brpc: a little source code
之前在https://www.yuque.com/treblez/qksu6c/nqe8ip59cwegl6rk?singleDoc# 《olap/clickhouse-编译器优化与向量化》中我谈过brpc的汇编控制bthread。本文就来看一下brpc作为一个高性能的rpc实现,除了自定义线程栈之外,代码还有什么优秀之处。
因为时间原因,本文不做深入分析,只是解读下几个有意思的模块。
用户态futex
brpc中worker间的状态同步是通过ParkingLot来实现的,ParkingLot就是一个futex的封装类,我们看下brpc如何实现的futex。注意这里的futex不是bthread的futex,而是实现的pthread系统futex。
https://github.com/apache/brpc/blob/master/src/bthread/sys_futex.cpp
一个标准的手写futex,在OS_MACOSX中使用(原因是macos没有实现futex)。
我们都知道,linux里面使用spinlock + futex作为pthread_mutex的实现(https://lwn.net/Articles/360699/):
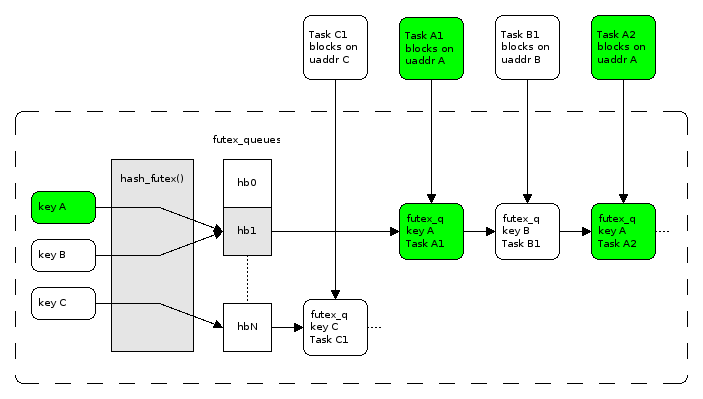
那我们在用户态没有唤醒线程队列的能力,怎么实现一个futex呢?答案是用mutex控制临界区(代表互斥锁的那个全局变量)访问,condition_variable实现睡眠和唤醒。
brpc给了一个教科书级别的实现,pthread_once + unordered_map:
// Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
// or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
// distributed with this work for additional information
// regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
// to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
// "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
// with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
//
// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
//
// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
// software distributed under the License is distributed on an
// "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
// KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
// specific language governing permissions and limitations
// under the License.
// bthread - An M:N threading library to make applications more concurrent.
// Date: Wed Mar 14 17:44:58 CST 2018
#include "bthread/sys_futex.h"
#include "butil/scoped_lock.h"
#include "butil/atomicops.h"
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unordered_map>
#if defined(OS_MACOSX)
namespace bthread {
class SimuFutex {
public:
SimuFutex() : counts(0)
, ref(0) {
pthread_mutex_init(&lock, NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL);
}
~SimuFutex() {
pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
}
public:
pthread_mutex_t lock;
pthread_cond_t cond;
// 有多少线程在等待
int32_t counts;
// 有多少线程有所有权
int32_t ref;
};
static pthread_mutex_t s_futex_map_mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
static pthread_once_t init_futex_map_once = PTHREAD_ONCE_INIT;
// 和linux中的hash_futex() + 队列实现类似
static std::unordered_map<void*, SimuFutex>* s_futex_map = NULL;
static void InitFutexMap() {
// Leave memory to process's clean up.
