Vue3的使用
一 Vue3的变化
1.性能的提升
-
打包大小减少41%
-
初次渲染快55%, 更新渲染快133%
-
内存减少54%
2.源码的升级
-
使用Proxy代替defineProperty实现响应式
-
重写虚拟DOM的实现和Tree-Shaking
3.拥抱TypeScript
- Vue3可以更好的支持TypeScript
4.新的特性
-
Composition API(组合API)
- setup配置
- ref与reactive
- watch与watchEffect
- provide与inject
-
新的内置组件
- Fragment
- Teleport
- Suspense
-
其他改变
- 新的生命周期钩子
- data 选项应始终被声明为一个函数
- 移除keyCode支持作为 v-on 的修饰符
5 组合式API和配置项API
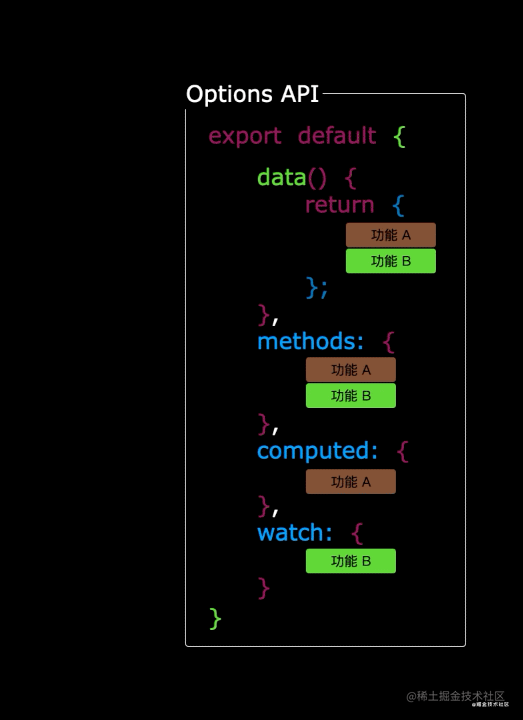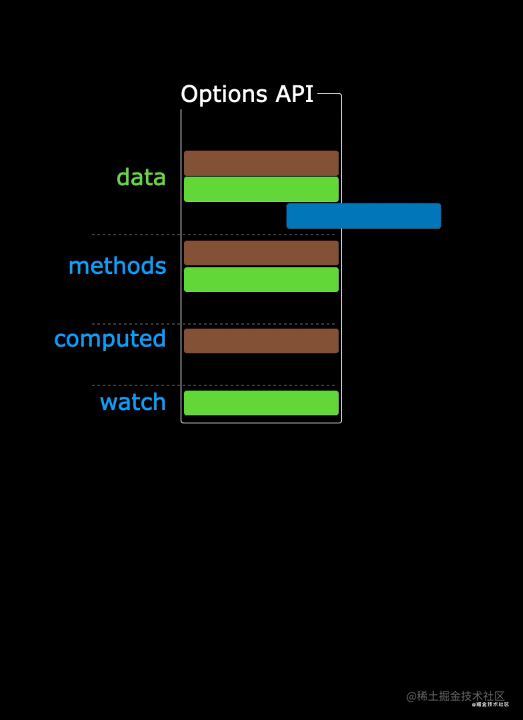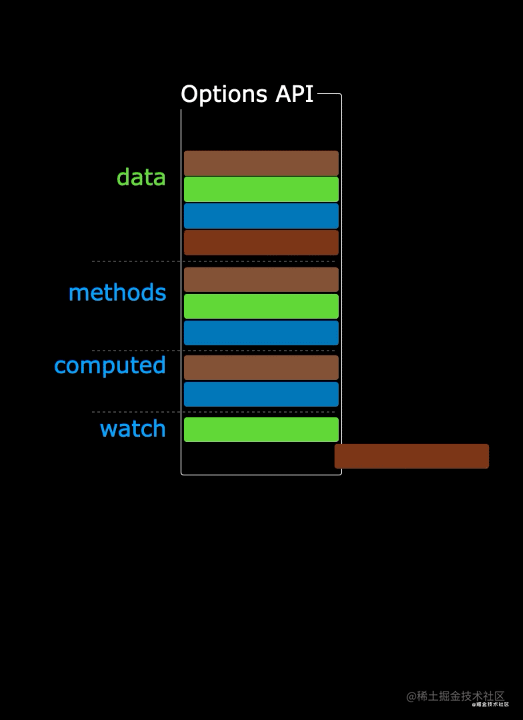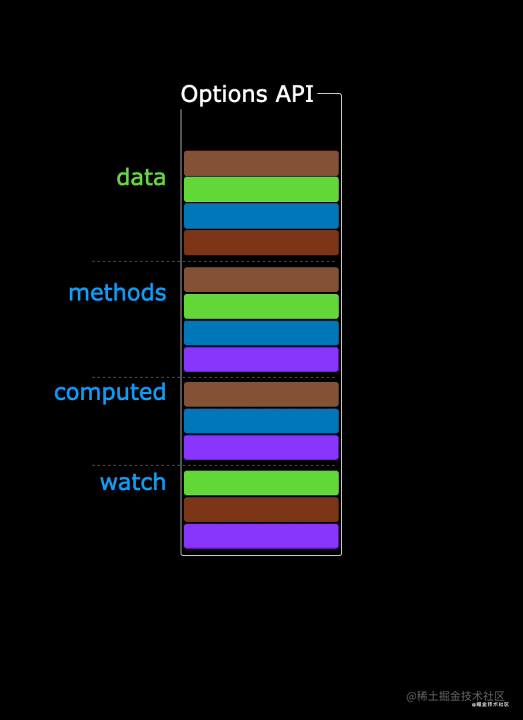
5.1 Options API 存在的问题
使用传统OptionsAPI中,新增或者修改一个需求,就需要分别在data,methods,computed里修改 。
5.2 Composition API 的优势
我们可以更加优雅的组织我们的代码,函数。让相关功能的代码更加有序的组织在一起。
6 项目分析
分析文件目录
main.js
Vue2项目的main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
看看vm是什么
const vm = new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
