Shiro框架:Shiro内置过滤器源码解析
目录
2.1 DefaultFilterChainManager构造并注册内置过滤器
3.3.2?FormAuthenticationFilter
3.3.2.4?FormAuthenticationFilter处理逻辑
3.3.3?RolesAuthorizationFilter
?3.3.3.2?RolesAuthorizationFilter处理逻辑
3.3.4?PermissionsAuthorizationFilter
Shiro框架作为登录鉴权安全模块一款较为流行的开源框架,通过简单的配置即可完成登录鉴权配置,其中离不开Shiro较为丰富、且简单易用的内置过滤器,本文主要对Shiro多种内置过滤器进行源码解析,方便更好的深入透析其执行原理;
想要全面了解Shiro内置过滤器是如何通过Shiro自定义拦截器SpringShiroFilter进行注册构造的,可移步:Shiro框架:ShiroFilterFactoryBean过滤器源码解析-CSDN博客
1. 常见项目中过滤器配置
在Spring项目中应用Shiro进行登录鉴权安全模块开发配置时,我们会对指定的url配置访问控制策略,一种常见的url配置如下:
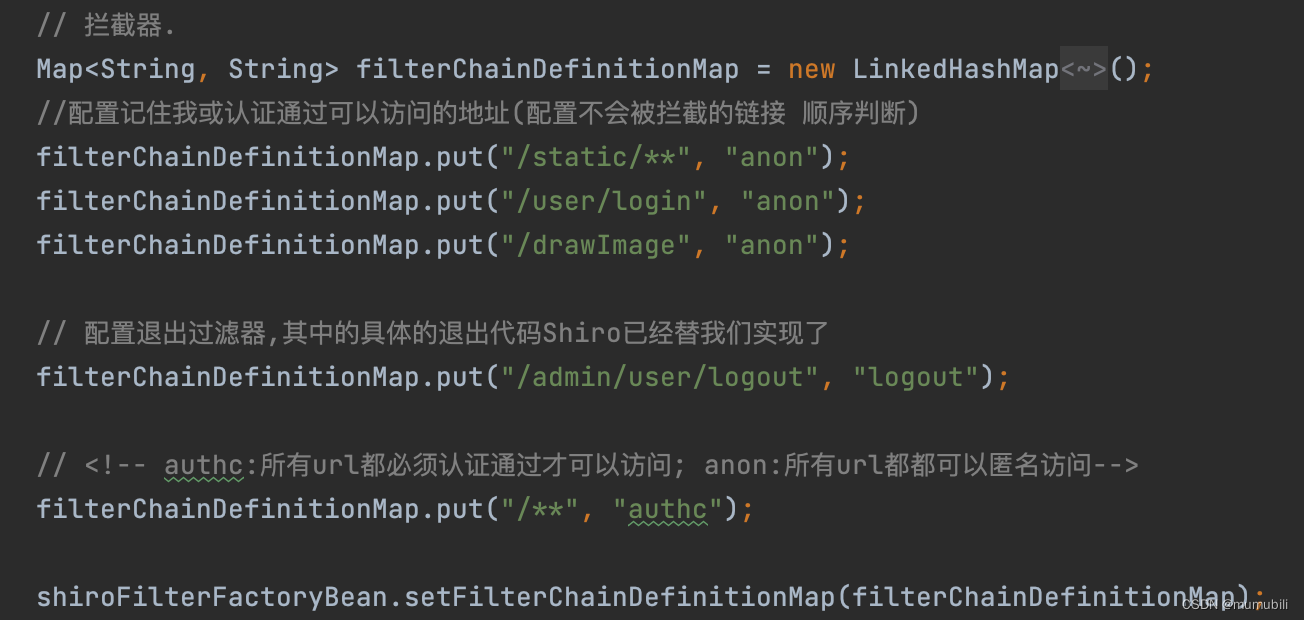
如上:
- anno:配置不会被拦截的url
- authc:配置必须认证通过才能访问的url
- logout:配置logout拦截器,执行退出处理流程
Shiro对如上Url的过滤器配置是如何解析的呢,下面对该解析过程进行详细说明;?
2.Url访问控制配置解析为内置过滤器?
