MySQL---多表查询
创建student和score表
mysql> CREATE? TABLE student (
??? -> id? INT(10)? NOT NULL? UNIQUE? PRIMARY KEY ,
??? -> name? VARCHAR(20)? NOT NULL ,
??? -> sex? VARCHAR(4) ,
??? -> birth? YEAR,
??? -> department? VARCHAR(20) ,
??? -> address? VARCHAR(50)
??? -> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.03 sec)
mysql> CREATE? TABLE score (
??? -> id? INT(10)? NOT NULL? UNIQUE? PRIMARY KEY? AUTO_INCREMENT ,
??? -> stu_id? INT(10)? NOT NULL ,
??? -> c_name? VARCHAR(20) ,
??? -> grade? INT(10)
??? -> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 3 warnings (0.05 sec)
为student表和score表增加记录
mysql> INSERT INTO student VALUES
( 901,'张老大', '男',1985,'计算机系', '北京市海淀区'),
( 902,'张老二', '男',1986,'中文系', '北京市昌平区'),
( 903,'张三', '女',1990,'中文系', '湖南省永州市'),
( 904,'李四', '男',1990,'英语系', '辽宁省阜新市'),
( 905,'王五', '女',1991,'英语系', '福建省厦门市'),
( 906,'王六', '男',1988,'计算机系', '湖南省衡阳市');
Query OK, 6 row affected (0.00 sec)
为student表和score表增加记录
INSERT INTO score VALUES
(NULL,901, '计算机',98),
(NULL,901, '英语', 80),
(NULL,902, '计算机',65),
(NULL,902, '中文',88),
(NULL,903, '中文',95),
(NULL,904, '计算机',70),
(NULL,904, '英语',92),
(NULL,905, '英语',94),
(NULL,906, '计算机',90),
(NULL,906, '英语',85);
Query OK, 10 rows affected (0.03 sec)
Records: 10? Duplicates: 0? Warnings: 0
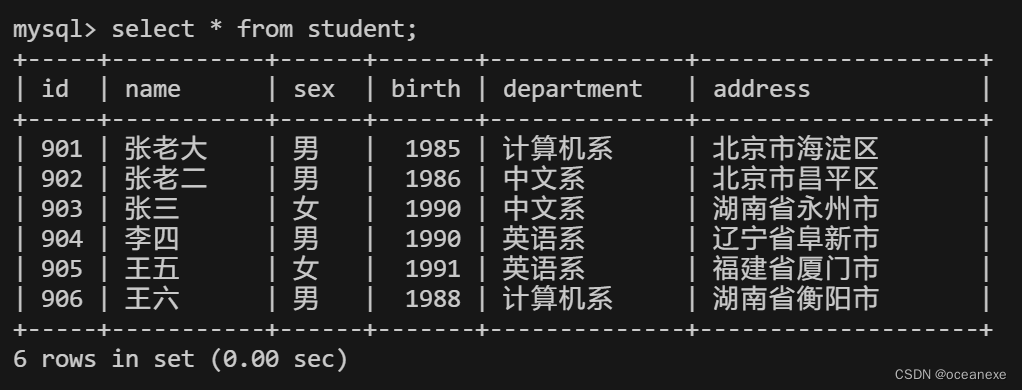
1.查询student表的所有记录
mysql> select * from student;
2.查询student表的第2条到4条记录
#在MySQL中,limit语句用于限制返回的记录数。它通常与select语句一起使用,以便从表中选择特定数量的行。
mysql> select * from student limit 2,4;?

