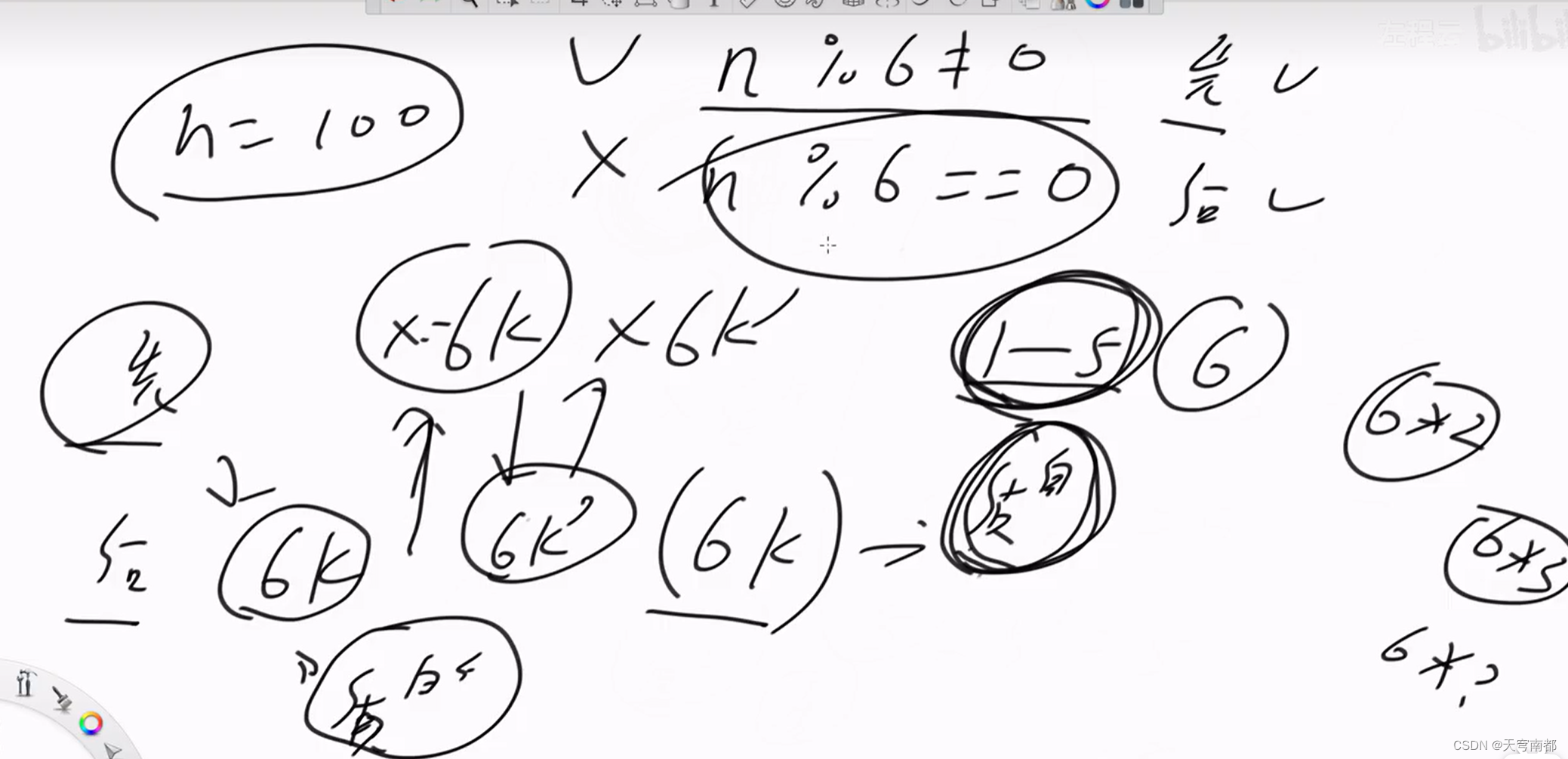
string compute(int n) {
return n % 6 != 0 ? "October wins!" : "Roy wins!";
}
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
int n;
cin >> n;
cout << compute(n) << '\n';
}
return 0;
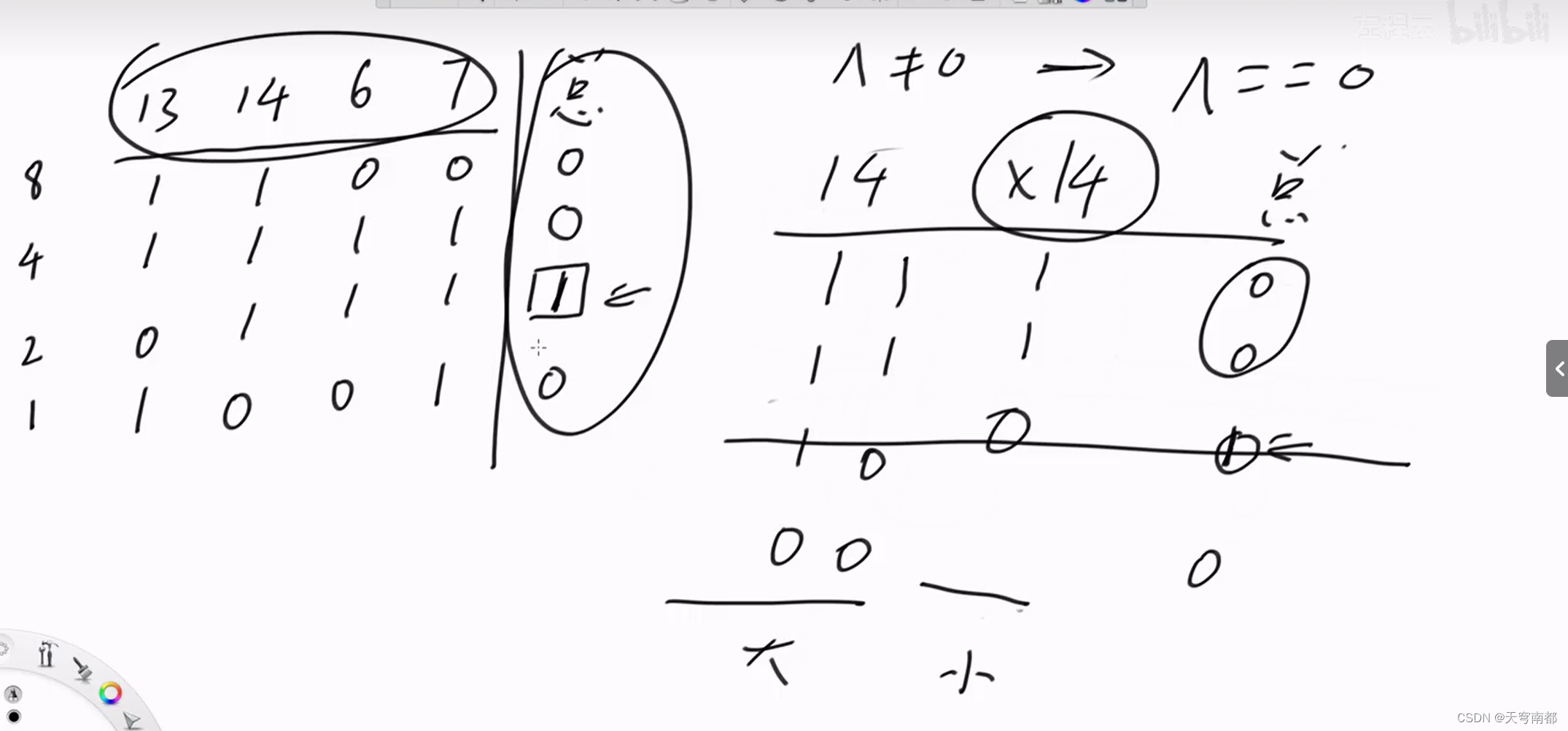
}Nim博弈
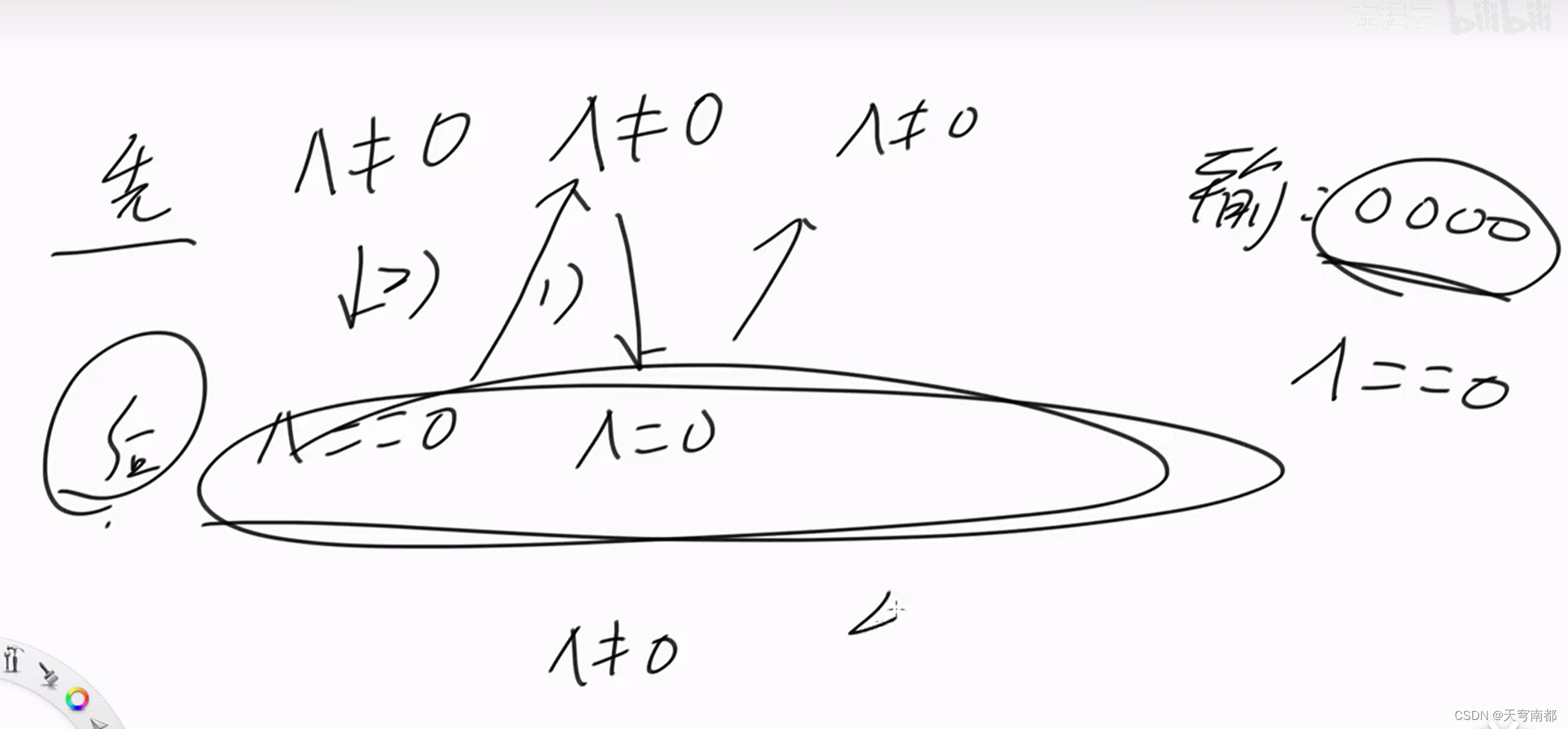
异或和等于0减去一个数一定可以变成不等于0
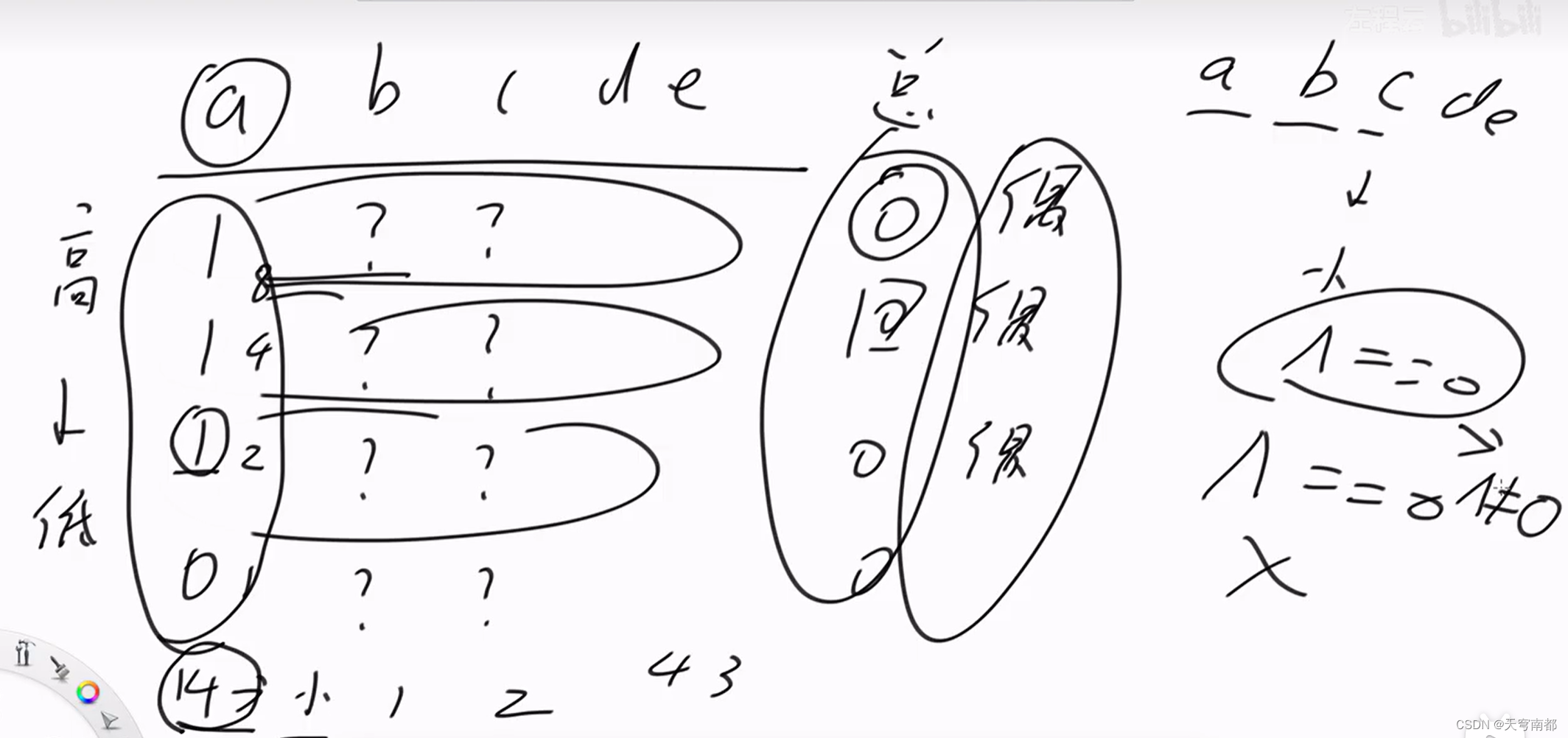
证明: 异或和不等于0减去一个数一定可以变成等于0
