Python自动化脚本高效应对重复工作

更多资料获取
📚 个人网站:ipengtao.com
在日常工作和生活中,我们往往会遇到许多重复性的任务,这不仅浪费时间,还降低了效率。幸运的是,Python作为一门强大而灵活的编程语言,可以帮助我们自动化这些重复任务,从而解放双手,提高工作效率。本文将介绍实用的Python自动化脚本,涵盖了文件操作、数据处理、网络爬虫等多个领域,通过详细的内容和丰富的示例代码,帮助读者更好地理解和运用这些脚本。
文件操作
1 批量重命名文件
有时需要批量重命名一组文件,可以使用Python的os模块和正则表达式来实现:
import os
import re
def batch_rename_files(folder_path, pattern, replacement):
for filename in os.listdir(folder_path):
new_filename = re.sub(pattern, replacement, filename)
os.rename(os.path.join(folder_path, filename), os.path.join(folder_path, new_filename))
# 示例:将所有文件中的"_old"替换为"_new"
batch_rename_files('/path/to/files', r'_old', '_new')
2 查找最大文件
查找文件夹中占用空间最大的文件,可以使用os.path.getsize函数:
import os
def find_largest_file(folder_path):
largest_file = max((os.path.join(folder_path, filename) for filename in os.listdir(folder_path)),
key=os.path.getsize)
return largest_file
# 示例:查找目录中最大的文件
largest_file_path = find_largest_file('/path/to/files')
print(f"The largest file is: {largest_file_path}")
数据处理
1 CSV文件处理
处理CSV文件是日常工作中常见的任务,使用pandas库可以简化这个过程:
import pandas as pd
def process_csv(input_path, output_path):
df = pd.read_csv(input_path)
# 进行数据处理,这里只是个示例
df['new_column'] = df['old_column'] * 2
df.to_csv(output_path, index=False)
# 示例:处理CSV文件
process_csv('/path/to/input.csv', '/path/to/output.csv')
2 数据库操作
与数据库交互时,使用sqlite3库可以轻松执行SQL查询:
import sqlite3
def execute_sql_query(database_path, query):
connection = sqlite3.connect(database_path)
cursor = connection.cursor()
cursor.execute(query)
result = cursor.fetchall()
connection.close()
return result
# 示例:执行SQL查询
query_result = execute_sql_query('/path/to/database.db', 'SELECT * FROM table_name')
print(f"Query Result: {query_result}")
网络爬虫
1 网页内容抓取
使用requests库可以轻松获取网页内容:
import requests
def fetch_web_content(url):
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
return response.text
else:
return None
# 示例:抓取网页内容
web_content = fetch_web_content('https://www.example.com')
print(f"Web Content: {web_content}")
2 图片下载
下载网络上的图片也是一项常见的任务,使用urllib库:
import urllib.request
def download_image(url, save_path):
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, save_path)
# 示例:下载图片
download_image('https://www.example.com/image.jpg', '/path/to/save/image.jpg')
自动化办公
1 发送邮件
使用smtplib库可以编写脚本自动发送邮件:
import smtplib
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
def send_email(sender_email, receiver_email, subject, message, smtp_server, smtp_port, username, password):
msg = MIMEText(message)
msg['Subject'] = subject
msg['From'] = sender_email
msg['To'] = receiver_email
with smtplib.SMTP(smtp_server, smtp_port) as server:
server.starttls()
server.login(username, password)
server.sendmail(sender_email, receiver_email, msg.as_string())
# 示例:发送邮件
send_email('sender@example.com', 'receiver@example.com', 'Subject', 'Hello, this is a test email.',
'smtp.example.com', 587, 'your_username', 'your_password')
2 定时任务
使用schedule库可以轻松实现定时任务:
import schedule
import time
def job():
print("Task is running...")
# 示例:每隔一小时执行任务
schedule.every().hour.do(job)
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
网络服务监控
1 HTTP服务状态检查
使用requests库可以定时检查HTTP服务的状态:
import requests
import schedule
import time
def check_http_service(url):
try:
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
print(f"The service at {url} is UP.")
else:
print(f"The service at {url} is DOWN with status code {response.status_code}.")
except requests.ConnectionError:
print(f"Could not connect to the service at {url}.")
# 示例:每隔5分钟检查一次HTTP服务状态
schedule.every(5).minutes.do(check_http_service, url='https://www.example.com')
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
2 日志监控
监控日志文件,定时检查是否有错误或异常信息:
import re
import schedule
import time
def monitor_log_file(log_file_path, error_pattern):
with open(log_file_path, 'r') as file:
log_content = file.read()
if re.search(error_pattern, log_content):
print("Error detected in the log file!")
