【Filament】材质系统
1 前言
????????本文主要介绍 Filament 的材质系统,官方介绍详见 →?Filament Materials Guide。材质系统中会涉及到一些空间和变换的知识点,可以参考:【Unity3D】空间和变换、【Unity3D】Shader常量、变量、结构体、函数、【OpenGL ES】MVP矩阵变换、【OpenGL ES】透视变换原理。
? ? ? ? 需要注意的是,Unity 世界空间是左手坐标系,OpenGL 和 Filament 的世界空间是右手坐标系,Filament 的世界空间坐标轴如下。
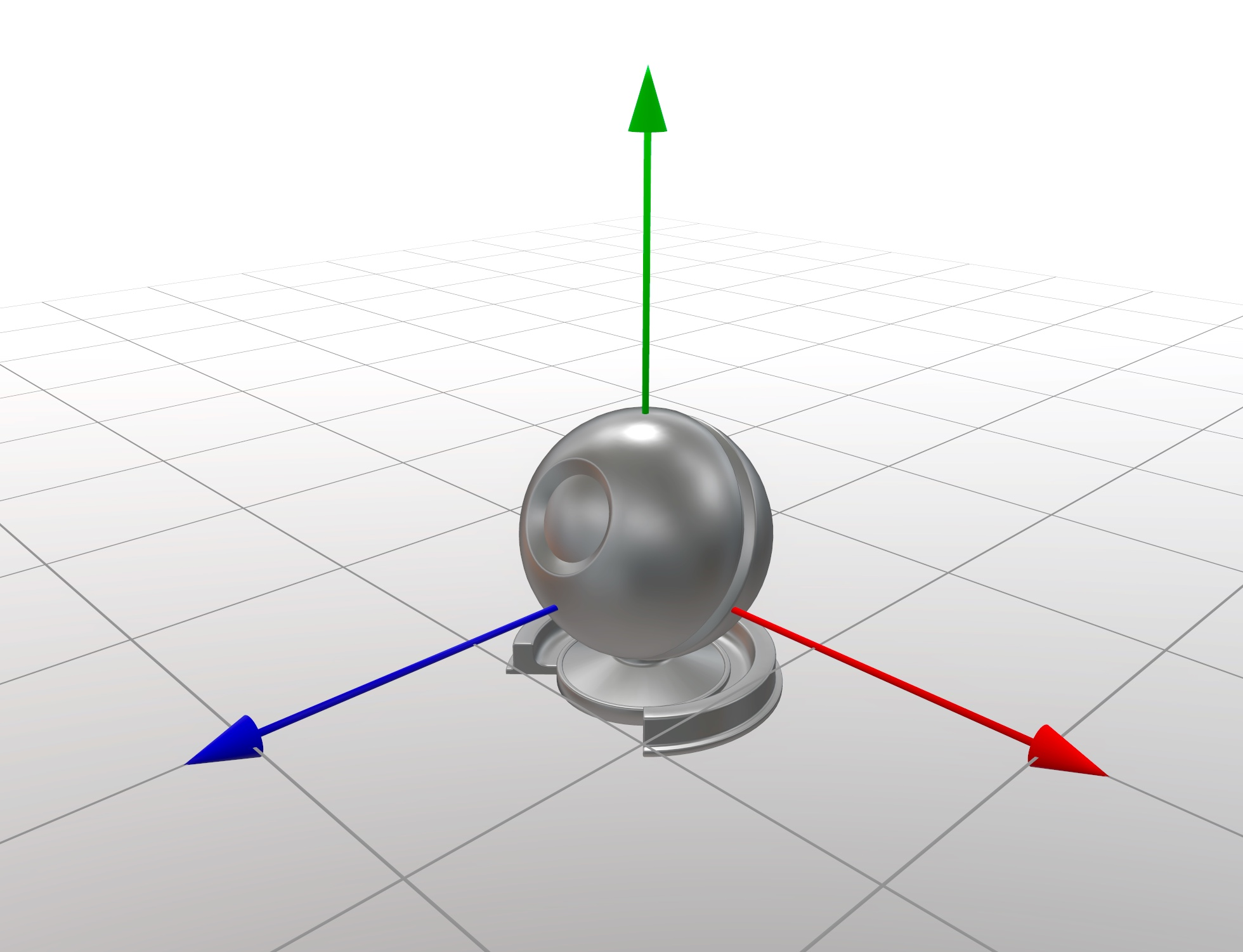
????????读者如果对 Filament 不太熟悉,请回顾以下内容。
2 材质结构
????????材质的格式是一种松散地基于 JSON 的格式,Filament 官方称之为 JSONish 格式。在顶层,材质定义由 JSON 对象表示的 3 个不同块组成,如下。其中,vertex 块是可选的,必须包含 material 和 fragment 块。
material {
// 材质属性
}
vertex {
// 顶点着色器(可选)
}
fragment {
// 片元着色器
}?????????JSONish 格式具有以下特点。
- JSON 格式为【"key" : value】;JSONish 格式为【key : value】,当字符串包含空格时,需要引号;
- 允许使用单行 C++ 样式的注释;
- key 区分大小写,value 不区分大小写。
2.1 材质属性(material)
? ? ? ? 材质属性(material)中可以定义材质名(name)、外部参数(parameters)、顶点属性参数(requires)、光照模型(shadingModel)、混合模式(blending)等。
material {
name : "Textured material",
parameters : [ // 外部参数
{
type : sampler2d,
name : texture
},
{
type : float,
name : metallic
},
{
type : float,
name : roughness
}
],
requires : [ // 顶点属性
uv0
],
shadingModel : lit, // 光照模型
blending : opaque // 混合模式
}- parameters:外部参数,纹理类型参数可以通过 materialParams_xxx 访问(如 materialParams_texture),其他类型参数可以通过?materialParams.xxx 访问(如 materialParams.metallic)。
- requires:顶点属性参数,会参与光栅化,取值有:uv0、uv1、color、position、tangents、custom0 ~ custom。
- shadingModel:光照模型,取值有 lit、subsurface、cloth、unlit、specularGlossiness,默认取 lit。
- blending:混合模式,取值有:opaque、transparent、fade、add、multiply、screen、masked,默认取 opaque。
2.2 顶点着色器(vertex)
????????顶点着色器(vertex)中可以对顶点的属性进行变换,如下。
vertex {
void materialVertex(inout MaterialVertexInputs material) {
float3 p = getPosition().xyz;
float3 u = mulMat4x4Float3(getViewFromClipMatrix(), p).xyz;
material.eyeDirection.xyz = mulMat3x3Float3(getWorldFromViewMatrix(), u);
}
}2.3 片元着色器块(fragment)
? ? ? ? 片元着色器(fragment)中可以计算光照模型所需的参数,如下。
fragment {
void material(inout MaterialInputs material) {
prepareMaterial(material);
material.baseColor = texture(materialParams_texture, getUV0());
material.metallic = materialParams.metallic;
material.roughness = materialParams.roughness;
}
}? ? ? ? ?其中,materialParams_texture、materialParams.metallic、materialParams.roughness 是材质属性中定义的外部参数。
3 输入结构
? ? ? ? 顶点着色器的输入结构体如下。
struct MaterialVertexInputs {
float4 color; // if the color attribute is required
float2 uv0; // if the uv0 attribute is required
float2 uv1; // if the uv1 attribute is required
float3 worldNormal; // only if the shading model is not unlit