s_futex_map = new (std::nothrow) std::unordered_map<void*, SimuFutex>();
if (NULL == s_futex_map) {
exit(1);
}
return;
}
int futex_wait_private(void* addr1, int expected, const timespec* timeout) {
// pthread_once用于控制多线程中某个函数只会被初始化一次
// init_futex_map_once 是一个pthread_once_t变量,必须全局可见
// 如果调用出错,那么返回非零值
if (pthread_once(&init_futex_map_once, InitFutexMap) != 0) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Fail to pthread_once";
exit(1);
}
std::unique_lock<pthread_mutex_t> mu(s_futex_map_mutex);
SimuFutex& simu_futex = (*s_futex_map)[addr1];
++simu_futex.ref;
mu.unlock();
int rc = 0;
{
std::unique_lock<pthread_mutex_t> mu1(simu_futex.lock);
// 冲突,并等待,使用内核态函数mutex
if (static_cast<butil::atomic<int>*>(addr1)->load() == expected) {
++simu_futex.counts;
if (timeout) {
timespec timeout_abs = butil::timespec_from_now(*timeout);
if ((rc = pthread_cond_timedwait(&simu_futex.cond, &simu_futex.lock, &timeout_abs)) != 0) {
errno = rc;
rc = -1;
}
} else {
if ((rc = pthread_cond_wait(&simu_futex.cond, &simu_futex.lock)) != 0) {
errno = rc;
rc = -1;
}
}
--simu_futex.counts;
} else {
errno = EAGAIN;
rc = -1;
}
}
std::unique_lock<pthread_mutex_t> mu1(s_futex_map_mutex);
if (--simu_futex.ref == 0) {
s_futex_map->erase(addr1);
}
mu1.unlock();
return rc;
}
// 能控制唤醒线程数的wake
int futex_wake_private(void* addr1, int nwake) {
if (pthread_once(&init_futex_map_once, InitFutexMap) != 0) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Fail to pthread_once";
exit(1);
}
std::unique_lock<pthread_mutex_t> mu(s_futex_map_mutex);
auto it = s_futex_map->find(addr1);
if (it == s_futex_map->end()) {
mu.unlock();
return 0;
}
SimuFutex& simu_futex = it->second;
++simu_futex.ref;
mu.unlock();
int nwakedup = 0;
int rc = 0;
{
std::unique_lock<pthread_mutex_t> mu1(simu_futex.lock);
nwake = (nwake < simu_futex.counts)? nwake: simu_futex.counts;
for (int i = 0; i < nwake; ++i) {
if ((rc = pthread_cond_signal(&simu_futex.cond)) != 0) {
errno = rc;
break;
} else {
++nwakedup;
}
}
}
std::unique_lock<pthread_mutex_t> mu2(s_futex_map_mutex);
if (--simu_futex.ref == 0) {
s_futex_map->erase(addr1);
}
mu2.unlock();
return nwakedup;
}
} // namespace bthread
