快速上手:探索Spring MVC的学习秘籍!
SpringMVC概述
SpringMVC是隶属于Spring框架的一部分,主要是用来进行Web开发,是对Servlet进行了封装。学习SpringMVC我们先来了解下现在web程序是如何做的,咱们现在web程序大都基于三层架构来实现。
三层架构
-
浏览器发送一个请求给后端服务器,后端服务器现在是使用Servlet来接收请求和数据。
-
如果所有的处理都交给Servlet来处理的话,所有的东西都耦合在一起,对后期的维护和扩展极为不利。
-
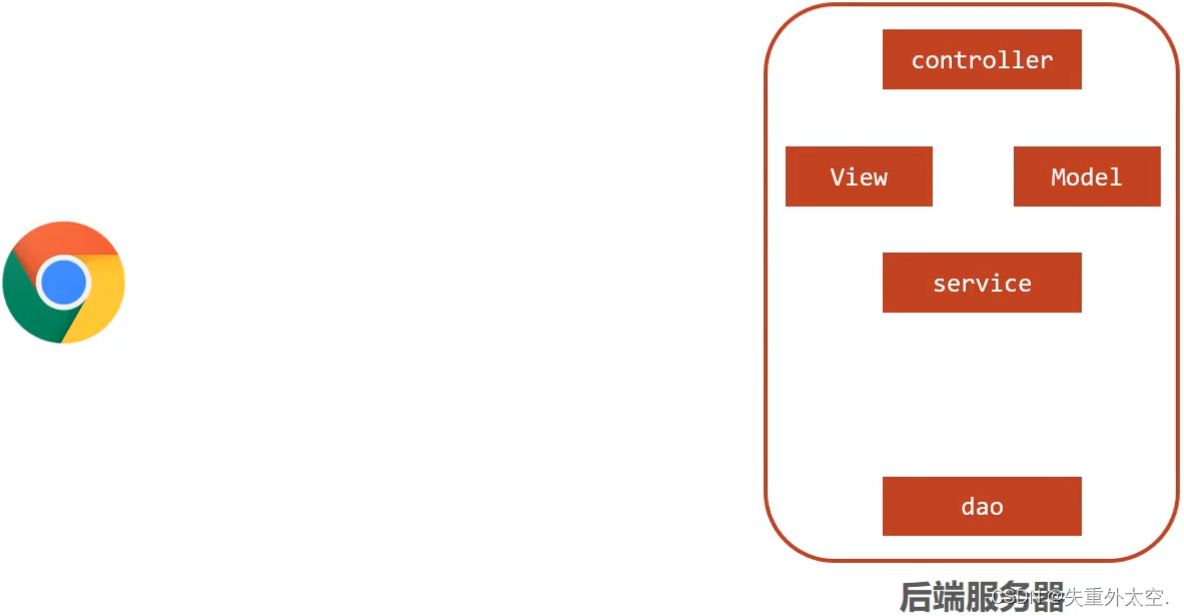
将后端服务器Servlet拆分成三层,分别是
web、service和dao。- web层主要由servlet来处理,负责页面请求和数据的收集以及响应结果给前端。
- service层主要负责业务逻辑的处理。
- dao层主要负责数据的增删改查操作。
-
servlet处理请求和数据的时候,存在的问题是一个servlet只能处理一个请求。
-
针对web层进行了优化,采用了MVC设计模式,将其设计为
controller、view和Model- controller负责请求和数据的接收,接收后将其转发给service进行业务处理
- service根据需要会调用dao对数据进行增删改查
- dao把数据处理完后将结果交给service,service再交给controller
- controller根据需求组装成Model和View,Model和View组合起来生成页面转发给前端浏览器。
- 这样做的好处就是controller可以处理多个请求,并对请求进行分发,执行不同的业务操作。
