力扣309. 买卖股票的最佳时机含冷冻期(动态规划,Java C++解法)
Problem: 309. 买卖股票的最佳时机含冷冻期
题目描述
思路
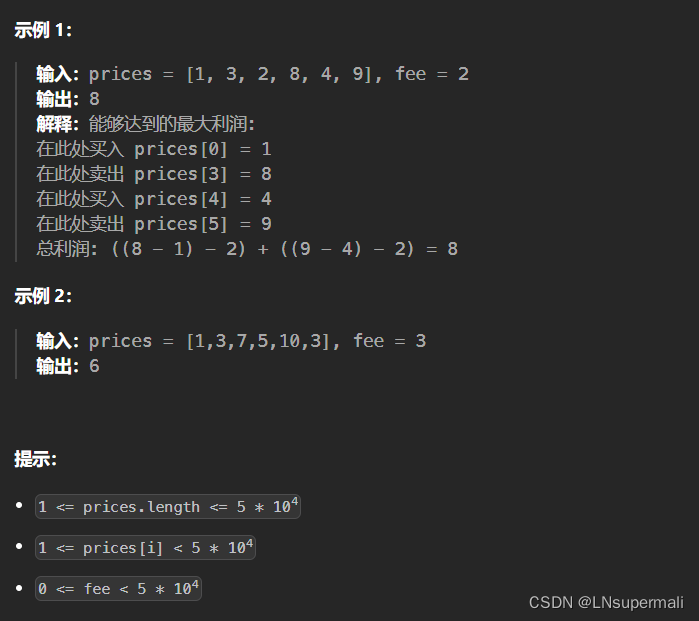
Problem: 714. 买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
该题目可以看作是上述题目的改编,该题目添加了一个冷冻期使得动态转移方程更加复杂,具体思路如下:
1.构建多阶段决策模型:n天对应n个阶段,每个阶段决策:买股票、卖股票、不操作
买股票:前一天不持有股票,并且处于冷冻期或者处于非冷冻期,而不是刚刚昨天卖掉股票
卖股票:当前持有股票
不操作无规则
2.定义状态:每天都有两种状态:持有股票、不持有股票。不持有股票又分为三小种情况。
int dp[n][4]表示n天的状态
dp[i][0]表示第i天持有股票时的利润
dp[i][1]表示第i天不持有股票时的利润(当天卖掉)
dp[i][2]表示第i天不持有股票时的利润(冷冻期),昨天刚卖掉了股票
dp[i][1]表示第i天不持有股票时的利润(非冷冻期),昨天也没持有
3.定义状态转移方程:
dp[i][0] = max3(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][2] - prices[i], dp[i - 1][3] - prices[i]);
dp[i][1] = dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i];
dp[i][2] = dp[i - 1][1];
dp[i][3] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][2], dp[i - 1][3]);
解题方法
1.获取prices数组的长度(假设为n),定义数组int[][] dp = new int[n][4];
2.初始化dp数组的第一行:dp[0][0] = -prices[0];dp[0][1] = 0;dp[0][2] = 0;dp[0][3] = 0;
3.从第一行开始完成动态转移方程;
4.返回dp数组的最后一行的最大值
复杂度
时间复杂度:
O ( n ) O(n) O(n);其中 n n n为数组prices的大小
空间复杂度:
O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
Code
class Solution {
/**
* Dynamic programming
* @param prices Given array(Recode the amount of each stock)
* @return int
*/
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
if (n == 1) {
return 0;
}
int[][] dp = new int[n][4];
/**
* dp[i][0] represents the profit from holding the stock on day i
* dp[i][1] represents the profit not held on day i (just sold on the day)
* dp[i][2] represents the profit from not holding the stock on day i (the freeze period),
* which was sold yesterday
* dp[i][3] represents the profit from not holding the stock on day i
* (non-freezing period) and not holding it yesterday
*/
dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
dp[0][1] = 0;
dp[0][2] = 0;
dp[0][3] = 0;
//Dynamic transfer
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][2] - prices[i], dp[i - 1][3] - prices[i]);
dp[i][1] = dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i];
dp[i][2] = dp[i - 1][1];
dp[i][3] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][2], dp[i - 1][3]);
}
return max(dp[n - 1][0], dp[n - 1][1], dp[n - 1][2], dp[n - 1][3]);
}
/**
* Returns the largest number in a set of numbers
* @param nums Given numbers
* @return int
*/
private int max(int... nums) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int num : nums) {
if (num > max) {
max = num;
}
}
return max;
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& prices) {
int n = prices.size();
if (n == 1) {
return 0;
}
vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(4));
dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
dp[0][1] = 0;
dp[0][2] = 0;
dp[0][3] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
dp[i][0] = ::std::max(dp[i - 1][0], ::std::max(dp[i - 1][2] - prices[i], dp[i - 1][3] - prices[i]));
dp[i][1] = dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i];
dp[i][2] = dp[i - 1][1];
dp[i][3] = ::std::max(dp[i - 1][2], dp[i - 1][3]);
}
return ::std::max({dp[n - 1][0], dp[n - 1][1], dp[n - 1][2], dp[n - 1][3]});
}
};
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!