float4 worldPosition; // always available (see note below about world-space)
mat4 clipSpaceTransform; // default: identity, transforms the clip-space position, only available for `vertexDomain:device`
// variable* names are replaced with actual names
float4 variable0; // if 1 or more variables is defined
float4 variable1; // if 2 or more variables is defined
float4 variable2; // if 3 or more variables is defined
float4 variable3; // if 4 or more variables is defined
};? ? ? ? 片元着色器的输入结构体如下。
struct MaterialInputs {
float4 baseColor; // default: float4(1.0)
float4 emissive; // default: float4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
float4 postLightingColor; // default: float4(0.0)
// no other field is available with the unlit shading model
float roughness; // default: 1.0
float metallic; // default: 0.0, not available with cloth or specularGlossiness
float reflectance; // default: 0.5, not available with cloth or specularGlossiness
float ambientOcclusion; // default: 0.0
// not available when the shading model is subsurface or cloth
float3 sheenColor; // default: float3(0.0)
float sheenRoughness; // default: 0.0
float clearCoat; // default: 1.0
float clearCoatRoughness; // default: 0.0
float3 clearCoatNormal; // default: float3(0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
float anisotropy; // default: 0.0
float3 anisotropyDirection; // default: float3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0)
// only available when the shading model is subsurface or refraction is enabled
float thickness; // default: 0.5
// only available when the shading model is subsurface
float subsurfacePower; // default: 12.234
float3 subsurfaceColor; // default: float3(1.0)
// only available when the shading model is cloth
float3 sheenColor; // default: sqrt(baseColor)
float3 subsurfaceColor; // default: float3(0.0)
// only available when the shading model is specularGlossiness
float3 specularColor; // default: float3(0.0)
float glossiness; // default: 0.0
// not available when the shading model is unlit
// must be set before calling prepareMaterial()
float3 normal; // default: float3(0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
// only available when refraction is enabled
float transmission; // default: 1.0
float3 absorption; // default float3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
float ior; // default: 1.5
float microThickness; // default: 0.0, not available with refractionType "solid"
