C++相关闲碎记录(17)
1、IO操作
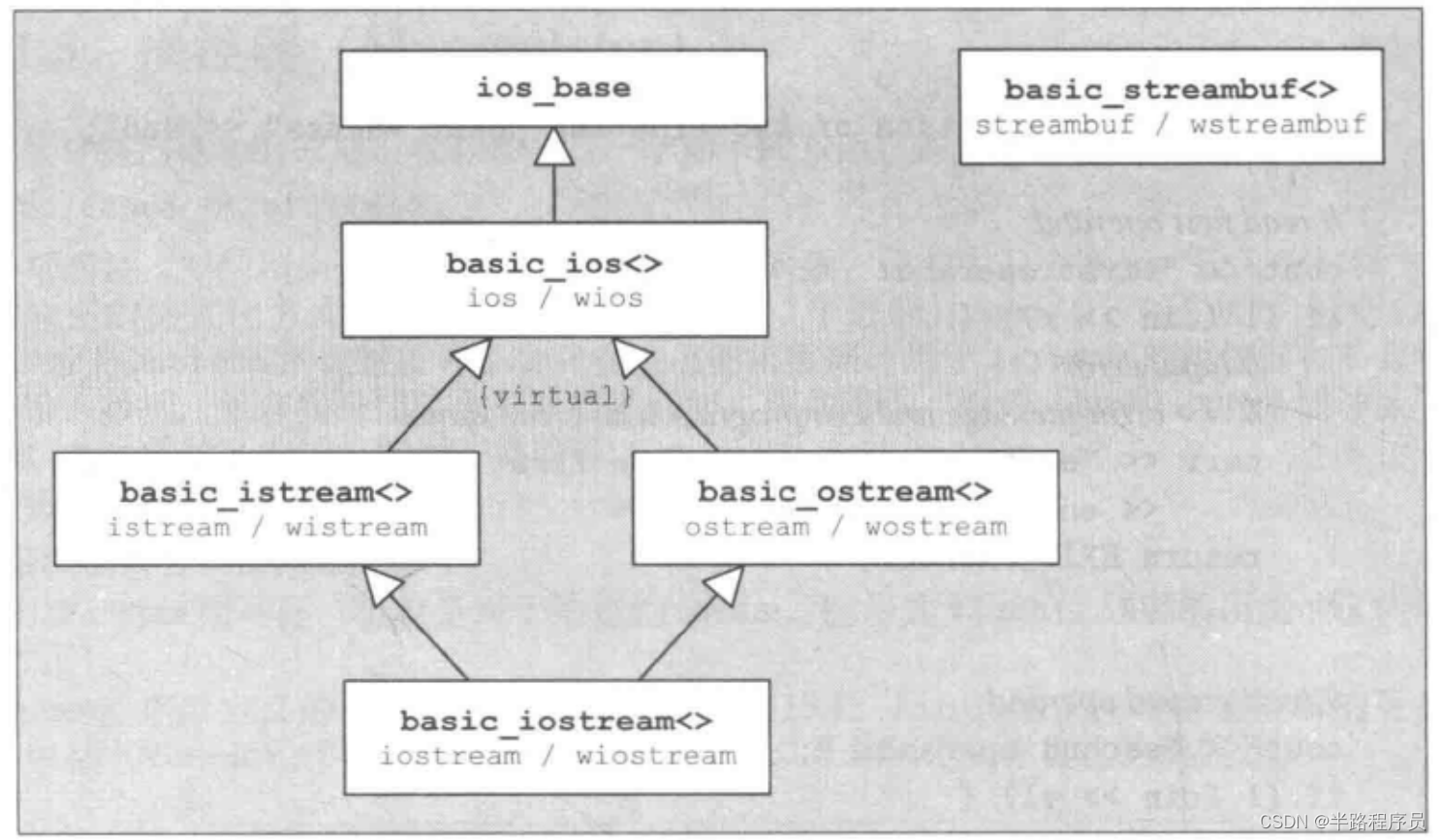
(1)class及其层次体系
?(2)全局性stream对象

?(3)用来处理stream状态的成员函数

?前四个成员函数可以设置stream状态并返回一个bool值,注意fail()返回是failbit或者badbit两者中是否任一个设置,如果调用不带参数的clear(),所有的error flag均会被清除。
?下面这个例子用于检查failbit是否设置,若设置则清除。
if(strm.rdstate() & std::ios::failbit){
std::cout << "failbit was set" << std::endl;
strm.clear(strm.rdstate() & ~std::ios::failbit);
}(4)stream异常
下面的例子要求所stream对所有的flag均抛出异常:
strm.exceptions(std::ios::eofbit | std::ios::failbit | std::ios::badbit);但是如果传入0或者goodbit,就不会引发异常。
strm.exceptions(std::ios::goodbit);?异常抛出的时机是在“程序调用clear()或setstate()之后”又设置了某些flag之际,如果某个标志已被设置但未被清除,也会抛出异常。
下面的例子从输入中读取浮点数,直到end-of-file为止,返回总和。
#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include <cstdlib>
namespace MyLib {
double readAndProcessSum (std::istream&);
}
int main()
{
using namespace std;
double sum;
try {
sum = MyLib::readAndProcessSum(cin);
}
catch (const ios::failure& error) {
cerr << "I/O exception: " << error.what() << endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
catch (const exception& error) {
cerr << "standard exception: " << error.what() << endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