# 示例:每小时检查一次日志文件
schedule.every().hour.do(monitor_log_file, log_file_path='/path/to/logfile.log', error_pattern='ERROR')
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
数据备份与同步
1 文件备份
定时备份文件到指定目录:
import shutil
import schedule
import time
def backup_files(source_folder, destination_folder):
timestamp = time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S")
backup_folder = f"{destination_folder}/backup_{timestamp}"
shutil.copytree(source_folder, backup_folder)
# 示例:每天备份一次文件夹
schedule.every().day.at("02:00").do(backup_files, source_folder='/path/to/files', destination_folder='/path/to/backup')
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
2 数据库备份
定时备份数据库到指定目录:
import subprocess
import schedule
import time
def backup_database(database_name, username, password, destination_folder):
timestamp = time.strftime("%Y%m%d%H%M%S")
backup_file = f"{destination_folder}/backup_{database_name}_{timestamp}.sql"
subprocess.run(['mysqldump', '-u', username, '-p' + password, database_name, '>', backup_file])
# 示例:每周备份一次数据库
schedule.every().week.at("03:00").do(backup_database, database_name='mydb', username='admin', password='admin123', destination_folder='/path/to/backup')
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
图像处理
1 图片压缩
使用PIL库对图片进行压缩:
from PIL import Image
import os
def compress_images(source_folder, destination_folder, quality=85):
for filename in os.listdir(source_folder):
if filename.endswith(".jpg"):
image_path = os.path.join(source_folder, filename)
img = Image.open(image_path)
img.save(os.path.join(destination_folder, filename), 'JPEG', quality=quality)
# 示例:批量压缩图片
compress_images('/path/to/source', '/path/to/compressed', quality=75)
2 图片水印
为图片添加水印,使用PIL库:
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
def add_watermark(image_path, output_path, watermark_text):
img = Image.open(image_path)
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