}4 数据类型
| Name | GLSL type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bool2 | bvec2 | A vector of 2 booleans |
| bool3 | bvec3 | A vector of 3 booleans |
| bool4 | bvec4 | A vector of 4 booleans |
| int2 | ivec2 | A vector of 2 integers |
| int3 | ivec3 | A vector of 3 integers |
| int4 | ivec4 | A vector of 4 integers |
| uint2 | uvec2 | A vector of 2 unsigned integers |
| uint3 | uvec3 | A vector of 3 unsigned integers |
| uint4 | uvec4 | A vector of 4 unsigned integers |
| float2 | float2 | A vector of 2 floats |
| float3 | float3 | A vector of 3 floats |
| float4 | float4 | A vector of 4 floats |
| float4×4 | mat4 | A 4×4 float matrix |
| float3×3 | mat3 | A 3×3 float matrix |
5 材质函数
5.1 Math
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PI | float | π |
| HALF_PI | float | π / 2 |
| saturate(float x) | float | 将 x 约束在 0 ~ 1 之间 |
| pow5(float x) | float | x ^ 5 |
| sq(float x) | float | x ^ 2 |
| max3(float3 v) | float | 获取向量中最大的分量 |
| mulMat4×4Float3(float4×4 m, float3 v) | float4 | m * v |
| mulMat3×3Float3(float4×4 m, float3 v) | float4 | m * v |
5.2 Matrices
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| getViewFromWorldMatrix() | float4×4 | [世界空间->观察空间]的变换矩阵V |
| getWorldFromViewMatrix() | float4×4 | [观察空间->世界空间]的变换矩阵V' |
| getClipFromViewMatrix() | float4×4 | [观察空间->裁剪空间]的变换矩阵P |
| getViewFromClipMatrix() | float4×4 | [裁剪空间->观察空间]的变换矩阵P' |
| getClipFromWorldMatrix() | float4×4 | [世界空间->裁剪空间]的变换矩阵VP |
| getWorldFromClipMatrix() | float4×4 | [裁剪空间->世界空间]的变换矩阵(VP)' |
| getUserWorldFromWorldMatrix() | float4×4 | [世界空间->用户世界空间]的变换矩阵 |
| getWorldFromModelMatrix() | float4×4 | [模型空间->世界空间]的变换矩阵M(Vertex only) |
| getWorldFromModelNormalMatrix() | float3×3 | [模型空间->世界空间]的法线变换矩阵(Vertex only) |
5.3 Frame constants
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| getResolution() | float4 | (width, height, 1 / width, 1 / height),单位:pixels |
| getWorldCameraPosition() | float3 | 相机的世界空间坐标 |
| getWorldOffset() | float3 | 获取 api 级世界空间的位置(已弃用,使用 getUserWorldPosition 替代) |
| getTime() | float | 获取当前时间,范围:0 ~ 1,单位:s |
| getUserTime() | float4 | (time, (double)time - time, 0, 0) |
| getUserTimeMod(float m) | float | 获取当前时间,范围:0 ~ m,单位:s |
| getExposure() | float | 照相机的曝光度 |
| getEV100() | float | 相机在 ISO 100 下的曝光度 |
5.4 Vertex only
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| getPosition() | float4 | 获取模型空间顶点坐标 |
| getCustom0()?to?getCustom7() | float4 | 获取模型的 Custom0 ~?Custom7 的值 |
