C++-赋值-string字符串类-函数
发布时间:2023年12月29日
赋值
1)通常编程中使用=进行赋值操作,C++增加了一些新的赋值语法。
#include?<iostream>
using namespace?std;
int main()
{
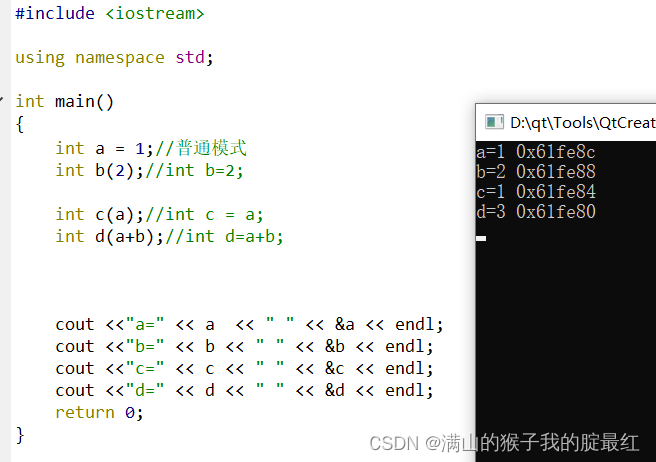
int?a?= 1;//普通模式
int b(2);//int?b=2;
int c(a);//int?c?=?a;
int d(a+b);//int?d=a+b;
????cout?<<"a=" <<?a??<< "?" << &a?<<?endl;
????cout?<<"b=" <<?b?<< "?" << &b?<<?endl;
????cout?<<"c=" <<?c?<< "?" << &c?<<?endl;
????cout?<<"d=" <<?d?<< "?" << &d?<<?endl;
return 0;
}
2)在C++11?又进行了升级
#include?<iostream>
using namespace?std;
int main()
{
int a(1);
????cout?<<?a?<<?endl;
double?b?= 2.42;
int?c{b}; //?升级:对数据窄化做出警告
int d(b);
int?e?=?b;
????cout?<<?b?<<?endl;
????cout?<<?c?<< "?" <<?d?<<?endl;
return 0;
}

键盘输入
可以使用cin把用户在命令行中输入的内容复制到变量当中。
cin与cout一样,都属于头文件iostream中的标准输入输出流。
#include?<iostream>
using namespace?std;
int main()
{
//?C++?的字符串是string
????string?str;
int?a?= 0;
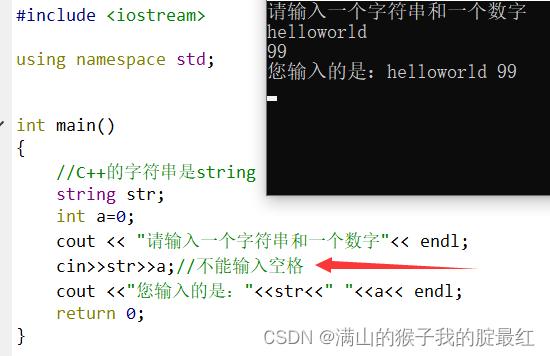
????cout?<< "请输入一个字符串和一个数字" <<?endl;
????cin?>>?str?>>?a; //?接收键盘输入,不能有空格??空格会结束输入
????cout?<< "您输入的是:" <<?str?<< "?" <<?a?<<?endl;
return 0;
}
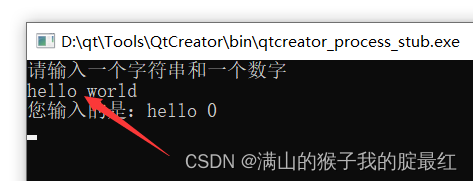
错误输入
string字符串类
string不是C++的基本数据类型,他是一个C++标准库中的字符串类。使用时需要引入头文件#include<string>,而不是string.h
string在绝大多数情况下可以替代C语言中的字符串,不用担心内存是否足够和字符串等等。其中内部还包含了很多字符串处理函数,可以完成各种情况下的字符串处理功能。
string和C语言相同,字符串编码使用ASCII编码,不支持中文。
size()\length()?计算字符串大小
#include?<iostream>
using namespace?std;
int main()
{
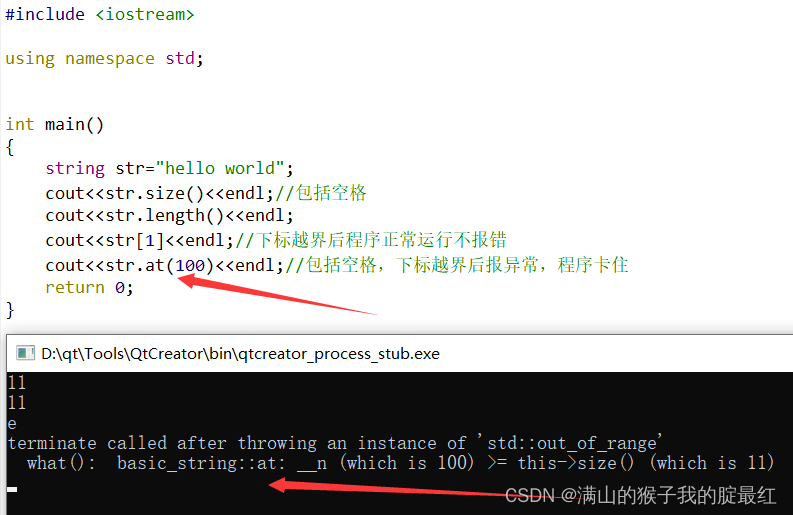
????string?str?= "helloworld";