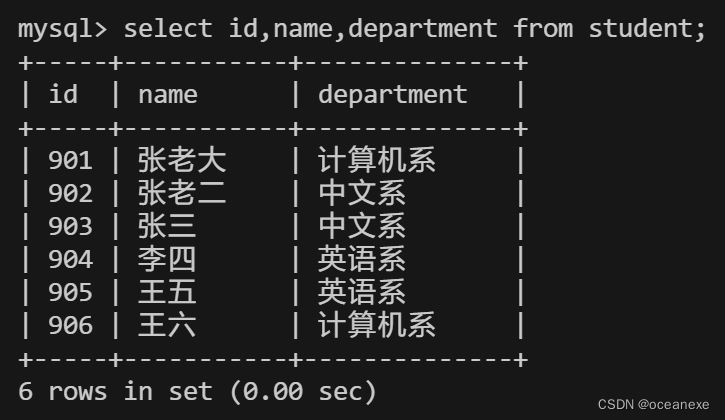
3.从student表查询所有学生的学号(id)、姓名(name)和院系(department)的信息
mysql> select id,name,department from student;
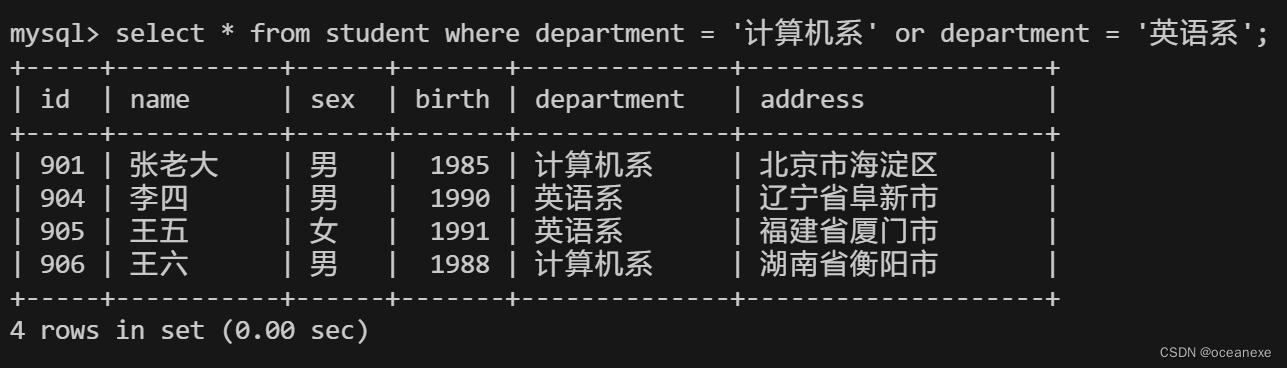
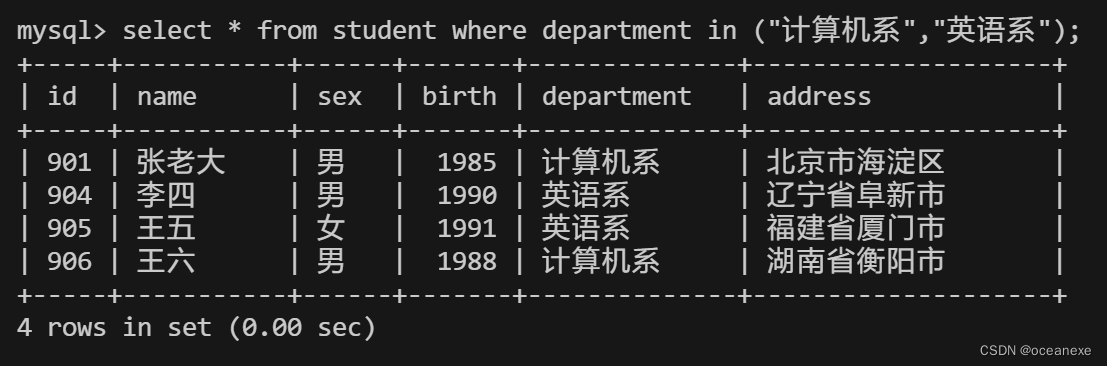
4.从student表中查询计算机系和英语系的学生的信息
#在MySQL中,in操作符用于在where子句中测试一个值是否在一组值中。它类似于多个or条件。
以下三种查询方式等价:
mysql> select * from student where department = '计算机系' or department = '英语系';
mysql> select * from student where department =( "计算机系" or "英语系");
mysql> select * from student where department in ("计算机系","英语系");
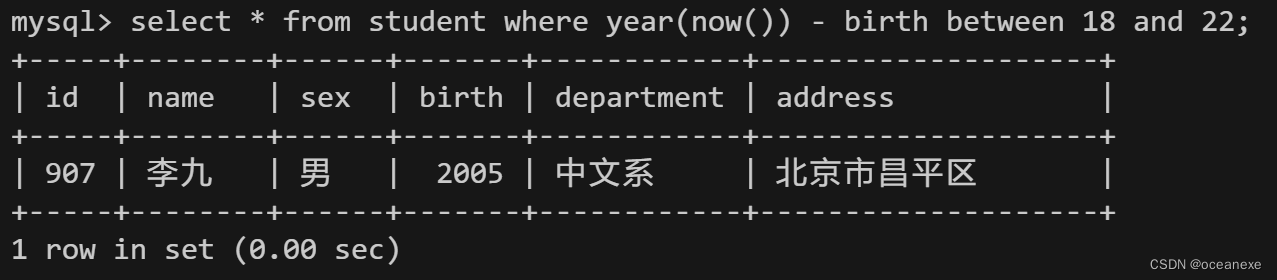
5.从student表中查询年龄18~22岁的学生信息
?#student表中插入一条数据
mysql> insert into student values(907,'李九','男','2005','中文系','北京市昌平区');???