})
console.log(vm)
vm.$mount('#app')
我们再来看看Vue3项目中的main.js
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
createApp(App).mount('#app')
我们来分析一下吧
// 引入的不再是Vue构造函数了,引入的是一个名为createApp的工厂函数
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 创建应用实例对象——app(类似于之前Vue2中的vm,但app比vm更“轻”)
const app = createApp(App)
console.log(app)
// 挂载
app.mount('#app')
这里的app到底是啥,我们输出到控制台看看
App.vue
我们再来看看组件
在template标签里可以没有根标签了
<template>
<!-- Vue3组件中的模板结构可以没有根标签 -->
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<HelloWorld msg="Welcome to Your Vue.js App"/>
</template>
二 创建Vue3.0工程
1.使用 vue-cli 创建
官方文档:创建一个项目 | Vue CLI
## 查看@vue/cli版本,确保@vue/cli版本在4.5.0以上
vue --version
## 安装或者升级你的@vue/cli
npm install -g @vue/cli
## 创建
vue create vue_test
## 启动
cd vue_test
npm run serve
2.使用 vite 创建
官方文档:快速上手 | Vue.js
vite官网:https://vitejs.cn
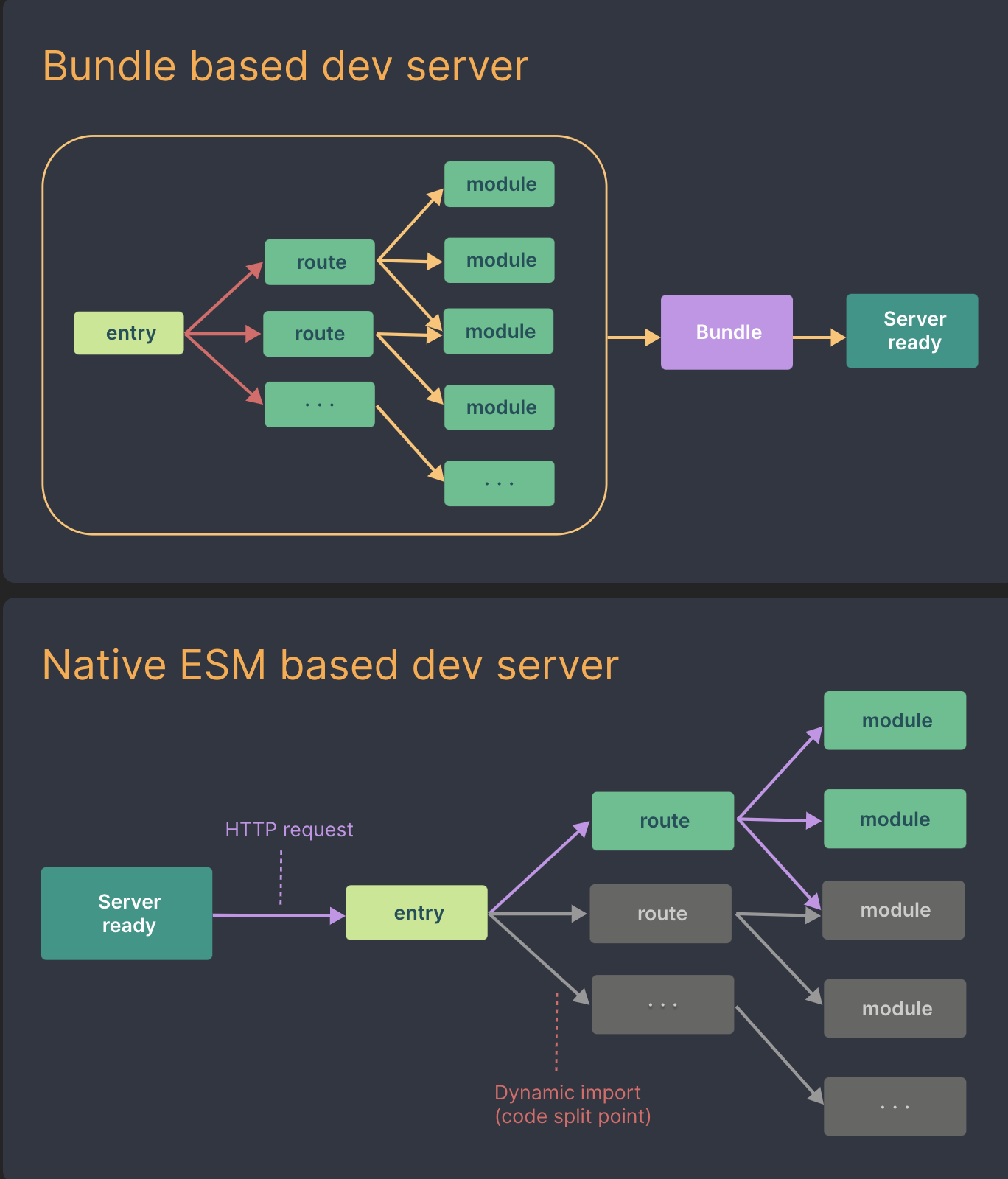
- 什么是vite?—— 新一代前端构建工具。
- 优势如下:
- 开发环境中,无需打包操作,可快速的冷启动。
- 轻量快速的热重载(HMR)。
- 真正的按需编译,不再等待整个应用编译完成。
- 传统构建 与 vite构建对比图
## 创建工程
npm init vite-app <project-name>
## 进入工程目录
cd <project-name>
## 安装依赖
npm install
## 运行
npm run dev
# 确保你安装了最新版本的 Node.js,然后在命令行中运行以下命令 (不要带上 > 符号):
> npm init vue@latest
# 这一指令将会安装并执行 create-vue,它是 Vue 官方的项目脚手架工具。你将会看到一些诸如 TypeScript 和测试支持之类的可选功能提示:
? Project name: … <your-project-name>
? Add TypeScript? … No / Yes
? Add JSX Support? … No / Yes
? Add Vue Router for Single Page Application development? … No / Yes
? Add Pinia for state management? … No / Yes
? Add Vitest for Unit testing? … No / Yes
? Add Cypress for both Unit and End-to-End testing? … No / Yes
? Add ESLint for code quality? … No / Yes
? Add Prettier for code formatting? … No / Yes
Scaffolding project in ./<your-project-name>...