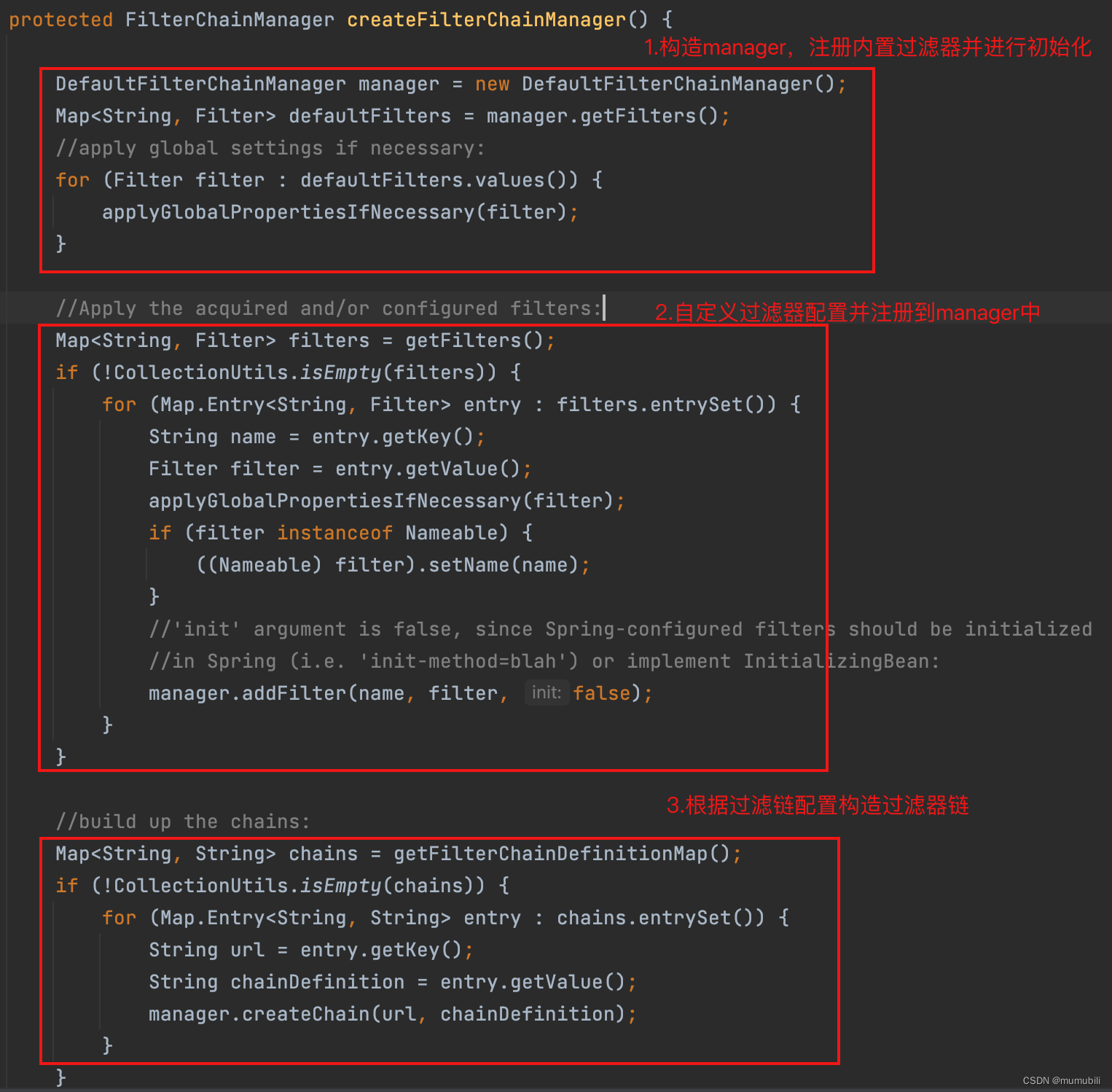
如上url过滤器配置添加到了ShiroFilterFactoryBean中,在ShiroFilterFactoryBean初始化bean的过程中,会对该过滤器配置进行解析;如下,其主要包含了以下几部分内容:
- 构造DefaultFilterChainManager,注册内置过滤器并初始化
- 自定义过滤器全局属性设置并注册
- Url过滤链配置解析,构造过滤器链
下面进行详细解析;
2.1 DefaultFilterChainManager构造并注册内置过滤器
注册内置过滤器逻辑主要在DefaultFilterChainManager构造函数中,如下:
public DefaultFilterChainManager() {
this.filters = new LinkedHashMap<String, Filter>();
this.filterChains = new LinkedHashMap<String, NamedFilterList>();
addDefaultFilters(false);
}
protected void addDefaultFilters(boolean init) {
for (DefaultFilter defaultFilter : DefaultFilter.values()) {
addFilter(defaultFilter.name(), defaultFilter.newInstance(), init, false);
}
}
protected void addFilter(String name, Filter filter, boolean init, boolean overwrite) {
