【数据结构】图的创建(邻接矩阵,邻接表)以及深度广度遍历(BFS,DFS)
发布时间:2023年12月21日
前言
图是由顶点集合及顶点间的关系组成的一种数据结构:G = (V, E),其中:
顶点集合V = {x|x属于某个数据对象集}是有穷非空集合;
E = {(x,y)|x,y属于V}或者E = {<x, y>|x,y属于V && Path(x, y)}是顶点间关系的有穷集合,也叫
做边的集合。
完全图:在有n个顶点的无向图中,若有n * (n-1)/2条边,即任意两个顶点之间有且仅有一条边,
则称此图为无向完全图,比如上图G1;在n个顶点的有向图中,若有n * (n-1)条边,即任意两个
顶点之间有且仅有方向相反的边,则称此图为有向完全图
1.图的存储结构
因为图中既有节点,又有边(节点与节点之间的关系),因此,在图的存储中,只需要保存:节点和
边关系即可。
节点保存比较简单,只需要一段连续空间即可,那边关系该怎么保存呢?
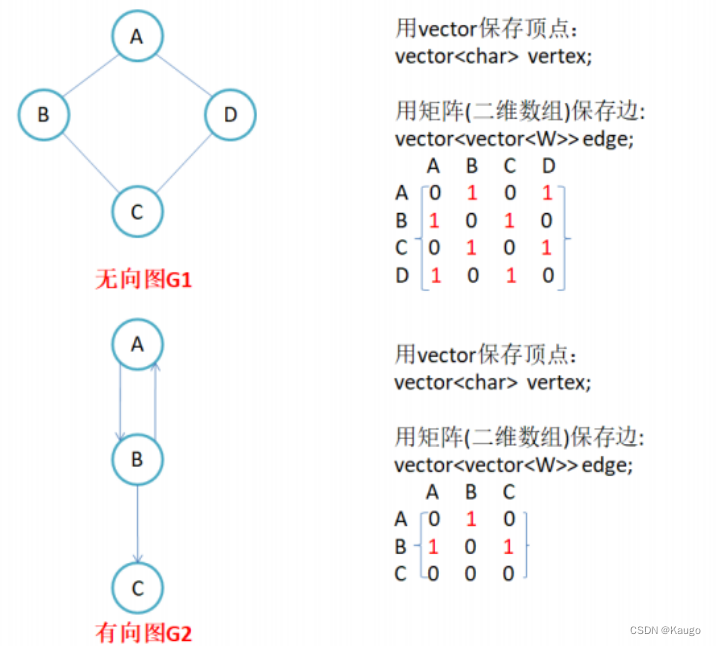
1.邻接矩阵
因为节点与节点之间的关系就是连通与否,即为0或者1,因此邻接矩阵(二维数组)即是:先用一
个数组将定点保存,然后采用矩阵来表示节点与节点之间的关系。
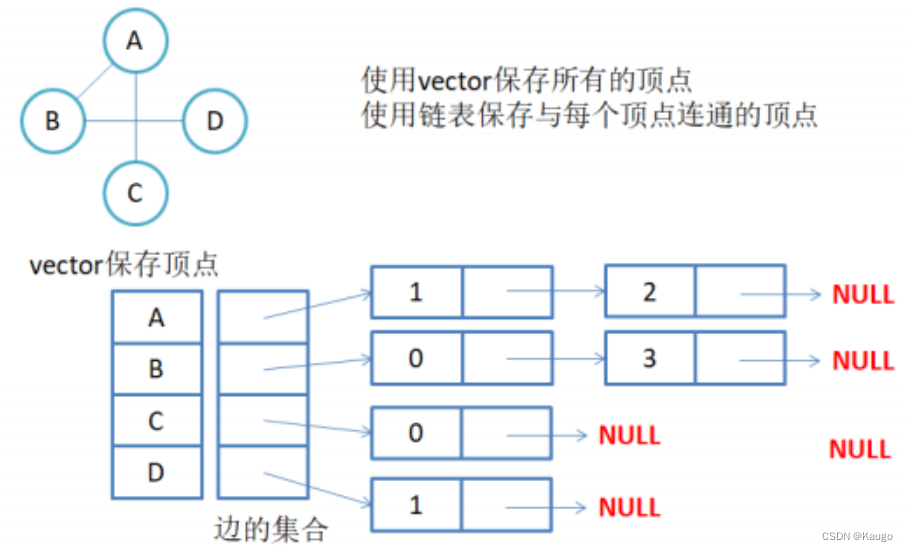
2.邻接表
一、邻接矩阵
主要思想就是,先建立顶点与数组下标的映射关系,我们通过这个两个顶点对应的下标,确定其在二维数组(邻接矩阵)中的位置,然后将邻接矩阵对应位置修改为权值(找顶点与下标关系之所以还要一个函数来控制而不用哈希表是因为我们要找的顶点可能不存在,如果用哈希表就会直接将这个不存在的顶点插入进去)
namespace matrix {
//V为顶点类型,W为边权值类型,MAX_W为权值最大值也就是无效值
//Direction用来判断是不是有向图,false为无向图
template<class V, class W, W MAX_W = INT_MAX, bool Direction = false>
class Graph {
public:
Graph(const V* a, size_t n) {
_vertexs.reserve(n);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
_vertexs.push_back(a[i]);
_indexMap[a[i]] = i;
//将顶点存入_vertexs,下标映射存进map
}
_matrix.resize(n);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _matrix.size(); i++) {
_matrix[i].resize(n, MAX_W);
//邻接矩阵默认初始值为无效值
}
}
size_t GetVertexIndex(const V& v) {
//获得对应顶点在数组中的下标
auto it = _indexMap.find(v);
if (it != _indexMap.end()) {
return it->second;
//有这个顶点返回其下标
}
else {
throw("顶点不存在");
return -1;
}
}
void _AddEdge(size_t srci, size_t dsti, const W& w) {
//存入权值
_matrix[srci][dsti] = w;
if (Direction == false) {
_matrix[dsti][srci] = w;
//无向图要两个方向都存
}
}
void AddEdge(const V& src, const V& dst, const W& w) {
//添加边与顶点的关系。从src到dst方向的关系
size_t srci = GetVertexIndex(src);
size_t dsti = GetVertexIndex(dst);
//先获取其对应的下标
_AddEdge(srci, dsti, w);
}
void Print() {
for (size_t i = 0; i < _vertexs.size(); i++) {
