高级鉴权网关设计二:SM2国密+协议SPI可扩展+动态配置
发布时间:2024年01月08日
? 上一篇文章是定义切面来做鉴权,针对接口时使用比较方便,还有一种是网关的鉴权如何处理?下面为大家介绍一种比较常用的方案,附带可扩展设计
? 既然是网关其实就是和外部的礼尚往来,每个第三方还有可能不一样,一般常用的有http的form表单,get,post,https,和每个第三方的交互签名方式、加密方式都可能不同,很多时候取决于你是甲方爸爸还是乙方儿子,如果是甲方就好了,对接就按你们的来,你们来对我们,乙方就痛苦了,得适配不同的甲方爸爸,那我们该如何设计呢?
简单框架如下,提取抽象出业务节点(加密签名可有可无)
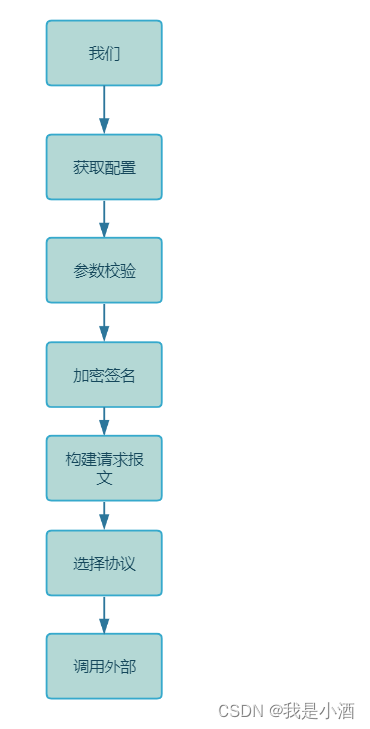
重点来了,我们可以根据channelType定义多套流程,
- 一个是simple简单扩展,驼峰下划线可支持转化
- 一个是normal常规扩展,定义公共参数,比如appid,version,sign,timestamp等等;支持驼峰转下划线,也可以支持更多
- 一个是个性化,一般按甲方的来很容易这样,可以定义多个个性化type,组装不同的甲方需要的个性化参数
关于加密和协议根据两个维度进行扩展,一个是加密类型encryptType,一个是协议类型protocolType,分别定义好枚举
动态配置是什么,就是配置上面我需要走哪条道所需要的配置,比如要配置encryptType=SM2,protocolType=https,channelType=simple,秘钥,域名等等
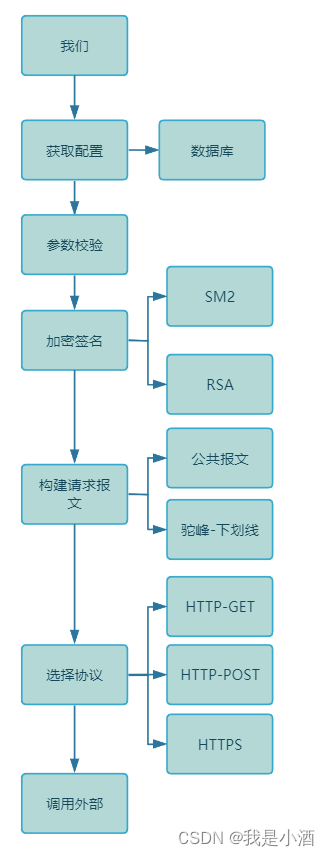
上面是完善后的流程,相对不是很难,重点在于考虑好扩展
关于加密以及签名sign,我们和外部如何友好的通信但是又不能把秘钥暴露给对方?给大家介绍一下
以SM2非对称加密为例,我们和外部都定义一套公钥私钥,分别把公钥给到对方
调用外部接口时,我们用外部给的的公钥加密,用我们的私钥加签。
外部收到请求后,使用我们的公钥验签,用外部自己的私钥解密。
然后外部将返回结果用我们的公钥加密,外部的私钥加签。我们使用外部的公钥验签,使用私钥解密。
这样保证了我们的私钥都在自己手里,实现了数据加密,并生成了sign保证了安全性
给大家附上SM2国密工具
@Slf4j
public class SM2Util {
@Data
public static class CryptoKey {
public String key;
public String VerKey;
}
/**
* 创建密钥对
*/
public static CryptoKey createKey() {
SM2Key sm2 = new SM2Key();
sm2.generateKey();
String key = ByteUtil.byte2hex(sm2.getPrivKeyBytes());
String verkey = ByteUtil.byte2hex(sm2.getPubKey()).substring(2);
CryptoKey cryptoKey = new CryptoKey();
cryptoKey.setKey(key);
cryptoKey.setVerKey(verkey);
return cryptoKey;
}
/**
* 加签
*/
public static String sign(String key, String messageRaw) {
try {
byte[] msgHash = HashUtil.sha256(messageRaw.getBytes());
BigInteger privKey = new BigInteger(key, 16);
SM2Key sM2Key = SM2Key.fromPrivate(privKey);
String rawData = sM2Key.sign(msgHash).toBase64();
return rawData;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("sm2 sign error ", e);
return null;
}
}
/**
* 校验
*/
public static boolean verify(String verkey, String messageRaw, String signatureRaw) {
try {
byte[] signedBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(signatureRaw);
byte[] msgHash = HashUtil.sha256(messageRaw.getBytes());
byte[] pkBytes = SM2Key.recoverPubBytesFromSignature(signedBytes, msgHash).getEncoded(false);
String pk = ByteUtil.byte2hex(pkBytes).substring(2);
if (verkey.equals(pk)) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("sm2 verify error ", e);
return false;
}
}
/**
* 加密
*/
public static String crypt(String verkey, String messageData) {
try {
byte[] rawBytes = SM2Key.encryptWithRandomKey(messageData.getBytes(), verkey);
String rawData = ByteUtil.byte2hex(rawBytes);
return rawData;
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("sm2 crypt error ", e);
return null;
}
}
/**
* 解密
*/
public static String decrypt(String key, String encryptedMessage) {
BigInteger privKey = new BigInteger(key, 16);
SM2Key sM2Key = SM2Key.fromPrivate(privKey);
byte[] rawData = ByteUtil.hex2byte(encryptedMessage);
try {
byte[] messageDataBytes = sM2Key.decryptWithRandomKey(rawData);
String messageData = new String(messageDataBytes);
return messageData;
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("sm2 decrypt error ", e);
return null;
}
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/Goligory/article/details/135465772
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!