随着互联网的发展,上面的模式因为是同步调用,性能慢慢的跟不是需求,所以异步调用慢慢的走到了前台,是现在比较流行的一种处理方式。
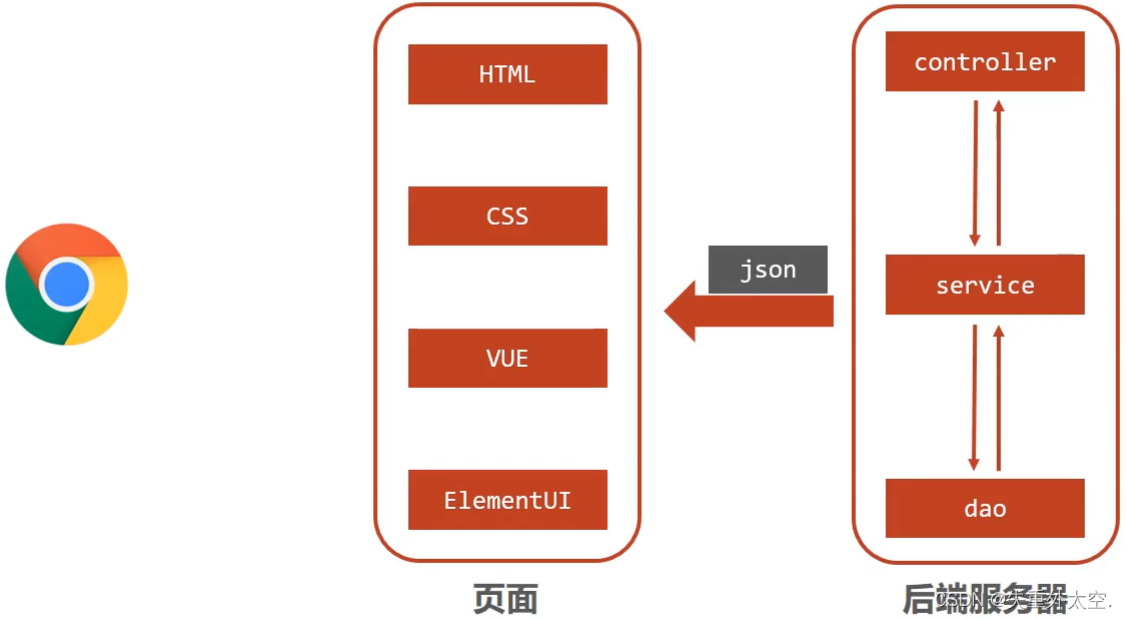
- 因为是异步调用,所以后端不需要返回view视图,将其去除。
- 前端如果通过异步调用的方式进行交互,后台就需要将返回的数据转换成json格式进行返回。
- SpringMVC主要负责的就是:
- controller如何接收请求和数据。
- 如何将请求和数据转发给业务层。
- 如何将响应数据转换成json发回到前端。
介绍了这么多,对SpringMVC进行一个定义
-
SpringMVC是一种基于Java实现MVC模型的轻量级Web框架。
-
优点
- 使用简单、开发便捷(相比于Servlet)。
- 灵活性强。
这里所说的优点,就需要我们在使用的过程中慢慢体会。
1,SpringMVC入门案例
因为SpringMVC是一个Web框架,将来是要替换Servlet,所以先来回顾下以前Servlet是如何进行开发的?
1.创建web工程(Maven结构)
2.设置tomcat服务器,加载web工程(tomcat插件)
3.导入坐标(Servlet)
4.定义处理请求的功能类(UserServlet)
5.设置请求映射(配置映射关系)
SpringMVC的制作过程和上述流程几乎是一致的,具体的实现流程是什么?
1.创建web工程(Maven结构)
2.设置tomcat服务器,加载web工程(tomcat插件)
3.导入坐标(SpringMVC+Servlet)
4.定义处理请求的功能类(UserController)