Filter existing = getFilter(name);
if (existing == null || overwrite) {
if (filter instanceof Nameable) {
((Nameable) filter).setName(name);
}
if (init) {
initFilter(filter);
}
this.filters.put(name, filter);
}
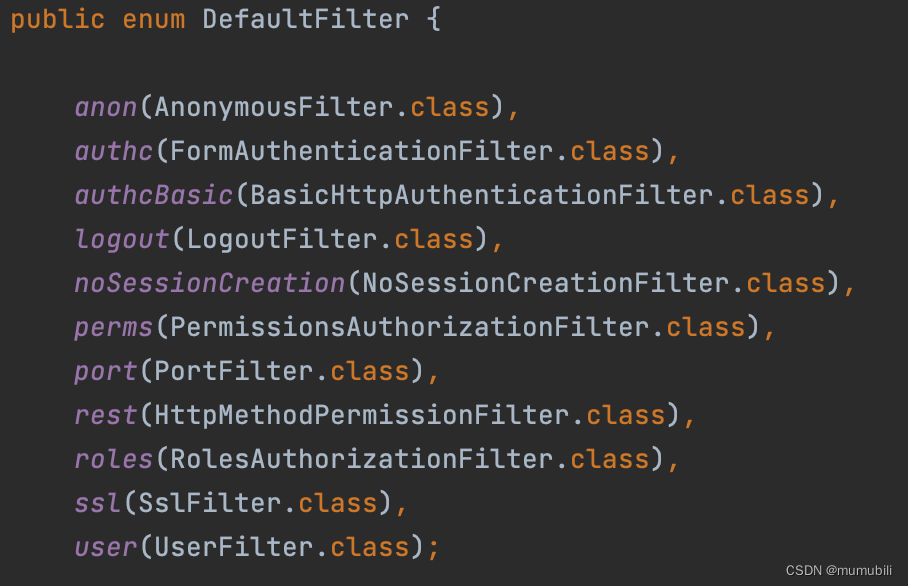
}通过遍历所有内置过滤器DefaultFilter.values()并实例化,完成了内置过滤器的注册;
内置过滤器枚举如下:
2.2 构造过滤器链
在完成内置过滤器以及自定义过滤器(如有)注册到DefaultFilterChainManager之后,下面对url过滤链配置进行解析,主要是通过过滤器名称(比如anno、auchc)映射到已注册的过滤器,具体过程如下:
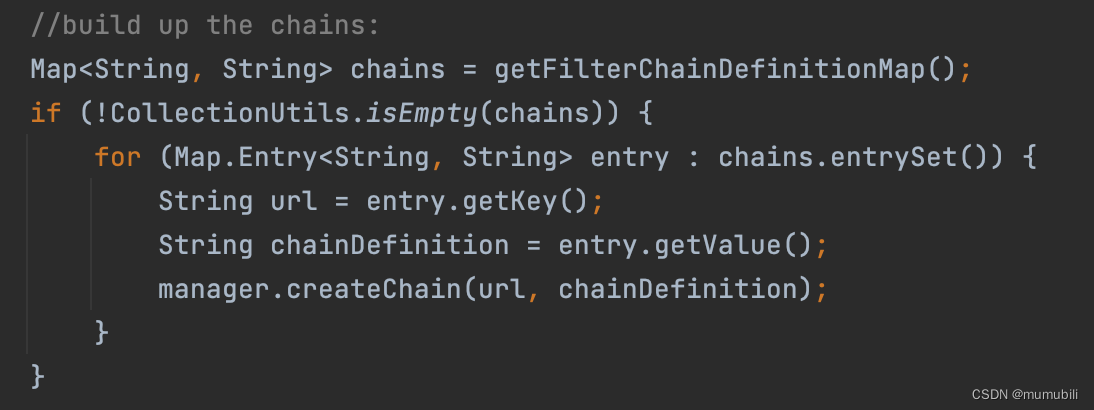
这里获取到前述已配置的url过滤器配置,并通过createChain方法构造过滤链,展开如下:
public void createChain(String chainName, String chainDefinition) {
String[] filterTokens = splitChainDefinition(chainDefinition);
//each token is specific to each filter.