cout << "[" << i << "]" << "->" << _vertexs[i] << endl;
}//打印顶点集
cout << endl;
//打印邻接矩阵
for (size_t i = 0; i < _matrix.size(); i++) {
cout << i << " ";
for (size_t j = 0; j < _matrix[i].size(); j++) {
if (_matrix[i][j] == MAX_W) {
printf("%4c", '*');
}
else {
printf("%4d", _matrix[i][j]);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
}
private:
vector<V>_vertexs;//顶点集合
map<V, int>_indexMap;//存顶点与数组下标的映射关系
vector<vector<W>>_matrix;//邻接矩阵
};
}
用邻接矩阵存储图的有点是能够快速知道两个顶点是否连通,缺陷是如果顶点比较多,边比
较少时,矩阵中存储了大量的0成为系数矩阵,比较浪费空间,并且要求两个节点之间的路
径不是很好求。
二、邻接表
namespace link_table {
template<class W>
struct Edge {//Edge用来保存边的关系,当作结点来使
int _dsti;//目标顶点对应下标
W _w;//权值
Edge<W>* _next;
Edge(int dsti, const W& w)
:_dsti(dsti),
_w(w),
_next(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class V, class W, bool Direction = false>
class Graph {
typedef Edge<W> Edge;//注意这里typedf要传参
public:
Graph(const V* a, size_t n) {
_vertexs.reserve(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
_vertexs.push_back(a[i]);
_indexMap[a[i]] = i;
//将顶点放入数组,并建立顶点与下标的映射关系
}
_tables.resize(n, nullptr);
}
size_t GetVertexIndex(const V& v) {
//查找顶点对应的下标,这里不直接用哈希表
//来查是因为顶点可能不存在
auto it = _indexMap.find(v);
if (it != _indexMap.end()) {
return it->second;
}
else {
throw ("顶点不存在");
return -1;
}
}
void AddEdge(const V& src, const V& dst, const W& w) {
size_t srci = GetVertexIndex(src);
size_t dsti = GetVertexIndex(dst);
Edge* eg = new Edge(dsti, w);
eg->_next = _tables[srci];
_tables[srci] = eg;
if (Direction == false) {//如果为无向图,两个顶点都要加权值记录
Edge* eg = new Edge(srci, w);
eg->_next = _tables[dsti];
_tables[dsti] = eg;
}
}
void Print() {
for (size_t i = 0; i < _vertexs.size(); i++) {
cout << "[" << i << "]" << _vertexs[i] << endl;
}//打印顶点集合
cout << endl;
//打印邻接表
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++) {