5.设置请求映射(配置映射关系)
6.将SpringMVC设定加载到Tomcat容器中
1.2 案例制作
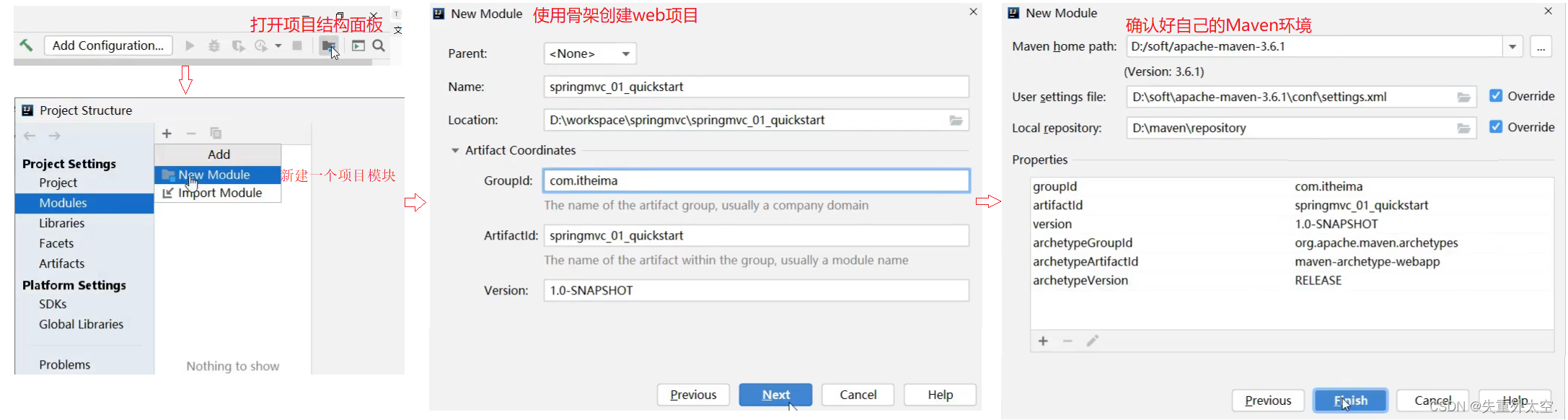
步骤1:创建Maven项目
打开IDEA,创建一个新的web项目。
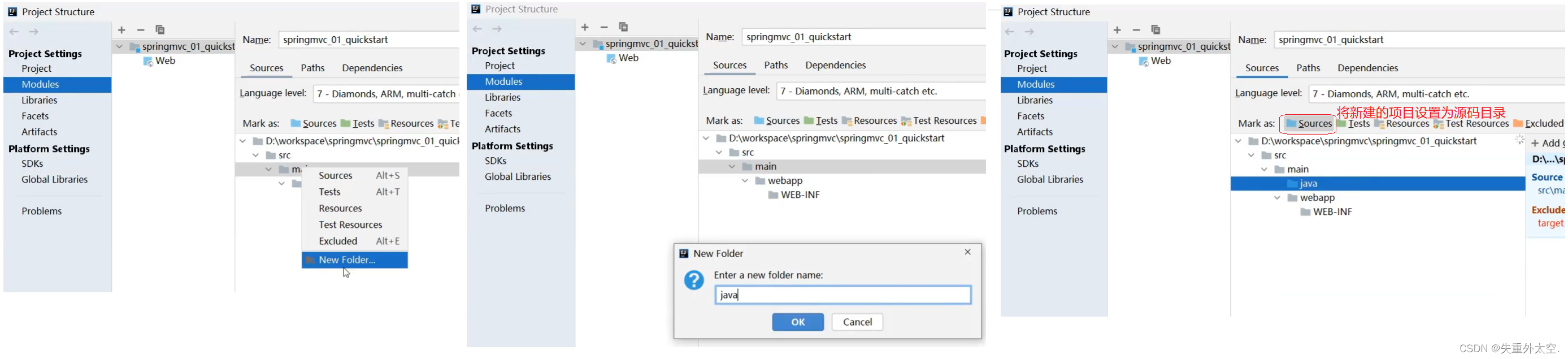
步骤2:补全目录结构
因为使用骨架创建的项目结构不完整,需要手动补全。
步骤3:导入jar包
将pom.xml中多余的内容删除掉,再添加SpringMVC需要的依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itheima</groupId>
<artifactId>springmvc_01_quickstart</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<configuration>
<port>80</port>
<path>/</path>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
说明:servlet的坐标为什么需要添加<scope>provided</scope>?
-
scope是maven中jar包依赖作用范围的描述,
-
如果不设置默认是
compile在在编译、运行、测试时均有效 -
如果运行有效的话就会和tomcat中的servlet-api包发生冲突,导致启动报错
-
provided代表的是该包只在编译和测试的时候用,运行的时候无效直接使用tomcat中的,就避免冲突.
