Java 异常处理
发布时间:2024年01月15日
一.Exception类的继承关系
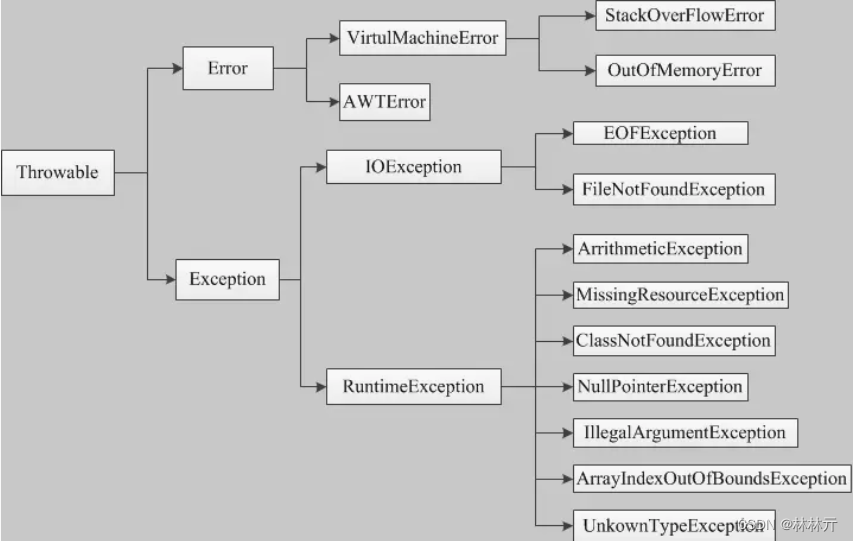
二.运行时异常和非运行时异常的区别
运行时异常都是RuntimeException类及其子类异常,如NullPointerException、IndexOutOfBoundsException等, 这些异常是非检查型异常,程序中可以选择捕获处理,也可以不处理。这些异常一般是由程序逻辑错误引起的,程序应该从逻辑角度尽可能避免这类异常的发生。
非运行时异常是RuntimeException以外的异常,类型上都属于Exception类及其子类。从程序语法角度讲是必须进行处理的异常,如果不处理,程序就不能编译通过。如IOException、SQLException等以及用户自定义的Exception异常,这些是检查型异常。一般情况下不自定义检查型异常。
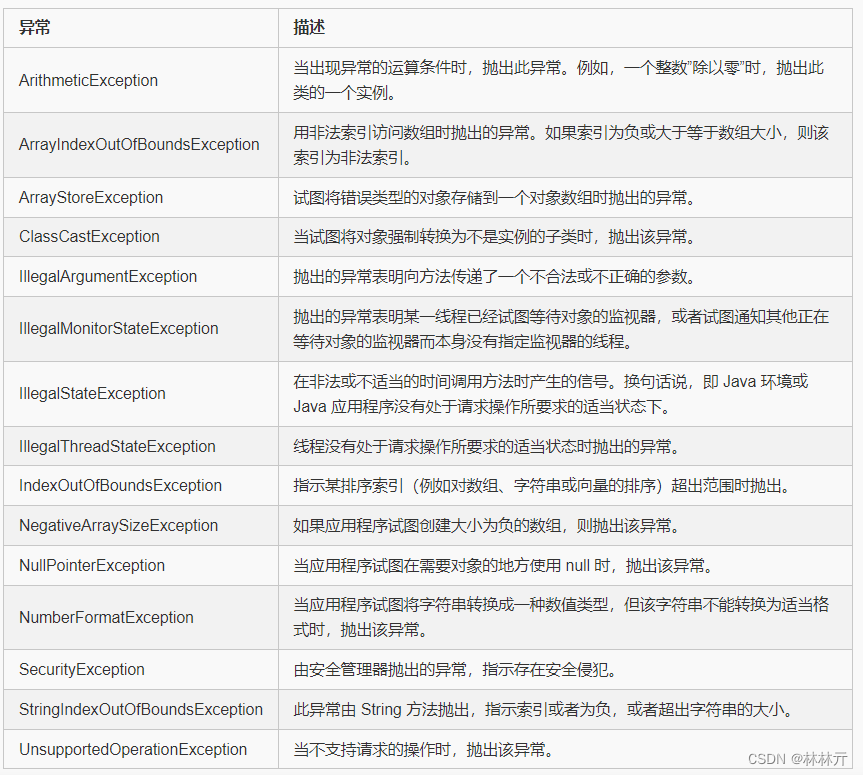
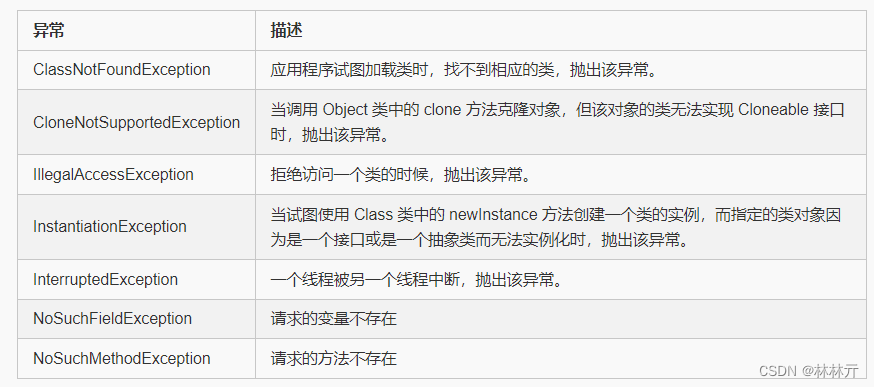
三.内置异常类
非检查性异常
检查性异常:
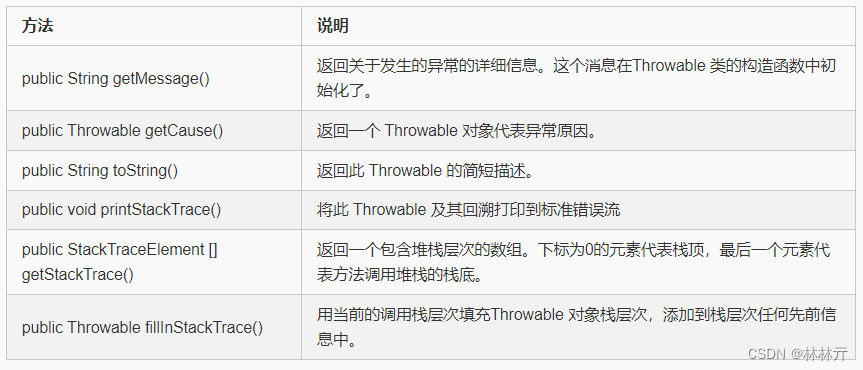
四、内置异常方法
五、捕获异常
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private static void foo() {
int[] array = new int[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i ++ )
array[i] = i;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int k = sc.nextInt();
int x = sc.nextInt();
try {
array[k] /= x;
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("除零错误!");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("数组越界!");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i ++ ) {
System.out.println(array[i]);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
foo();
}
}
六、抛出异常
throw: 在函数内抛出一个异常。
throws:在函数定义时抛出一些可能的异常。
检查型异常必须被捕获或者抛出。
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private static void foo() throws IOException, NoSuchFieldException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int x = sc.nextInt();
if (x == 1)
throw new IOException("找不到文件!!!");
else
throw new NoSuchFieldException("自定义异常");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
foo();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IOException!");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
System.out.println("NoSuchFieldException!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
七、try-with-resources
JDK7 之后,Java 新增的 try-with-resource 语法糖来打开资源,并且可以在语句执行完毕后确保每个资源都被自动关闭 。
try 用于声明和实例化资源,catch 用于处理关闭资源时可能引发的所有异常。
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String line;
try (
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("input.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("output.txt"));
) {
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println("Line => " + line);
bw.write("copy: " + line + "\n");
}
bw.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("IOException in try block =>" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/mumuhaoshuai/article/details/135608928
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!