【Seata源码学习 】 扫描@GlobalTransaction注解 篇一
1. SeataAutoConfiguration 自动配置类的加载
基于SpringBoot的starter机制,在应用上下文启动时,会加载SeataAutoConfiguration自动配置类
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=io.seata.spring.boot.autoconfigure.SeataAutoConfiguration
此配置类将会往应用上下文中注册四个组件
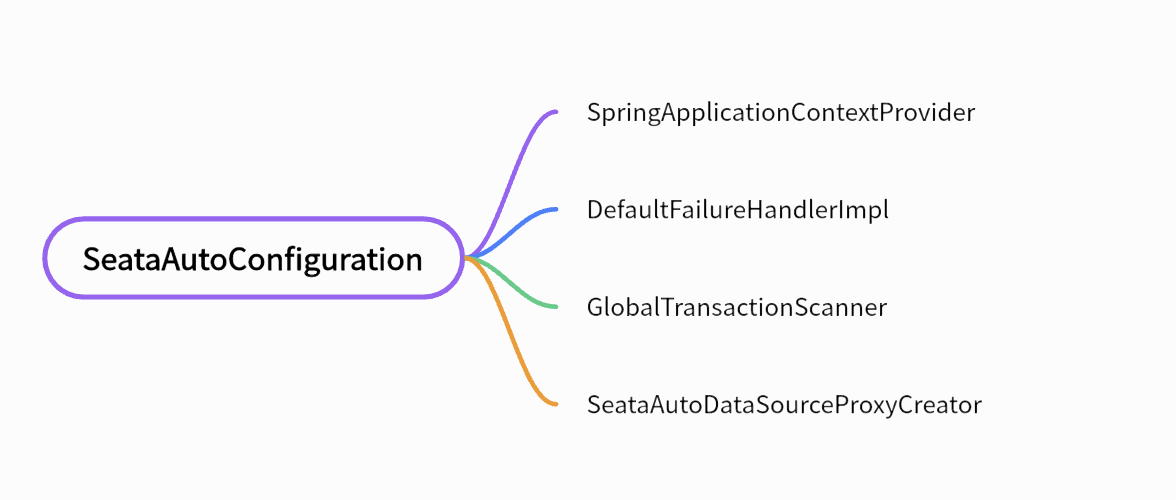
从名字就知道,此组件负责扫描@GlobalTransaction
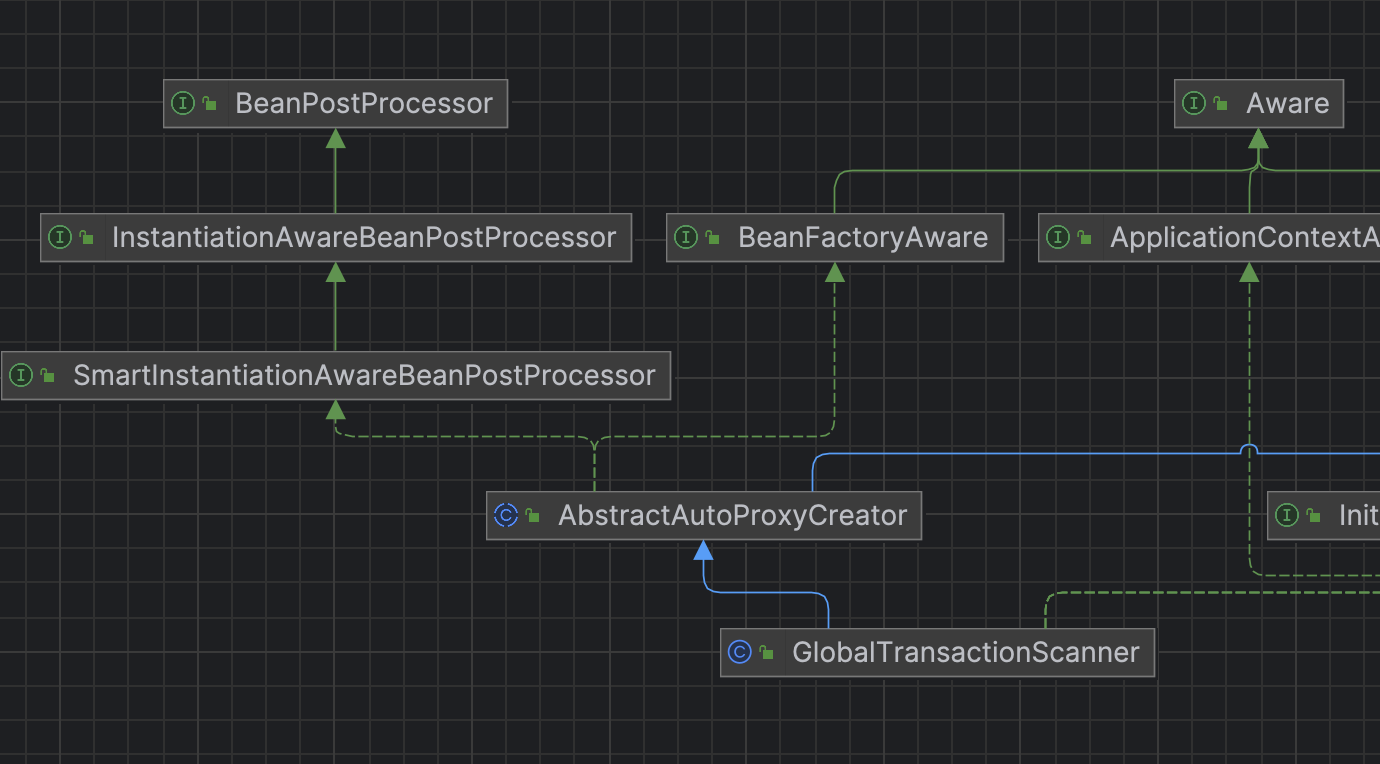
此类的继承关系如下图所示
2. @GlobalTransaction注解扫描
父类 AbstractAutoProxyCreator 实现了 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 接口,重写了 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
io.seata.spring.annotation.GlobalTransactionScanner#wrapIfNecessary
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// do checkers
if (!doCheckers(bean, beanName)) {
return bean;
}
try {
synchronized (PROXYED_SET) {
if (PROXYED_SET.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
interceptor = null;
//check TCC proxy
if (TCCBeanParserUtils.isTccAutoProxy(bean, beanName, applicationContext)) {
// init tcc fence clean task if enable useTccFence
TCCBeanParserUtils.initTccFenceCleanTask(TCCBeanParserUtils.getRemotingDesc(beanName), applicationContext);
//TCC interceptor, proxy bean of sofa:reference/dubbo:reference, and LocalTCC
interceptor = new TccActionInterceptor(TCCBeanParserUtils.getRemotingDesc(beanName));
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)interceptor);
} else {
//很实用的两个工具类
//查找类的原始类 而非代理类
Class<?> serviceInterface = SpringProxyUtils.findTargetClass(bean);
//查找类所有实现的接口
Class<?>[] interfacesIfJdk = SpringProxyUtils.findInterfaces(bean);
// 类上面是否有GlobalTransactional 注解 方法上面是否有标 GlobalTransactional GlobalLock注解
if (!existsAnnotation(new Class[]{serviceInterface})
// 接口上面是否有GlobalTransactional 注解 方法上面是否有标 GlobalTransactional GlobalLock注解
&& !existsAnnotation(interfacesIfJdk)) {
return bean;
}
//如果有 成员变量 MethodInterceptor interceptor 赋值
if (globalTransactionalInterceptor == null) {
globalTransactionalInterceptor = new GlobalTransactionalInterceptor(failureHandlerHook);
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(
ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)globalTransactionalInterceptor);
}
interceptor = globalTransactionalInterceptor;
}
LOGGER.info("Bean[{}] with name [{}] would use interceptor [{}]", bean.getClass().getName(), beanName, interceptor.getClass().getName());
