C++核心编程之通过类和对象的思想对文件进行操作
发布时间:2024年01月17日
目录
???????一、文件操作
一、文件操作
程序运行时产生的数据都属于临时数据,程序一旦运行结束都会被释放
通过文件可以将数据持久化
C++中对文件操作需要包含头文件< fstream >
1. 文件类型分类:
- 文本文件:? -文件以文本的ASCII码形式存储在计算机中
- 二进制文本: - 文件以文本的二进制形式存储在计算机中,用户一般不能直接读懂他们
2. 操作文件的三大类
- ofstream :写文加
- ifstream :读文件
- fstream:读写操作
二、文本文件
1.写文件
? ? ? ? 1.包含头文件
????????????????#include<fstream>
? ? ? ? 2.创建流对象
????????????????ofstream? ofs;
? ? ? ? 3.打开文件
????????????????ofs.open("文件路径",打开方式);
? ? ? ? 4.写数据
????????????????ofs<<"写入数据";
? ? ? ? 5.关闭文件
????????????????ofs.close();
文件打开方式
| 打开方式 | 功能 |
| ios::in | 为读文件而打开文件 |
| ios::out | 为写文件而打开文件 |
| ios::ate | 初始位置,文件尾 |
| ios::app | 以追加的方式写入 |
| ios::trunc | 如果文件存在,先删除,再创建一个新的 |
| ios::binary | 二进制方式写文件 |
注意:
文件打开方式可以配合使用,? 利用? |? 操作符(位或)
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
??? // 1. 包含头文件<fstream>
??? // 2. 创建流对象?? ofstream ofs;
??? // 3. 打开文件 ofs.open("文件路径",打开方式)
??? // 4. 写数据?? ofs<<"写入数据"
??? // 5. 关闭文件 ofs.close()
?
??? ofstream ofs;
??? ofs.open("E:/test.txt", ios::out); // 没有指定具体路径存放到当前项目的文件夹下
??? ofs << "helo " << endl;
??? ofs << "文件操作" << endl;
??? ofs.close();
??? return 0;
}结果示例:

总结:
- 文件操作必须包含头文件fstheam
- 读文件可以利用 ofstream ,或者fstream类
- 打开文件时候需要指定操作文件的路径,以及打开方式
- 利用<<可以向文件中写数据
- 操作完毕,要关闭文件
2.读文件
? ? ? ? 1.包含头文件
????????????????#include<fstream>
????????2.创建流对象
????????????????ifstream? ifs;
? ? ? ? 3.打开文件
????????????????ifs.open("文件路径",打开方式);
? ? ? ? 4.读数据
????????????????四种方式读取
? ? ? ? 5.关闭文件
????????????????ifs.close();
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
??? // 1. 包含头文件<fstream>
??? // 2. 创建流对象?? ifstream ifs;
??? // 3. 打开文件 ofs.open("文件路径",打开方式)
??? // 4. 读数据?? 四种方式读取
??? // 5. 关闭文件 ifs.close()
?
??? ifstream ifs;
??? ifs.open("E:/test.txt", ios::in);
??? if( !ifs.is_open()){
???? cout<<"文件打开失败"<<endl;
???? //return;
}
// 第一种:字符数组
char buf[1024]={0};
while(ifs>>buf){
cout<<buf<<endl;
}
// 第二种
char buf1[1024]={0};
// 获取一行
while(ifs.getline(buf1,sizeof(buf1))){
cout<<buf1<<endl;
}
// 第三种:字符串中
string buf2;
while(getline(ifs,buf2)){
cout<<buf2<<endl;
}
// 第四种:一个一个读取没有一行一行读取快
char c;// 判断是否读取到了文件的尾部
while((c = ifs.get())!=EOF){ // end of file
cout<<c;
}
??? ifs.close();
??? return 0;
}运行结果:
第一种:

第二种:
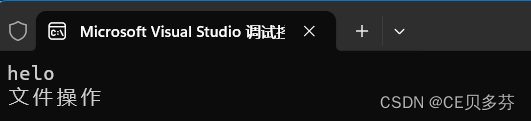
第三种:

第四种:

总结:
- 读文件可以利用ifstream,或者fstream类
- 利用is._open函数可以断文件是否打开成功
- close关闭文件
?
三、二进制文件
1.写二进制文件
- 打开方式要指定为ios::binary
- 二进制方式写文件主要利用流对象调用成员函数write
- 函数原型:ostream? &? write(const? char*? buffer,? int? len);
- 参数:字符指针buffer指向内存中一段存储空间,len是读写得到字节数
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class person{
public:
char Name[64];
int Age;
};
int main()
{
??? // 打开的方式要指定为 iOS::binary
??? // 函数原型 ostream &write(const char *buffer,int len);
??? // 1. 包含头文件
// 2. 创建流对象
ofstream ofs;
// 3. 打开文件
ofs.open("E:/text.txt",ios::out|ios::binary);
// 4. 写文件
person p ={"张三",18};
ofs.write((const char *)&p,sizeof(p));
// 5. 关闭文件
ofs.close();
??? return 0;
}运行结果示例:

2.读二进制文件
- 二进制方式读文件主要利用流对象调用成员函数read
- 函数原型:itream? &? read(char*? buffer,? int? len);
- 参数:字符指针buffer指向内存中一段存储空间,len是读写的字节数
示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class person{
public:
char Name[64];
int Age;
};
int main()
{
??? // 打开的方式要指定为 iOS::binary
??? // 函数原型 istream &read(const char *buffer,int len);
??? // 1. 包含头文件
// 2. 创建流对象
ifstream ifs;
// 3. 打开文件? 判断文件是否读取成功
ifs.open("E:/text.txt",ios::in|ios::binary);
if(!ifs.is_open()){
return 0;
}
// 4. 读文件
person p ;
ifs.read((char *)&p,sizeof(p));
?
cout<<"姓名: "<<p.Name<<endl<<"年龄: "<<p.Age<<endl;
// 5. 关闭文件
ifs.close();
??? return 0;
}运行结果:

文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/hjl011006/article/details/135655196
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Linux lpr命令教程:如何使用lpr命令打印文件(附案例详解和注意事项)
- 最新AI创作系统ChatGPT源码,Midjourney绘画系统,GPT语音对话+ChatFile文档对话总结+DALL-E3文生图+思维导图+GPT-4识图理解+自定义知识库一站式解决方案
- python和pygame实现烟花特效
- mint-ui///mui
- 博途1200PLC脉冲轴绝对定位往复运动控制FB(完整SCL源代码)
- Koordinator 助力云原生应用性能提升:小红书混部技术实践
- 0121-1-计算机网络安全
- 2023年浙大城市学院新生程序设计竞赛(同步赛)G
- JAVA判断两个时间之间的差
- 静态代理和动态代理样例