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
int n;
cin >> n;
int eor = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int num;
cin >> num;
eor ^= num;
}
if (eor != 0) {
cout << "Yes" << '\n';
}
else {
cout << "No" << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}反常游戏

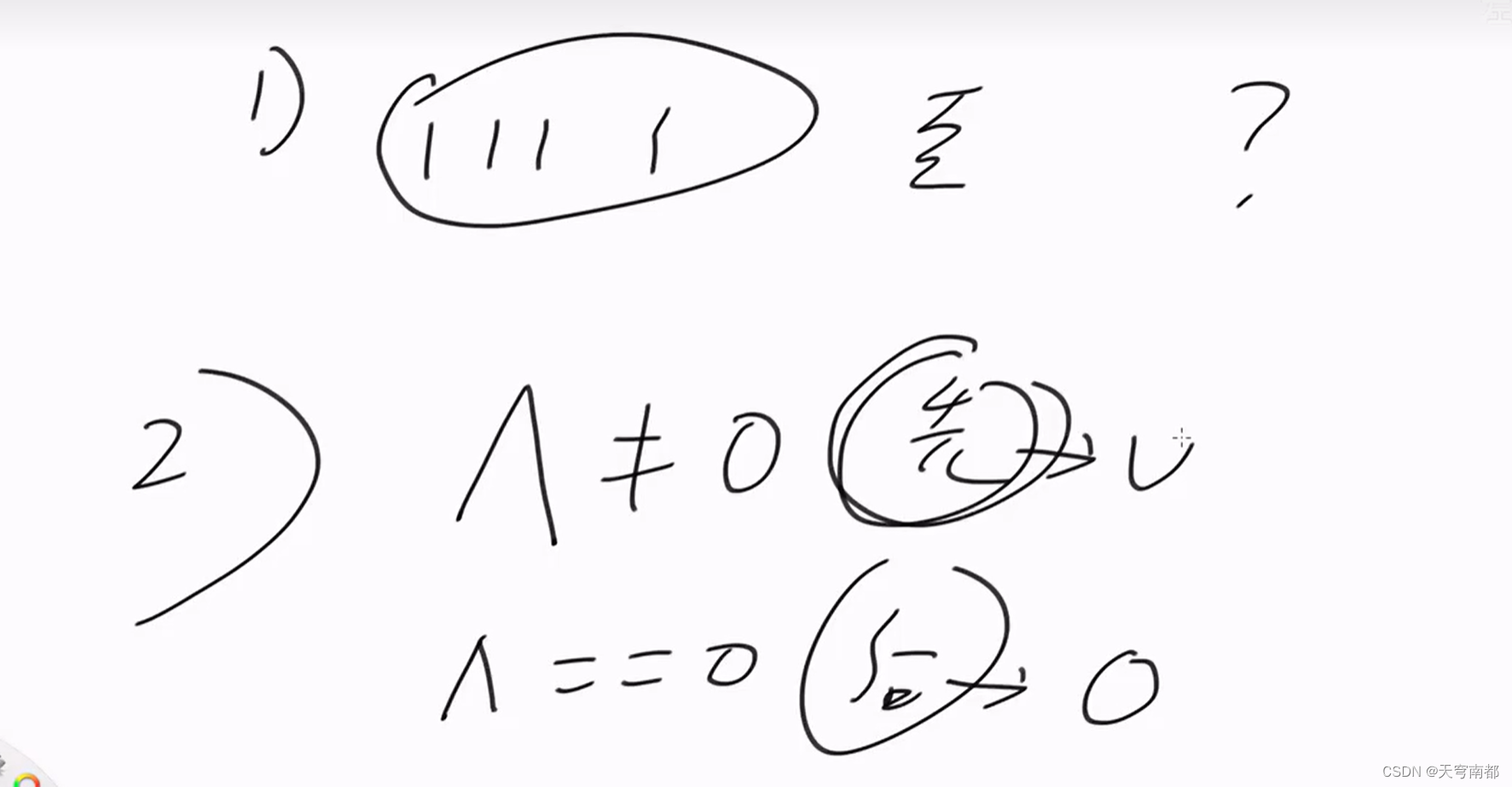
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int t;
cin >> t;