if (!AopUtils.isAopProxy(bean)) {
//当前类没有被AOP代理过
bean = super.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
} else {
//当前类被AOP代理过
//AdvisedSupport对象是Spring框架中用于支持AOP的核心类之一,它封装了AOP代理的配置信息和运行时状态。
// 通过获取AdvisedSupport对象,可以进一步了解和操作代理对象的AOP配置
AdvisedSupport advised = SpringProxyUtils.getAdvisedSupport(bean);
// AdvisedSupport : Advisor 一对多
//Spring AOP 中的 Advisor 是一种拦截器,
// 它可以拦截特定的方法调用,并在方法调用前、后或异常时执行一些特定的操作
//getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean 方法将返回我们上一步创建的GlobalTransactionalInterceptor
//buildAdvisors 方法 将 MethodInterceptor 构建成一个 Advisor 用于后续创建代理类
Advisor[] advisor = buildAdvisors(beanName, getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(null, null, null));
int pos;
for (Advisor avr : advisor) {
// Find the position based on the advisor's order, and add to advisors by pos
//调整advisor 的位置
pos = findAddSeataAdvisorPosition(advised, avr);
advised.addAdvisor(pos, avr);
}
}
//记录已经代理过的beanName
PROXYED_SET.add(beanName);
//返回当前bean
return bean;
}
} catch (Exception exx) {
throw new RuntimeException(exx);
}
}
创建代理类情况一 :当前bean已经被AOP代理过
通常@GlobalTransation注解标注在业务层,而业务层的bean大多走到这已经被AOP代理过。如果你项目中使用的是MybatisPlus,那么通常会被org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor创建代理类
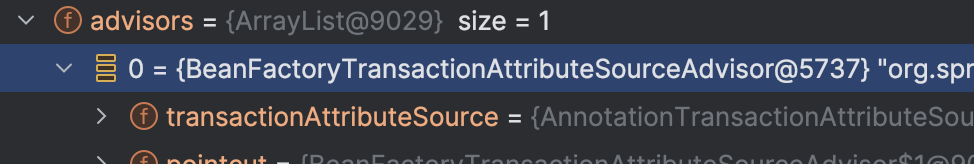
AdvisedSupport 添加一个Advisor( GlobalTransactionalInterceptor )后,将之前就被代理过的bean返回,你可能会好奇,添加一个 Advisor 就不管了 ? 最终谁来调用呢 ?
class org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
继承了 AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 继承了 AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 继承了 AbstractAutoProxyCreator 实现了 SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,
将在每个bean实例化后执行 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法,
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#postProcessAfterInitialization
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#wrapIfNecessary
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator#findEligibleAdvisors
最终将找到 org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor:
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//查找所有的Advisor
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
//判断当前bean是否满足Advisor的拦截要求
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
Advisor 你可以理解为绑定了ponitcut的Advice 容器 , BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor绑定的为 TransactionAttributeSourcePointcut