步骤4:创建配置类
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itheima.controller")
public class SpringMvcConfig {
}
步骤5:创建Controller类
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
public void save(){
System.out.println("user save ...");
}
}
步骤6:使用配置类替换web.xml
将web.xml删除,换成ServletContainersInitConfig
public class ServletContainersInitConfig extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
//加载springmvc配置类
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
//初始化WebApplicationContext对象
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
//加载指定配置类
ctx.register(SpringMvcConfig.class);
return ctx;
}
//设置由springmvc控制器处理的请求映射路径
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
//加载spring配置类
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
return null;
}
}
步骤7:配置Tomcat环境
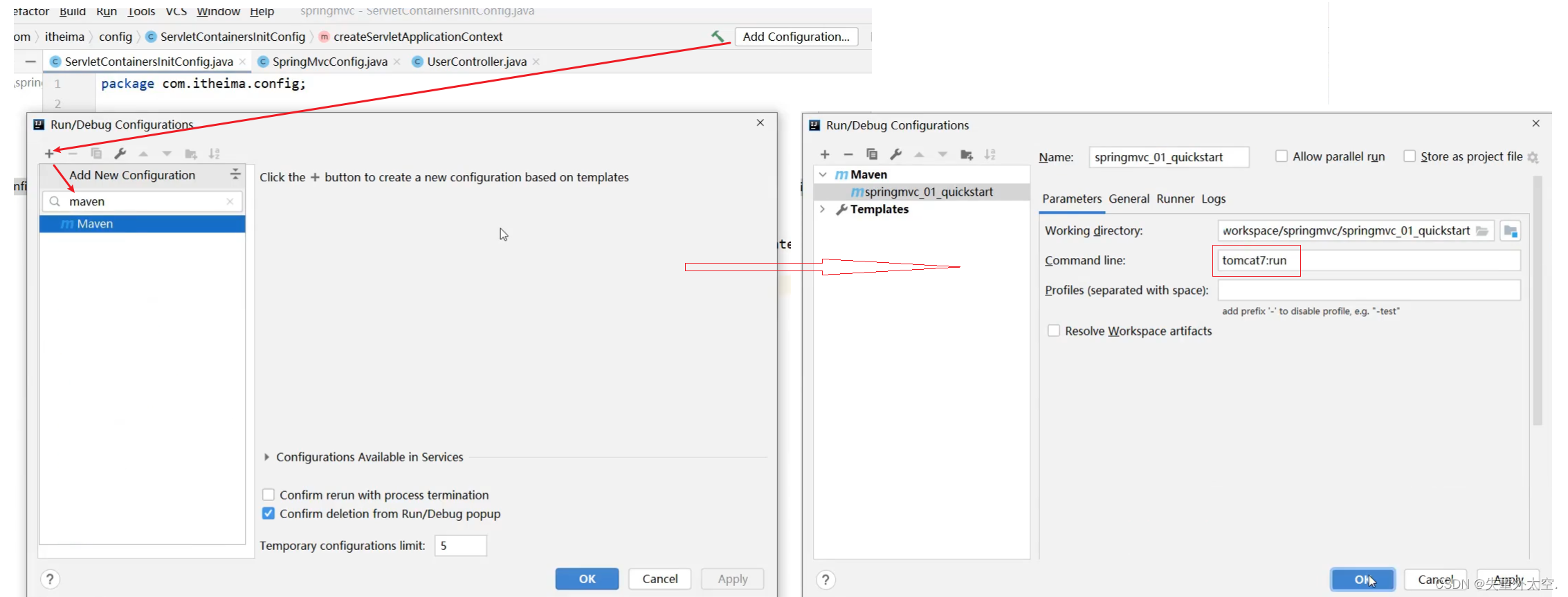
步骤8:启动运行项目
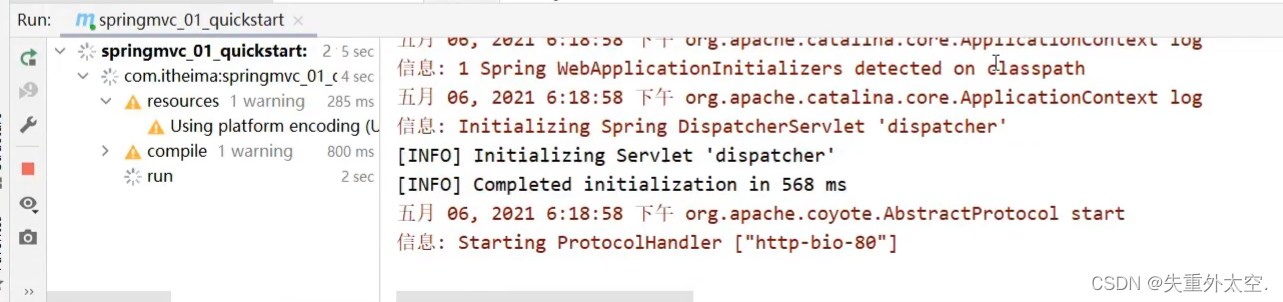
步骤9:浏览器访问
浏览器输入http://localhost/save进行访问,会报如下错误:
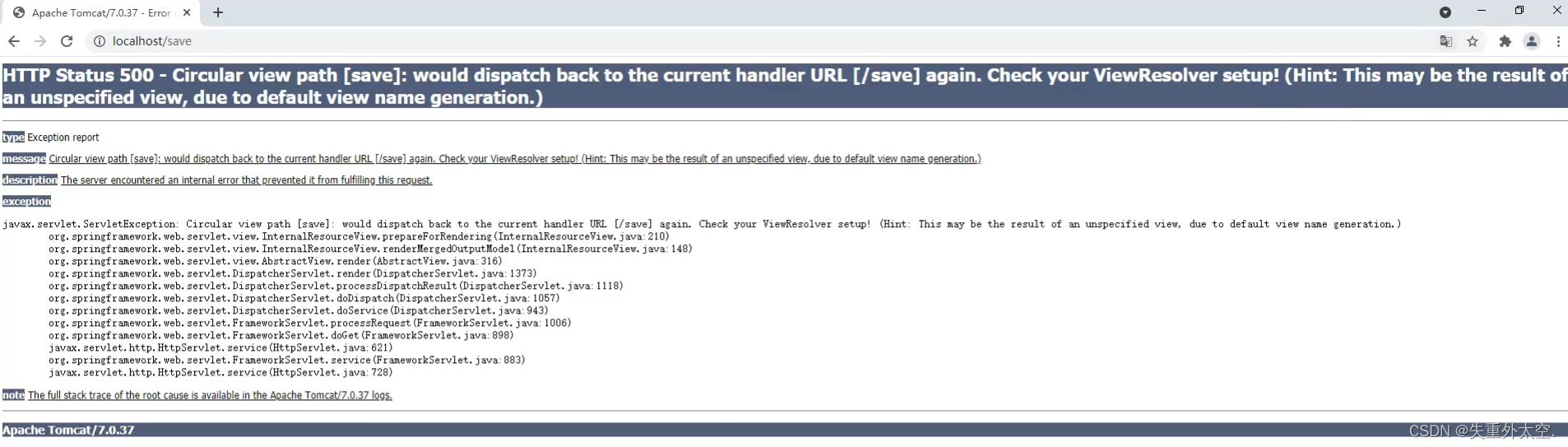
页面报错的原因是后台没有指定返回的页面,目前只需要关注控制台看user save ...有没有被执行即可。
步骤10:修改Controller返回值解决上述问题
前面我们说过现在主要的是前端发送异步请求,后台响应json数据,所以接下来我们把Controller类的save方法进行修改
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
public String save(){
System.out.println("user save ...");
return "{'info':'springmvc'}";
}
}
再次重启tomcat服务器,然后重新通过浏览器测试访问,会发现还是会报错,这次的错是404
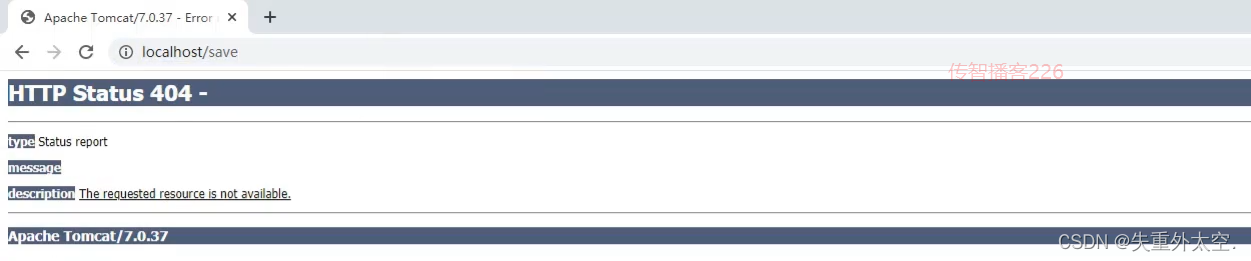
出错的原因是,如果方法直接返回字符串,springmvc会把字符串当成页面的名称在项目中进行查找返回,因为不存在对应返回值名称的页面,所以会报404错误,找不到资源。
而我们其实是想要直接返回的是json数据,具体如何修改呢?