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
int n, sum = 0, eor = 0;
cin >> n;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int num;
cin >> num;
sum += (num == 1) ? 1 : 0;
eor ^= num;
}
if (sum == n) {
cout << ((n & 1) ? "Brother" : "John")<<'\n';
}
else {
cout << ((eor != 0) ? "John" : "Brother") << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}斐波那契博弈
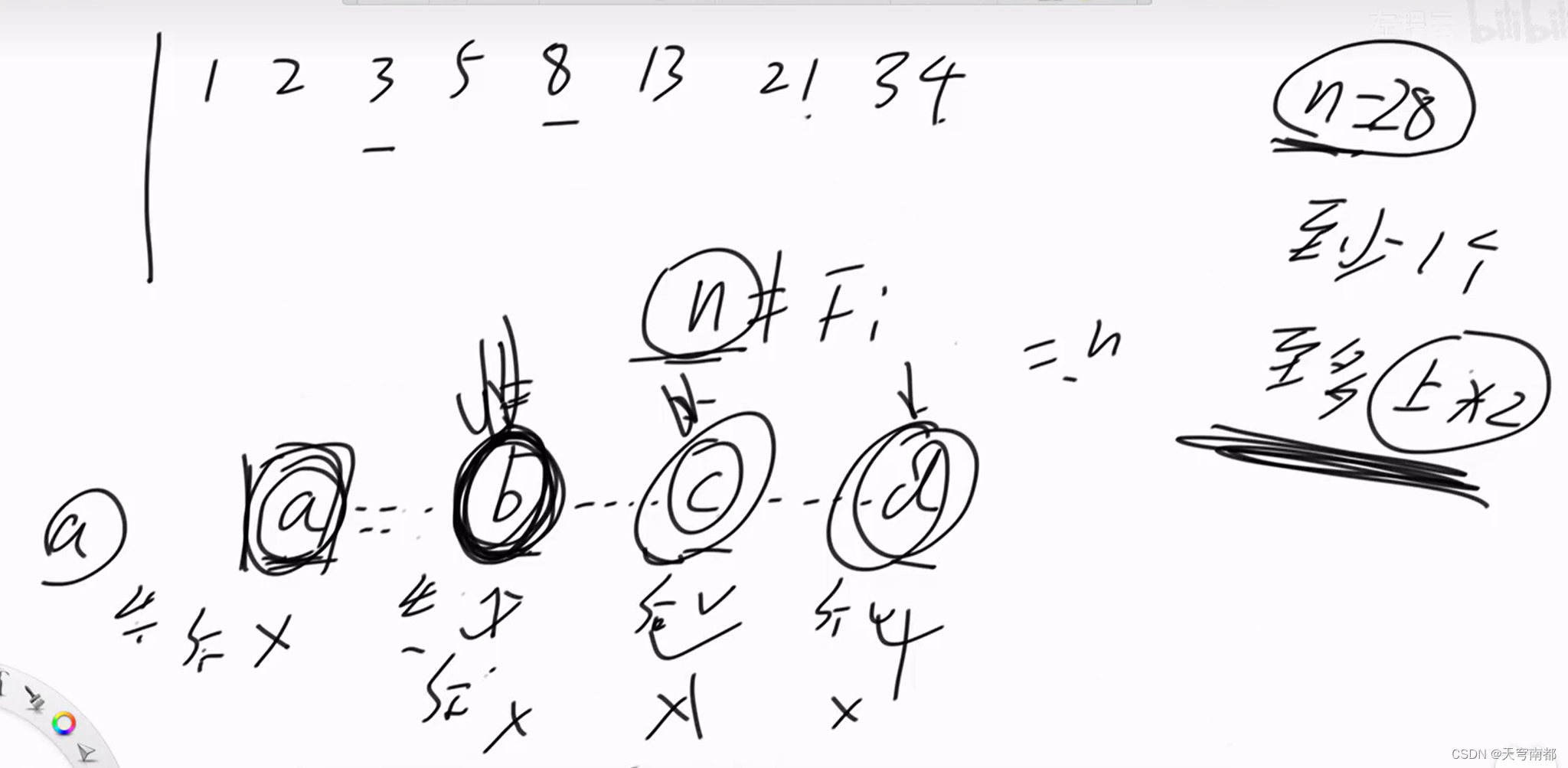