catch (...) {
cerr << "unknown exception" << endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// print sum
cout << "sum: " << sum << endl;
}
#include <istream>
namespace MyLib {
double readAndProcessSum (std::istream& strm)
{
using std::ios;
double value, sum;
// save current state of exception flags
ios::iostate oldExceptions = strm.exceptions();
// let failbit and badbit throw exceptions
// - NOTE: failbit is also set at end-of-file
strm.exceptions (ios::failbit | ios::badbit);
try {
// while stream is OK
// - read value and add it to sum
sum = 0;
while (strm >> value) {
sum += value;
}
}
catch (...) {
// if exception not caused by end-of-file
// - restore old state of exception flags
// - rethrow exception
if (!strm.eof()) {
strm.exceptions(oldExceptions); // restore exception flags
throw; // rethrow
}
}
// restore old state of exception flags
strm.exceptions (oldExceptions);
// return sum
return sum;
}
}(5)读写字符的成员函数

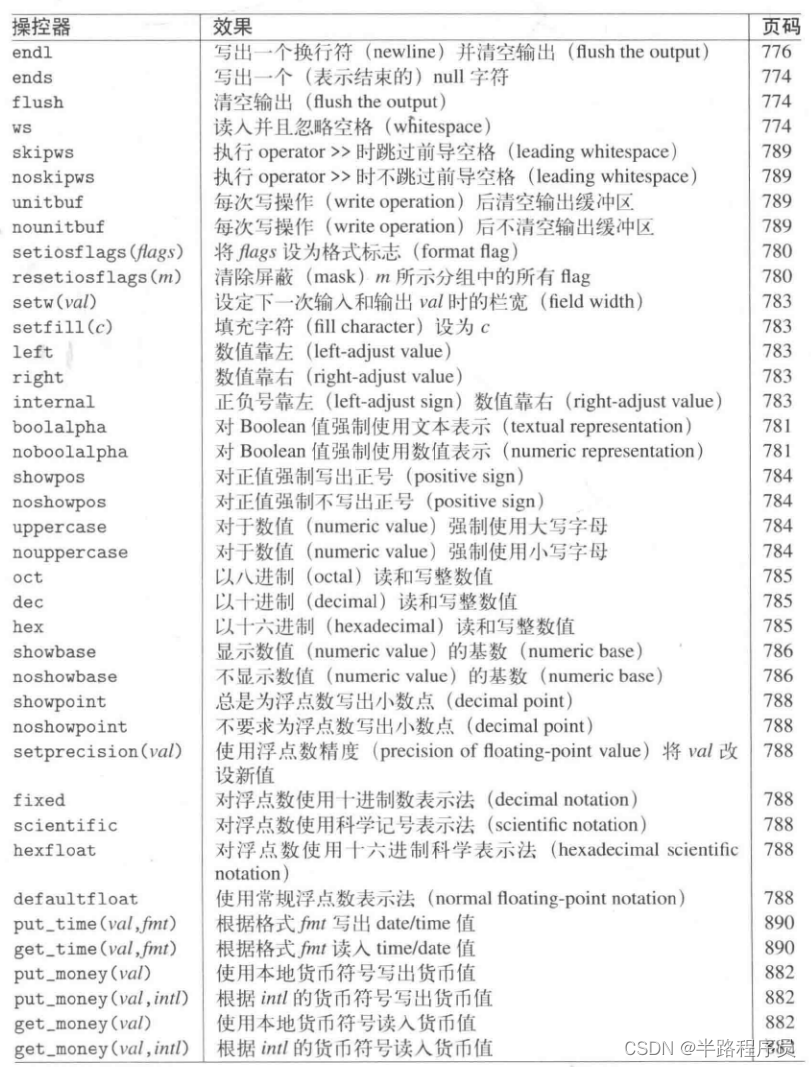
?(6)输出控制manipulator
?(7)用户自定义操控器
#include <istream>
#include <limits>
template <typename charT, typename traits>
inline
std::basic_istream<charT,traits>&