Done.
# 如果不确定是否要开启某个功能,你可以直接按下回车键选择 No。在项目被创建后,通过以下步骤安装依赖并启动开发服务器:
> cd <your-project-name>
> npm install
> npm run dev
三
三、常用API
3.1 setup
-
setup为Vue3.0中一个新的配置项,值为一个函数
-
setup是所有Composition API(组合API)编写的位置
-
组件中所用到的:数据、方法等等,均要配置在setup中
-
setup函数的返回值:返回一个对象,对象中的属性、方法, 在模板中均可以直接使用
-
注意:
尽量不要与Vue2.x配置混用
- Vue2.x配置(data、methos、computed...)中可以访问到setup中的属性、方法。
- 但在setup中不能访问到Vue2.x配置(data、methos、computed...)。
- 如果有重名, setup优先。
<template>
{{name}}--{{age}}--{{xx}}
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return {
xx:this.name
}
},
setup(){
let name='lqz'
let age =19
return {
name,age
}
},
}
</script>
3.2 ref函数
- 作用: 定义一个响应式的数据
- 语法:?
const xxx = ref(initValue)- 创建一个包含响应式数据的引用对象(reference对象,简称ref对象)。
- JS中操作数据:?
xxx.value - 模板中读取数据: 不需要.value,直接:
<div>{{xxx}}</div>
- 备注:
- 接收的数据可以是:基本类型、也可以是对象类型。
- 基本类型的数据:响应式依然是靠
Object.defineProperty()的get与set完成的 - 对象类型的数据:内部 求助 了Vue3.0中的一个新函数——?
reactive函数
3.3 reactive函数
- 作用: 定义一个对象类型的响应式数据(基本类型不要用它,要用
ref函数) - 语法:
const 代理对象= reactive(源对象)接收一个对象(或数组),返回一个代理对象(Proxy的实例对象,简称proxy对象) - reactive定义的响应式数据是“深层次的”
- 内部基于 ES6 的 Proxy 实现,通过代理对象操作源对象内部数据进行操作
<template>
{{ name }}--{{ age }}--{{ xx }}
<br>
{{person}}
<button @click="handleClick">点我</button>
<br>
</template>
<script>
import {ref, reactive} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data() {
return {
xx: this.name
}
},
setup() {
let name = 'lqz'
let age = ref(19)
// const person = ref({ // 内部包装成reactive
const person = reactive({
name: '彭于晏',
age: 88
})
function handleClick() {
// console.log(age)
// age.value++
console.log(person)
person.age++
}
return {
name, age, handleClick,person
}
},
}
</script>
3.4 reactive对比ref
- 从定义数据角度对比:
- ref用来定义:基本类型数据
- reactive用来定义:对象(或数组)类型数据
- 备注:ref也可以用来定义对象(或数组)类型数据, 它内部会自动通过
reactive转为代理对象
- 从原理角度对比:
- ref通过
Object.defineProperty()的get与set来实现响应式(数据劫持)。 - reactive通过使用Proxy来实现响应式(数据劫持), 并通过Reflect操作源对象内部的数据。
- ref通过
- 从使用角度对比:
- ref定义的数据:操作数据需要
.value,读取数据时模板中直接读取不需要.value。 - reactive定义的数据:操作数据与读取数据:均不需要
.value。
- ref定义的数据:操作数据需要
3.5 setup的两个注意点
-
setup执行的时机
- 在beforeCreate之前执行一次,this是undefined。
-
setup的参数
- props:值为对象,包含:组件外部传递过来,且组件内部声明接收了的属性。
- context:上下文对象
- attrs: 值为对象,包含:组件外部传递过来,但没有在props配置中声明的属性, 相当于?
