springboot中引入AOP切面编程
发布时间:2024年01月05日
在Spring Boot 3.0中引入AOP的过程如下所示:
1、首先,确保已经添加了相关依赖。可以通过Maven或Gradle来管理项目的依赖。对于使用Maven构建的项目,需要将以下依赖添加到pom.xml文件中
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>2、创建切面类(Aspect)并定义切点(Pointcut)、前置通知(Before Advice)等逻辑。切面类应该被注解为@Component,这样才能被自动扫描到。在com.lingyi.mybatis.aop包下创建一个TimeCustomAspect.java的AOP类,增强方法执行的行为。
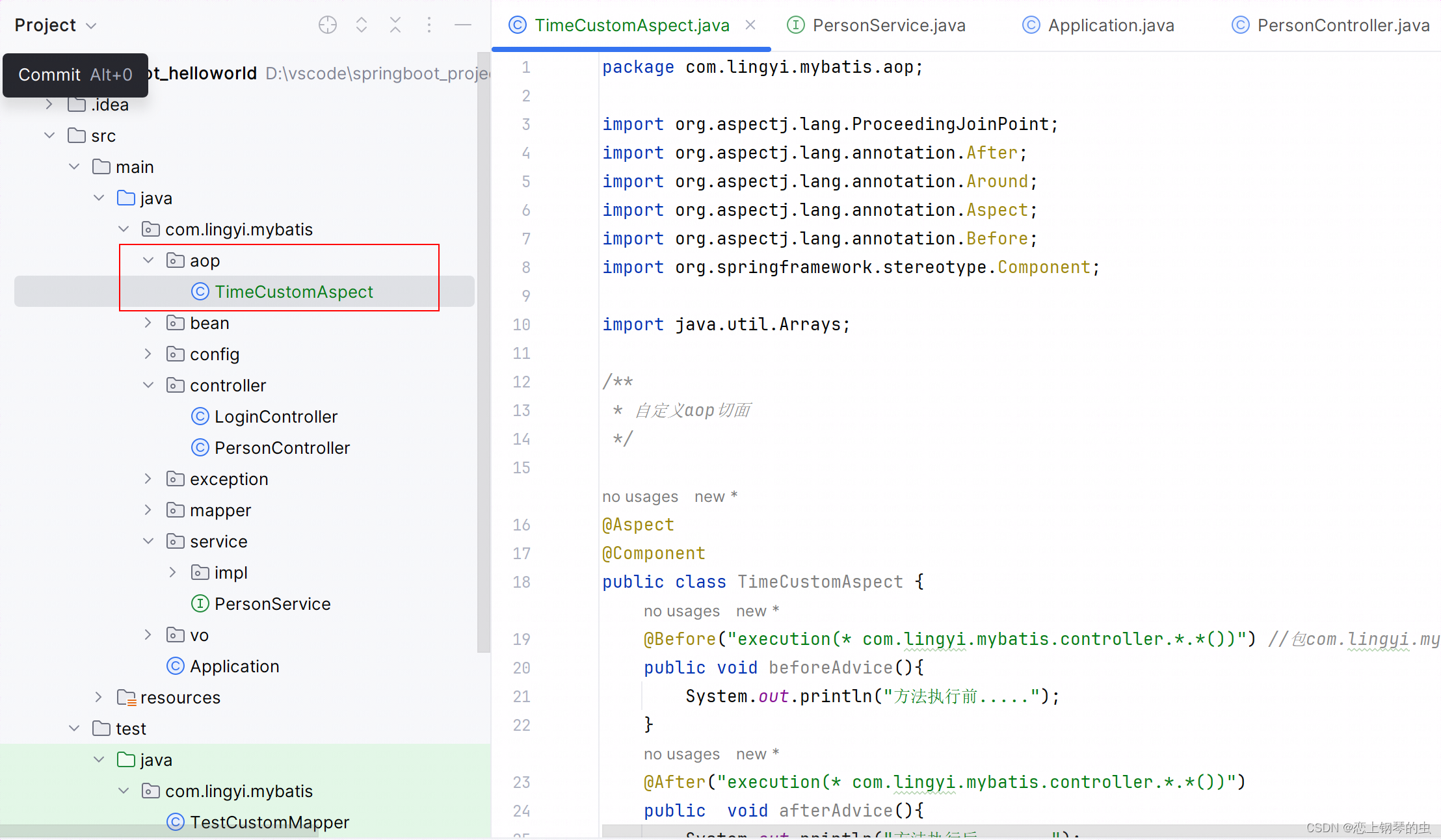
package com.lingyi.mybatis.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 自定义aop切面
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class TimeCustomAspect {
@Before("execution(* com.lingyi.mybatis.controller.*.*())") //包com.lingyi.mybatis.controller下的所有类和类中的方法都满足该AOP的条件
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("方法执行前.....");
}
@After("execution(* com.lingyi.mybatis.controller.*.*())")
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println("方法执行后.......");
}
@Around("execution(* com.lingyi.mybatis.controller.*.*())")