cout << _vertexs[i] << "[" << i << "]->";
Edge* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur) {
cout << "[" << _vertexs[cur->_dsti] << ":" << cur->_dsti << ":" << cur->_w << endl;
cur = cur->_next;
}
cout << "nullptr" << endl;
}
}
private:
vector<V>_vertexs;//顶点数组
vector<Edge*>_tables;//邻接表
map<V, int> _indexMap;//顶点与下标的映射关系
};
}
二、图的遍历
1.DFS
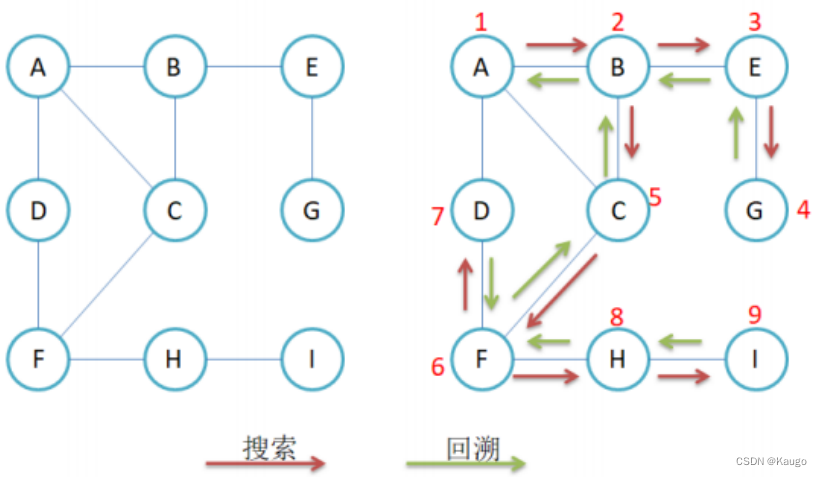
void _DFS(size_t srci, vector<bool>& visited) {
cout << srci << ":" << _vertexs[srci] << endl;
visited[srci] = true;//标记这个顶点被访问过了
for (size_t i = 0; i < _vertexs.size(); i++) {
if (_matrix[srci][i] != MAX_W && visited[i] == false) {
_DFS(i, visited);
}
}
}
void DFS(const V& src) {
size_t srci = GetVertexIndex(src);
vector<bool>visited(_vertexs.size(), false);
_DFS(srci, visited);
}
2.BFS
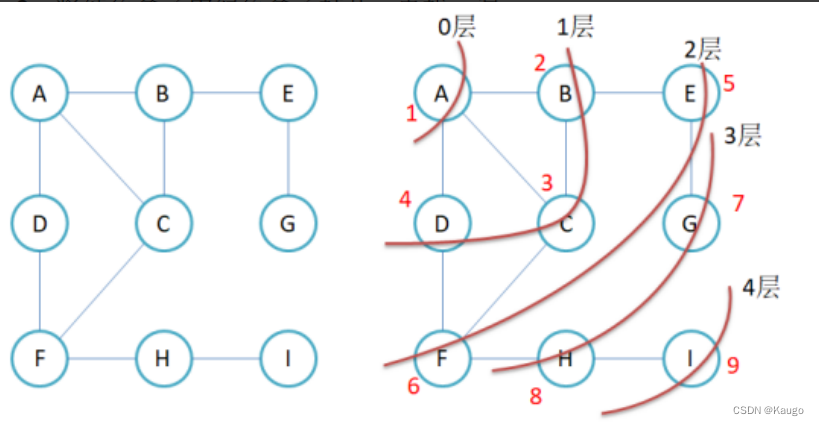
void BFS(const V& src) {
size_t srci = GetVertexIndex(src);
queue<int>q;
q.push(srci);
vector<bool>visited(_vertexs.size(), false);
visited[srci] = true;//标记这个顶点被访问过了
int levelSize = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
//levelSize为当前层的大小
for (size_t i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
int front = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << front << ":" << _vertexs[front]<<" ";
for (size_t i = 0; i < _vertexs.size(); i++) {
if (_matrix[front][i] != MAX_W && visited[i] == false) {
q.push(i);
visited[i] = true;//标记这个顶点被访问过了
}
}
}
levelSize = q.size();//更新当前层的数量
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_74774759/article/details/135138885
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- DH群密钥交换算法
- 使用anaconda创建notebook工程
- 【Vue事件修饰符详细介绍】
- 中国泛娱乐出海视频字幕解决方案
- [pytorch入门] 5. DataLoader的使用
- MT6739/MTK6739安卓核心板规格参数_MTK平台核心板定制
- vue中实现使用相框点击拍照,canvas进行前端图片合并下载
- 数据湖存储解决方案之Iceberg
- 【uniapp】 uniapp 修改tabBar图标大小和navigationBar字体大小
- 系列十一、重载 & 重写