Python无法拒绝的表白界面完整代码
发布时间:2023年12月28日

运行时弹出界面
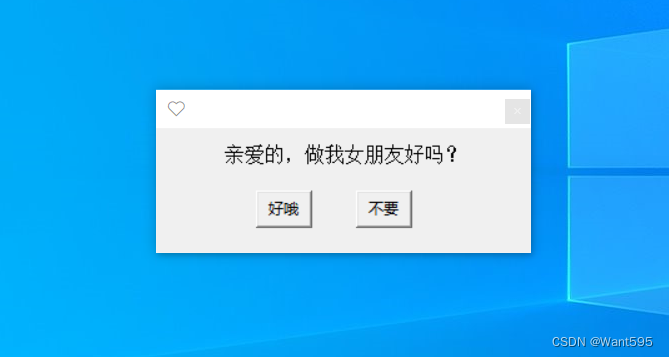
当点击“不要”时弹出
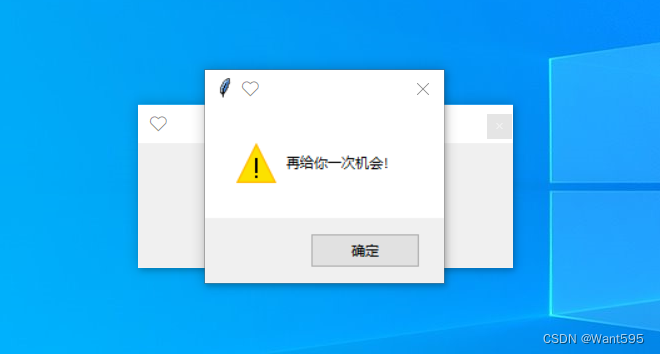
当点击“×”时弹出
环境需求
- python3.11.4及以上版本
- PyCharm Community Edition 2023.2.5
- pyinstaller6.2.0(可选,这个库用于打包,使程序没有python环境也可以运行,如果想发给好朋友的话需要这个库哦~)
【注】
- python环境搭建请见:https://want595.blog.csdn.net/article/details/134586653
- pyinstaller使用教程见:https://want595.blog.csdn.net/article/details/134106807
完整代码
import tkinter as tk
import tkinter.messagebox
root = tk.Tk()
root.title('?')
root.resizable(0, 0)
root.wm_attributes("-toolwindow", 1)
screenwidth = root.winfo_screenwidth()
screenheight = root.winfo_screenheight()
widths = 300
heights = 100
x = (screenwidth - widths) / 2
y = (screenheight - heights) / 2
root.geometry('%dx%d+%d+%d' % (widths, heights, x, y)) # 设置在屏幕中居中显示
tk.Label(root, text='亲爱的,做我女朋友好吗?', width=37, font=('宋体', 12)).place(x=0, y=10)
def OK(): # 同意按钮
root.destroy()
# 同意后显示漂浮爱心
def NO(): # 拒绝按钮,拒绝不会退出,必须同意才可以退出哦~
tk.messagebox.showwarning('?', '再给你一次机会!')
def closeWindow():
tk.messagebox.showwarning('?', '逃避是没有用的哦')
tk.Button(root, text='好哦', width=5, height=1, command=OK).place(x=80, y=50)
tk.Button(root, text='不要', width=5, height=1, command=NO).place(x=160, y=50)
root.protocol('WM_DELETE_WINDOW', closeWindow) # 绑定退出事件
root.mainloop()
详细分析
这是一段使用Python的tkinter库实现的简单GUI程序,目的是用一个小窗口向用户求爱,请求对方成为自己的女朋友。
先介绍一下代码的基本框架:
- 导入tkinter库
- 创建一个tk对象,即窗口
- 在窗口中添加一个Label和两个Button
- 定义两个Button的回调函数
- 调用mainloop()函数,开始显示窗口
下面我们来详细分析一下代码:
- 导入tkinter库
Python的tkinter库是一个方便易用的GUI库,用于创建窗口和各种GUI组件,如Label、Button、Entry等等。使用前需要先导入tkinter库。
import tkinter as tk
import tkinter.messagebox
其中tkinter库被导入并重命名为tk,这样可以更方便地调用其函数。
- 创建一个tk对象,即窗口
在程序中创建一个窗口对象:
root = tk.Tk()
其中root是窗口对象的名称,可以自己定义。这一行代码创建了一个名为root的窗口对象。
接下来为窗口设置标题、大小和位置:
root.title('?')
