Godot之StringName解析
类描述
在Godot中,StringName是唯一字符串的内置类型。
StringName 是不可变的字符串,用于唯一名称的通用表示(也叫“字符串内嵌”)。值相同的两个 StringName 是同一个对象。进行比较时比普通 String 要快很多。
对于需要 StringName 的方法,你通常可以只传 String,会自动进行转换,不过有时候你可能会想要提前使用 StringName 构造函数来构造 StringName,在 GDScript 中也可以用 &"example" 语法。
Godot中的NodePath,这是与此类似的概念,针对存储预解析的场景树路径设计,NodePath我们后面会进行解析。
String 的所有方法都在这个类中可用。它们会将 StringName 转换为字符串,返回的也是字符串。这样做效率非常低,应该只在需要字符串时使用。
注意:转换为布尔值时,空的 StringName(StringName(""))为 false,其他 StringName 均为 true。不能使用 not 运算符。请改用 is_empty 来检查空的 StringName。
核心思想概述
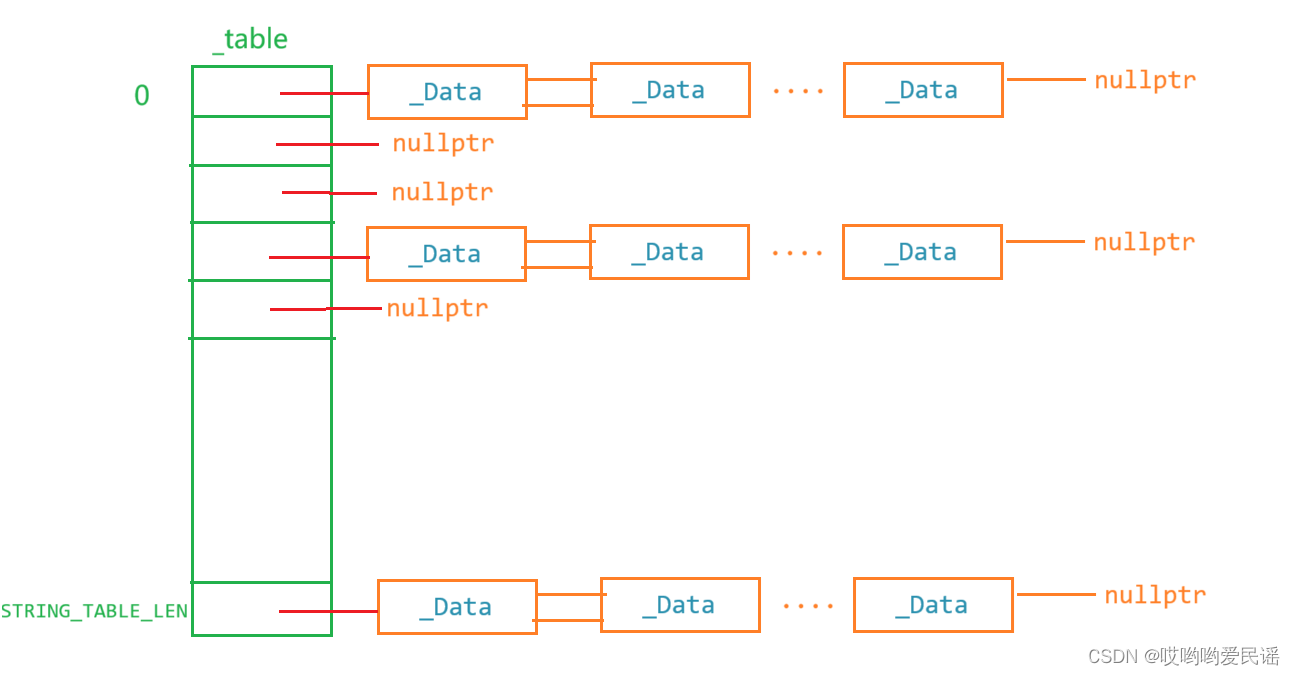
StringName内部实现了一个静态哈希表_table,将所有值相同的字符串,在_table中存储唯一一份,并对字符串值实现了引用计数,创建时+1,销毁时-1,为0时,从_table中移除对应节点,并释放字符串占用的内存。
关键代码
关键成员变量
_Data
_Data 是一个用于存储字符串的双端链表,支持引用计数、C string和String两种格式字符串。其他见代码注释。
// 一个存储字符串的双端链表
struct _Data {
SafeRefCount refcount;
// 静态引用次数
SafeNumeric<uint32_t> static_count;
// 所存储的字符串,可以以const char *和String两种形式存在
const char *cname = nullptr;
String name;
#ifdef DEBUG_ENABLED
uint32_t debug_references = 0;
#endif
String get_name() const { return cname ? String(cname) : name; }
// 记录在_table中的索引
int idx = 0;
// 存储字符串的哈希值
uint32_t hash = 0;
// 前向节点指针
_Data *prev = nullptr;
// 后向节点指针
_Data *next = nullptr;
_Data() {}
};
// 在StringName变量中,只关心_data指向的节点,在静态_table中,才关心它的前向和后向节点
_Data *_data = nullptr;_table
_table定义为静态的目的,就是唯一且被所有StringName共享,从而实现在字符串相等时,可以共享一个字符串
enum {
STRING_TABLE_BITS = 16,
STRING_TABLE_LEN = 1 << STRING_TABLE_BITS, // 静态_table数组大小
STRING_TABLE_MASK = STRING_TABLE_LEN - 1 // 静态_table数组索引的掩码
};
// 静态_table,即被所有StringName共享,从而实现在字符串相等时,可以共享一个字符串
static _Data *_table[STRING_TABLE_LEN];静态哈希表_table的原理图如下所示,也是StringName的精髓所在。
关键成员函数
构造函数
StringName::StringName(const String &p_name, bool p_static) {
_data = nullptr;
ERR_FAIL_COND(!configured);
if (p_name.is_empty()) {
return;
}
MutexLock lock(mutex);
// 计算字符串的哈希值
uint32_t hash = p_name.hash();
// 计算在静态_table中的索引
uint32_t idx = hash & STRING_TABLE_MASK;
_data = _table[idx];
while (_data) {
// 相等的条件:哈希值相等 and 字符串相等
if (_data->hash == hash && _data->get_name() == p_name) {
break;
}
_data = _data->next;
}
// 如果找到,引用计数+1
if (_data && _data->refcount.ref()) {
// exists
if (p_static) {
_data->static_count.increment();
}
#ifdef DEBUG_ENABLED
if (unlikely(debug_stringname)) {
_data->debug_references++;
}
#endif
return;
}
// 如果在静态_table中没有找到,则创建一个新的,并添加到_table
_data = memnew(_Data);
_data->name = p_name;
_data->refcount.init();
_data->static_count.set(p_static ? 1 : 0);
_data->hash = hash;
_data->idx = idx;
_data->cname = nullptr;
_data->next = _table[idx];
_data->prev = nullptr;
#ifdef DEBUG_ENABLED
if (unlikely(debug_stringname)) {
// Keep in memory, force static.