ignoreLine (std::basic_istream<charT,traits>& strm)
{
// skip until end-of-line
strm.ignore(std::numeric_limits<std::streamsize>::max(),
strm.widen('\n'));
// return stream for concatenation
return strm;
}这个控制器用来忽略一行,如果要忽略多行,就调用多次
std::cin >> ignoreLine >> ignoreLine;
函数ignore(max, c)会略去input stream中的字符c之前的所有字符,如果前面的字符多余max个,就略去max个,如果先遇到stream结尾,就全部忽略。
#include <iostream>
#include "ignore1.hpp"
int main()
{
int i;
std::cout << "read int and ignore rest of the line" << std::endl;
std::cin >> i;
// ignore the rest of the line
std::cin >> ignoreLine;
std::cout << "int: " << i << std::endl;
std::cout << "read int and ignore two lines" << std::endl;
std::cin >> i;
// ignore two lines
std::cin >> ignoreLine >> ignoreLine;
std::cout << "int: " << i << std::endl;
}#include <istream>
#include <limits>
class ignoreLine
{
private:
int num;
public:
explicit ignoreLine (int n=1) : num(n) {
}
template <typename charT, typename traits>
friend std::basic_istream<charT,traits>&
operator>> (std::basic_istream<charT,traits>& strm,
const ignoreLine& ign)
{
// skip until end-of-line num times
for (int i=0; i<ign.num; ++i) {
strm.ignore(std::numeric_limits<std::streamsize>::max(),