this.$attrs。 - slots: 收到的插槽内容, 相当于?
this.$slots。 - emit: 分发自定义事件的函数, 相当于?
this.$emit。
- attrs: 值为对象,包含:组件外部传递过来,但没有在props配置中声明的属性, 相当于?
3.6 计算属性与监视
1.computed函数
-
与Vue2.x中computed配置功能一致
-
写法
<template> <p>姓:<input type="text" v-model="person.firstName"></p> <p>名:<input type="text" v-model="person.lastName"></p> <p>全名:{{ person.fullName }}</p> <p>全名修改:<input type="text" v-model="person.fullName"></p> </template> <script> import {ref, reactive} from 'vue' import {computed} from 'vue' export default { name: 'App', setup() { const person = reactive({ firstName: '刘', lastName: '亦非' }) // let fullName = computed(() => { // return person.firstName + '-' + person.lastName // }) // 或者,传入箭头函数 // person.fullName=computed(() => { // return person.firstName + '-' + person.lastName // }) // 修改,传入配置项目 person.fullName = computed({ get() { return person.firstName + '-' + person.lastName }, set(value) { const nameArr = value.split('-') person.firstName = nameArr[0] person.lastName = nameArr[1] } }) return {person} }, } </script>
2.watch函数
-
与Vue2.x中watch配置功能一致
-
两个小“坑”:
- 监视reactive定义的响应式数据时:oldValue无法正确获取、强制开启了深度监视(deep配置失效)。
- 监视reactive定义的响应式数据中某个属性时:deep配置有效。
<template> <h2>年龄是:{{ age }}</h2> <button @click="age++">点我年龄增加</button> <hr> <h2>姓名是:{{ person.name }}</h2> <button @click="person.name+='?'">点我姓名变化</button> <hr> <h2>sum是:{{ sum }},msg是:{{ msg }}</h2> <button @click="sum++">点我sum变化</button> | <button @click="msg+='?'">点我msg变化</button> </template> <script> import {ref, reactive} from 'vue' import {watch} from 'vue' export default { name: 'App', setup() { const age = ref(19) const person = reactive({ name: 'lqz', age: 20 }) //1 监听普通 watch(age, (newValue, oldValue) => { console.log('sum变化了', newValue, oldValue) }) // 2 监听对象 watch(() => person.name, (newValue, oldValue) => { console.log('person.name变化了', newValue, oldValue) }) // 3 监听多个 const sum = ref(100) const msg = ref('很好') watch([sum, msg], (newValue, oldValue) => { console.log('sum或msg变化了', newValue, oldValue) }) return {person, age, sum, msg} }, } </script>