#在MySQL中,year函数用于从给定的日期或日期时间表达式中提取年份。这个函数可以用于基于年份进行计算或比较。
#在MySQL中,now函数用于获取当前的日期和时间。这个函数返回的是服务器当前的日期和时间。
mysql> select * from student where year(now()) - birth between 18 and 22;
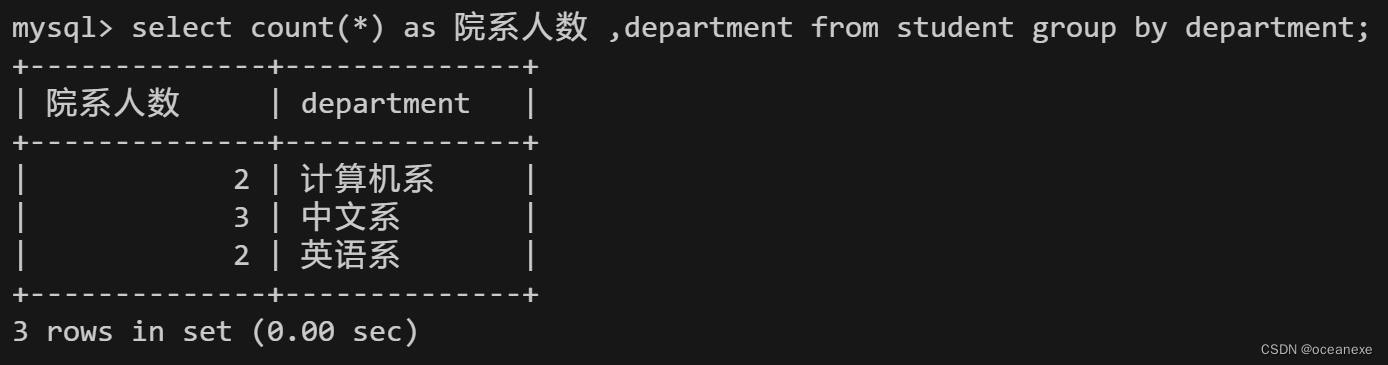
6.从student表中查询每个院系有多少人
#在MySQL中, group by语句用于将具有相同值进行分组,通常与聚合函数(如??count(),max,min(),sum(),avg())一起使用;
#注意,group? by语句必须放在where语句之后, order by语句之前。
mysql> select count(*) as 院系人数 ,department from student group by department;

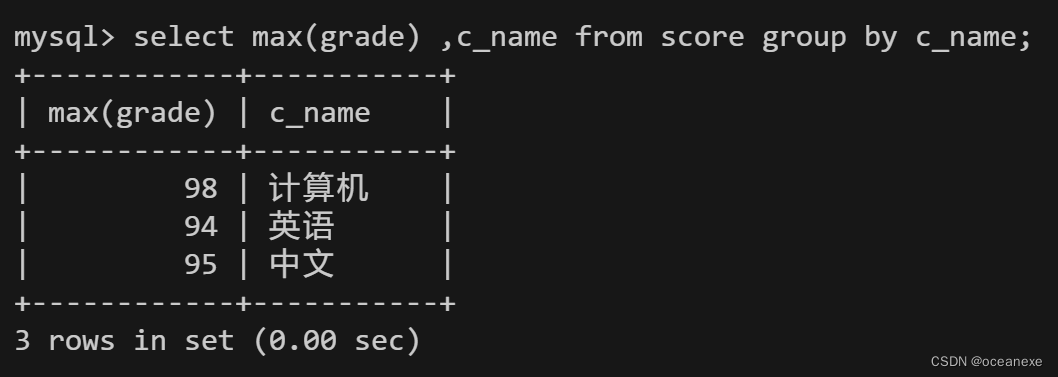
7.从score表中查询每个科目的最高分
#注意,除非使用了聚合函数,否则select语句中的列必须包含在group? by语句中,或者必须包含在聚合函数
mysql> select max(grade) ,c_name from score group by c_name;
8.查询李四的考试科目(c_name)和考试成绩(grade)
#在MySQL中,inner join 语句用于从两个或更多的表中选择记录,这些表之间存在某种关系。inner? join只会返回那些在两个表中都有匹配项的记录。
#在MySQL中, inner join …on 语句中的 on 关键字用于指定连接条件。也就是说,它告诉数据库如何将两个表连接在一起。
#当我们在两个表之间使用inner join 时,我们需要提供一个条件来确定如何将这两个表的行匹配起来。
mysql> select c_name 科目,grade 考试成绩 from score s inner join student stu on s.stu_id=stu.id where stu.name="李四";?