步骤11:设置返回数据为json
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save(){
System.out.println("user save ...");
return "{'info':'springmvc'}";
}
}
再次重启tomcat服务器,然后重新通过浏览器测试访问,就能看到返回的结果数据
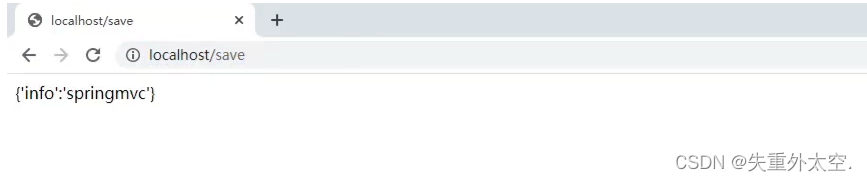
至此SpringMVC的入门案例就已经完成。
注意事项
- SpringMVC是基于Spring的,在pom.xml只导入了
spring-webmvcjar包的原因是它会自动依赖spring相关坐标 - AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer类是SpringMVC提供的快速初始化Web3.0容器的抽象类
- AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer提供了三个接口方法供用户实现。
- createServletApplicationContext方法,创建Servlet容器时,加载SpringMVC对应的bean并放入WebApplicationContext对象范围中,而WebApplicationContext的作用范围为ServletContext范围,即整个web容器范围。
- getServletMappings方法,设定SpringMVC对应的请求映射路径,即SpringMVC拦截哪些请求。
- createRootApplicationContext方法,如果创建Servlet容器时需要加载非SpringMVC对应的bean,使用当前方法进行,使用方式和createServletApplicationContext相同。
- createServletApplicationContext用来加载SpringMVC环境。
- createRootApplicationContext用来加载Spring环境。
知识点1:@Controller
| 名称 | @Controller |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 类注解 |
| 位置 | SpringMVC控制器类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设定SpringMVC的核心控制器bean |
知识点2:@RequestMapping
| 名称 | @RequestMapping |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 类注解或方法注解 |
| 位置 | SpringMVC控制器类或方法定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置当前控制器方法请求访问路径 |
| 相关属性 | value(默认),请求访问路径 |
知识点3:@ResponseBody
| 名称 | @ResponseBody |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 类注解或方法注解 |
| 位置 | SpringMVC控制器类或方法定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置当前控制器方法响应内容为当前返回值,无需解析 |
1.3 入门案例总结
- 一次性工作
- 创建工程,设置服务器,加载工程
- 导入坐标
- 创建web容器启动类,加载SpringMVC配置,并设置SpringMVC请求拦截路径
- SpringMVC核心配置类(设置配置类,扫描controller包,加载Controller控制器bean)
- 多次工作
- 定义处理请求的控制器类
- 定义处理请求的控制器方法,并配置映射路径(@RequestMapping)与返回json数据(@ResponseBody)
2.4 工作流程解析
为了更好的使用SpringMVC,我们将SpringMVC的使用过程总共分两个阶段来分析,分别是启动服务器初始化过程和单次请求过程
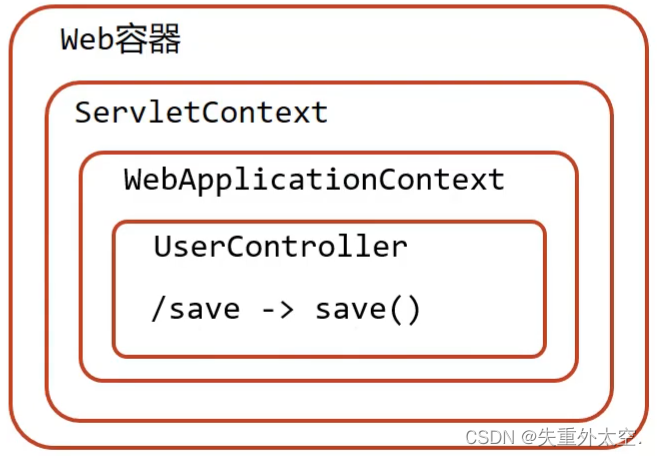
2.4.1 启动服务器初始化过程
-
服务器启动,执行ServletContainersInitConfig类,初始化web容器。
- 功能类似于以前的web.xml。
-
执行createServletApplicationContext方法,创建了WebApplicationContext对象。
- 该方法加载SpringMVC的配置类SpringMvcConfig来初始化SpringMVC的容器。
-
加载SpringMvcConfig配置类

-
执行@ComponentScan加载对应的bean。
- 扫描指定包及其子包下所有类上的注解,如Controller类上的@Controller注解。
-
加载UserController,每个@RequestMapping的名称对应一个具体的方法。

- 此时就建立了
/save和 save方法的对应关系。
- 此时就建立了
-
执行getServletMappings方法,设定SpringMVC拦截请求的路径规则。

/代表所拦截请求的路径规则,只有被拦截后才能交给SpringMVC来处理请求。
1.4.2 单次请求过程
- 发送请求
http://localhost/save - web容器发现该请求满足SpringMVC拦截规则,将请求交给SpringMVC处理.
- 解析请求路径/save
- 由/save匹配执行对应的方法save()
- 上面的第五步已经将请求路径和方法建立了对应关系,通过/save就能找到对应的save方法
- 执行save()
- 检测到有@ResponseBody直接将save()方法的返回值作为响应体返回给请求方。
1.5 bean加载控制
1.5.1 问题分析
入门案例的内容已经做完了,在入门案例中我们创建过一个SpringMvcConfig的配置类,Spring也创建过一个配置类SpringConfig。这两个配置类都需要加载资源,那么它们分别都需要加载哪些内容?