#endif
bthread创建
bthread并不是在用户态栈上创建的,而是通过malloc/mmap:
int allocate_stack_storage(StackStorage* s, int stacksize_in, int guardsize_in) {
const static int PAGESIZE = getpagesize();
const int PAGESIZE_M1 = PAGESIZE - 1;
const int MIN_STACKSIZE = PAGESIZE * 2;
const int MIN_GUARDSIZE = PAGESIZE;
// Align stacksize
const int stacksize =
(std::max(stacksize_in, MIN_STACKSIZE) + PAGESIZE_M1) &
~PAGESIZE_M1;
if (guardsize_in <= 0) {
void* mem = malloc(stacksize);
if (NULL == mem) {
PLOG_EVERY_SECOND(ERROR) << "Fail to malloc (size="
<< stacksize << ")";
return -1;
}
s_stack_count.fetch_add(1, butil::memory_order_relaxed);
s->bottom = (char*)mem + stacksize;
s->stacksize = stacksize;
s->guardsize = 0;
if (RunningOnValgrind()) {
s->valgrind_stack_id = VALGRIND_STACK_REGISTER(
s->bottom, (char*)s->bottom - stacksize);
} else {
s->valgrind_stack_id = 0;
}
return 0;
} else {
// Align guardsize
const int guardsize =
(std::max(guardsize_in, MIN_GUARDSIZE) + PAGESIZE_M1) &
~PAGESIZE_M1;
const int memsize = stacksize + guardsize;
void* const mem = mmap(NULL, memsize, (PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE),
(MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS), -1, 0);
if (MAP_FAILED == mem) {
PLOG_EVERY_SECOND(ERROR)
<< "Fail to mmap size=" << memsize << " stack_count="
<< s_stack_count.load(butil::memory_order_relaxed)
<< ", possibly limited by /proc/sys/vm/max_map_count";
// may fail due to limit of max_map_count (65536 in default)
return -1;
}
void* aligned_mem = (void*)(((intptr_t)mem + PAGESIZE_M1) & ~PAGESIZE_M1);
if (aligned_mem != mem) {
LOG_ONCE(ERROR) << "addr=" << mem << " returned by mmap is not "
"aligned by pagesize=" << PAGESIZE;
}
const int offset = (char*)aligned_mem - (char*)mem;
if (guardsize <= offset ||
mprotect(aligned_mem, guardsize - offset, PROT_NONE) != 0) {
munmap(mem, memsize);
PLOG_EVERY_SECOND(ERROR)
<< "Fail to mprotect " << (void*)aligned_mem << " length="
<< guardsize - offset;
return -1;
}
s_stack_count.fetch_add(1, butil::memory_order_relaxed);
s->bottom = (char*)mem + memsize;
s->stacksize = stacksize;
s->guardsize = guardsize;
if (RunningOnValgrind()) {
