数据结构:3_栈和队列
发布时间:2024年01月24日
栈和队列
一.栈
1. 栈的概念及结构
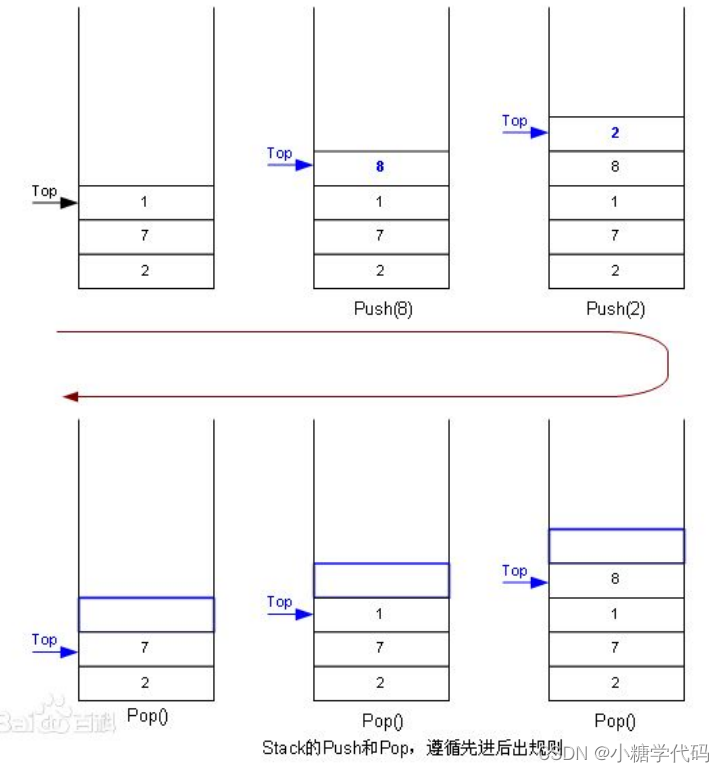
- 栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。**进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。**栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
- 压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
- 出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。

2. 栈的实现
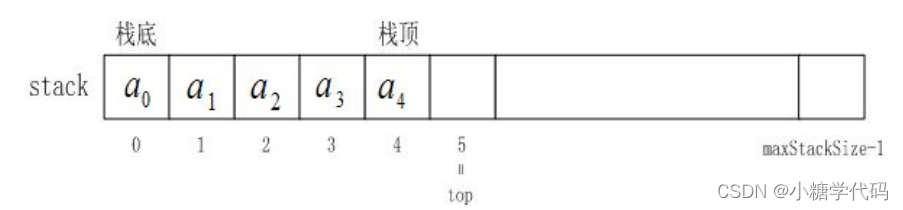
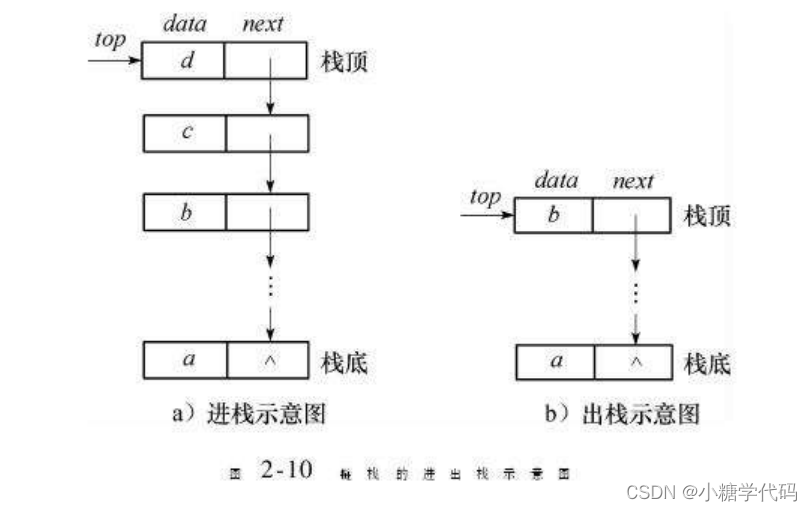
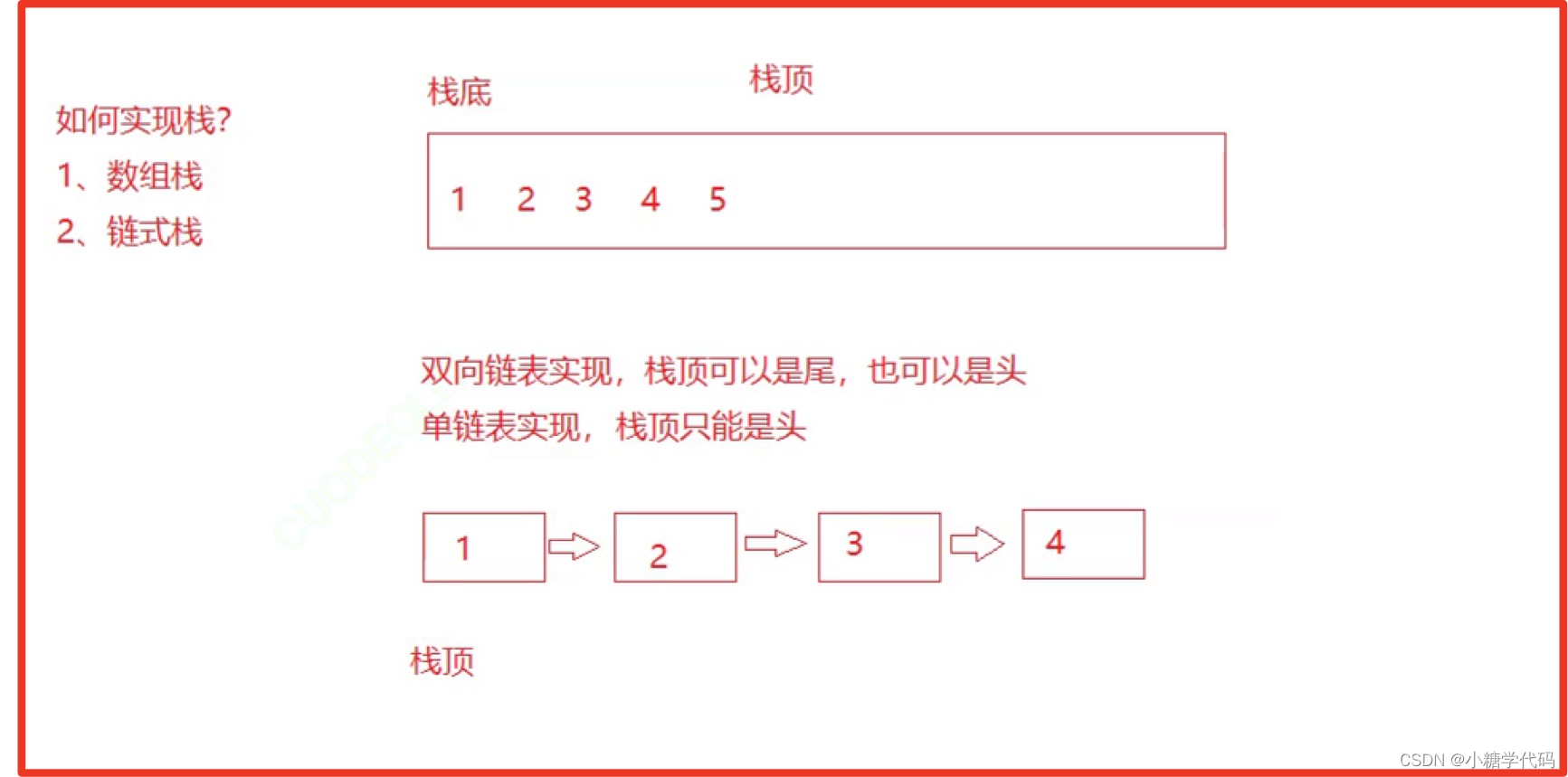
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
// 下面是定长的静态栈的结构,实际中一般不实用,所以我们主要实现下面的支持动态增长的栈
typedef int STDataType;
#define N 10
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType _a[N];
int _top; // 栈顶
}Stack;
// 支持动态增长的栈
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* _a;
int _top; // 栈顶
int _capacity; // 容量
}Stack;
// 初始化栈
void StackInit(Stack* ps);
// 入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, STDataType data);
// 出栈
void StackPop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(Stack* ps);
// 获取栈中有效元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps);
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
int StackEmpty(Stack* ps);
// 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(Stack* ps);
//栈的实现
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; // 标识栈顶位置的
int capacity;
}ST;
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
// 表示top指向栈顶元素的下一个位置
pst->top = 0;
// 表示top指向栈顶元素
//pst->top = -1;
}
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
// 栈顶插入删除
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
// 不为空
assert(pst->top > 0);
pst->top--;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
// 不为空
assert(pst->top > 0);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
/*if (pst->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}*/
return pst->top == 0;
}
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
- 注意:

二.队列
1. 队列的概念及结构
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
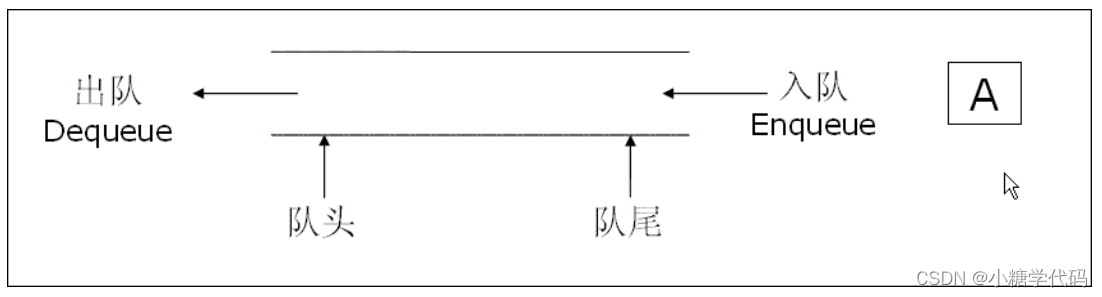
2. 队列的实现
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
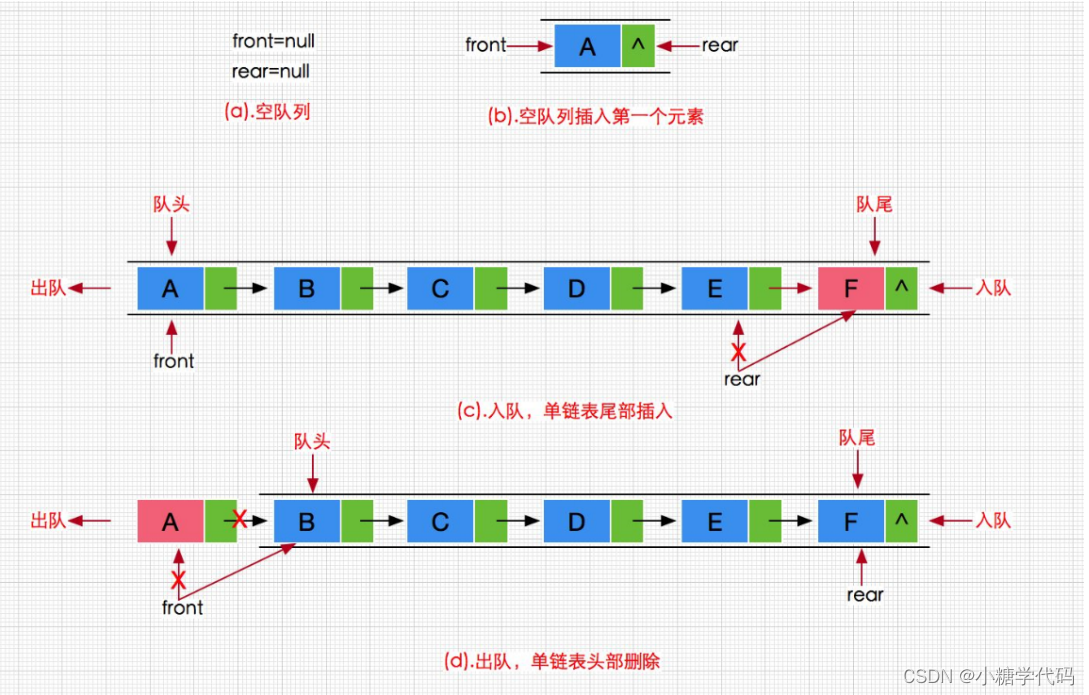
// 链式结构:表示队列
typedef struct QListNode
{
struct QListNode* _pNext;
QDataType _data;
}QNode;
// 队列的结构
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* _front;
QNode* _rear;
}Queue;
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* q);
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* q, QDataType data);
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* q);
// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* q);
// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* q);
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* q);
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Queue* q);
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* q);
//队列的实现
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType val;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
pq->ptail = pq->phead = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
QNode* del = pq->phead;
pq->phead = pq->phead->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
if (pq->phead == NULL)
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->val;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->ptail);
return pq->ptail->val;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
三.栈和队列面试题
1. 有效的括号
https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/description/
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; //标识栈顶位置的
int capacity;
}ST;
void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDetory(ST* pst);
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* pst);
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
int STSize(ST* pst);
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
// 表示top指向栈顶元素的下一个位置
pst->top = 0;
// 表示top指向栈顶元素
//pst->top = -1;
}
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
pst->top--;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
bool isValid(char* s) {
ST st;
STInit(&st);
while(*s)
{
//顺序不匹配
if(*s=='('||*s=='['||*s=='{')
{
STPush(&st,*s);
}
else
{
if(st.top==0)
{
STDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
char top=STTop(&st);
STPop(&st);
if(*s==')'&&top!='('||
*s==']'&&top!='['||
*s=='}'&&top!='{')
{
STDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
}
s++;
}
if(st.top!=0)
{
STDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
STDestroy(&st);
return true;
}
2. 用队列实现栈
https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/description/
-
- 一个队列存数据
-
- 另一个队列用来出数据时,导数据
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QDataType val;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
pq->ptail = pq->phead = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
QNode* del = pq->phead;
pq->phead = pq->phead->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
if (pq->phead == NULL)
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->val;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->ptail);
return pq->ptail->val;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* pst=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&pst->q1);