//strip the name and extract any filter-specific config between brackets [ ]
for (String token : filterTokens) {
String[] nameConfigPair = toNameConfigPair(token);
//now we have the filter name, path and (possibly null) path-specific config. Let's apply them:
addToChain(chainName, nameConfigPair[0], nameConfigPair[1]);
}
}nameConfigPair[0]即为解析到的过滤器名称,继续跟踪addToChain方法如下:
public void addToChain(String chainName, String filterName, String chainSpecificFilterConfig) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(chainName)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("chainName cannot be null or empty.");
}
Filter filter = getFilter(filterName);
if (filter == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("There is no filter with name '" + filterName +
"' to apply to chain [" + chainName + "] in the pool of available Filters. Ensure a " +
"filter with that name/path has first been registered with the addFilter method(s).");
}
applyChainConfig(chainName, filter, chainSpecificFilterConfig);
NamedFilterList chain = ensureChain(chainName);
chain.add(filter);
}
public Filter getFilter(String name) {
return this.filters.get(name);
}
protected NamedFilterList ensureChain(String chainName) {
NamedFilterList chain = getChain(chainName);
if (chain == null) {
chain = new SimpleNamedFilterList(chainName);
this.filterChains.put(chainName, chain);
}
return chain;
}如上,getFilter方法根据过滤器名称获取已注册的过滤器,?ensureChain方法创建url对应的过滤器链,并添加上url映射到的过滤器;
至此,完成了Url访问控制配置解析为内置过滤器的解析;?
下面开始对本篇的核心内容-Shiro内置过滤器进行深入解析;
3. Shiro内置过滤器解析
3.1 内置过滤器概览
前述也给出了内置过滤器枚举的图示,如下:

其内部继承结构展示如下:
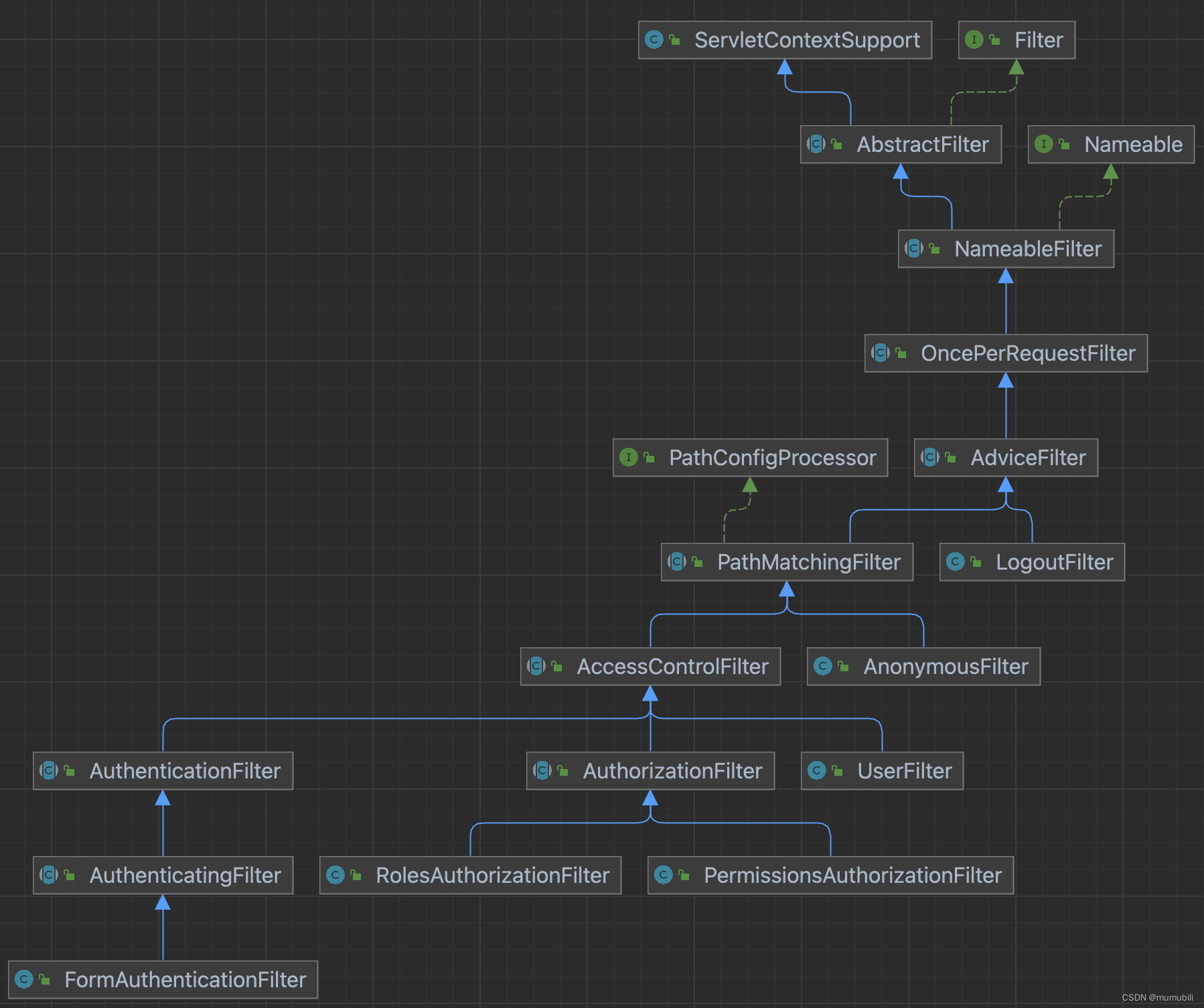
可以看到内置过滤器的种类以及类继承层次结构还是比较复杂的,我们已平时项目中较常用到的几种内置过滤器进行源码剖析,包括AnonymousFilter、FormAuthenticationFilter、RolesAuthorizationFilter、PermissionsAuthorizationFilter以及logout;
在具体分析内置过滤器之前,我们首先对继承结构中一些关键的类按照由上到下的顺序进行解析说明,方便更好的理解每个类继承层次的关键职责以及整体过滤器的处理逻辑,然后再对分别具体的内置过滤器进行解析;
3.2 公共继承类解析
3.2.1 顶层Filter接口
Servlet Filter接口,调用doFilter方法执行过滤逻辑:
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException;
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException;
public void destroy();3.2.2?AbstractFilter
实现了Servlet Filter的初始化方法init,并定义了onFilterConfigSet的空实现:
/**
* Sets the filter's {@link #setFilterConfig filterConfig} and then immediately calls
* {@link #onFilterConfigSet() onFilterConfigSet()} to trigger any processing a subclass might wish to perform.
*
* @param filterConfig the servlet container supplied FilterConfig instance.
* @throws javax.servlet.ServletException if {@link #onFilterConfigSet() onFilterConfigSet()} throws an Exception.
*/
public final void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
setFilterConfig(filterConfig);
try {
onFilterConfigSet();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (e instanceof ServletException) {