3.watchEffect函数
-
watch的套路是:既要指明监视的属性,也要指明监视的回调。
-
watchEffect的套路是:不用指明监视哪个属性,监视的回调中用到哪个属性,那就监视哪个属性。
-
watchEffect有点像computed:
- 但computed注重的计算出来的值(回调函数的返回值),所以必须要写返回值。
- 而watchEffect更注重的是过程(回调函数的函数体),所以不用写返回值。
//watchEffect所指定的回调中用到的数据只要发生变化,则直接重新执行回调。 watchEffect(() => { const x1 = sum.value const x2 = person.age console.log('watchEffect配置的回调执行了') })
3.7 生命周期
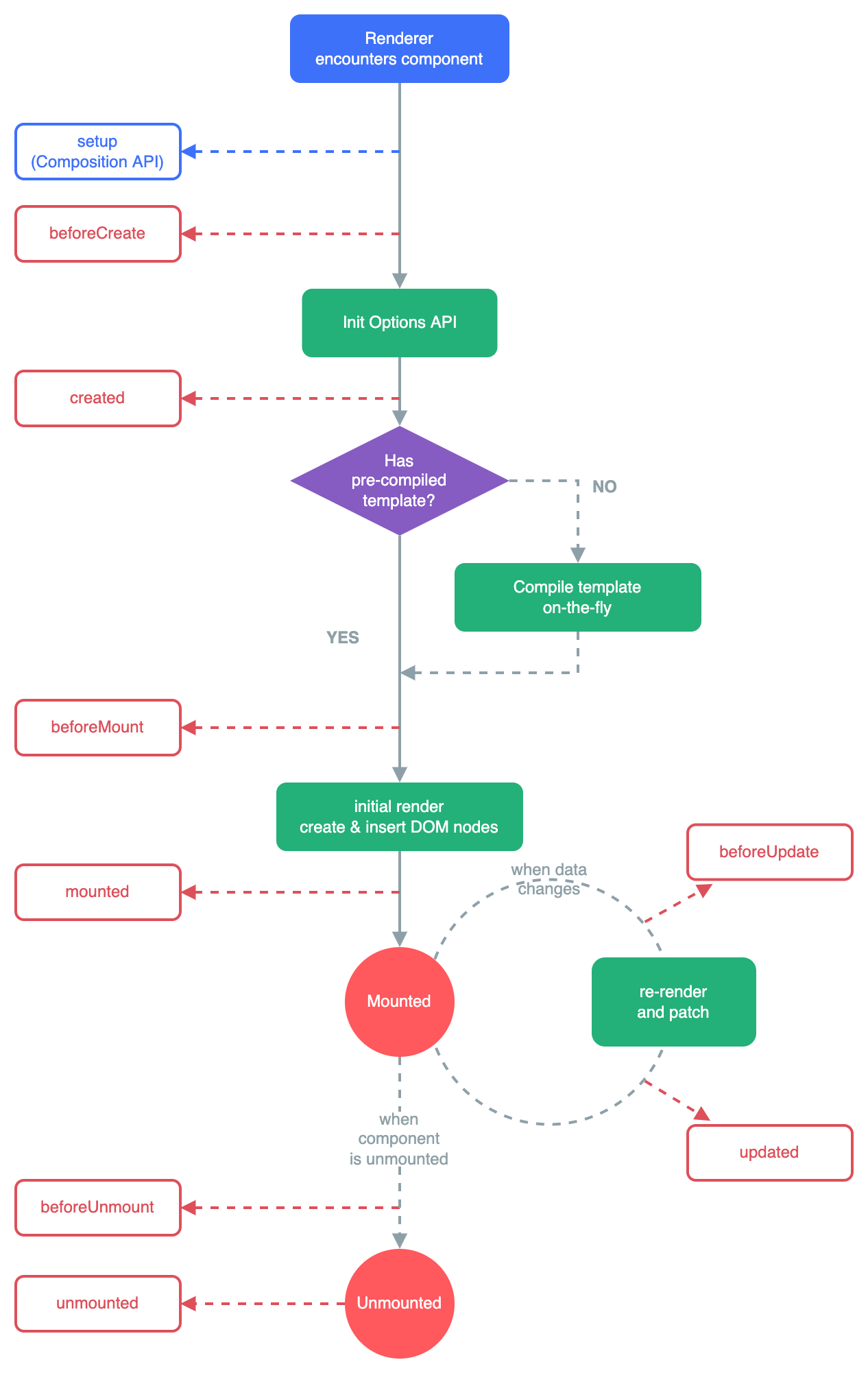
- Vue3.0中可以继续使用Vue2.x中的生命周期钩子,但有有两个被更名:
beforeDestroy改名为?beforeUnmountdestroyed改名为?unmounted
- Vue3.0也提供了 Composition API 形式的生命周期钩子,与Vue2.x中钩子对应关系如下:
beforeCreate===>setup()created=======>setup()beforeMount?===>onBeforeMountmounted=======>onMountedbeforeUpdate===>onBeforeUpdateupdated?=======>onUpdatedbeforeUnmount?==>onBeforeUnmountunmounted?=====>onUnmounted
3.8 自定义hook函数
-
什么是hook?—— 本质是一个函数,把setup函数中使用的Composition API进行了封装。
-
类似于vue2.x中的mixin。
-
自定义hook的优势: 复用代码, 让setup中的逻辑更清楚易懂。
3.8.1 打点功能
<template>
<h2>点击的x坐标:{{ point.x }},y坐标:{{ point.y }}</h2>
</template>
<script>
import {reactive} from 'vue'
import {onMounted, onBeforeUnmount} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'Point',
setup() {
const point = reactive({
x: 0,
y: 0
})
function getPoint(event) {
console.log(event.pageX)
console.log(event.pageY)
point.x = event.pageX
point.y = event.pageY
}
// 挂在完成开始执行
onMounted(() => {
window.addEventListener('click', getPoint)
})
// 接除挂载时执行
onBeforeUnmount(() => {
console.log('sss')
window.removeEventListener('click', getPoint)
})
return {point}
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<button @click="isShow=!isShow">点我显示隐藏</button>
<Point v-if="isShow"></Point>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {ref, reactive} from 'vue'
import Point from "./components/Point.vue";
import Demo from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {Demo, Point},