| getVertexIndex() | int | 获取顶点的索引 |
5.5 Fragment only
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| getWorldTangentFrame() | float3×3 | 世界空间列向量:tangent、bi-tangent、normal,如果材质没有计算凹凸贴图的切空间法线,或者材质不是各向异性的,那么在这个矩阵中只有法线是有效的。 |
| getWorldPosition() | float3 | 片元的世界空间坐标 |
| getUserWorldPosition() | float3 | 片元的用户世界空间坐标 |
| getWorldViewVector() | float3 | 世界空间下,片元指向相机的单位方向向量 |
| getWorldNormalVector() | float3 | 世界空间下,经凹凸映射后的片元的单位法线向量(必须在 prepareMaterial() 之后使用) |
| getWorldGeometricNormalVector() | float3 | 世界空间下,凹凸映射前的片元的单位法线向量 (可以在 prepareMaterial() 之前使用) |
| getWorldReflectedVector() | float3 | view 向量关于法线的反向量(必须在 prepareMaterial() 之后使用) |
| getNormalizedViewportCoord() | float3 | 标准化的用户视口位置(即 NDC 坐标标准化为 [0,1] 的位置,[1,0] 的深度,可以在prepareMaterial() 之前使用)。因为用户视口比实际的物理视口小,所以在物理视口的不可见区域中,这些坐标可以为负或大于 1。 |
| getNdotV() | float | 获取法线向量与观察向量的点积,即:dot(normal, view),返回结果严格大于 0(必须在 prepareMaterial() 之后使用) |
| getColor() | float4 | 获取片元经光栅化插值后的颜色(当 required 中包含 color 时才可用) |
| getUV0() | float2 | 获取 uv0 纹理坐标(当 required 中包含 uv0 时才可用) |
| getUV1() | float2 | 获取 uv1 纹理坐标(当 required 中包含 uv1 时才可用) |
| getMaskThreshold() | float | 获取遮罩阈值(当 blending 设置为 masked 才可用) |
| inverseTonemap(float3) | float3 | 将逆色调映射操作应用于指定的线性 sRGB 颜色并返回线性 sRGB 颜色。此操作可能是近似的,并且与 “Filmic” 色调映射操作一起使用效果最好 |
| inverseTonemapSRGB(float3) | float3 | 将逆色调映射操作应用于指定的非线性 sRGB 颜色并返回线性 sRGB 颜色。此操作可能是近似的,并且与 “Filmic” 色调映射操作一起使用效果最好 |
| luminance(float3) | float | 计算指定的线性 sRGB 颜色的亮度 |
| ycbcrToRgb(float, float2) | float3 | 将亮度和 CbCr 对转换为 sRGB 颜色 |
| uvToRenderTargetUV(float2) | float2 | 转换 UV 坐标以允许从 RenderTarget 中采样 |
6 光照模型(Lighting model)
? ? ? ? 在?material 块中,通过 shadingModel 属性配置光照模型,取值主要有:lit、subsurface、cloth、unlit、specularGlossiness,默认取 lit。
6.1 lit model
????????lit model 官方介绍见 →?litmodel,可以配置的参数如下。
| Property | Type | Range | Note | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseColor | float4 | [0..1] | Linear RGB | 非金属表面的漫射反照率和金属表面的镜面颜色 |
| metallic | float | [0..1] | 0 or 1 | 表面是介电(0)还是导体(1) |
| roughness | float | [0..1] | 感知表面的平滑度(1)或粗糙(0) | |
| reflectance | float | [0..1] | Prefer values > 0.35 | 表面正入射菲涅耳反射率,控制了反射的强度 |
| sheenColor | float3 | [0..1] | Linear RGB | 光泽层的强度 |
| sheenRoughness | float | [0..1] | 光泽层的平滑度或粗糙度 | |
| clearCoat | float | [0..1] | 0 or 1 | 透明涂层的强度 |
| clearCoatRoughness | float | [0..1] | 可感知的透明涂层的平滑度或粗糙度 | |
| anisotropy | float | [?1..1] | 当该值为正值时,各向异性在切线方向上 | 在正切或双切方向上各向异性的数量 |