9.用连接的方式查询所有学生的信息和考试信息
#在MySQL中,inner join是一种连接两个或更多表的方式,只返回那些在两个表中都有匹配项的记录。
mysql> select * from student stu inner join score s on stu.id=s.stu_id;

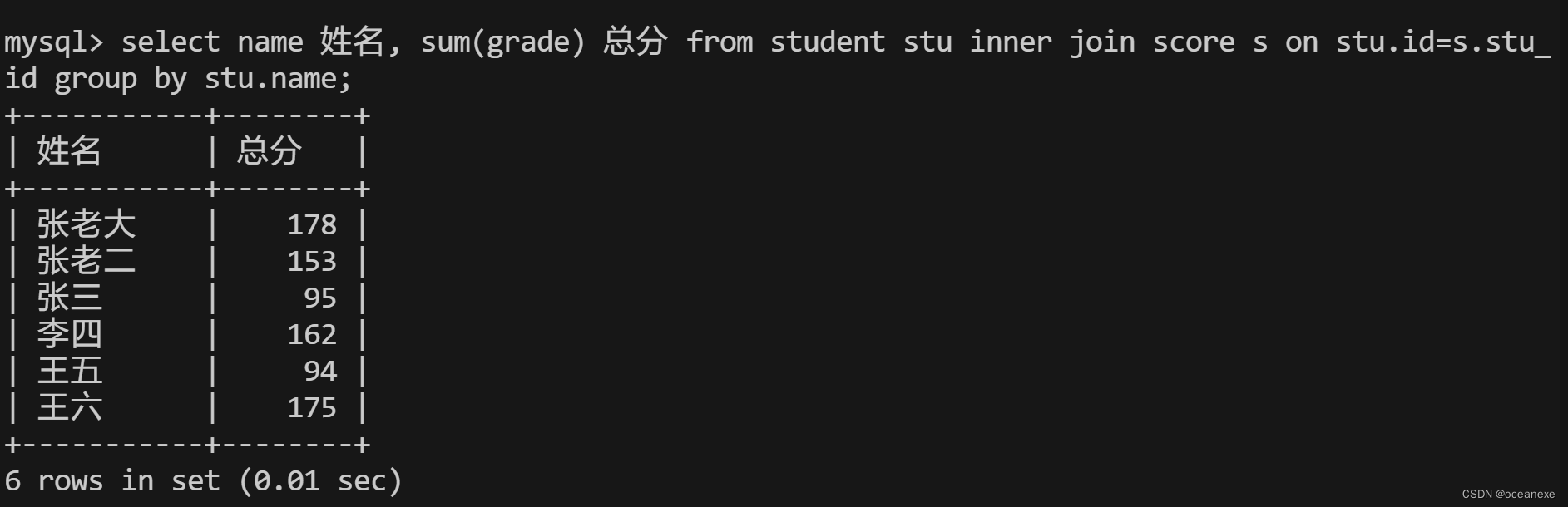
10.计算每个学生的总成绩
mysql> select name 姓名, sum(grade) 总分 from student stu inner join score s on stu.id=s.stu_id group by stu.name;
?11.计算每个考试科目的平均成绩
mysql> select c_name 考试科目,avg(grade) 平均分 from score group by c_name;
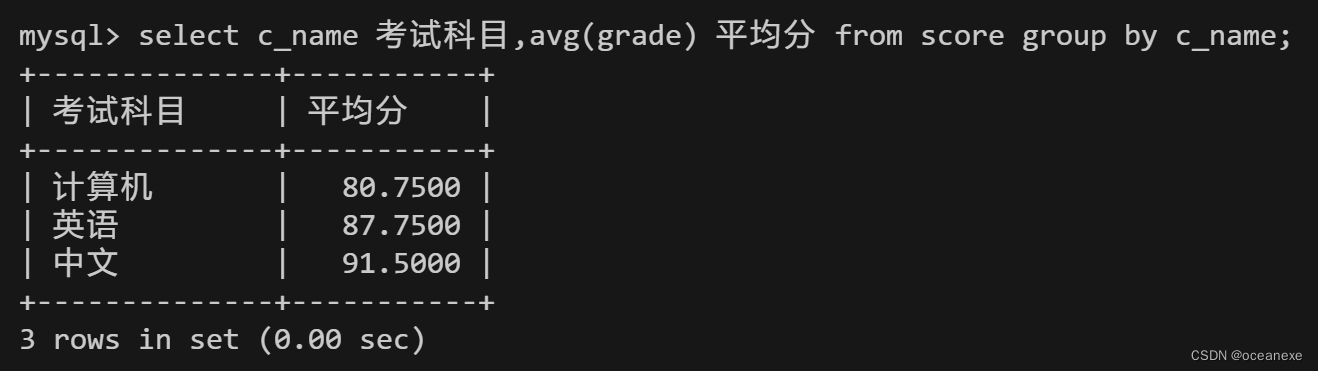
12.查询计算机成绩低于95的学生信息
mysql> select stu.*,s.c_name,s.grade from student stu inner join score s on stu.id=s.stu_id where s.c_name="计算机" and s.grade<95;
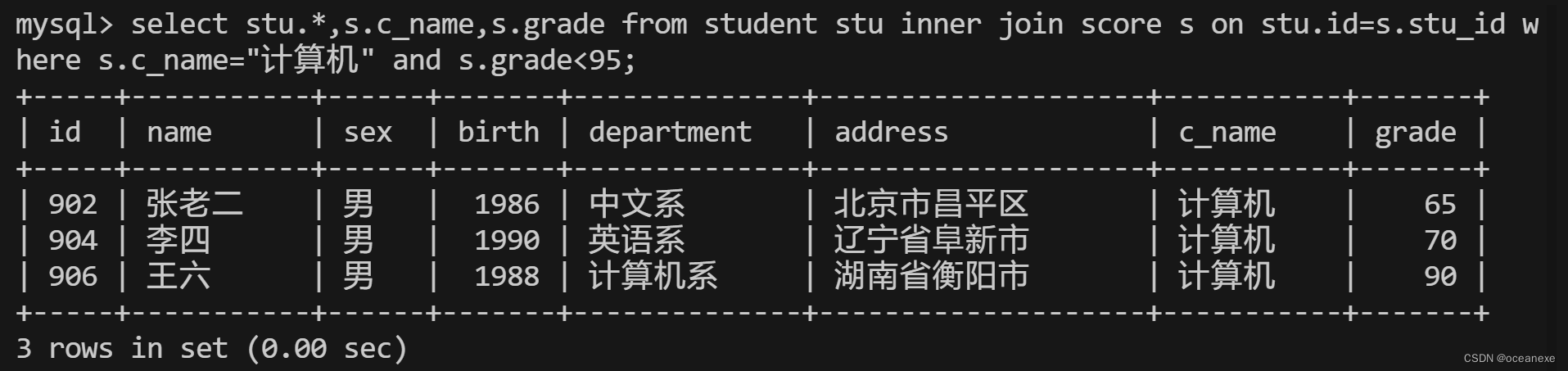
13.查询同时参加计算机和英语考试的学生的信息
方法一:
mysql> select * from student inner join score on? student.id=score.stu_id where score.stu_id in (select stu_id from score
?where stu_id in (select stu_id from score where c_name="计算机") and c_name="英语");
以下是MySQL语句分析
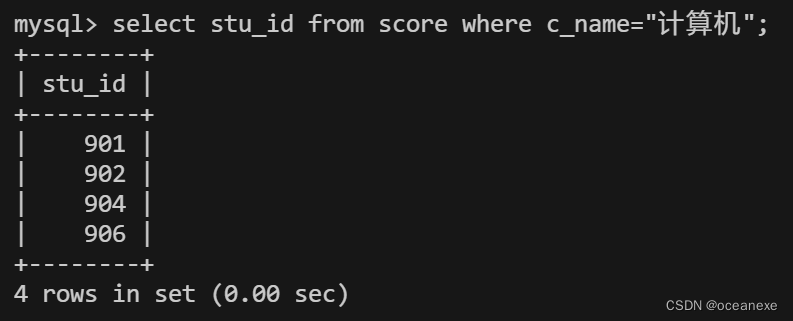
#先找到计算机的stu_id
mysql> select stu_id from score where c_name="计算机";
#子查询找到stu_id, 在c_name="计算机"的基础上 满足 c_name="英语"???
mysql> select stu_id from score where stu_id in (select stu_id from score where c_name="计算机") and c_name="英语";

#where 后面的条件找到了同时参加英语考试和计算机考试的学生stu_id,之后将两表连接
mysql> select * from student inner join score on? student.id=score.stu_id where score.stu_id in (select stu_id from score