setup() {
const isShow = ref(true)
return {isShow}
},
}
</script>
3.8.2 使用hook实现打点
uesPoint.js
import {onBeforeUnmount, onMounted, reactive} from "vue";
export default function () {
let point = reactive({
x: 0,
y: 0
})
function getPoint(event) {
console.log(event.pageX)
console.log(event.pageY)
point.x = event.pageX
point.y = event.pageY
}
// 挂在完成开始执行
onMounted(() => {
window.addEventListener('click', getPoint)
})
// 接除挂载时执行
onBeforeUnmount(() => {
console.log('sss')
window.removeEventListener('click', getPoint)
})
return point
}
Point.vue
<template>
<h2>点击的x坐标:{{ point.x }},y坐标:{{ point.y }}</h2>
</template>
<script>
import usePoint from '../hooks/usePoint.js'
export default {
name: 'Point',
setup() {
let point = usePoint()
console.log(point)
return {point}
},
}
</script>
10.toRef
-
作用:创建一个 ref 对象,其value值指向另一个对象中的某个属性。
-
语法:
const name = toRef(person,'name') -
应用: 要将响应式对象中的某个属性单独提供给外部使用时。
-
扩展:
toRefs?与toRef功能一致,但可以批量创建多个 ref 对象,语法:toRefs(person)
<template>
<div>
<h2>姓名:{{ name }}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{ age }}</h2>
<button @click="age++">改年龄</button>| <button @click="name+='~'">改姓名</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {ref, reactive,toRefs} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
setup() {
const person = reactive({
name: 'lqz',
age: 19
})
return {
...toRefs(person)
}
},
}
</script>
//对象展开语法
let obj1 = {foo: 'bar', x: 42};
let obj2 = {foo: 'baz', y: 13};
let mergedObj = {...obj1, ...obj2};
console.log(mergedObj)本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Vulnhub靶机:Corrosion 2
- Ubuntu18.04 安装 qt 5.15.2
- Nginx配置压缩和解压缩
- 技术应用|MySQL命令之mysqlshow
- 学会使用ubuntu——ubuntu22.04使用Google、git的魔法操作
- 用文本创建图表的工具PlantUML
- 【华为机试真题Java】符号运算
- 搜索百度百科官方创建入口,怎么创建更新公司的百度百科词条呢?
- 分布式链路追踪专栏——分布式链路追踪:Skywalking 探针模型设计
- 基于SSM的宠物管理系统--56932(免费领源码)可做计算机毕业设计JAVA、PHP、爬虫、APP、小程序、C#、C++、python、数据可视化、大数据、全套文案