| anisotropyDirection | float3 | [0..1] | Linear RGB,在切空间中编码方向向量 | 切线空间的局部曲面方向 |
| ambientOcclusion | float | [0..1] | 定义一个表面点可以接触到多少环境光,它是一个介于 0 和 1 之间的每像素阴影因子 | |
| normal | float3 | [0..1] | Linear RGB,在切空间中编码方向向量 | 使用凹凸贴图(法线贴图)来扰动表面的细节法线。 |
| bentNormal | float3 | [0..1] | Linear RGB,在切空间中编码方向向量 | 指向平均不包含方向的法线,可以用来改善间接照明的质量 |
| clearCoatNormal | float3 | [0..1] | Linear RGB,在切空间中编码方向向量 | 使用凹凸贴图(法线贴图)来扰动透明涂层的细节法线 |
| emissive | float4 | rgb=[0..n], a=[0..1] | Linear RGB,alpha 编码曝光权重 | 额外的漫射反照率来模拟发射表面(如霓虹灯等)这个属性在带有 bloom 通道的 HDR 管道中非常有用 |
| postLightingColor | float4 | [0..1] | Linear RGB | 额外的颜色,可以与照明计算的结果混合,见 postLightingBlending |
| ior | float | [1..n] | 可选,通常由反射率推断 | 折射率,折射物的折射率或作为反射率的替代品 |
| transmission | float | [0..1] | 定义了有多少电介质的漫射光通过物体传播,它定义了物体的透明度 | |
| absorption | float3 | [0..n] | 折射率物体的吸收系数 | |
| microThickness | float | [0..n] | 折射率物体的薄层厚度 | |
| thickness | float | [0..n] | 折射物体的固体体积的厚度 |
6.2 subsurface?model
????????subsurface?model 官方介绍见 →?subsurfacemodel,官方文档只留着标题,无内容介绍。
6.3 cloth?model
????????cloth?model 官方介绍见 →?clothmodel,可以配置的参数如下。
| Property | Type | Range | Note | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sheenColor | float3 | [0..1] | Linear RGB | 高光色调创建双色高光织物(默认值:sqrt(baseColor)) |
| subsurfaceColor | float3 | [0..1] | Linear RGB | 通过材料散射和吸收后的漫射色着色 |
6.4 unlit?model
????????unlit?model 官方介绍见 →?unlitmodel,可以配置的参数如下。
| Property | Type | Range | Note | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseColor | float4 | [0..1] | Linear RGB | 表面漫反射色 |
| emissive | float4 | rgb=[0..n], a=[0..1] | Linear RGB,alpha 编码曝光权重 | 额外的漫射颜色来模拟发射表面,该属性在带有 bloom pass 的 HDR 管道中非常有用 |
| postLightingColor | float4 | [0..1] | Linear RGB | 额外的颜色与基色和发射色混合 |
6.5?specularGlossiness
????????specularGlossiness?官方介绍见 →?specularglossiness,可以配置的参数如下。
| Property | Type | Range | Note | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| baseColor | float4 | [0..1] | Linear RGB | 表面漫反射色 |
| specularColor | float3 | [0..1] | Linear RGB | 高光色调(默认为黑色) |
| glossiness | float | [0..1] | Inverse of roughness | 光泽度(默认为 0) |
7 混合和透明(Blending and transparency)
7.1 blending
????????在?material 块中,通过 blending?属性配置混合模式,取值有:opaque、transparent、fade、add、multiply、screen、masked,默认取 opaque,官方介绍见 →?blending。
- opaque:不透明模式,混合被禁用,材质输出的 alpha 通道被忽略。
- transparent:透明模式,启用混合,材质输出的是与渲染目标通过 alpha 混合的,使用 Porter-Duff 的 source over 规则,这种混合模式假定预先乘以 alph。
- fade:半透明模式,启用混合,表现透明效果,但透明度也应用到镜面反射光照,在 transparent 模式下,材质的 alpha 值只应用到漫射光照,fade 混合模式对于淡化被照亮的物体很有用。