QueueInit(&pst->q2);
return pst;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* emptyq=&obj->q1;
Queue* nonemptyq=&obj->q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
emptyq=&obj->q2;
nonemptyq=&obj->q1;
}
while(QueueSize(nonemptyq)>1)
{
QueuePush(emptyq,QueueFront(nonemptyq));
QueuePop(nonemptyq);
}
int top=QueueFront(nonemptyq);
QueuePop(nonemptyq);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
/**
* Your MyStack struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack* obj = myStackCreate();
* myStackPush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myStackPop(obj);
* int param_3 = myStackTop(obj);
* bool param_4 = myStackEmpty(obj);
* myStackFree(obj);
*/
3. 用栈实现队列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/
//法一:
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; // 标识栈顶位置的
int capacity;
}ST;
void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDestroy(ST* pst);
// 栈顶插入删除
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* pst);
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
int STSize(ST* pst);
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
// 表示top指向栈顶元素的下一个位置
pst->top = 0;
// 表示top指向栈顶元素
//pst->top = -1;
}
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
// 栈顶插入删除
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
// 不为空
assert(pst->top > 0);
pst->top--;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
// 不为空
assert(pst->top > 0);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
/*if (pst->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}*/
return pst->top == 0;
}
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
typedef struct {
ST q1;
ST q2;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* pst=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
STInit(&pst->q1);
STInit(&pst->q2);
return pst;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
if(!STEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
STPush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else
{
STPush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
ST* emptyq=&obj->q1;
ST* nonemptyq=&obj->q2;
if(!STEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
emptyq=&obj->q2;
nonemptyq=&obj->q1;
}
while(STSize(nonemptyq)>0)
{
STPush(emptyq,STTop(nonemptyq));
STPop(nonemptyq);
}
int top =STTop(emptyq);
STPop(emptyq);
while(STSize(emptyq)>0)
{
STPush(nonemptyq,STTop(emptyq));
STPop(emptyq);
}
return top;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