public Object recordTimeCustom(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = pjp.proceed();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
String className = pjp.getTarget().getClass().getName();
String method = pjp.getSignature().getName();
String args = Arrays.toString(pjp.getArgs());
System.out.println("类:"+className + ",方法:"+method +",参数:"+args +",执行耗时:"+ (end - start));
return result;
}
}
3、测试,登录swagger UI界面,访问controller层某个接口。下面已/person接口为例
http://127.0.0.1:8081/swagger-ui/index.html

 经过测试,编写的AOP切面编程程序生效,AOP会根据切点表达式自动进行切面处理。当符合条件的方法调用发生时,就会执行相应的通知逻辑。
经过测试,编写的AOP切面编程程序生效,AOP会根据切点表达式自动进行切面处理。当符合条件的方法调用发生时,就会执行相应的通知逻辑。
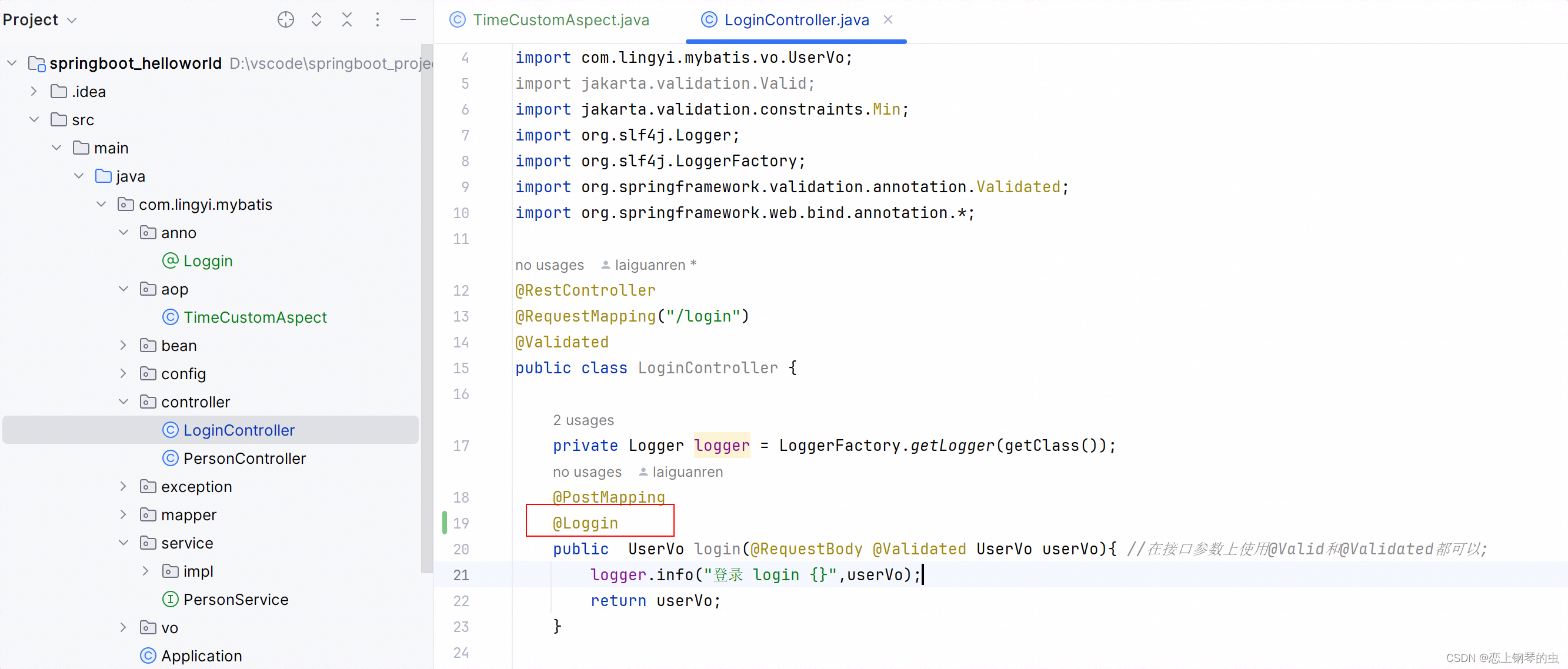
4、精细化切入
为了更加精细化对指定方法进行切入,切面还可以针对某些注解进行切入,从而实现对指定方法进行增强。

在方法上添加@Loggin注解
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42670590/article/details/135351976
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!