strm.widen('\n'));
}
// return stream for concatenation
return strm;
}
};#include <iostream>
#include "ignore2.hpp"
int main()
{
int i;
std::cout << "read int and ignore rest of the line" << std::endl;
std::cin >> i;
// ignore the rest of the line
std::cin >> ignoreLine();
std::cout << "int: " << i << std::endl;
std::cout << "read int and ignore two lines" << std::endl;
std::cin >> i;
// ignore two lines
std::cin >> ignoreLine(2);
std::cout << "int: " << i << std::endl;
std::cout << "read int: " << std::endl;
std::cin >> i;
std::cout << "int: " << i << std::endl;
}(8)format flag格式标志

//set flags showpos and uppercase
std::cout.setf(std::ios::showpos | std::ios::uppercase);
//set only the flag hex in the group basefield
std::cout.setf(std::ios::hex, std::ios::basefield);
//clear the flag uppercase
std::cout.unsetf(std::ios::uppercase);using std::ios;
using std::cout;
//save current format flags
ios::fmtflags oldFlags = cout.flags();
//do some changes
cout.setf(ios::showpos | ios::showbase | ios::uppercase);
cout.setf(ios::internal, ios::adjustfield);
cout << std::hex << x << std::endl;
cout.flags(oldFlags);
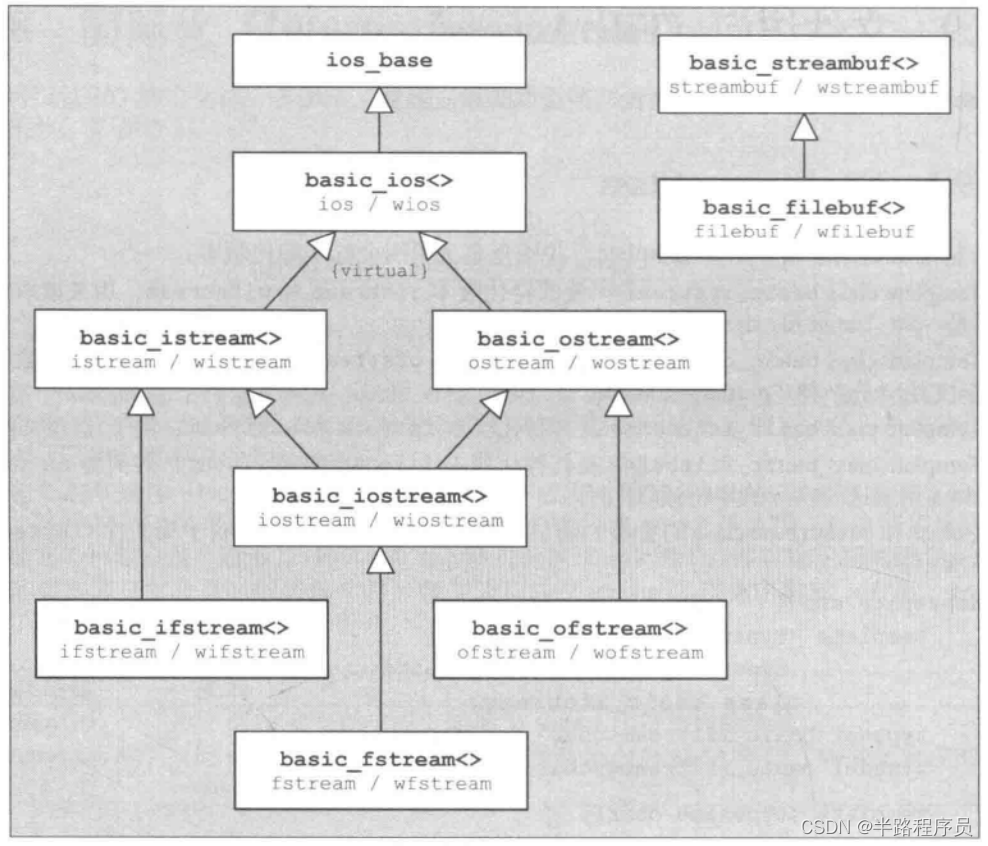
?(9)文件读写
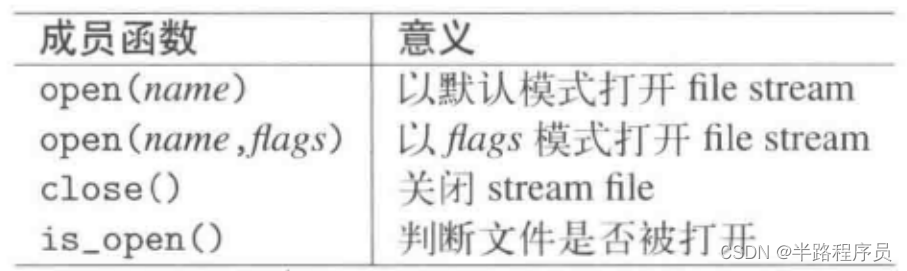
?(10)文件flag


//seek to the beginning of the file
file.seek(0, std::ios::beg);
//seek 20 characters forward
file.seek(20, std::ios::cur);
//seek 10 characters before the end
file.seek(-10, std::ios::end);(11)重定向
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
void redirect(ostream&);
int main()
{
cout << "the first row" << endl; //输出控制台
redirect(cout); //重定向到文件中,执行完毕之后,又重新指向控制台
cout << "the last row" << endl;//指向控制台
}
void redirect (ostream& strm)
{
// save output buffer of the stream
// - use unique pointer with deleter that ensures to restore
// the original output buffer at the end of the function
// 定义了一个删除器
auto del = [&](streambuf* p) {
strm.rdbuf(p);
};
// 使用智能指针的目的时在退出函数时,还原ostream
unique_ptr<streambuf,decltype(del)> origBuffer(strm.rdbuf(),del);
// redirect ouput into the file redirect.txt
ofstream file("redirect.txt");
// strm指向file缓冲区
strm.rdbuf (file.rdbuf());
// 此两字符都会写入到文件中
file << "one row for the file" << endl;
strm << "one row for the stream" << endl;
// 程序结束时,调用智能指针的删除器,将输出重新指向p,而这个p就是strm.rdbuf()
} //(12)可读写的stream
定义一个file stream缓冲区,并将它安装在两个stream对象上,
