第十四章 集合(Set)
一、Set 接口(P518)
1. Set 接口基本介绍
(1)无序(添加和取出的顺序不一致),没有索引。
(2)不允许重复元素,所以最多包含一个 null。
2. Set 接口的常用方法
和 List 接口一样,Set 接口也是 Collection 的子接口,因此,常用方法和 Collection 接口一样。
3. Set 接口的遍历方式
同 Collection 的遍历方式一样,因为 Set 接口是 Collection 接口的子接口。
(1)可以使用选代器
(2)增强for
(3)不能使用 索引的方式来获取
二、HashSet(P519)
1. Hashset 的说明
(1)HashSet 实现了 Set 接口。
(2)HashSet 实际上是 HashMap。
(3)可以存放 null 值,但是只能有一个 null。
(4)HashSet 不保证元素是有序的,取决于 hash 后,再确定索引的结果。
(5)不能有重复元素/对象。
2. Hashset底层机制源码说明(P522)
分析 Hashset 底层是 HashMap,HashMap 底层是(数组+链表+红黑树)。
public class HashMap_<K, V> {
transient Node<K, V>[] table;
transient int modCount;
transient int size;
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K, V>[] tab;
Node<K, V> p;
int n, i;
// 属性table为null或table的长度为0,就扩容
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) {
n = (tab = resize()).length;
}
// 如果tab[i]为null,表示没有存放元素,就创建节点并赋值给tab[i]
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) {
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
} else {
Node<K, V> e;
K k;
// p 和添加元素的hash值相同 并且 (key相同或equals相同),p赋值给e
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
e = p;
}
// 链表循环比较
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
break;
}
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) {
e.value = value;
}
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold) {
resize();
}
return null;
}
int threshold;
final float loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // 16
// 加载因子
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
final Node<K, V>[] resize() {
Node<K, V>[] oldTab = table;
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
} else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) {
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
} else if (oldThr > 0) {
newCap = oldThr;
} else {
// 扩容
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int) (DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float) newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float) MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int) ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
// 初始化数组,并赋值给属性table
Node<K, V>[] newTab = (Node<K, V>[]) new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
return newTab;
}
Node<K, V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) {
return new Node<>(hash, key, value, next);
}
static class Node<K, V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K, V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
(1)HashSet 底层是 HashMap。
(2)添加一个元素时,先得到 hash 值 --> 会转成 --> 索引值。
(3)找到存储数据表 table,看这个索引位置是否已经存放的有元素。
(4)如果没有,直接加入。
(5)如果有,调用 equals 比较,如果相同,就放弃添加,如果不相同,则添加到最后。
(6)在 Java8 中,如果一条链表的元素个数达到 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认是8),并且 table 的大小 >= MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(默认64),就会进行树化(红黑树)。
红黑树机制:
(1)HashSet 底层是 HashMap,第一次添加时,table 数组扩容到16,临界值(threshold)是16,加载因子(loadFactor)是0.75=12。
(2)如果table数组使用到了临界值12,就会扩容到162=32,新的临界值就是320.75=24,依次类推。
(3)在Java8中,如果一条链表的元素个数到达TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认是8),并且table的大小>=MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY(默认64)就会进行树化(红黑树),否则仍然采用数组扩容机制。
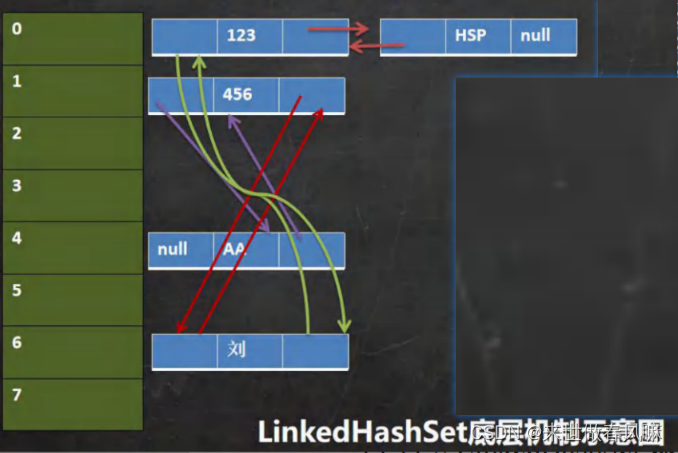
三、LinkedHashSet (P528)
1. LinkedHashSet 的说明
(1)LinkedHashSet 是 Hashset 的子类。
(2)LinkedHashSet 底层是一个 LinkedHashMap,底层维护了一个 数组+双向链表。
(3)LinkedHashSet 根据元素的 hashCode 值来决定元素的存储位置,同时使用链表维护元素的 次序(图),这使得元素看起来是以插入顺序保存的。
(4)LinkedHashset 不允许添重复元素。
(1)在 LinkedHashSet 中维护了一个 hash 表和双向链表(LinkedHashSet 有 head 和 tail)。
(2)每一个节点有 pre 和 next 属性,这样可以形成双向链表。
(3)在添加一个元素时,先求hash值,在求索引,确定该元素在 hashtable 的位置,然后将添加的元素加入到双向链表(如果已经存在,不添加【原则和 hashset 一样】)。
(4)遍历 LinkedHashSet 也能确保插入顺序和遍历顺序一致。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 无法打开输入文件“Qt5Core.lib”的解决方案
- 数据库调研
- 调用Java线程相关的API为什么能够控制操作系统线程?
- MATLAB实现逐步回归数学建模算法
- yolov5_master的下载、环境搭建、数据处理及训练全过程
- 康谋新闻丨走进康谋科技——您的自动驾驶解决方案合作伙伴
- 常用注解/代码解释(仅个人使用)
- 位运算:Leetcode371.两整数之和
- ACES 增强版不丹水稻作物地图(2016-2022 年)
- 计算机架构“寒武纪爆发”,操作系统进化迸发中国浪潮