QGIS二次开发(C++/Qt):表格文件转矢量
发布时间:2024年01月18日
需求规格说明
要求:将含有x/y数据的excel文件转换为矢量图层并挂接到图层树显示。
设计思路:创建一个ui界面,在界面中能够根据读取的excel文件,选择文件中的字段设置为矢量点的X/Y字段。读取excel文件,获取给定X/Y字段的字段索引,读取这两个字段所在的列,将其转换为坐标对,根据坐标对创建点要素,最后写入shp文件加载到地图中进行显示。
代码实现
在项目工程中添加新建项“Qt Widgets Class”,生成三个文件readExcel.ui、readExcel.h、readExcel.cpp
在Qt Creator中设计界面如下所示:

在readExcel.h中添加代码:
#pragma once
#include <QDialog>
#include "ui_readExcel.h"
class readExcel : public QDialog
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
readExcel(QWidget* parent = nullptr);
~readExcel();
void loadExcelFields(); //添加下拉框内容,选择X、Y坐标
private:
void selectPath(); //选择文件路径
private slots:
void on_pushButton_OK_clicked(); //ok按钮点击事件
void comboBoxXChanged(int index); //选项改变处理事件
void comboBoxYChanged(int index);
private:
Ui::readExcelClass ui;
QString excelFilePath; //路径
};在readExcel.cpp中添加代码:
#include "readExcel.h"
#include<QFileDialog>
#include<QtXlsx>
#include<QgsVectorLayer.h>
#include<QMessageBox>
#include<QgsProject.h>
#include "xlsxdocument.h"
readExcel::readExcel(QWidget* parent)
: QDialog(parent)
{
ui.setupUi(this);
connect(ui.selectFile, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &readExcel::selectPath);
connect(ui.comboBox_X, QOverload<int>::of(&QComboBox::currentIndexChanged), this, &readExcel::comboBoxXChanged);
connect(ui.comboBox_Y, QOverload<int>::of(&QComboBox::currentIndexChanged), this, &readExcel::comboBoxYChanged);
}
readExcel::~readExcel()
{}
void readExcel::selectPath() //选择路径
{
excelFilePath = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, QStringLiteral("选择Excel文件"), "", "Excel Files (*.xls *.xlsx)");
ui.lineEdit->setText(excelFilePath);
loadExcelFields();
}
void readExcel::loadExcelFields() //添加combox下拉框内容
{
QXlsx::Document excelFile(excelFilePath);
// 获取第一行(标题行)的数据
QStringList headerRow;
for (int col = 1; col <= excelFile.dimension().columnCount(); ++col)