std::filebuf buffer;
std::ostream out(&buffer);
std::istream in(&buffer);
buffer.open("example.txt", std::ios::in | std::ios::out);#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// open file "example.dat" for reading and writing
filebuf buffer;
ostream output(&buffer);
istream input(&buffer);
buffer.open ("example.dat", ios::in | ios::out | ios::trunc);
for (int i=1; i<=4; i++) {
// write one line
output << i << ". line" << endl;
// print all file contents
input.seekg(0); // seek to the beginning
char c;
while (input.get(c)) {
cout.put(c);
}
cout << endl;
input.clear(); // clear eofbit and failbit
}
}
输出:
1. line
1. line
2. line
1. line
2. line
3. line
1. line
2. line
3. line
4. line
(13)stream 缓冲区接口



?函数pubseekoff()和pubseekpos()控制读写动作的当前位置,究竟是控制读或者写,取决于最后实参,其类型为ios_base::openmode,如果没有特别指定,实参默认值为ios_base::in|ios_base::out,一旦设置ios_base::in,读的位置就会跟着改变,一旦设置ios_base::out,写的位置也会跟着变化,函数pubseekpos()会把stream当前位置移至第一实参指示的绝对位置上,函数pubseekoff()则把stream当前位置移至某个相对位置,偏移量由第一实参决定,起始位置由第二实参决定,可以是ios_base::cur, ios_base::beg, ios_base::end。两个函数都返回stream所在的位置或者一个无效的位置,将函数的结果拿来和对象pos_type(off_type(-1))比较(pos_type和off_type是处理stream位置时所用的类型),如果希望获取stream当前位置,可以使用pubseekoff(): sbuf.pubseekoff(0, std::ios:cur)。