s->valgrind_stack_id = VALGRIND_STACK_REGISTER(
s->bottom, (char*)s->bottom - stacksize);
} else {
s->valgrind_stack_id = 0;
}
return 0;
}
}
创建之后,会执行一段汇编代码(bthread_make_fcontext):
template <typename StackClass> struct StackFactory {
struct Wrapper : public ContextualStack {
explicit Wrapper(void (*entry)(intptr_t)) {
if (allocate_stack_storage(&storage, *StackClass::stack_size_flag,
FLAGS_guard_page_size) != 0) {
storage.zeroize();
context = NULL;
return;
}
context = bthread_make_fcontext(storage.bottom, storage.stacksize, entry);
stacktype = (StackType)StackClass::stacktype;
}
~Wrapper() {
if (context) {
context = NULL;
deallocate_stack_storage(&storage);
storage.zeroize();
}
}
};
static ContextualStack* get_stack(void (*entry)(intptr_t)) {
return butil::get_object<Wrapper>(entry);
}
static void return_stack(ContextualStack* sc) {
butil::return_object(static_cast<Wrapper*>(sc));
}
};
虽然contex.cpp里面的汇编代码看起来多,但是一个bthread_make_fcontext就根据平台不同实现了九遍,这个故事告诉我们要珍爱生命,远离汇编。
以linux_x86为例,我们看看这里做了什么:
#if defined(BTHREAD_CONTEXT_PLATFORM_linux_x86_64) && defined(BTHREAD_CONTEXT_COMPILER_gcc)
__asm (
".text\n"
".globl bthread_make_fcontext\n"
".type bthread_make_fcontext,@function\n"
".align 16\n"
"bthread_make_fcontext:\n"
// 第一个参数的值作为栈基址
" movq %rdi, %rax\n"
// 16字节对齐
" andq $-16, %rax\n"
// 减去0x48,存储上下文信息
" leaq -0x48(%rax), %rax\n"
// 寄存器偏移 0x38 的位置 存储栈大小
" movq %rdx, 0x38(%rax)\n"
// 保存浮点数运算的状态
" stmxcsr (%rax)\n"
// 保存FPU 控制字寄存器
" fnstcw 0x4(%rax)\n"
// 将 finish 标签的地址存储到 %rcx 寄存器中
" leaq finish(%rip), %rcx\n"
// 保存协程结束点位置
" movq %rcx, 0x40(%rax)\n"
" ret \n"
"finish:\n"
" xorq %rdi, %rdi\n"
" call _exit@PLT\n"
// 退出失败,程序挂起
" hlt\n"
".size bthread_make_fcontext,.-bthread_make_fcontext\n"
".section .note.GNU-stack,\"\",%progbits\n"
".previous\n"
);
对象池
brpc没有实现自己的内存分配器,但是做了对象池缓存。
对象池是个单例实现,brpc用了C++11但是并没有用Meyers’ Singleton来创建这个静态单例,而是用static_atomic解决静态变量加载顺序的问题:
template <typename T>
butil::static_atomic<ObjectPool<T>*> ObjectPool<T>::_singleton = BUTIL_STATIC_ATOMIC_INIT(NULL);
加上经典的单例实现:
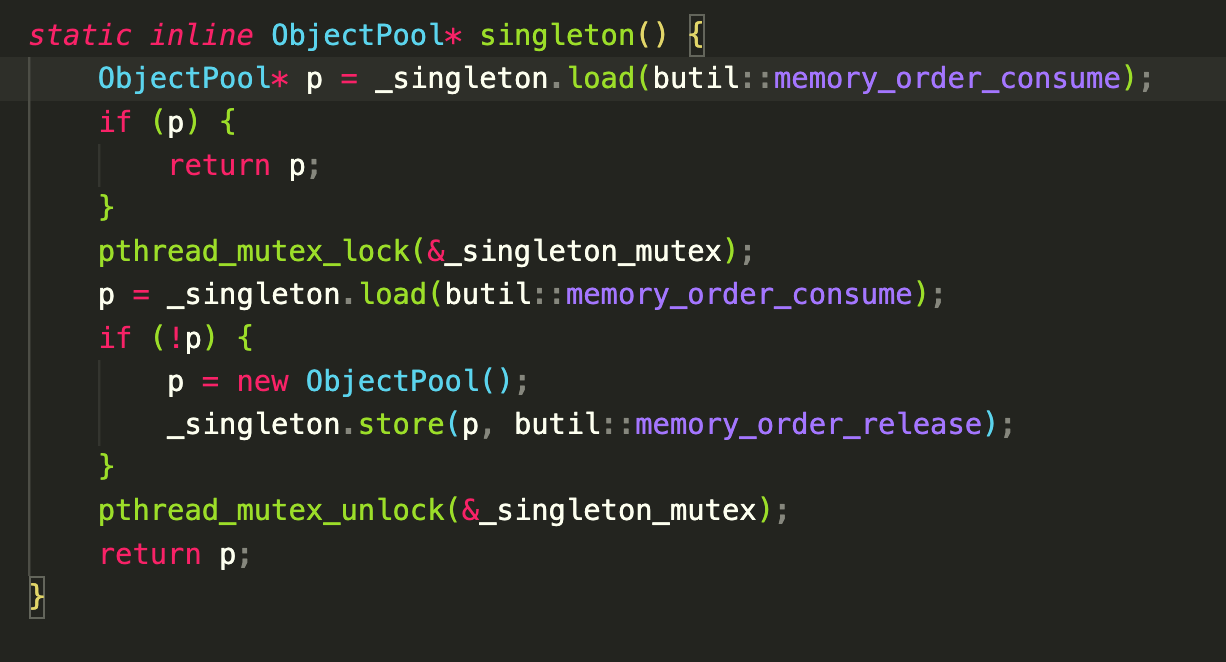
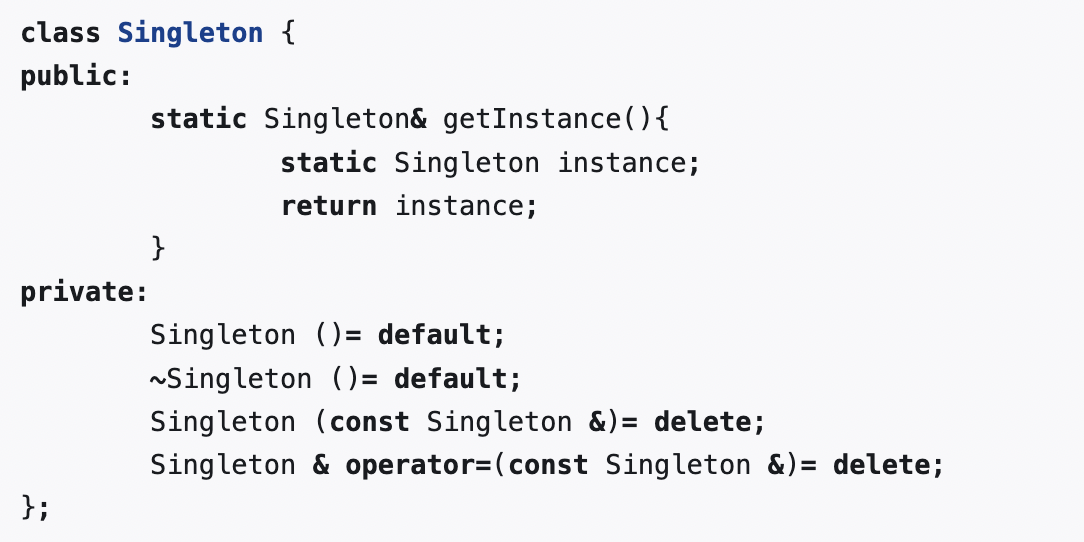
我没找到不用Meyers’ Singleton的理由,或许可以改进一下?(Meyers’ Singleton如下所示)