????cout?<<?str.size() <<?endl; //?10
????cout?<<?str.length() <<?endl; //?10
????cout?<<?str[1] <<?endl; //?e
????cout?<<?str.at(5) <<?endl; //?w
return 0;
}

at函数:获取字符中某个字符
两种方式都可以,但是在C++当中更推荐使用at函数。原因是at函数更加安全。但是[?]的方式效率更高。
#include?<iostream>
using namespace?std;
int main()
{
????string?str?= "helloworld";
//????cout?<<?str[100]?<<?endl;?//?输出一个垃圾数据
//????cout?<<?str.at(100)?<<?endl;?//?程序停止运行
return 0;
}
string类支持多种遍历方式(for循环)
- 普通循环(以for循环为主)
- C++11?for?each循环,只能访问集合中的元素,但不能对其中的元素进行修改
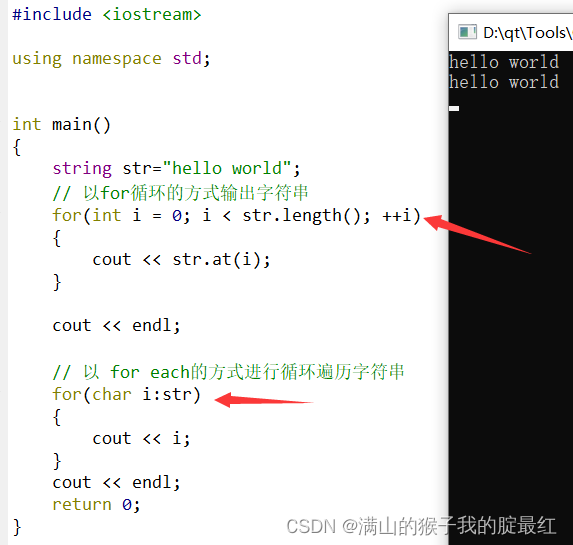
#include?<iostream>
using namespace?std;
int main()
{
????string?str?= "helloworld";
//?以for循环的方式输出字符串
for(int?i?= 0;?i?<?str.length(); ++i)
{
????????cout?<<?str.at(i);
}
????cout?<<?endl;
//?以?for?each的方式进行循环遍历字符串,结构简单,但有局限性
//foreach存在局限性,在循环遍历数组集合时,只能访问集合中的元素,但不能对其中的元素进行修改
for(char?i:str)
{
????????cout?<<?i;
}
return 0;
}
5函数
1?内联函数?inline
内联函数用于取代C语言中宏定义的函数,内联函数的正确使用可以提升程序的执行效率。内联函数在编译的时候,直接把函数体展开到主函数中遍历,在运行期间可以减少调用的开销。
通常将具有以下性质的函数写为内联函数:
- 代码长度5行以内
- 不包含复杂的控制语句
- 频繁被调用
内联函数关键字:inline
#include?<iostream>
using namespace?std;
inline void print_string(string?s)
{
????cout?<<?s?<<?endl;
}
int main()
{
print_string("hello");
return 0;
}
后续学的成员函数默认添加inline关键字修饰。
我们添加的inline关键字,将函数声明为内联函数。这个不是我们能决定的。编译器有自己的判断准则,我们只是给编译器提一个建议。具体是否能变成内联函数,还是编译器自己决定的。
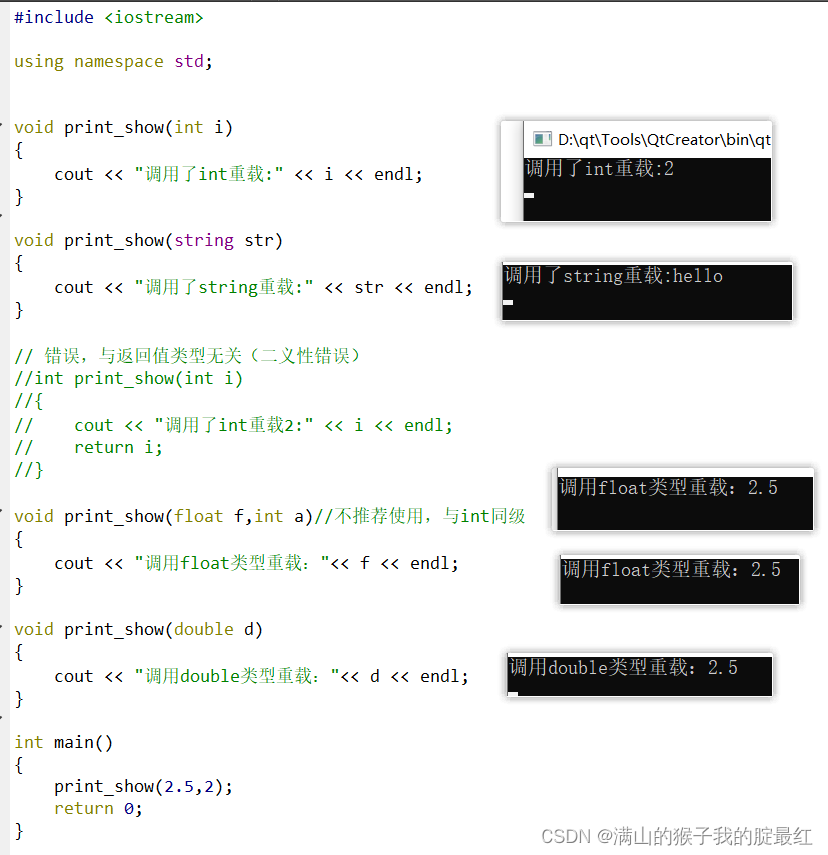
2?函数重载?overload
C++中允许多个函数使用同一个名称,这种用法就是函数重载。函数重载要求函数名称相同,但是参数不同(类型或者数量)或者前后顺序不同。与返回值?等其他因素无关。