(14)output stream 缓冲区的iterator
使用ostreambuf_iterator将一个字符串写入stream缓冲区内:
std::ostreambuf_iterator<char> bufWriter(std::cout);
std::string hello("hello, world\n");
std::copy(hello.begin(), hello.end(), bufWriter);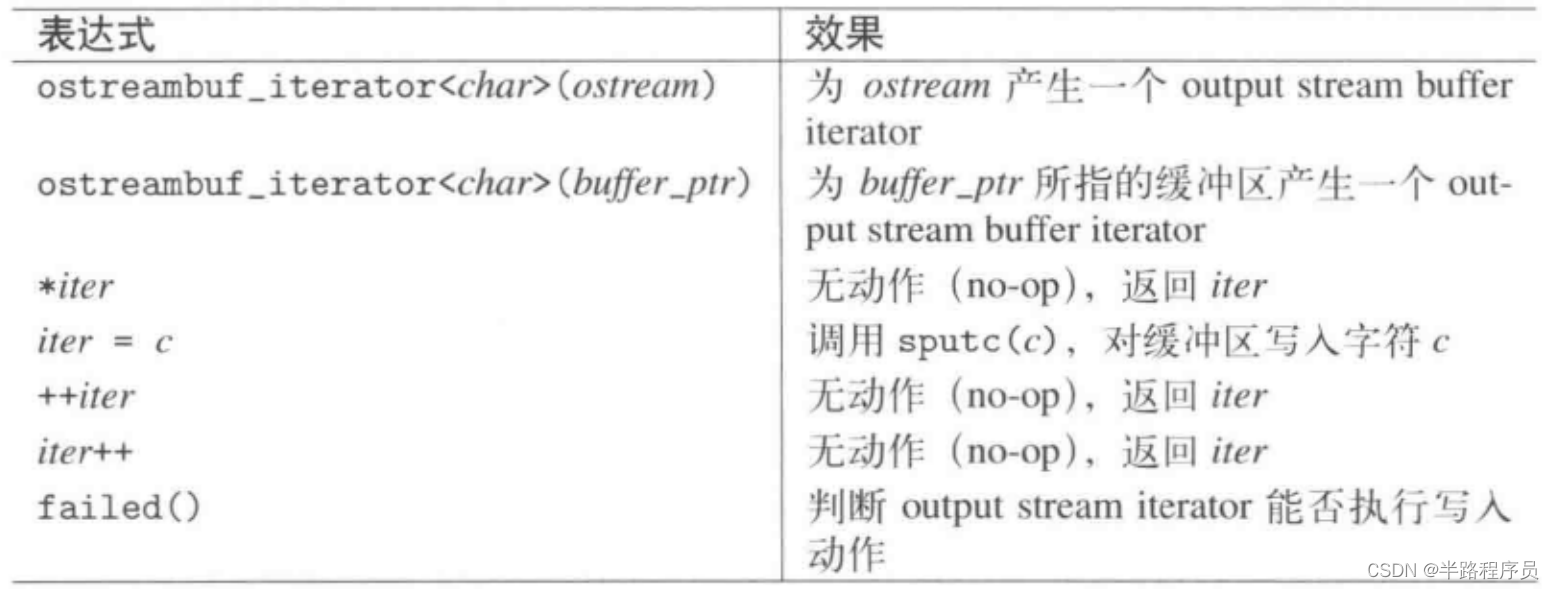
?(15)input stream 缓冲区的iterator
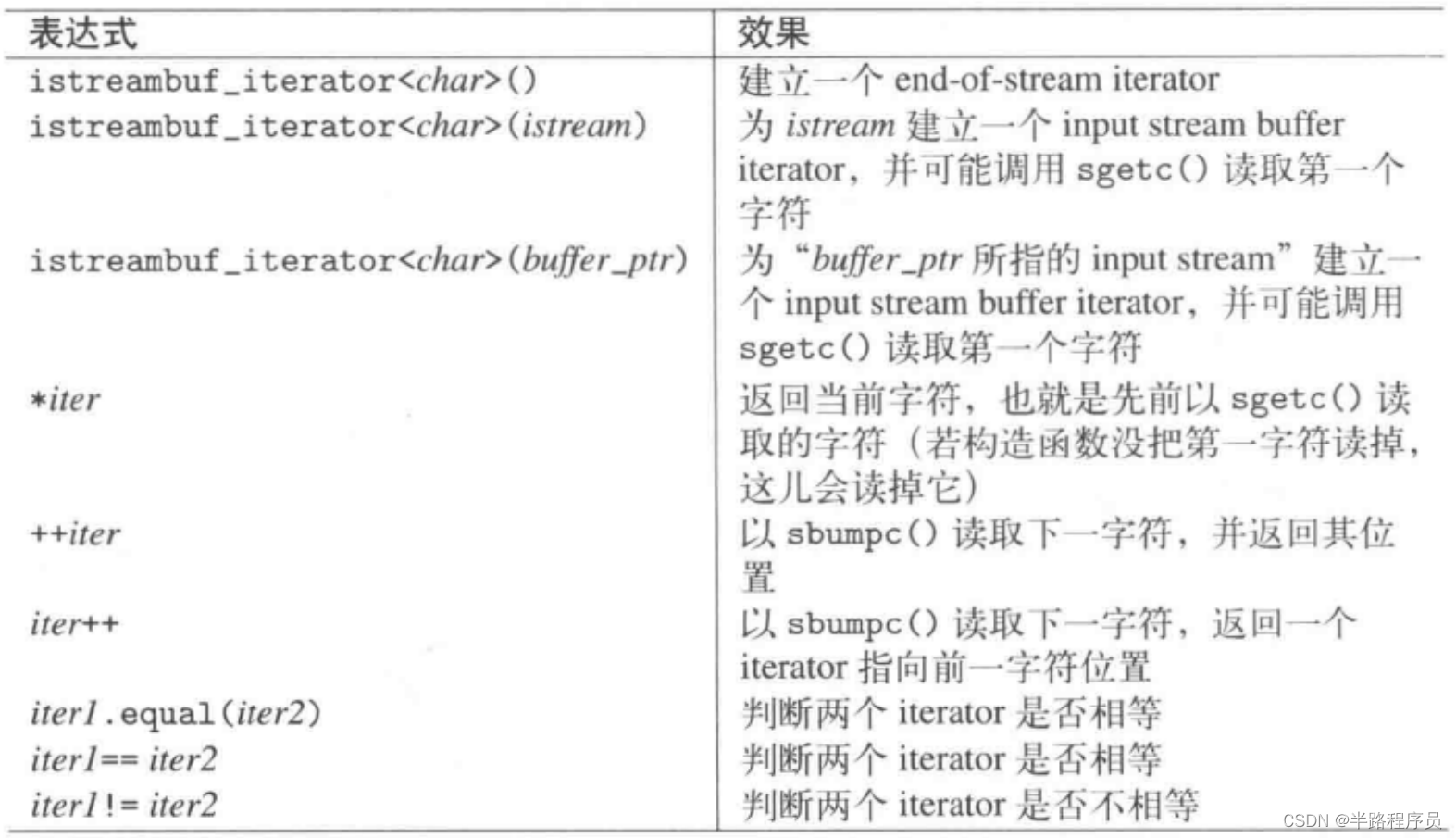
?将输入缓冲区的字符输出:
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// input stream buffer iterator for cin
istreambuf_iterator<char> inpos(cin);
// end-of-stream iterator
istreambuf_iterator<char> endpos;
// output stream buffer iterator for cout
ostreambuf_iterator<char> outpos(cout);
// while input iterator is valid
while (inpos != endpos) {
*outpos = *inpos; // assign its value to the output iterator
++inpos;
++outpos;
}
}本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 禁用windows更新
- UI设计中的2.5D插画是什么?
- 图怎么遍历
- 使用Windows批处理命令行和ImageMagick批量将文件夹中的图片转换为PDF文档的方法
- Java 21 神仙特性:虚拟线程使用指南(一)
- 深入理解 JavaScript 函数:提升编程技能的必备知识(上)
- 智能优化算法应用:基于人工兔算法3D无线传感器网络(WSN)覆盖优化 - 附代码
- 这是我在 2023 年最大的收获
- 智能优化算法应用:基于学生心理学算法3D无线传感器网络(WSN)覆盖优化 - 附代码
- Ubuntu 常用命令之 chmod 命令用法介绍