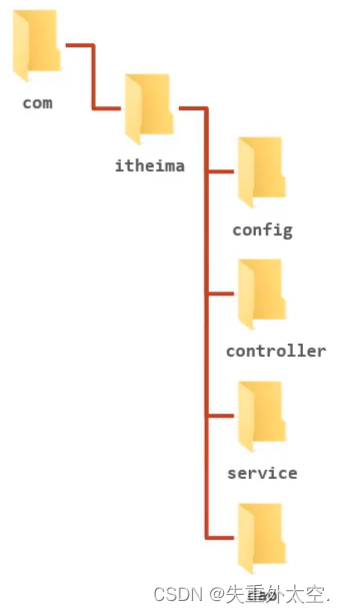
我们先来看下项目目录结构:
-
config目录存入的是配置类,写过的配置类有:
- ServletContainersInitConfig
- SpringConfig
- SpringMvcConfig
- JdbcConfig
- MybatisConfig
-
controller目录存放的是SpringMVC的controller类
-
service目录存放的是service接口和实现类
-
dao目录存放的是dao/Mapper接口
controller、service和dao这些类都需要被容器管理成bean对象,那么到底是该让SpringMVC加载还是让Spring加载呢?
- SpringMVC加载其相关bean(表现层bean),也就是controller包下的类.
- Spring控制的bean
- 业务bean(Service)
- 功能bean(DataSource,SqlSessionFactoryBean,MapperScannerConfigurer等)
分析清楚谁该管哪些bean以后,接下来要解决的问题是如何让Spring和SpringMVC分开加载各自的内容。
在SpringMVC的配置类SpringMvcConfig中使用注解@ComponentScan,我们只需要将其扫描范围设置到controller即可,如

在Spring的配置类SpringConfig中使用注解@ComponentScan,当时扫描的范围中其实是已经包含了controller,如:
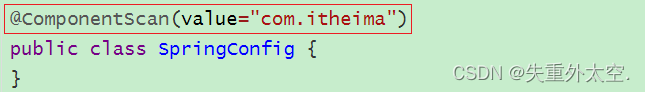
从包结构来看的话,Spring已经多把SpringMVC的controller类也给扫描到,所以针对这个问题该如何解决。(因为功能不同,如何避免Spring错误加载到SpringMVC的bean?)
2.5.2 思路分析
针对上面的问题,解决方案也比较简单,就是:
- 加载Spring控制的bean的时候排除掉SpringMVC控制的bean
具体该如何排除:
- 方式一:Spring加载的bean设定扫描范围为精准范围,例如service包、dao包等
- 方式二:Spring加载的bean设定扫描范围为com.itheima,排除掉controller包中的bean
- 方式三:不区分Spring与SpringMVC的环境,加载到同一个环境中[了解即可]
2.5.4 环境准备
-
创建一个Web的Maven项目
-
pom.xml添加Spring依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.itheima</groupId> <artifactId>springmvc_02_bean_load</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.16</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>5.1.47</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> <version>1.3.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId> <artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.1</version> <configuration> <port>80</port> <path>/</path> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project> -
创建对应的配置类
public class ServletContainersInitConfig extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer { protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() { AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); ctx.register(SpringMvcConfig.class); return ctx; } protected String[] getServletMappings() { return new String[]{"/"}; } protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() { return null; } } @Configuration @ComponentScan("com.itheima.controller") public class SpringMvcConfig { } @Configuration @ComponentScan("com.itheima") public class SpringConfig { } -
编写Controller,Service,Dao,Domain类
@Controller public class UserController { @RequestMapping("/save") @ResponseBody public String save(){ System.out.println("user save ..."); return "{'info':'springmvc'}"; } } public interface UserService { public void save(User user); } @Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { public void save(User user) { System.out.println("user service ..."); } } public interface UserDao { @Insert("insert into tbl_user(name,age)values(#{name},#{age})") public void save(User user); } public class User { private Integer id; private String name; private Integer age; //setter..getter..toString略 }
2.5.5 设置bean加载控制
方式一:修改Spring配置类,设定扫描范围为精准范围。
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.itheima.service","comitheima.dao"})
public class SpringConfig {
}
说明:
上述只是通过例子说明可以精确指定让Spring扫描对应的包结构,真正在做开发的时候,因为Dao最终是交给MapperScannerConfigurer对象来进行扫描处理的,我们只需要将其扫描到service包即可。
方式二:修改Spring配置类,设定扫描范围为com.itheima,排除掉controller包中的bean
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(value="com.itheima",
excludeFilters=@ComponentScan.Filter(
type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,
classes = Controller.class
)
)
public class SpringConfig {
}
-
excludeFilters属性:设置扫描加载bean时,排除的过滤规则。
-
type属性:设置排除规则,当前使用按照bean定义时的注解类型进行排除。
- ANNOTATION:按照注解排除
- ASSIGNABLE_TYPE:按照指定的类型过滤
- ASPECTJ:按照Aspectj表达式排除,基本上不会用
- REGEX:按照正则表达式排除
- CUSTOM:按照自定义规则排除
大家只需要知道第一种ANNOTATION即可
-
classes属性:设置排除的具体注解类,当前设置排除@Controller定义的bean
如何测试controller类已经被排除掉了?