方法的匹配规则
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null);
}
类的匹配规则
org.springframework.transaction.annotation.SpringTransactionAnnotationParser#isCandidateClass
@Override
public boolean isCandidateClass(Class<?> targetClass) {
//当前类上是否有 Transactional 注解
return AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetClass, Transactional.class);
}
而获取方法是的代码如下
org.springframework.aop.support.AopUtils#canApply(org.springframework.aop.Pointcut, java.lang.Class<?>, boolean)
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
//getAllDeclaredMethods 获取当前类包括父类的所有方法
Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz);
for (Method method : methods) {
if (introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null ?
introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions) :
methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) {
return true;
}
}
}
我们使用的MybatisPlus通常业务层的类会继承ServiceImpl,而ServiceImpl类中有不少方法就是标注了@Transactional注解,因此 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor 对当前的业务层bean来说,是满足匹配规则的

回到
org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#wrapIfNecessary
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
//拿到 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
//创建代理类
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
//创建 ProxyFactory 对象,
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
//创建 Advisor 链
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
//设置代理目标类
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
//创建目标代理类
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
通常情况下会使用CGLB进行创建代理类
org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy#getProxy(java.lang.ClassLoader)
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
//设置默认回调函数
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
//默认回调函数匹配规则
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
//增强目标代理类
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}
private Callback[] getCallbacks(Class<?> rootClass) throws Exception {
// Parameters used for optimization choices...
boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy();
boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen();
boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();
// Choose an "aop" interceptor (used for AOP calls).