相同优先级也会有二异性,如:int、float同级
#include?<iostream>
using namespace?std;
void print_show(int?i)
{
????cout?<< "调用了int重载:" <<?i?<<?endl;
}
void print_show(string?str)
{
????cout?<< "调用了string重载:" <<?str?<<?endl;
}
//?错误,与返回值类型无关(二义性错误)
//int?print_show(int?i)
//{
//????cout?<<?"调用了int重载2:"?<<?i?<<?endl;
//????return?i;
//}
void print_show(float?f)
{
????cout?<< "调用float类型重载:"<<?f?<<?endl;
}
void print_show(double?d)
{
????cout?<< "调用double类型重载:"<<?d?<<?endl;
}
int main()
{
print_show(2);
return 0;
}
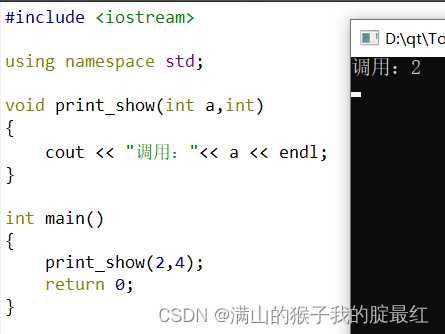
3?哑元函数
函数的参数只有类型,没有名称
#include?<iostream>
using namespace?std;
void print_show(int?a,int)
{
????cout?<< "调用:"<<?a?<<?endl;
}
int main()
{
print_show(2,4);
return 0;
}
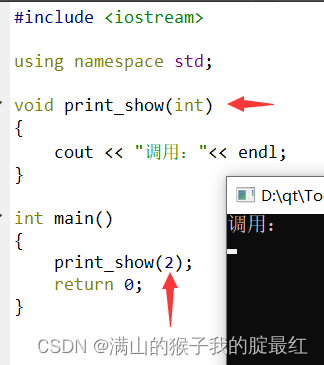
作用1:“哑元函数用来区分函数重载”
作用2:运算符重载中会用到?1
#include?<iostream>
using namespace?std;
void print_show(int?a,int)
{
????cout?<< "调用1:"<<?a?<<?endl;
}
void print_show(int?a)
{
????cout?<< "调用2:"<<?a?<<?endl;
}
int main()
{
print_show(2);
return 0;
}

文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_74937538/article/details/135282597
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- SpringBoot 整合 Redis 缓存
- Python Generator函数的实例详解
- 分享超级好用的视频网站
- 《绝地求生大逃杀》画面声音设置与单排技巧
- Unity DOTS物理引擎的核心分析与详解
- 【日常聊聊】运维工程师的职业发展路径解析
- Spring Cloud Alibaba nacos配置中心
- 利用哈希传递登录 RDP 远程桌面
- MSVS C# Matlab的混合编程系列1 - 看似简单的问题引出
- MyBatis 使用报错:org.xml.sax.SAXParseException 元素内容必须由格式正确的字符数据或标记组成