TikTok真题第11天 | 1249.移除无效的括号、23.合并K个升序链表、773.滑动谜题
今天开始整hard题,果然费时。
1249.移除无效的括号
题目链接:1249.minimum-remove-to-make-valid-parentheses
解法:
这个题用栈来处理,用栈来记录左括号的位置,同时用一个向量来记录左括号和右括号是否有效(有效则不需要删除)。
如果遇到左括号,那么栈中弹入,同时该位置为无效(需要删除),待后面遇到右括号再置为有效。
如果遇到右括号,那么如果栈为空(前面没有左括号可以匹配),那么该位置无效;如果栈不为空,那么该位置有效,且把前面左括号(栈顶元素)改为有效。
最后把有效的元素取出来即可。
还有一种做法是直接在遍历字符的过程中,记录左括号,并且即时删除无效的右括号,最后遍历结束再删除左括号。这种即时删除的写法会在遍历过程中就改变字符串s,感觉还是容易出错,所以推荐遍历结束后,再同一删除。
参考题解:栈
边界条件:无
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
class Solution {
public:
string minRemoveToMakeValid(string s) {
stack<int> leftStack;
// 如果是有效的,那么值为true
vector<bool> validIdx(s.size(), true);
for (int i=0; i<s.size(); i++) {
if (s[i]=='(') {
leftStack.push(i);
// 暂时没匹配到右括号,所以目前是无效
validIdx[i] = false;
} else if (s[i]==')') {
if (leftStack.empty()) {
// 没有左括号,所以右括号无效
validIdx[i] = false;
} else {
// 前面的左括号改为有效
// 右括号初始化为有效,所以不用改
validIdx[leftStack.top()] = true;
leftStack.pop();
}
}
}
string res;
for (int i=0; i<s.size(); i++) {
if (validIdx[i]) {
res += s[i];
}
}
return res;
}
};23.合并K个升序链表
解法:
(1)第一种方法是优先队列,即构造小根堆(队首元素最小),然后把所有链表添加到优先队列中,那么从队首到队尾是根据val进行升序排列的。
建立一个虚拟头节点,每次都把val最小的node添加作为next,同时把该node的next添加到优先队列中。最近返回虚拟头节点的next即可。
优先队列的思路比较好理解。
(2)第二种方法是分治合并。将?k个链表两两配对并将同一对中的链表合并;不断重复这个过程,直到剩下一个链表。
参考题解:优先队列
边界条件:
优先队列的复杂度:

分治合并的复杂度:

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
// 优先队列
class Solution {
public:
struct Status {
int val;
ListNode *ptr;
// 重载小于操作符,val大的反而认为是小的
// 因为优先队列默认是最大堆,即队首的元素是最大的,但是我们这里需要最小堆,所以把比较的逻辑反向
bool operator < (const Status& sta) const {
return val > sta.val;
}
};
// 注意元素是Status而不是Status*,所以取属性是通过 s.val 而不是 s->val
priority_queue<Status> q;
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
for (auto& node: lists) {
if (node) {
q.push({node->val, node});
}
}
ListNode head, *tail = &head;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto s = q.top();
q.pop();
tail->next = s.ptr;
tail = tail->next;
if (s.ptr->next) {
q.push({s.ptr->next->val, s.ptr->next});
}
}
// 注意head不是指针,而是一个真正的对象,所以使用.而不是->来获取
return head.next;
}
};/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
// 分治合并
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* a, ListNode* b) {
if ((!a) || (!b)) return a? a:b;
// 为啥不直接用 a和b 这俩指针呢
ListNode head, *tail=&head, *aPtr=a, *bPtr=b;
while (aPtr && bPtr) {
if (aPtr->val < bPtr->val) {
tail->next = aPtr;
aPtr = aPtr->next;
} else {
tail->next = bPtr;
bPtr = bPtr->next;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = (aPtr ? aPtr:bPtr);
return head.next;
}
ListNode* merge(vector<ListNode*>& lists, int l, int r) {
if (l==r) return lists[l];
if (l > r) return nullptr;
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
return mergeTwoLists(merge(lists, l, mid),merge(lists, mid+1, r));
}
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
return merge(lists, 0, lists.size()-1);
}
};773.滑动谜题
题目链接:773.sliding-puzzle
解法:
这个题实名表扬labuladong同志,题解写得很详细很通俗易懂,从0开始讲解,不需要前置知识。
这个题用BFS来处理,一次?移动?定义为选择?0?与一个相邻的数字(上下左右)进行交换,所以每次搜索的过程如下图所示:
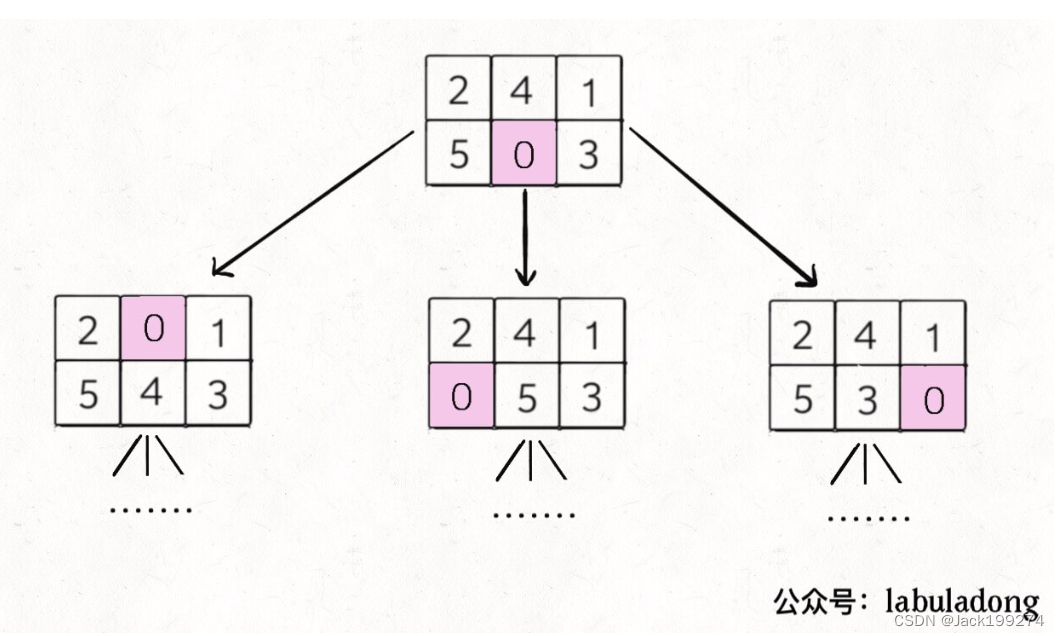
一直搜下去,直到第一次出现了目标矩阵,那返回交换次数即可。
?其他的看题解吧,题解写得不错。参考题解:labuladong的BFS
边界条件:

class Solution {
public:
int slidingPuzzle(vector<vector<int>>& board) {
int m = 2, n = 3;
string start;
string target = "123450";
// 将矩阵转为行优先的字符串
for (int i=0; i<m; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<n; j++) {
start += board[i][j] +'0';
}
}
// 记录一维字符串中i位置的相邻索引
vector<vector<int>> neighbor = {
{1,3},
{0,4,2},
{1,5},
{0,4},
{3,1,5},
{4,2}
};
queue<string> q;
unordered_set<string> visited;
q.push(start);
visited.insert(start);
int step = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int size = q.size();
for (int i=0; i<size; i++) {
string cur = q.front();
q.pop();
// 如果已经调整为目标矩阵,则返回结果
if (cur == target) return step;
// 找到数字0的索引
int idx = 0;
while (cur[idx]!='0') {
idx++;
}
// 将数字0与相邻数字交换位置
for (int adj: neighbor[idx]) {
string newBorad = cur;
swap(newBorad[adj], newBorad[idx]);
if (!visited.count(newBorad)) {
q.push(newBorad);
visited.insert(newBorad);
}
}
}
step++;
}
return -1;
}
};本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Java医院信息管理系统
- Redis和MySQL如何保持数据一致性
- 关于Python里xlwings库对Excel表格的操作(三十二)
- 初识STL
- vue-drag-resize-rotate 拖拉拽旋转
- 拼多多商品详情数据接口封装技术
- 超40k star的网络请求库,助你打造优质Android应用
- 【科研】[3.番外篇] 常见基础科研词汇的介绍!非常基础的一期,大家选择观看哟~
- 问题:java:无效的目标发行版:11(报错)
- 员工考勤管理难题,今天终于有答案了!