//用于aop的回调函数
Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
// Choose a "straight to target" interceptor. (used for calls that are
// unadvised but can return this). May be required to expose the proxy.
Callback targetInterceptor;
if (exposeProxy) {
targetInterceptor = (isStatic ?
new StaticUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :
new DynamicUnadvisedExposedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()));
}
else {
targetInterceptor = (isStatic ?
new StaticUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) :
new DynamicUnadvisedInterceptor(this.advised.getTargetSource()));
}
// Choose a "direct to target" dispatcher (used for
// unadvised calls to static targets that cannot return this).
Callback targetDispatcher = (isStatic ?
new StaticDispatcher(this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget()) : new SerializableNoOp());
//6个默认的回调函数
Callback[] mainCallbacks = new Callback[] {
aopInterceptor, // for normal advice
targetInterceptor, // invoke target without considering advice, if optimized
new SerializableNoOp(), // no override for methods mapped to this
targetDispatcher, this.advisedDispatcher,
new EqualsInterceptor(this.advised),
new HashCodeInterceptor(this.advised)
};
Callback[] callbacks;
// If the target is a static one and the advice chain is frozen,
// then we can make some optimizations by sending the AOP calls
// direct to the target using the fixed chain for that method.
if (isStatic && isFrozen) {
Method[] methods = rootClass.getMethods();
Callback[] fixedCallbacks = new Callback[methods.length];
this.fixedInterceptorMap = new HashMap<>(methods.length);
// TODO: small memory optimization here (can skip creation for methods with no advice)
for (int x = 0; x < methods.length; x++) {
Method method = methods[x];
//将 advisor集合转化为 MethodInterceptor 集合
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, rootClass);
fixedCallbacks[x] = new FixedChainStaticTargetInterceptor(
chain, this.advised.getTargetSource().getTarget(), this.advised.getTargetClass());
this.fixedInterceptorMap.put(method, x);
}
// Now copy both the callbacks from mainCallbacks
// and fixedCallbacks into the callbacks array.
callbacks = new Callback[mainCallbacks.length + fixedCallbacks.length];
System.arraycopy(mainCallbacks, 0, callbacks, 0, mainCallbacks.length);
System.arraycopy(fixedCallbacks, 0, callbacks, mainCallbacks.length, fixedCallbacks.length);
this.fixedInterceptorOffset = mainCallbacks.length;
}
else {
callbacks = mainCallbacks;
}
return callbacks;
}
看一下callbackFilter 设置的 callback回调规则
public int accept(Method method) {
if (AopUtils.isFinalizeMethod(method)) {
logger.trace("Found finalize() method - using NO_OVERRIDE");
return NO_OVERRIDE; //如果是finalize方法,执行targetInterceptor回调函数,相当于什么都没做
}
//方法是否在Advised接口上声明。如果是,则返回DISPATCH_ADVISED,表示需要回调 advisedDispatcher 函数
if (!this.advised.isOpaque() && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() &&
method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Method is declared on Advised interface: " + method);
}
return DISPATCH_ADVISED;
}
// 检查方法是否为equals()方法或hashCode()方法,如果是,则分别返回INVOKE_EQUALS和INVOKE_HASHCODE,表示需要调用EqualsInterceptor 回调函数或 HashCodeInterceptor 回调函数
if (AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found 'equals' method: " + method);
}
return INVOKE_EQUALS;
}
// We must always calculate hashCode based on the proxy.
if (AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found 'hashCode' method: " + method);
}
return INVOKE_HASHCODE;
}
//获取目标类
Class<?> targetClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
// Proxy is not yet available, but that shouldn't matter.