- add:叠加模式,启用混合,材质的输出被叠加到渲染目标的内容中。
- multiply:累乘模式,启用混合,材质的输出与渲染目标的内容相乘,使内容变暗。
- screen:屏幕模式,启用混合,与 multiply 的效果相反,渲染目标的内容会变亮。
- masked:遮罩模式,禁用混合,这种混合模式启用 alpha 遮罩,材质输出的 alpha 通道定义了片元是否被丢弃。此外,ALPHA_TO_COVERAGE 对于非半透明视图是启用的,有关更多信息,请参阅 maskThreshold 部分。
material {
blending?: opaque
}7.2 postLightingBlending
????????postLightingColor 属性定义了如何将 postLightingColor 材质属性与光照计算结果混合,官方介绍见 →?postlightingblending。取值主要有:opaque、transparent、add、Screen,默认取值:transparent。
material {
postLightingBlending : add
}7.3?transparency
????????transparency 控制透明物体的渲染方式,它仅在混合模式不是 opaque 且 refractionMode 为 none 时有效,这些方法都不能准确地渲染凹形物体,但在实践中它们往往足够好,官方介绍见 →?transparency。取值主要有:default、twoPassesOneSide、twoPassesTwoSides,默认取值:default。
- default:透明物体正常呈现,遵循剔除模式。
- twoPassesOneSide:透明物体首先在深度缓冲区中渲染,然后再在颜色缓冲区中渲染,遵循剔除模式,这实际上只呈现了透明物体的一半。
- twoPassesTwoSides:透明物体在颜色缓冲区中渲染两次,第一次渲染背面,然后渲染正面,该模式允许渲染两面,同时减少或消除排序问题,twoPassesTwoSides?可以与 doubleSided?结合使用,效果更好。
material {
transparency : twoPassesOneSide
}7.4?maskThreshold
????????当混合模式设置为?masked?时,maskThreshold 用于控制片元不被丢弃的最小 alpha 值;当混合模式未被设置为 masked?时,maskThreshold 将被忽略,官方介绍见 →?maskThreshold。取值为 0.0 ~ 1.0 之间的浮点数,默认取值:0.4??????。
material {
blending : masked,
maskThreshold : 0.5
}7.5?refractionMode
????????refractionMode 用于控制折射模式,官方介绍见 → refractionMode。取值主要有:none、cubemap、screenspace,默认取值:none。当 refractionMode 设置为非 none 时才激活折射。
????????cubemap 模式只使用 IBL cubemap 作为折射源,这是非常有效的,没有场景对象被折射,只有在 cubemap 中编码的远处环境被折射,该模式对于对象查看器来说是足够的。screenspace 模式采用更先进的屏幕空间折射算法,该算法允许场景中不透明的物体被折射。
????????在 cubemap 模式中,假定折射光线从物体的中心发出,厚度参数仅用于计算吸收,而对折射本身没有影响。在 screenspace 模式中,假定折射光线在离开折射介质时平行于观看方向。
material {
refractionMode : cubemap,
}7.6?refractionType
????????refractionType 用于设置折射模型,官方介绍见 → refractionType。取值主要有:solid、thin,默认取值:solid。当 refractionMode 设置为非 none 时 refractionType 才会生效。
????????solid 模型用于厚的物体,如水晶球、冰块或雕塑;thin 模型用于薄的物体,如窗户、装饰球或肥皂泡。
????????solid 模型假定所有的折射物体都是与入射点相切且半径厚度的球体。thin 模型假定所有的折射物体都是平面的、薄的、均匀厚度的。
material {
refractionMode : cubemap,
refractionType : thin,
}8 光栅化(Rasterization)
8.1?culling
????????culling 用于控制需要剔除哪些三角形,官方介绍见 → culling。取值主要有:none、front、back、frontAndBack,默认取值:back。
- none:不剔除,渲染双面。
- front:剔除正面三角形,渲染背面。
- back:剔除背面三角形,渲染正面。
- frontAndBack:正面和背面全部剔除。
material {
culling : none
}8.2?colorWrite
????????colorWrite 用于控制开启 / 禁用写入颜色缓冲区,官方介绍见 → colorWrite。取值有:true、false,默认取值:true。
material {
colorWrite : false
}8.3?depthWrite
????????depthWrite 用于控制开启 / 禁用写入深度缓冲区,官方介绍见 → depthWrite。取值有:true、false,不透明物体默认取值:true,透明物体默认取值:false。