?where stu_id in (select stu_id from score where c_name="计算机") and c_name="英语");

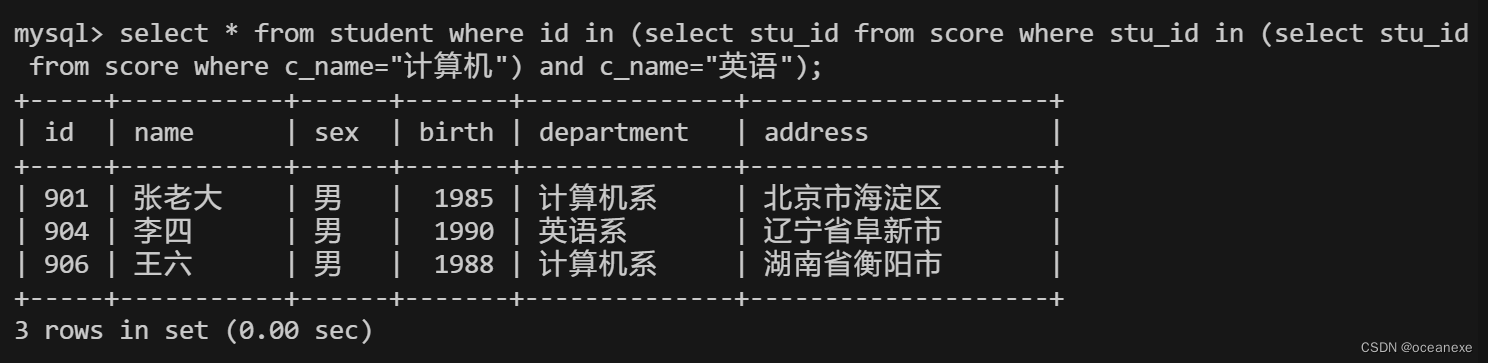
方法二:由上面SQL语句可知,我们找到了同时参加英语和计算机考试的stu_id,由于student 表中的id和score表中的stu_id 数据一致, 我们可以用如下简便方法:
mysql> select * from student where id in (select stu_id from score where stu_id in (select stu_id??from score where c_name="计算机") and c_name="英语");
14.将计算机考试成绩按从高到低进行排序
#在MySQL中,order by语句用于对结果集进行排序。我们可以根据一个或多个列来排序。默认情况下,order by按照升序(ASC)排序,(desc)降序。
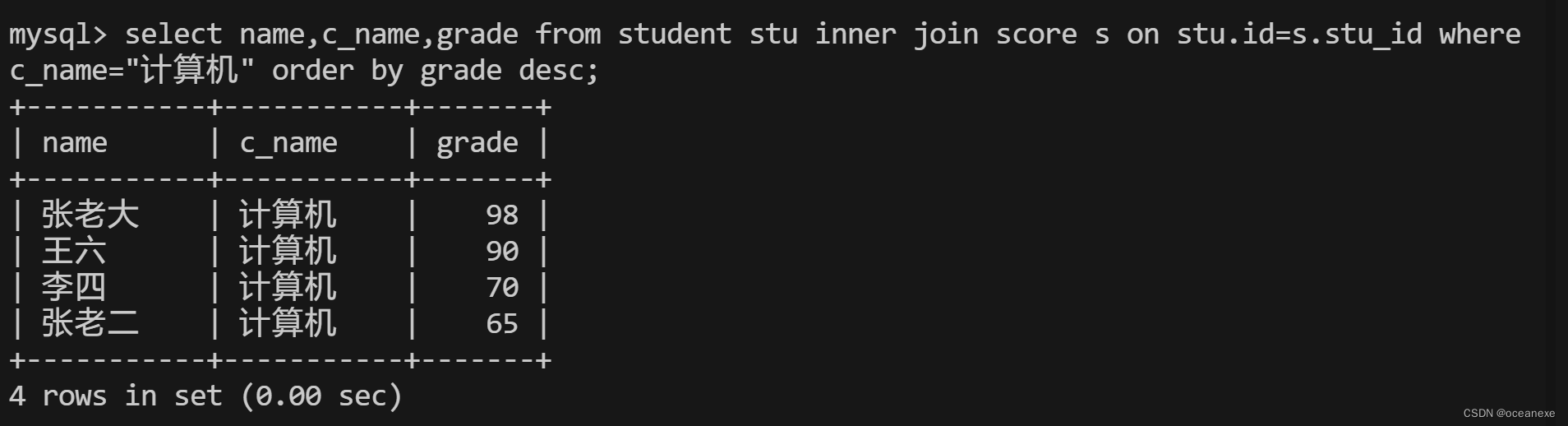
mysql> select name,c_name,grade from student stu inner join score s on stu.id=s.stu_id where c_name="计算机" order by grade desc;
15.从student表和score表中查询出学生的学号,然后合并查询结果