对象池的获取逻辑被实现为了一个宏,依次从local free chunk、global free chunk获取对象。
这里还注释了对于POD类型,brpc用new T替代new T(),省去赋值0的开销。
// We need following macro to construct T with different CTOR_ARGS
// which may include parenthesis because when T is POD, "new T()"
// and "new T" are different: former one sets all fields to 0 which
// we don't want.
#define BAIDU_OBJECT_POOL_GET(CTOR_ARGS) \
/* Fetch local free ptr */ \
if (_cur_free.nfree) { \
BAIDU_OBJECT_POOL_FREE_ITEM_NUM_SUB1; \
return _cur_free.ptrs[--_cur_free.nfree]; \
} \
/* Fetch a FreeChunk from global. \
TODO: Popping from _free needs to copy a FreeChunk which is \
costly, but hardly impacts amortized performance. */ \
if (_pool->pop_free_chunk(_cur_free)) { \
BAIDU_OBJECT_POOL_FREE_ITEM_NUM_SUB1; \
return _cur_free.ptrs[--_cur_free.nfree]; \
} \
/* Fetch memory from local block */ \
if (_cur_block && _cur_block->nitem < BLOCK_NITEM) { \
T* obj = new ((T*)_cur_block->items + _cur_block->nitem) T CTOR_ARGS; \
if (!ObjectPoolValidator<T>::validate(obj)) { \
obj->~T(); \
return NULL; \
} \
++_cur_block->nitem; \
return obj; \
} \
/* Fetch a Block from global */ \
_cur_block = add_block(&_cur_block_index); \
if (_cur_block != NULL) { \
T* obj = new ((T*)_cur_block->items + _cur_block->nitem) T CTOR_ARGS; \
if (!ObjectPoolValidator<T>::validate(obj)) { \
obj->~T(); \
return NULL; \
} \
++_cur_block->nitem; \
return obj; \
} \
return NULL; \
和大多数内存池实现一样,归还的时候先往thread local放,再往global pool放:
inline int return_object(T* ptr) {
// Return to local free list
if (_cur_free.nfree < ObjectPool::free_chunk_nitem()) {
_cur_free.ptrs[_cur_free.nfree++] = ptr;
BAIDU_OBJECT_POOL_FREE_ITEM_NUM_ADD1;
return 0;
}
// Local free list is full, return it to global.
// For copying issue, check comment in upper get()
if (_pool->push_free_chunk(_cur_free)) {
_cur_free.nfree = 1;
_cur_free.ptrs[0] = ptr;
BAIDU_OBJECT_POOL_FREE_ITEM_NUM_ADD1;
return 0;
}
return -1;
}
TaskGroup
这里的任务调度主要是task_runner,task_runner通过调用ending_sched来进行task steal。
void TaskGroup::ending_sched(TaskGroup** pg) {
TaskGroup* g = *pg;
bthread_t next_tid = 0;
// Find next task to run, if none, switch to idle thread of the group.