material {
depthWrite : false
}8.4?depthCulling
????????depthCulling 用于控制开启 / 禁用深度测试?,官方介绍见 → depthCulling。取值有:true、false,默认取值:true。
????????当深度测试被禁用时,用此材质渲染的物体将始终出现在其他不透明物体的前面。
material {
depthCulling : false
}8.5?doubleSided
????????doubleSided 用于控制开启 / 禁用双面渲染,官方介绍见 → doubleSided。取值有:true、false,默认取值:false。当设置为 true 时,culling 自动设置为 none。
????????如果三角形是面向背面的,则三角形的法线将翻转为面向正面。当显式设置为 false 时,这允许在运行时切换双面性。
material {
doubleSided : true
}8.6?alphaToCoverage
????????alphaToCoverage 用于控制开启 / 禁用 alpha 覆盖,官方介绍见 → alphaToCoverage。取值有:true、false,默认取值:false。
????????当覆盖的 alpha 被启用时,片元的覆盖是从它的 alpha 派生出来的。此属性仅在启用 MSAA 时才可用。注意:将混合模式设置为 masked 会自动启用 alpha 覆盖,如果不希望这样做,可以通过将 alpha 的覆盖设置为 false 来取消此行为。
material {
blending : masked,
alphaToCoverage : false
}9 光照属性(Lighting)
9.1?reflections
????????reflections 用于控制材质的镜面反射源,官方介绍见 → reflections。取值有:default、screenspace,默认取值:default。
????????当 reflections 设置为 default 时,反射仅来自基于图像的光照(image-based lights,IBL);当此 reflections 设置为 screenspace 时,反射除了来自 IBL 之外,还来自屏幕空间的颜色缓冲区。
material {
reflections : screenspace
}9.2?shadowMultiplier
????????shadowMultiplier 用于控制开启 / 禁用阴影,该属性仅在 unlit 光照模型下才可用,官方介绍见 → shadowMultiplier。取值有:true、false,默认取值:false。
? ? ? ? 当 shadowMultiplier 设置为 true 时,材质计算的最终颜色需要乘以阴影因子(或可见性),它允许创建透明的且接收阴影投射的物体(如:AR 中不可见的地面),它仅接收直射光(directional lights)的阴影。
material {
shadingModel : unlit,
shadowMultiplier : true,
blending : transparent
}9.3?transparentShadow
????????transparentShadow 用于控制开启 / 禁用透明阴影,官方介绍见 → transparentShadow。取值有:true、false,默认取值:false。
????????当 shadowMultiplier 设置为 true 时,Filament 使用抖动模式(dithering pattern)模拟透明阴影,它们在方差阴影地图(VSM)和模糊启用时效果最好。阴影的不透明度直接来源于材质的 baseColor 属性的 alpha 通道,透明阴影可以在不透明的物体上启用,使它们与不透明的折射 / 透射物体兼容。
material {
transparentShadow : true,
blending : transparent
}
fragment {
void material(inout MaterialInputs material) {
prepareMaterial(material);
material.baseColor = texture(materialParams_baseColor, getUV0());
}
}9.4?clearCoatIorChange
????????clearCoatIorChange 用于控制开启 / 禁用清除折射率变化图层,官方介绍见 → clearCoatIorChange。取值有:true、false,默认取值:true。
????????当 clearCoatIorChange 设置为 true 时,会添加一个清除图层,它考虑到折射率(IoR)的变化来修改底层的镜面颜色,这会使 baseColor 变暗。当此效果被禁用时,baseColor 保持不变。
material {
clearCoatIorChange : false
}9.5?multiBounceAmbientOcclusion
????????multiBounceAmbientOcclusion 用于控制开启 / 禁用多反弹环境遮挡,官方介绍见 → multiBounceAmbientOcclusion。取值有:true、false,默认取值:false。