如果石头堆成斐波那契数列

如果不成
齐肯多夫定理(Zeckendorf's theorem)是一个有关斐波那契数列的数学定理。
定理陈述:每一个正整数都可以唯一地表示为若干个不连续的斐波那契数之和。
#include<iostream>
typedef long long LL;
const LL N = 1e15;
constexpr int M = 101;
LL f[M];
int size;
void build() {
f[0] = 1;
f[1] = 2;
size = 1;
while (f[size] <= N) {
f[size + 1] = f[size] + f[size - 1];
size++;
}
}
LL bs(LL n) {
int l = 0;
int r = size;
int m;
LL ans = -1;
while (l <= r) {
m = (l + r) / 2;
if (f[m] <= n) {
ans = f[m];
l = m + 1;
}
else {
r = m - 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
using namespace std;
build();
LL n;
cin >> n;
LL ans = -1, find;
while (n != 1 && n != 2) {
find = bs(n);
if (n == find) {
ans = find;
break;
}
else {
n -= find;
}
}
if (ans != -1)
cout << ans << '\n';
else
cout << n << '\n';
return 0;
}? 威佐夫博弈

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL N = 1e15 + 10;
int main() {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
double split = (sqrt(5.0) + 1.0) / 2.0;
int min_val = min(a, b);
int max_val = max(a,b);
if (min_val != (int)(split * (max_val - min_val)))
cout << 1 << '\n';
else
cout << 0 << '\n';
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/b1169909203/article/details/135542978
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