#ifndef BTHREAD_FAIR_WSQ
// When BTHREAD_FAIR_WSQ is defined, profiling shows that cpu cost of
// WSQ::steal() in example/multi_threaded_echo_c++ changes from 1.9%
// to 2.9%
const bool popped = g->_rq.pop(&next_tid);
#else
const bool popped = g->_rq.steal(&next_tid);
#endif
if (!popped && !g->steal_task(&next_tid)) {
// Jump to main task if there's no task to run.
next_tid = g->_main_tid;
}
TaskMeta* const cur_meta = g->_cur_meta;
TaskMeta* next_meta = address_meta(next_tid);
if (next_meta->stack == NULL) {
if (next_meta->stack_type() == cur_meta->stack_type()) {
// also works with pthread_task scheduling to pthread_task, the
// transfered stack is just _main_stack.
next_meta->set_stack(cur_meta->release_stack());
} else {
ContextualStack* stk = get_stack(next_meta->stack_type(), task_runner);
if (stk) {
next_meta->set_stack(stk);
} else {
// stack_type is BTHREAD_STACKTYPE_PTHREAD or out of memory,
// In latter case, attr is forced to be BTHREAD_STACKTYPE_PTHREAD.
// This basically means that if we can't allocate stack, run
// the task in pthread directly.
next_meta->attr.stack_type = BTHREAD_STACKTYPE_PTHREAD;
next_meta->set_stack(g->_main_stack);
}
}
}
sched_to(pg, next_meta);
}
在ending_sched()中,会有依次从TG的rq、remote_rq取任务,找不到再窃取其他TG的任务,如果都找不到任务,则设置_cur_meta为_main_tid,然后就会回到run_main_task()的主循环,继续wait_task()等待新任务。
找到任务后,执行sched_to跳转到新任务。
void TaskGroup::sched_to(TaskGroup** pg, TaskMeta* next_meta) {
TaskGroup* g = *pg;
#ifndef NDEBUG
if ((++g->_sched_recursive_guard) > 1) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Recursively(" << g->_sched_recursive_guard - 1
<< ") call sched_to(" << g << ")";
}
#endif
// Save errno so that errno is bthread-specific.
const int saved_errno = errno;
void* saved_unique_user_ptr = tls_unique_user_ptr;
TaskMeta* const cur_meta = g->_cur_meta;
const int64_t now = butil::cpuwide_time_ns();
const int64_t elp_ns = now - g->_last_run_ns;
g->_last_run_ns = now;
cur_meta->stat.cputime_ns += elp_ns;
if (cur_meta->tid != g->main_tid()) {
g->_cumulated_cputime_ns += elp_ns;
}
++cur_meta->stat.nswitch;
++ g->_nswitch;
// Switch to the task
if (__builtin_expect(next_meta != cur_meta, 1)) {
g-> = next_meta;
// Switch tls_bls
cur_meta->local_storage = tls_bls;
tls_bls = next_meta->local_storage;
// Logging must be done after switching the local storage, since the logging lib
// use bthread local storage internally, or will cause memory leak.
if ((cur_meta->attr.flags & BTHREAD_LOG_CONTEXT_SWITCH) ||
(next_meta->attr.flags & BTHREAD_LOG_CONTEXT_SWITCH)) {
LOG(INFO) << "Switch bthread: " << cur_meta->tid << " -> "
<< next_meta->tid;
}
if (cur_meta->stack != NULL) {
if (next_meta->stack != cur_meta->stack) {
jump_stack(cur_meta->stack, next_meta->stack);
// probably went to another group, need to assign g again.
g = BAIDU_GET_VOLATILE_THREAD_LOCAL(tls_task_group);
}
#ifndef NDEBUG
else {
// else pthread_task is switching to another pthread_task, sc
// can only equal when they're both _main_stack
CHECK(cur_meta->stack == g->_main_stack);
}
#endif
}
// else because of ending_sched(including pthread_task->pthread_task)
} else {
LOG(FATAL) << "bthread=" << g->current_tid() << " sched_to itself!";
}
while (g->_last_context_remained) {
RemainedFn fn = g->_last_context_remained;
g->_last_context_remained = NULL;
fn(g->_last_context_remained_arg);
g = BAIDU_GET_VOLATILE_THREAD_LOCAL(tls_task_group);
}
// Restore errno
errno = saved_errno;
// tls_unique_user_ptr probably changed.