{
headerRow.append(excelFile.read(1, col).toString());
}
ui.comboBox_Y->addItems(headerRow);
ui.comboBox_X->addItems(headerRow);
}
void readExcel::comboBoxXChanged(int index)
{
// 获取用户选择的 X 字段名称
QString selectedXField = ui.comboBox_X->itemText(index);
}
void readExcel::comboBoxYChanged(int index)
{
// 获取用户选择的 Y 字段名称
QString selectedYField = ui.comboBox_Y->itemText(index);
}
void readExcel::on_pushButton_OK_clicked()
{
// 确保 comboBox_X 和 comboBox_Y 已经选择了有效的字段
QString selectedXField = ui.comboBox_X->currentText();
QString selectedYField = ui.comboBox_Y->currentText();
if (selectedXField.isEmpty() || selectedYField.isEmpty())
{
QMessageBox::warning(this, "警告", "请选择有效的 X 和 Y 字段。");
return;
}
// 获取 Excel 文件路径
QString excelFilePath = ui.lineEdit->text();
// 打开 Excel 文件
QXlsx::Document excelFile(excelFilePath);
// 创建矢量图层
QString layerName = "Excel_Layer";
QgsVectorLayer* pointLayer = new QgsVectorLayer("Point?crs=EPSG:4326", layerName, "memory");
if (!pointLayer) {
QMessageBox::critical(this, "错误", "无法创建矢量图层。");
return;
}
// 向矢量图层添加其他属性字段
QStringList headerRow;
for (int col = 1; col <= excelFile.dimension().columnCount(); ++col)
{
QString fieldName = excelFile.read(1, col).toString();
// 获取 Excel 中列的数据类型
// 获取 Excel 中列的数据类型
QVariant::Type dataType = QVariant::Invalid;
for (int row = 2; row <= excelFile.dimension().rowCount(); ++row)
{
QVariant cellValue = excelFile.read(row, col);
if (cellValue.isValid())
{
dataType = cellValue.type();
break;
}
}
if (dataType != QVariant::Invalid)
{
QgsField field(fieldName, dataType);
pointLayer->dataProvider()->addAttributes({ field });
}
}
pointLayer->updateFields();
// 获取选定字段的列号
int xCol = -1;
int yCol = -1;
for (int col = 1; col <= excelFile.dimension().columnCount(); ++col)
{
QString fieldName = excelFile.read(1, col).toString(); //字段名
if (fieldName == selectedXField)
