最值查找max,min及类似函数用法与说明
发布时间:2024年01月08日
本篇介绍了在算法竞赛中最为常用的关于最值查找的部分函数
一、max和min函数的基本用法
max(a, b)返回a和b中较大的那个值,只能传入两个值,或传入一个列表。
传入两个值
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b; //输入两个数a和b
cout << max(a, b) << endl;//打印最大值
return 0;
}
传入一个列表
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << max({2, 4, 7, 9, 21}) << endl; //打印输出21
return 0;
}
同理,min(a, b)返回a和b中较小的那个值,只能传入两个值,或传入一个列表。
传入两个值
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b; //输入两个数a和b
cout << min(a, b) << endl;//打印最大值
return 0;
}
传入一个列表
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << min({2, 4, 7, 9, 21}) << endl; //打印输出2
return 0;
}
二、max_element和min_element函数用法及说明
max_element的用法
max_element(st, ed)返回地址[st, ed)中最大的那个值的地址(迭代器), 传入参数为两个地址或迭代器。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> arr = {2, 5, 7, 3, 4}; //这里可以使用容器,也可以使用数组
int main()
{
cout << *max_element(arr.begin(), arr.end()) << endl; //输出最大元素7,通过*来解引用得到地址的值
return 0;
}
min_element的用法
min_element(st, ed)返回地址[st, ed)中最小的那个值的地址(迭代器), 传入参数为两个地址或迭代器。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> arr = {2, 5, 7, 3, 4}; //这里可以使用容器,也可以使用数组
int main()
{
cout << *min_element(arr.begin(), arr.end()) << endl; //输出最小元素2,通过*来解引用得到地址的值
return 0;
}
三、nth_element函数的基本用法
nth_element函数属于一种排序函数,是一种特殊的部分排序逻辑。其用法为:
nth_element(st, k, ed)返回值为void, 传入参数为三个地址或迭代器。其中第二个参数位置的元素将处于正确的位置,其他位置的元素顺序可能是任意的,但前面的都比它小,后面的都比它大。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
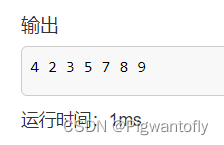
vector<int> arr = {4, 2, 5, 8, 3, 7, 9};
int main()
{
nth_element(arr.begin(), arr.begin() + 3, arr.end());
for(int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i ++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
return 0;
}
代码结果:
这是最值查找的全部内容了,之后有了更深入的学习后会进行进一步完善和修改。觉得这篇文章对您有帮助的可以点一个赞,这是对我最大的支持和动力。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/WDJ54068923/article/details/135448213
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Ubuntu envs setting
- 基于GBM和随机森林模型探索影响学生压力的主要因素
- nacos配置mysql
- 利用STM32CubeMX和keil模拟器,3天入门FreeRTOS(2.1) —— 任务挂起和恢复
- c语言的初始学习(练习)
- Docker exec报 the input device is not a TTY错误
- 【MySQL】字符集与排序规则
- Spring Boot统一功能处理(Spring拦截器)
- 【递归、搜索与回溯】综合练习
- CGAL 多段线(多边形)三角化