BAIDU_SET_VOLATILE_THREAD_LOCAL(tls_unique_user_ptr, saved_unique_user_ptr);
#ifndef NDEBUG
--g->_sched_recursive_guard;
#endif
*pg = g;
}
通过传入的参数:next_tid找到TM:next_meta,和对应的ContextualStack信息:stk。
如果task_meta切换了,那么调用jump_stack
while (g->_last_context_remained) {
RemainedFn fn = g->_last_context_remained;
g->_last_context_remained = NULL;
fn(g->_last_context_remained_arg);
g = tls_task_group;
}
// Restore errno
errno = saved_errno;
tls_unique_user_ptr = saved_unique_user_ptr;
*pg = g;
jump_stack把函数调用方的相关寄存器入栈,也就是保存调用方的运行环境。在当前函数执行结束之后要从栈中还原数据到相应的寄存器中,从而让调用方继续执行。所以末尾有出栈操作。
#if defined(BTHREAD_CONTEXT_PLATFORM_linux_x86_64) && defined(BTHREAD_CONTEXT_COMPILER_gcc)
__asm (
".text\n"
".globl bthread_jump_fcontext\n"
".type bthread_jump_fcontext,@function\n"
".align 16\n"
"bthread_jump_fcontext:\n"
" pushq %rbp \n"
" pushq %rbx \n"
" pushq %r15 \n"
" pushq %r14 \n"
" pushq %r13 \n"
" pushq %r12 \n"
" leaq -0x8(%rsp), %rsp\n"
" cmp $0, %rcx\n"
" je 1f\n"
" stmxcsr (%rsp)\n"
" fnstcw 0x4(%rsp)\n"
"1:\n"
" movq %rsp, (%rdi)\n"
" movq %rsi, %rsp\n"
" cmp $0, %rcx\n"
" je 2f\n"
" ldmxcsr (%rsp)\n"
" fldcw 0x4(%rsp)\n"
"2:\n"
" leaq 0x8(%rsp), %rsp\n"
" popq %r12 \n"
" popq %r13 \n"
" popq %r14 \n"
" popq %r15 \n"
" popq %rbx \n"
" popq %rbp \n"
" popq %r8\n"
" movq %rdx, %rax\n"
" movq %rdx, %rdi\n"
" jmp *%r8\n"
".size bthread_jump_fcontext,.-bthread_jump_fcontext\n"
".section .note.GNU-stack,\"\",%progbits\n"
);
栈切换代码如下,其中rdi是&from->context, rsi是 to->context
1:
movq %rsp, (%rdi)
movq %rsi, %rsp
我们知道%rdi和%rsi表示的是第一个参数和第二个参数,也就是:&from->context 和 to->context。
最后依次将参数出栈之后,%r8寄存器保留了饭回地址,最后会跳转到这个地址恢复bthread执行。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- APM32 移植 RTX5
- Python之Selenium自动化浏览器测试详解
- 数学建模常见算法的通俗理解(更新中)
- 鸿蒙开发笔记(二十二): 页面路由(router),组件导航 Navigation, Tabs
- 全系统各类型工程水土保持方案编制实践技术
- 【智慧门店】东胜物联蓝牙网关助力解决方案商,推动汽车后市场企业智能化升级
- go work
- HarmonyOS—构建第一个ArkTS应用(Stage模型)
- Android OpenCV(七十七):官方指南方式编译 OpenCV Android SDK.md
- Java与前端开发:真相还是焦虑?