{
xCol = col;
}
else if (fieldName == selectedYField)
{
yCol = col;
}
}
if (xCol == -1 || yCol == -1) {
QMessageBox::critical(this, "错误", "未能找到选定字段的列号。");
return;
}
// // 向矢量图层添加要素
QgsFeatureList features;
for (int row = 2; row <= excelFile.dimension().rowCount(); ++row)
{
double xCoord = excelFile.read(row, xCol).toDouble(); // 读入 X、Y 坐标
double yCoord = excelFile.read(row, yCol).toDouble();
QgsFeature feature;
QgsGeometry geometry = QgsGeometry::fromPointXY(QgsPointXY(xCoord, yCoord));
feature.setGeometry(geometry);
// 设置属性
for (int col = 1; col <= excelFile.dimension().columnCount(); ++col)
{
QString fieldName = excelFile.read(1, col).toString();
QgsField field = pointLayer->fields().field(fieldName);
// 判断属性字段类型,如果是字符串类型,则直接使用 toString()
// 如果是其他类型,根据实际类型使用 toDouble()、toInt() 等方法
if (field.type() == QVariant::String)
{
feature.setAttribute(fieldName, excelFile.read(row, col).toString());
}
else
{
feature.setAttribute(fieldName, excelFile.read(row, col));
}
}
features.append(feature);
}
pointLayer->dataProvider()->addFeatures(features);
// 将矢量图层添加到地图中
QgsProject::instance()->addMapLayer(pointLayer);
close();
}在工程的主界面中添加一个action。新建一个readExcel对象,调用该界面。
//excel转点
void DataViewer::on_actionexcelTopoint_triggered()
{
readExcel* r = new readExcel(); //创建一个新界面
r->show();
m_mapCanvas->refresh();
}运行结果
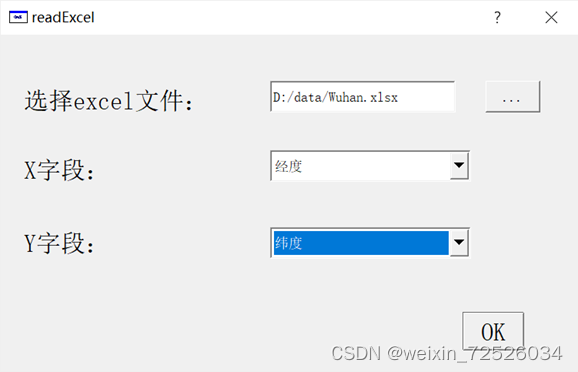

存在问题
创建的图层中无法显示属性数据:
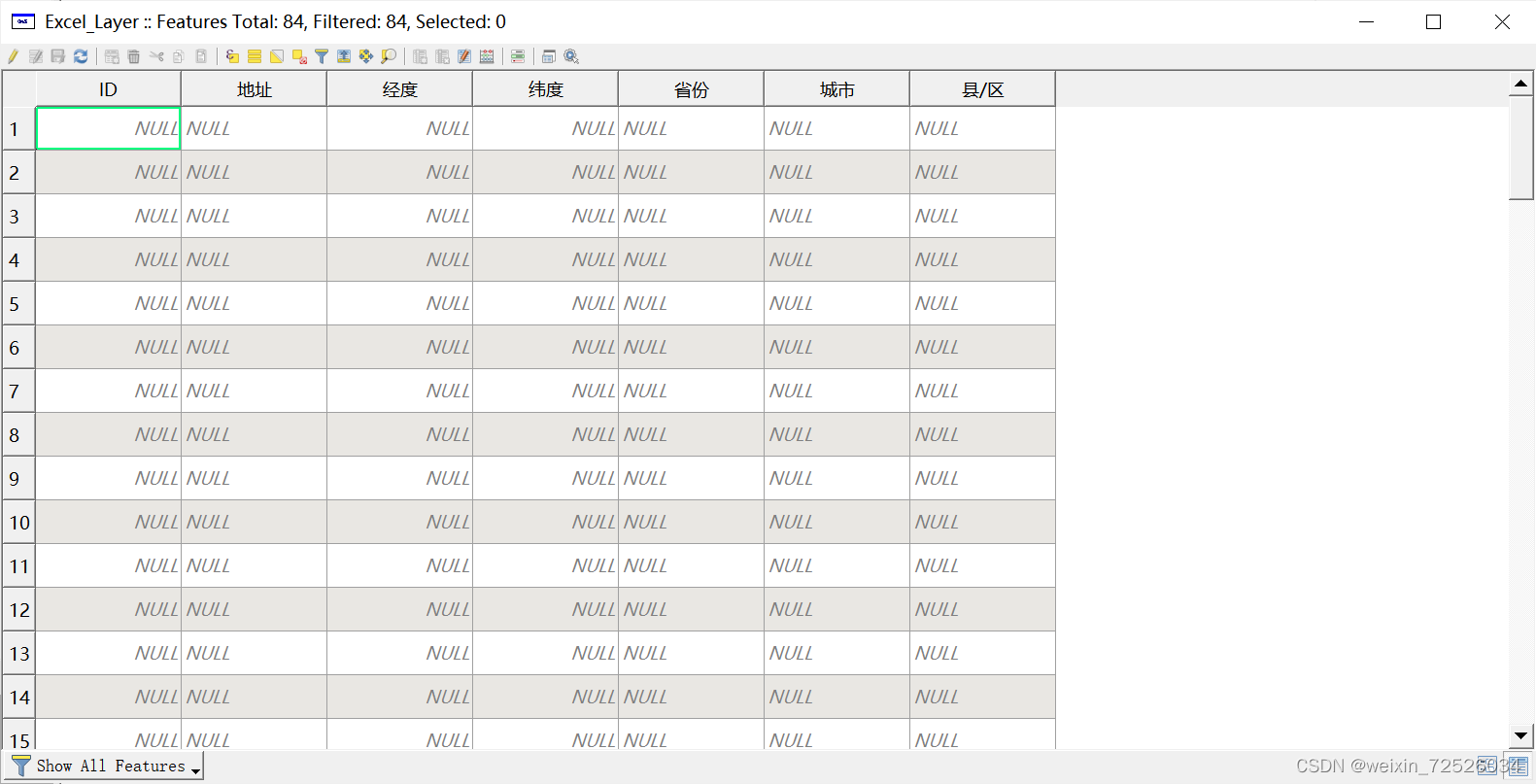
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_72526034/article/details/135655598
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 羊奶牧场的健康奶源,对儿童有多重要?
- 自动化革命:大象机器人的Mercury A1机械臂
- PHP Fatal error: Unparenthesized `a ? b : c ? d : e` is not supported.
- 获取多个PDF文件的内容并保存到excel上
- 高效办公:如何通过在文件名称右边添加关键字提升工作效率
- 每天五分钟计算机视觉:掌握迁移学习使用技巧
- Python学习笔记(二) 数据类型及相关函数
- 利用“与非”运算实现布尔代数中的与,或,非三种运算
- Linux多线程
- Redis底层数据结构原理