#在MySQL中,union操作符用于合并两个或更多的select语句的结果集。union操作符会自动去除重复的行。union操作符必须由两个或多个select语句组成,每个select语句的列数和对应位置的数据类型必须相同。
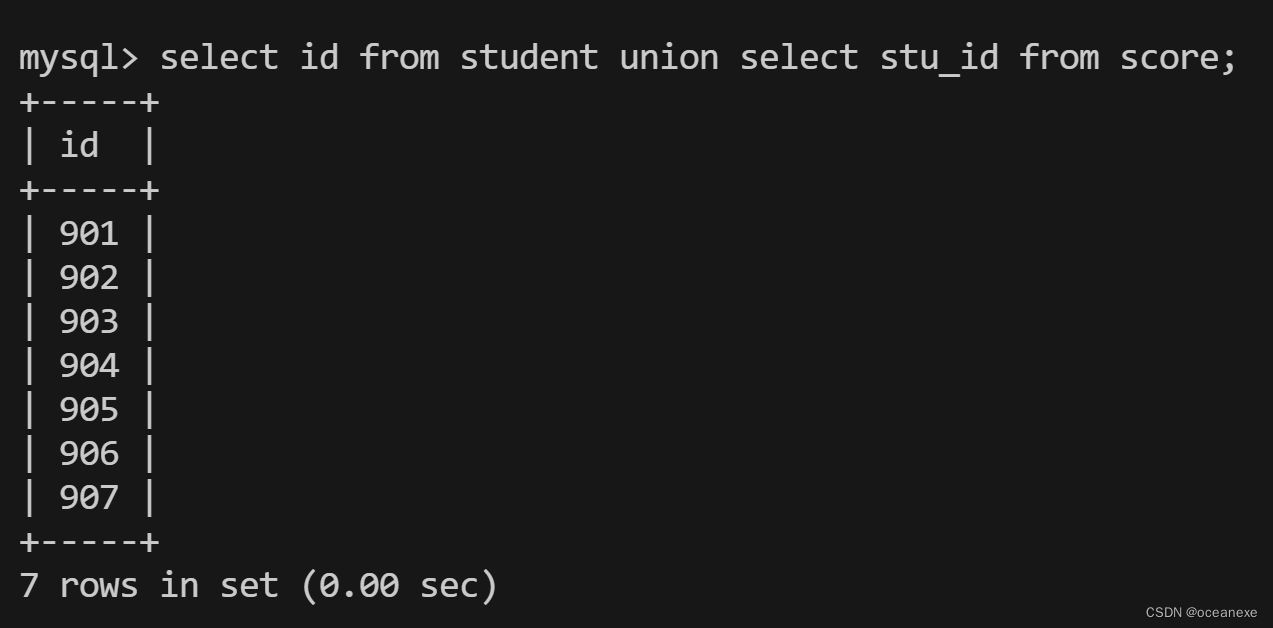
mysql> select id from student union select stu_id from score;
#代码分析
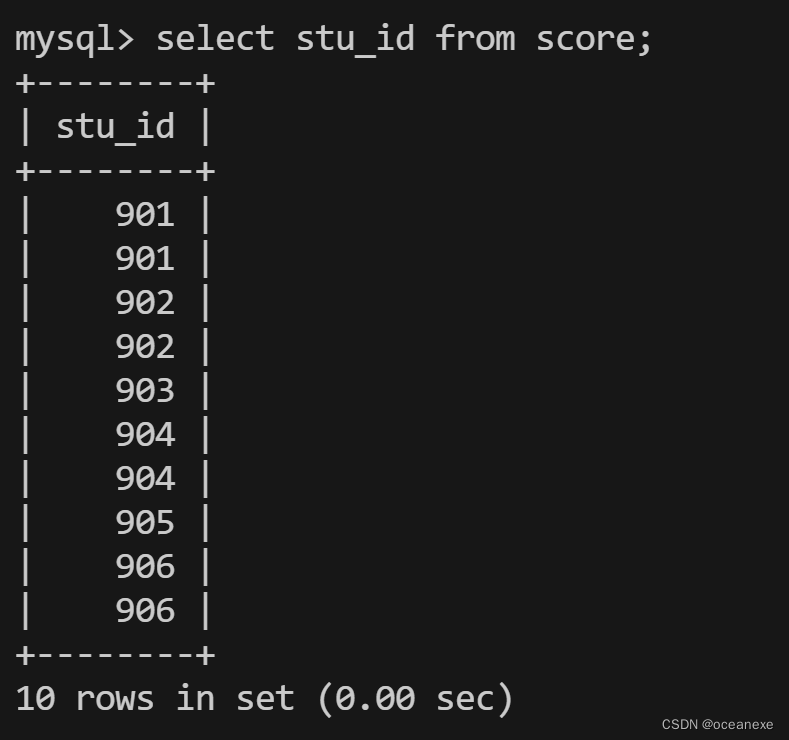
mysql> select stu_id from score;? ? ? ? ? #先找出score表中的stu_id
mysql> select id from student union select stu_id from score;#查找student中的id,并union已查找到score表中的stu_id
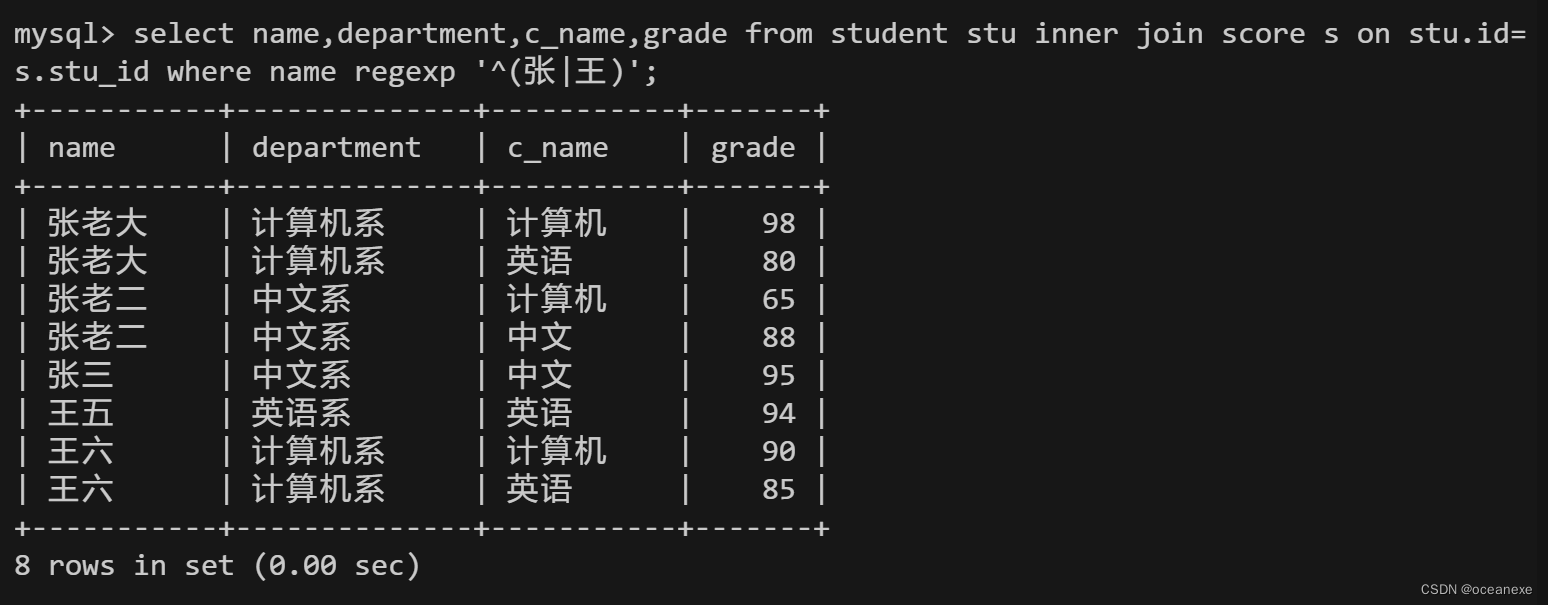
16.查询姓张或者姓王的同学的姓名、院系和考试科目及成绩
#在MySQL中,如果我们想要匹配以特定字符串开头的记录,我们可以在正则表达式(regexp)中使用^符号。^符号表示字符串的开始位置。
mysql> select name,department,c_name,grade from student stu inner join score s on stu.id=s.stu_id where name regexp '^(张|王)';
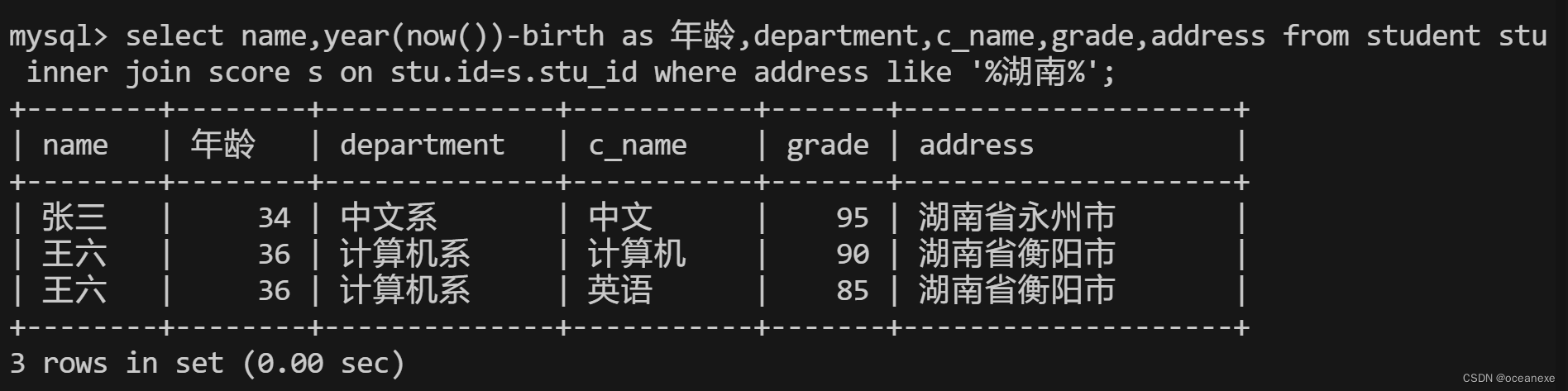
17.查询都是湖南的学生的姓名、年龄、院系和考试科目及成绩
#在MySQL中,like操作符用于在where子句中搜索列中的指定模式。然而,MySQL的like操作符并不支持完整的正则表达式语法,相当于是模糊查询;
# ??%(代表任何字符序列)和_(代表任何单个字符)。
mysql> select name,year(now())-birth as 年龄,department,c_name,grade,address from student stu inner join score? s on stu.id=s.stu_id where address like '%湖南%';
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 交叉编译含义
- RK3568驱动指南|第九篇 设备模型-第111章 platform总线注册驱动流程实例分析实验
- 怎么缩小动图的大小?一分钟快速压缩gif体积
- 横版长图一键切割,短图制作高效又便捷!
- GULP 案例 4:如何计算热力学性质(热容、熵、焓、自由能等)?
- (南京观海微电子)——色温介绍
- uniapp 【专题详解 -- 时间】云数据库时间类型设计,时间生成、时间格式化渲染(uni-dateformat 组件的使用)
- x-cmd pkg | qrencode - 二维码生成工具
- 【QT】QFileSystemModel类的应用介绍
- k8s operator从0到1实践