root.resizable(0, 0)
root.wm_attributes("-toolwindow", 1)
screenwidth = root.winfo_screenwidth()
screenheight = root.winfo_screenheight()
widths = 300
heights = 100
x = (screenwidth - widths) / 2
y = (screenheight - heights) / 2
root.geometry('%dx%d+%d+%d' % (widths, heights, x, y))
- 设置标题:使用title()函数可以设置窗口的标题,这里将标题设置为心形。
- 设置大小和位置:使用geometry()函数可以设置窗口的大小和位置,这里将窗口设置为宽300,高100,并将窗口显示在屏幕中央。
其中设置窗口大小和位置的代码比较复杂,可以简单解释一下:
- 获取当前屏幕的宽高:使用winfo_screenwidth()和winfo_screenheight()函数分别获取屏幕的宽和高。
- 设置窗口的宽高:将窗口的宽设置为300,高设置为100。
- 计算窗口的位置:通过计算得到窗口左上角的坐标(x,y),使得窗口在屏幕中间显示。
其他还设置了以下两行代码:
root.resizable(0, 0)
root.wm_attributes("-toolwindow", 1)
- 禁止窗口大小可调:使用resizable()函数可以设置窗口是否可以改变大小,这里将其设置为不可改变。
- 将窗口设置为工具窗口:使用wm_attributes()函数可以设置窗口的属性,这里将其设置为工具窗口,这样可以在任务栏中不显示窗口。
- 在窗口中添加一个Label和两个Button
在窗口中添加Label和Button:
tk.Label(root, text='亲爱的,做我女朋友好吗?', width=37, font=('宋体', 12)).place(x=0, y=10)
tk.Button(root, text='好哦', width=5, height=1, command=OK).place(x=80, y=50)
tk.Button(root, text='不要', width=5, height=1, command=NO).place(x=160, y=50)
- 添加Label:使用Label()函数创建一个Label组件,其中设置文本内容为“亲爱的,做我女朋友好吗?”,设置宽度为37,字体大小为12,然后将其显示在窗口中,位置为(x,y)=(0,10)。
- 添加Button:使用Button()函数创建两个Button组件,分别设置文本内容为“好哦”和“不要”,大小为5×1,设置回调函数为OK和NO,最后将它们分别显示在窗口中的位置(x,y)=(80,50)和(x,y)=(160,50)。
- 定义两个Button的回调函数
定义两个Button的回调函数:
def OK():
root.destroy()
# 同意后显示漂浮爱心
def NO():
tk.messagebox.showwarning('?', '再给你一次机会!')
def closeWindow():
tk.messagebox.showwarning('?', '逃避是没有用的哦')
这里定义了三个函数,分别是OK、NO、closeWindow。其中:
- OK函数:当用户点击“好哦”按钮时,调用destroy()函数来关闭窗口,表示同意成为男友女友。此外,可以在这个函数中添加一些代码,比如显示漂浮的爱心。
- NO函数:当用户点击“不要”按钮时,调用showwarning()函数显示一个弹窗,提示用户再给一次机会。注意,此时窗口不会关闭,必须同意才能退出。
- closeWindow函数:当用户点击窗口右上角的关闭按钮时,调用showwarning()函数来弹出一个窗口,提示用户逃避是没有用的。
- 调用mainloop()函数,开始显示窗口
调用mainloop()函数,开始显示窗口并等待用户操作。
root.mainloop()
当用户点击“好哦”按钮时,窗口会关闭,程序结束。当用户点击“不要”按钮时,窗口不会关闭,继续等待用户操作。当用户点击窗口右上角的关闭按钮时,弹出提示框后,窗口不会关闭,继续等待用户操作。
这就是整个程序的代码和逻辑。虽然是一个简单的小例子,但是体现了tkinter库的基本用法,也比较有趣。
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_68111267/article/details/135279611
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!