_data->refcount.ref();
_data->static_count.increment();
}
#endif
if (_table[idx]) {
_table[idx]->prev = _data;
}
_table[idx] = _data;
}析构函数
void StringName::unref() {
ERR_FAIL_COND(!configured);
// _data有效 且 unref后,引用为0,才会进行释放
if (_data && _data->refcount.unref()) {
MutexLock lock(mutex);
if (CoreGlobals::leak_reporting_enabled && _data->static_count.get() > 0) {
if (_data->cname) {
ERR_PRINT("BUG: Unreferenced static string to 0: " + String(_data->cname));
} else {
ERR_PRINT("BUG: Unreferenced static string to 0: " + String(_data->name));
}
}
// 删除双向链表中的节点
if (_data->prev) {
_data->prev->next = _data->next;
} else {
if (_table[_data->idx] != _data) {
ERR_PRINT("BUG!");
}
_table[_data->idx] = _data->next;
}
if (_data->next) {
_data->next->prev = _data->prev;
}
// 释放内存
memdelete(_data);
}
_data = nullptr;
}
// 析构函数
_FORCE_INLINE_ ~StringName() {
if (likely(configured) && _data) { //only free if configured
unref();
}
}查找函数
StringName StringName::search(const char *p_name) {
ERR_FAIL_COND_V(!configured, StringName());
// 判断指针非空
ERR_FAIL_NULL_V(p_name, StringName());
// 字符串不以'\0'开头
if (!p_name[0]) {
return StringName();
}
MutexLock lock(mutex);
//计算哈希值,进而计算在静态_table中的索引
uint32_t hash = String::hash(p_name);
uint32_t idx = hash & STRING_TABLE_MASK;
_Data *_data = _table[idx];
// 检索在链表中的结点
while (_data) {
// compare hash first
if (_data->hash == hash && _data->get_name() == p_name) {
break;
}
_data = _data->next;
}
// 节点有效 且 引用计数+1
if (_data && _data->refcount.ref()) {
#ifdef DEBUG_ENABLED
if (unlikely(debug_stringname)) {
_data->debug_references++;
}
#endif
// 返回
return StringName(_data);
}
return StringName(); //does not exist
}赋值函数
// 赋值
void StringName::operator=(const StringName &p_name) {
if (this == &p_name) {
return;
}
// 赋新值,需先减少以前的字符的引用串数
unref();
// 引用计数+1
if (p_name._data && p_name._data->refcount.ref()) {
_data = p_name._data;
}
}一个重要的宏
SNAME(m_arg)用于优化 StringName(字符串名称)对象的创建。在许多编程场景中,频繁地创建和销毁同一字符串名称可能会对性能产生影响,特别是在高性能要求的场合。SNAME?宏通过内部的静态局部变量实现了一种高效的缓存机制,在首次使用时创建并存储特定字符串名称,后续调用时直接返回已创建的实例。
#define SNAME(m_arg) ([]() -> const StringName & { static StringName sname = _scs_create(m_arg, true); return sname; })()
SNAME 宏旨在提升高频率创建特定字符串名称场景下的性能,但在大多数情况下并不推荐滥用,仅在确实需要提高性能的关键路径上使用。
推荐在以下场景使用:
- 在 Control::get_theme_() 和 Window::get_theme_() 等高频主题方法中;
- 在 emit_signal(,..) 和 call_deferred(,..) 等信号关联的方法中;
- 在重写 _set 和 _get 方法时与 StringName 进行比较的情况。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- C语言之枚举类型
- 14.迭代器模式
- 安卓(雷电)模拟器清除屏幕密码
- Linux命令大全
- 简单高效 Learn LaTeX 008 - LaTex Font Color 字体与颜色 (32 mins)
- 基于Java SSM框架实现点餐系统网站系统项目【项目源码】计算机毕业设计
- 谷歌新一轮大裁员!俩同事正上着班突然电脑就重启了!连老板一起都被裁了!
- 机器视觉之尺度不变特征变换(SFIT)算法的实例教程
- openmediavault(OMV) (17)云相册(1)piwigo
- 直流电子负载如何实现的