//获取方法拦截器链
List<?> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
boolean haveAdvice = !chain.isEmpty();
boolean exposeProxy = this.advised.isExposeProxy();
boolean isStatic = this.advised.getTargetSource().isStatic();
boolean isFrozen = this.advised.isFrozen();
//chain 不为空 且未冻结
if (haveAdvice || !isFrozen) {
// If exposing the proxy, then AOP_PROXY must be used.
if (exposeProxy) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Must expose proxy on advised method: " + method);
}
return AOP_PROXY; // 使用aopInterceptor 回调函数
}
// Check to see if we have fixed interceptor to serve this method.
// Else use the AOP_PROXY.
//方法是静态的、代理已被冻结,并且存在固定的拦截器来处理该方法,则返回固定拦截器的索引加上固定拦截器偏移量。这段代码用于判断是否存在固定的拦截器来处理该方法,并返回相应的处理方式。如果存在固定的拦截器,则返回固定拦截器的索引加上偏移量;否则,返回AOP_PROXY,表示需要使用AOP代理进行处理。
if (isStatic && isFrozen && this.fixedInterceptorMap.containsKey(method)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Method has advice and optimizations are enabled: " + method);
}
// We know that we are optimizing so we can use the FixedStaticChainInterceptors.
int index = this.fixedInterceptorMap.get(method);
return (index + this.fixedInterceptorOffset);
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Unable to apply any optimizations to advised method: " + method);
}
return AOP_PROXY;
}
}
else {
// See if the return type of the method is outside the class hierarchy of the target type.
// If so we know it never needs to have return type massage and can use a dispatcher.
// If the proxy is being exposed, then must use the interceptor the correct one is already
// configured. If the target is not static, then we cannot use a dispatcher because the
// target needs to be explicitly released after the invocation.
if (exposeProxy || !isStatic) {
return INVOKE_TARGET;
}
Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType();
if (targetClass != null && returnType.isAssignableFrom(targetClass)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Method return type is assignable from target type and " +
"may therefore return 'this' - using INVOKE_TARGET: " + method);
}
return INVOKE_TARGET;
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Method return type ensures 'this' cannot be returned - " +
"using DISPATCH_TARGET: " + method);
}
return DISPATCH_TARGET;
}
}
}
在回到之前那个问题,AdvisedSupport 添加一个Advisor( GlobalTransactionalInterceptor )后,将之前就被代理过的bean返回,当前bean的业务方法在执行时,就会由callbackFilter匹配上 aopInterceptor 回调函数并执行
Callback aopInterceptor = new DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(this.advised);
DynamicAdvisedInterceptor 是 CglibAopProxy 的静态内部类 ,实现了 MethodInterceptor 接口
private static class DynamicAdvisedInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
private final AdvisedSupport advised;
public DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(AdvisedSupport advised) {
this.advised = advised;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Object target = null;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
// 获取方法拦截器链
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
//拦截器链路调用
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
//返回值处理
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) {
return (this == other ||
(other instanceof DynamicAdvisedInterceptor &&
this.advised.equals(((DynamicAdvisedInterceptor) other).advised)));
}
/**
* CGLIB uses this to drive proxy creation.