ST* emptyq=&obj->q1;
ST* nonemptyq=&obj->q2;
if(!STEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
emptyq=&obj->q2;
nonemptyq=&obj->q1;
}
while(STSize(nonemptyq)>0)
{
STPush(emptyq,STTop(nonemptyq));
STPop(nonemptyq);
}
int top =STTop(emptyq);
while(STSize(emptyq)>0)
{
STPush(nonemptyq,STTop(emptyq));
STPop(emptyq);
}
return top;
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return STEmpty(&obj->q1)&&STEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
STDestroy(&obj->q1);
STDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
/**
* Your MyQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = myQueueCreate();
* myQueuePush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myQueuePop(obj);
* int param_3 = myQueuePeek(obj);
* bool param_4 = myQueueEmpty(obj);
* myQueueFree(obj);
*/
//法二:
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; // 标识栈顶位置的
int capacity;
}ST;
void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDestroy(ST* pst);
// 栈顶插入删除
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* pst);
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
int STSize(ST* pst);
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
// 表示top指向栈顶元素的下一个位置
pst->top = 0;
// 表示top指向栈顶元素
//pst->top = -1;
}
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
// 栈顶插入删除
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
// 不为空
assert(pst->top > 0);
pst->top--;
}
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
// 不为空
assert(pst->top > 0);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
/*if (pst->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}*/
return pst->top == 0;
}
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
typedef struct {
ST pushst;
ST popst;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* pst=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
STInit(&pst->pushst);
STInit(&pst->popst);
return pst;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
STPush(&obj->pushst,x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
int top;
if(!STEmpty(&obj->popst))
{
top =STTop(&obj->popst);
STPop(&obj->popst);
}
else
{
while(STSize(&obj->pushst)>0)
{
STPush(&obj->popst,STTop(&obj->pushst));
STPop(&obj->pushst);
}
top =STTop(&obj->popst);
STPop(&obj->popst);
}
return top;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
int top;
if(!STEmpty(&obj->popst))
{
top =STTop(&obj->popst);
}
else
{
while(STSize(&obj->pushst)>0)
{
STPush(&obj->popst,STTop(&obj->pushst));
STPop(&obj->pushst);
}
top =STTop(&obj->popst);
}
return top;