????????当将环境遮挡(ambient occlusion)应用于基于图像的光照(image-based lighting,IBL)时,多反弹环境遮挡(multi-bounce ambient occlusion)考虑了相互反射。开启此功能可避免遮挡区域过度变暗。它还考虑了表面颜色来生成彩色环境遮挡。
material {
multiBounceAmbientOcclusion : true
}9.6?specularAmbientOcclusion
????????specularAmbientOcclusion 用于控制开启 / 禁用多反弹环境遮挡,官方介绍见 → multiBounceAmbientOcclusion。取值有:none、simple、 bentNormals,默认取值:none。
????????静态环境遮挡贴图和动态环境遮挡贴图(SSAO 等)适用于漫射间接光照。当将此属性设置为非 none 时,一个新的环境遮挡项将从表面粗糙度中衍生出来,并应用于镜面间接光照。这种效果有助于消除不需要的镜面反射。当这个值设置为 simple 时,Filament 使用一种便宜但近似的方法来计算高光环境遮挡项。如果将此值设置为 bentNormals, Filament 将使用更精确但更昂贵的方法。
material {
specularAmbientOcclusion : simple
}10 抗锯齿(Anti-aliasing)
10.1?specularAntiAliasing
????????specularAntiAliasing 用于控制开启 / 禁用镜面抗锯齿,官方介绍见 → specularAntiAliasing。取值有:true、false,默认取值:false。
????????当一个对象远离相机,开启抗锯齿可用减少镜面锯齿,并保留镜面高光的形状。这种抗锯齿方案对光滑材料(低粗糙度)特别有效,但增加了渲染成本。抗锯齿效果的强度可以使用另外两个属性来控制:specularAntiAliasingVariance 和 specularAntiAliasingThreshold。
material {
specularAntiAliasing : true
}10.2 specularAntiAliasingVariance
????????specularAntiAliasingVariance 用于设置应用镜面抗锯齿时使用的过滤器内核的屏幕空间方差,官方介绍见 → specularAntiAliasingVariance。取值类型是 float 型,取值范围是 0 ~ 1,默认取值:0.15。
????????较高的 specularAntiAliasingVariance?值将增加过滤器的效果,但可能增加不需要的区域的粗糙度。
material {
specularAntiAliasingVariance : 0.2
}10.3?specularAntiAliasingThreshold
????????specularAntiAliasingThreshold 用于设置应用镜面抗锯齿时抑制估计误差的夹持阈值(clamping threshold),官方介绍见 → specularAntiAliasingThreshold。取值类型是 float 型,取值范围是 0 ~ 1,默认取值:0.2。
????????当设置为 0 时,镜面抗锯齿被禁用。
material {
specularAntiAliasingThreshold : 0.1
}11 颜色处理(Handling colors)
11.1?Linear colors
????????线性颜色空间的介绍见 → 【Unity3D】伽马校正,Filament 在线性颜色空间中使用 RGB 颜色,官方介绍见 →?linearcolors。
????????如果颜色数据来自纹理,请确保使用 sRGB 纹理,以从 sRGB 自动进行硬件转换为线性。如果颜色数据作为材质的参数传递,可以通过在每个颜色通道上运行以下算法将其从 sRGB 转换为线性。
float sRGB_to_linear(float color) {
return color <= 0.04045 ? color / 12.92 : pow((color + 0.055) / 1.055, 2.4);
}????????可以使用以下两个更便宜但不太准确的方法。
// Cheaper
linearColor = pow(color, 2.2);
// Cheapest
linearColor = color * color;11.2?Pre-multiplied alpha
????????如果一种颜色的 RGB 分量都乘以 alpha 通道,那么它使用了预乘 alpha,官方介绍见 →?pre-multipliedalpha。
// Compute pre-multiplied color
color.rgb *= color.a;????????如果颜色是从纹理中取样的,可以简单地确保纹理数据在上传时进行了预乘。在 Android 上,从 Bitmap 上传的任何纹理默认都会进行预乘。?
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- docker-harbor私有仓库
- ISO三体系认证的条件及流程有哪些您知道吗?
- 随机森林 2(决策树)
- 笔试面试题——继承和多态
- 【MATLAB源码-第108期】基于matlab的OFDM-OQAM系统仿真,包含PHYDYAS滤波器模块和PNN结构,输出误码率曲线。
- 全正版商用视频素材网站,一个字:绝
- 机器学习(八) — K-means
- android studio使用总结
- 备忘: java 查询es7索引补全
- C# Image Caption