*/
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.advised.hashCode();
}
}
跟进 org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy.CglibMethodInvocation#proceed
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
try {
return super.proceed();
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (ReflectionUtils.declaresException(getMethod(), ex.getClass())) {
throw ex;
}
else {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(ex);
}
}
}
父类 org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation#proceed
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
// 如果当前拦截器链已经是最后一个了 调用目标方法
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
// currentInterceptorIndex 从 -1 开始,此时获取下表为0的方法拦截器
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
//拦截器在此处调用 注意此处把 this 给传递过去了,每个拦截器在执行完毕后又会调用 this.proceed 进行递归调用
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
创建代理类情况二 :当前bean已经未被AOP代理
回调 io.seata.spring.annotation.GlobalTransactionScanner#wrapIfNecessary
if (!AopUtils.isAopProxy(bean)) {
//如果当前类未被代理,则调用父类的wrapIfNecessary 方法
bean = super.wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
} else {
AdvisedSupport advised = SpringProxyUtils.getAdvisedSupport(bean);
Advisor[] advisor = buildAdvisors(beanName, getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(null, null, null));
for (Advisor avr : advisor) {
advised.addAdvisor(0, avr);
}
}
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
//调用子类 重写的 io.seata.spring.annotation.GlobalTransactionScanner#getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean 方法
// 返回 GlobalTransactionalInterceptor
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
调用org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.AbstractAutoProxyCreator#createProxy,
创建 ProxyFactory 对象,设置目标代理类,添加advisors,最终创建代理类,对目标方法进行拦截来增强目标方法
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
//构建Advisor[] 用于方法拦截
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
//设置被代理类
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
//创建代理对象 最终底层通过 JDK动态代理或CGILIB代理创建代理对象
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
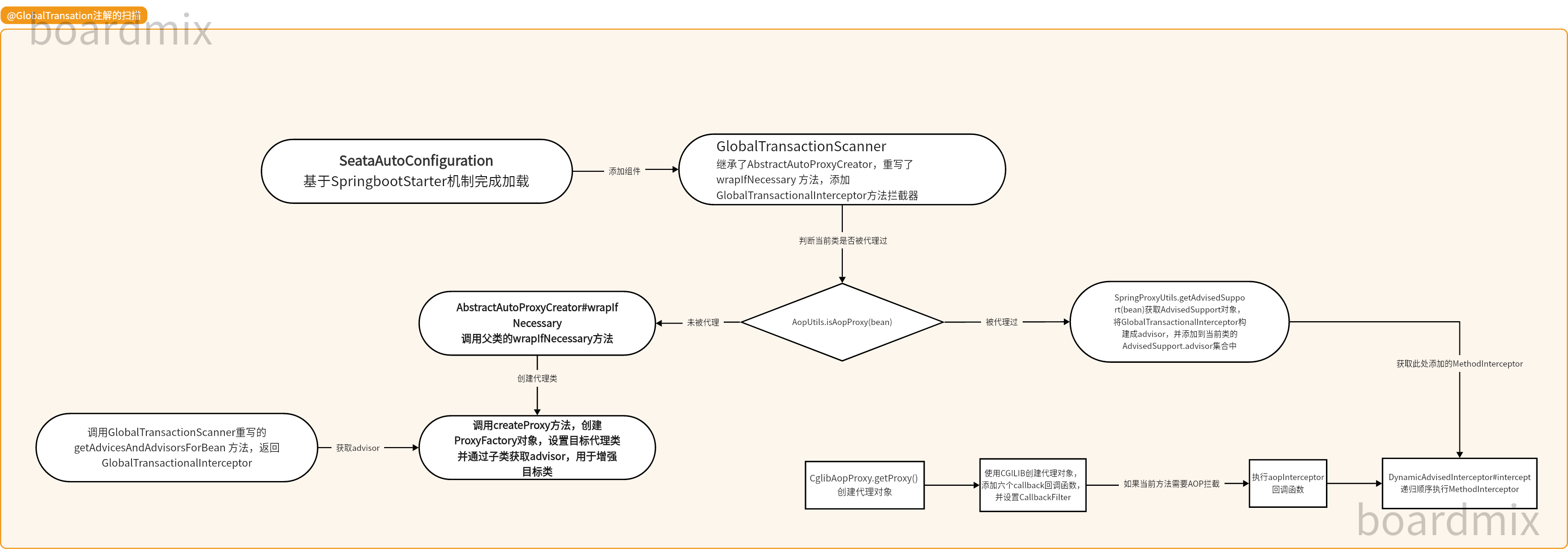
3.流程图
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 【薅羊毛攻略】低价骨折服务器,2核2G每天只需2毛7,快来抢购!
- nodejs+vue+微信小程序+python+PHP校园二手交易系统的设计与实现-计算机毕业设计推荐
- 【习题】属性动画
- RocketMQ Dashboard可视化工具
- IDEA中也能用Postman了,这款插件平替
- 算法训练营Day42(背包问题)
- win10录屏文件在哪?这里告诉你答案
- ssm基于java的自助医疗服务系统的设计与实现+jsp论文
- IOS-ViewController与Storyboard进行绑定-Swift
- 开发微信小程序时,提示不在以下 request 合法域名解决办法