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return STEmpty(&obj->pushst)&&STEmpty(&obj->popst);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
STDestroy(&obj->pushst);
STDestroy(&obj->popst);
free(obj);
}
/**
* Your MyQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = myQueueCreate();
* myQueuePush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myQueuePop(obj);
* int param_3 = myQueuePeek(obj);
* bool param_4 = myQueueEmpty(obj);
* myQueueFree(obj);
*/
4. 设计循环队列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/design-circular-queue/description/
typedef struct {
int* a;
int front;
int back;
int k;
} MyCircularQueue;
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj);
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj);
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue* obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
obj->a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int*)*(k+1));
obj->front=0;
obj->back=0;
obj->k=k;
return obj;
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->a[obj->back]=value;
obj->back=(obj->back+1)%(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->front=(obj->front+1)%(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
return obj->a[obj->front];
}
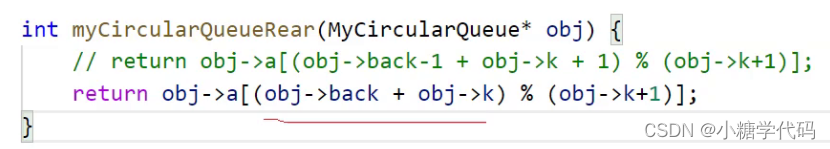
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
{
return -1;
}
if(obj->back==0)
{
return obj->a[obj->k];
}
else
{
return obj->a[obj->back-1];
}
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->front==obj->back;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return (obj->back+1)%(obj->k+1)==obj->front;
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
free(obj->a);
free(obj);
}
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularQueue* obj = myCircularQueueCreate(k);
* bool param_1 = myCircularQueueEnQueue(obj, value);
* bool param_2 = myCircularQueueDeQueue(obj);
* int param_3 = myCircularQueueFront(obj);
* int param_4 = myCircularQueueRear(obj);
* bool param_5 = myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj);
* bool param_6 = myCircularQueueIsFull(obj);
* myCircularQueueFree(obj);
*/
- 优化写法
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/Open__Ai/article/details/135819519
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 入门IC必读书目推荐!你真的不能错过
- 48 分布式id的生成策略
- 笙默考试管理系统-MyExamTest----codemirror(68)
- 运算符的优先级
- YOLOv8-Seg改进:轻量化改进 | MobileNetV3,轻量级骨架首选
- 2000~2020年全球日光诱导叶绿素荧光SIF数据分享
- C++: string类
- git仓库操作之二:git迁移仓库地址并保留分支和历史提交
- concrt140.dll丢失怎么恢复?分享给你六种方法用于解决问题
- 《数据库开发实践》之触发器