public class App{
public static void main (String[] args){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
System.out.println(ctx.getBean(UserController.class));
}
}
如果被排除了,该方法执行就会报bean未被定义的错误
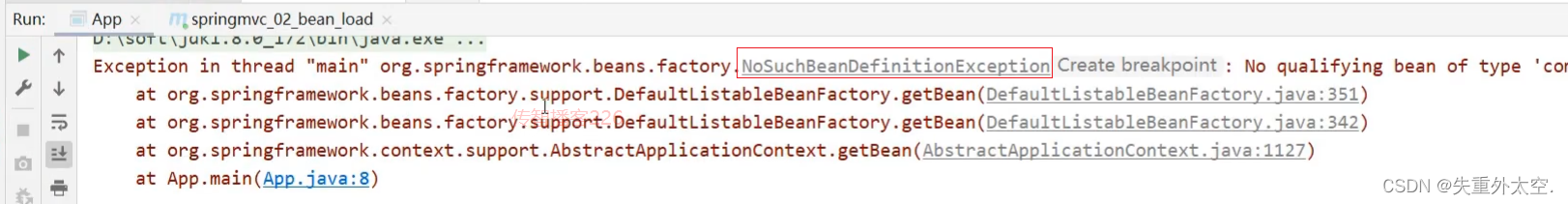
注意:测试的时候,需要把SpringMvcConfig配置类上的@ComponentScan注解注释掉,否则不会报错
出现问题的原因是,
- Spring配置类扫描的包是
com.itheima - SpringMVC的配置类,
SpringMvcConfig上有一个@Configuration注解,也会被Spring扫描到。 - SpringMvcConfig上又有一个@ComponentScan,把controller类又给扫描进来了。
- 所以如果不把@ComponentScan注释掉,Spring配置类将Controller排除,但是因为扫描到SpringMVC的配置类,又将其加载回来,演示的效果就出不来。
- 解决方案,也简单,把SpringMVC的配置类移出Spring配置类的扫描范围即可。
最后一个问题,有了Spring的配置类,要想在tomcat服务器启动将其加载,我们需要修改ServletContainersInitConfig
public class ServletContainersInitConfig extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ctx.register(SpringMvcConfig.class);
return ctx;
}
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ctx.register(SpringConfig.class);
return ctx;
}
}
对于上述的配置方式,Spring还提供了一种更简单的配置方式,可以不用再去创建AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext对象,不用手动register对应的配置类,如何实现?
public class ServletContainersInitConfig extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringConfig.class};
}
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringMvcConfig.class};
}
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
}
知识点1:@ComponentScan
| 名称 | @ComponentScan |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 类注解 |
| 位置 | 类定义上方 |
| 作用 | 设置spring配置类扫描路径,用于加载使用注解格式定义的bean |
| 相关属性 | excludeFilters:排除扫描路径中加载的bean,需要指定类别(type)和具体项(classes) includeFilters:加载指定的bean,需要指定类别(type)和具体项(classes) |
后记
👉👉💕💕美好的一天,到此结束,下次继续努力!欲知后续,请看下回分解,写作不易,感谢大家的支持!! 🌹🌹🌹
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- K8S学习指南(34)-k8s权限管理模型ABAC
- Spring Cloud Gateway请求路径修改指南:详解ServerWebExchange的完美解决方案及代码示例
- MyBatis第四课动态SQL
- Mac M系列安装配置VSCode
- golang生成12个月
- 回归预测 | Python实现OOA-LightGBM基于人工鱼鹰优化算法优化LightGBM的多输入单输出数据回归预测模型 (多指标,多图)
- 弧形导轨的类型及应用
- 【JaveWeb教程】(9)Web前端基础:Vue组件库Element之Dialog对话框组件和Form表单组件 详细示例介绍
- 聊聊软件行业那些事
- C++之模板