font = ImageFont.load_default()
draw.text((10, 10), watermark_text, (255, 255, 255), font=font)
img.save(output_path)
# 示例:为图片添加水印
add_watermark('/path/to/image.jpg', '/path/to/output.jpg', 'Watermark Text')
定制脚本
1 任务调度器
使用schedule库创建自定义的任务调度器:
import schedule
import time
def custom_scheduler():
print("Custom Scheduler is running...")
# 示例:每隔30秒执行一次任务调度器
schedule.every(30).seconds.do(custom_scheduler)
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
2 文件监控器
监控文件夹中文件的变化:
import os
import time
def file_monitor(folder_path):
current_files = set(os.listdir(folder_path))
while True:
time.sleep(5)
updated_files = set(os.listdir(folder_path))
if current_files != updated_files:
print("Files in the folder have changed.")
current_files = updated_files
# 示例:监控文件夹变化
file_monitor('/path/to/files')
总结
在这篇文章中,深入探讨了解决重复任务的10个Python自动化脚本,涵盖了多个领域,包括文件操作、数据处理、网络爬虫、自动化办公、网络服务监控、数据备份与同步、以及图像处理。通过详细的示例代码和解释,读者能够全面了解每个脚本的实现原理和实际应用场景。
从文件操作中的批量重命名到网络服务监控的定时检查,再到数据备份与同步的数据库和文件备份,每个脚本都展示了Python的灵活性和强大功能。这些脚本不仅提高了工作效率,还降低了手动操作可能带来的错误风险。
同时,介绍了网络爬虫的应用,包括网页内容抓取和图片下载,展示了Python在数据获取方面的优势。图像处理领域中,通过图片压缩和添加水印的实例,展示了Python在处理图像任务上的便捷性。
最后,还创建了自定义的任务调度器和文件监控器,突显了Python在定制脚本方面的强大表现。这些脚本不仅仅是实用工具,更是启发更多创意和实践的媒介。
通过阅读这篇文章,可以加深对Python自动化脚本的理解,并在实际工作中灵活运用,提高工作效率,实现任务自动化,为更有趣、更高效的编程体验打开新的可能性。
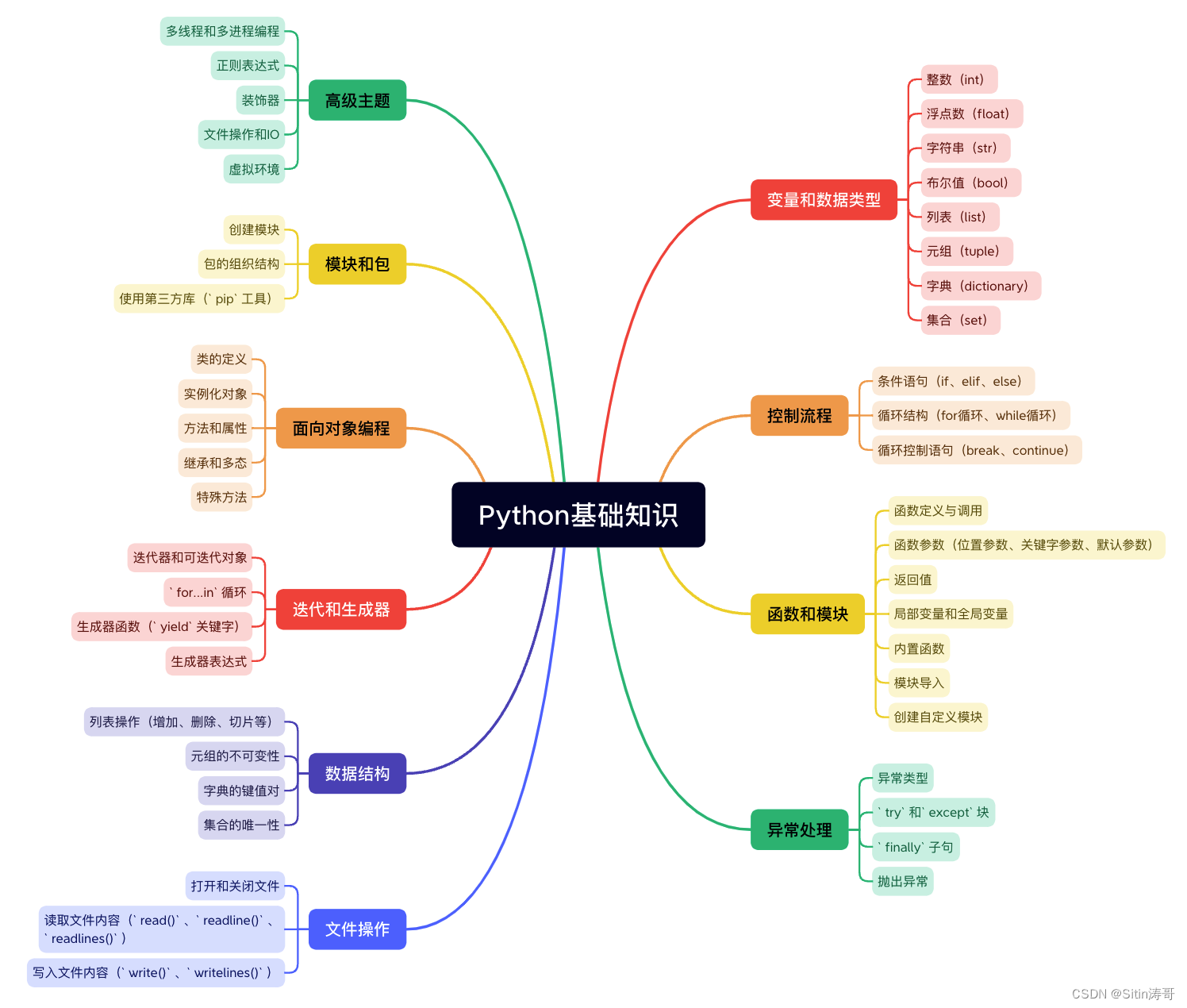
Python学习路线
更多资料获取
📚 个人网站:ipengtao.com
如果还想要领取更多更丰富的资料,可以点击文章下方名片,回复【优质资料】,即可获取 全方位学习资料包。
点击文章下方链接卡片,回复【优质资料】,可直接领取资料大礼包。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 装饰装潢企业网站建设的效果如何
- 代码随想录算法训练营第21天 |530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对差 501.二叉搜索树中的众数 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
- Collections.reverse对list进行反转
- 【Java 设计模式】创建型之抽象工厂模式
- 国考省考行测:语句排序,选择首句、选择尾句
- Python高级编程之IO模型与协程详解
- 华为鸿蒙应用--欢迎页SplashPage+倒计时跳过(自适应手机和平板)-ArkTs
- 每日算法打卡:逆序对的数量 day 24
- 如何修复concrt140.dll丢失问题,分享4种有效的方法
- Color Control