【数据结构】LRU缓存的简单模拟实现(leetcode力扣146LRU缓存)
发布时间:2023年12月25日
一、定义
LRU是Least Recently Used的缩写,意思是最近最少使用,它是一种Cache替换算法。
Cache的容量有限,因此当Cache的容量用完后,而又有新的内容需要添加进来时, 就需要挑选并舍弃原有的部分内容,从而腾出空间来放新内容。LRU Cache 的替换原则就是将最近最少使用的内容替换掉。
二、LRU模拟实现
下面我们就借力扣的这道题来简单实现一个
题目中要求我们以O(1)的时间复杂度来完成,查找的话我们首先肯定会想到哈希表,但又涉及一个问题,我们查找完之后还需要更新一下刚刚查找数据的位置,将这个数据置为是新的数据,我们如何解决查找完改变数据的标识也做到O(1)呢?
要保持高效实现O(1)的put和get,那么使用双向链表和
哈希表的搭配是最高效和经典的。使用双向链表是因为双向链表可以实现任意位置O(1)的插入和删除,使用哈希表是因为哈希表的增删查改也是O(1)。
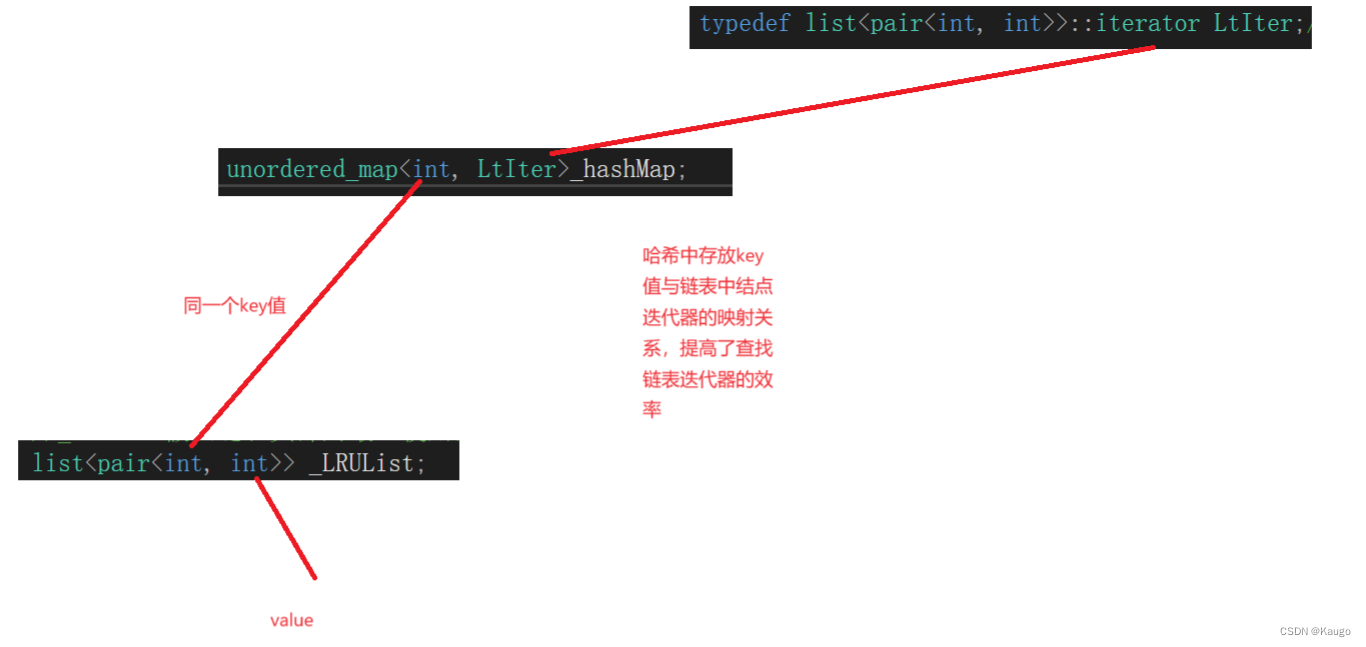
需要注意:这里最巧的设计就是将unordered_map的value type放成list<pair<int, int>>::iterator,因为这样,当get一个已有的值以后,就可以直接找到key在list中对应的iterator,然后将这个值移动到链表的头部,保持LRU。
二、代码实现
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class LRUCache {
public:
LRUCache(int capacity)
:_capacity(capacity)
{}
int get(int key) {
auto ret = _hashMap.find(key);
//在hash中找到了key存的地方
if (ret != _hashMap.end()) {
LtIter it = ret->second;
//将it移动到_LRUList的头部
_LRUList.splice(_LRUList.begin(), _LRUList, it);
return it->second;
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
void put(int key, int value) {
auto ret = _hashMap.find(key);
//原来没有key的数据则添加
if (ret == _hashMap.end()) {
//LRU满了,删除最近最少使用的就是链表尾部
if (_capacity == _hashMap.size()) {
pair<int, int>back = _LRUList.back();
_hashMap.erase(back.first);//删哈希里面
//链表里面k存的和哈希的是同一个key
_LRUList.pop_back();//删链表尾部
}
//放入新的数据到链表头部
_LRUList.push_front(make_pair(key, value));
//哈希表中添加
_hashMap[key] = _LRUList.begin();
}
//原来有key的数据则更新
else {
LtIter it = ret->second;
it->second = value;
//将这个位置移到链表头部
_LRUList.splice(_LRUList.begin(), _LRUList, it);
}
}
private:
//链表存kv结构
//k为key值,v为我们要更新的数据
typedef list<pair<int, int>>::iterator LtIter;//重命名链表迭代器
int _capacity; // 容量大小,超过容量则换出,保持LRU
//_LRUList假设链表头部为最近使用的,尾部为最近最少使用
list<pair<int, int>> _LRUList;
//hash中存放的是key值与对应链表迭代器的的映射关系
unordered_map<int, LtIter>_hashMap;
};
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_74774759/article/details/135208002
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- SQL注入绕过正则及无列名注入
- 恐龙岛如何正确的选择服务器
- LINUX 网络
- (高数)数量积与向量积
- 网络安全B模块(笔记详解)- 隐藏信息探索
- 万界星空科技低代码平台:制造业数字化转型的捷径
- 浙大恩特客户资源管理系统 CrmBasicAction.entcrm任意文件上传
- ClickHouse中的CPU调度
- 基于Spring Boot、Mybatis、Redis和Layui的企业电子招投标系统源码实现与立项流程
- [Redis] Redisson实现分布式锁