throw (ServletException) e;
} else {
if (log.isErrorEnabled()) {
log.error("Unable to start Filter: [" + e.getMessage() + "].", e);
}
throw new ServletException(e);
}
}
}
protected void onFilterConfigSet() throws Exception {
}3.2.3?NameableFilter
见名知义,定义了过滤器的名称,以及名称的解析逻辑:
/**
* The name of this filter, unique within an application.
*/
private String name;
/**
* Returns the filter's name.
* <p/>
* Unless overridden by calling the {@link #setName(String) setName(String)} method, this value defaults to the
* filter name as specified by the servlet container at start-up:
* <pre>
* this.name = {@link #getFilterConfig() getFilterConfig()}.{@link javax.servlet.FilterConfig#getFilterName() getName()};</pre>
*
* @return the filter name, or {@code null} if none available
* @see javax.servlet.GenericServlet#getServletName()
* @see javax.servlet.FilterConfig#getFilterName()
*/
protected String getName() {
if (this.name == null) {
FilterConfig config = getFilterConfig();
if (config != null) {
this.name = config.getFilterName();
}
}
return this.name;
}3.2.4?OncePerRequestFilter
实现了“每次请求、单次执行”的语义,内部是通过设置标志位属性的方式实现的,如下:
public final void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String alreadyFilteredAttributeName = getAlreadyFilteredAttributeName();
if ( request.getAttribute(alreadyFilteredAttributeName) != null ) {
log.trace("Filter '{}' already executed. Proceeding without invoking this filter.", getName());
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
} else //noinspection deprecation
if (/* added in 1.2: */ !isEnabled(request, response) ||
/* retain backwards compatibility: */ shouldNotFilter(request) ) {
log.debug("Filter '{}' is not enabled for the current request. Proceeding without invoking this filter.",
getName());
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
// Do invoke this filter...
log.trace("Filter '{}' not yet executed. Executing now.", getName());
request.setAttribute(alreadyFilteredAttributeName, Boolean.TRUE);
try {
doFilterInternal(request, response, filterChain);
} finally {
// Once the request has finished, we're done and we don't
// need to mark as 'already filtered' any more.
request.removeAttribute(alreadyFilteredAttributeName);
}
}
}
/**
* Same contract as for
* {@link #doFilter(javax.servlet.ServletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse, javax.servlet.FilterChain)},
* but guaranteed to be invoked only once per request.
*
* @param request incoming {@code ServletRequest}
* @param response outgoing {@code ServletResponse}
* @param chain the {@code FilterChain} to execute
* @throws ServletException if there is a problem processing the request
* @throws IOException if there is an I/O problem processing the request
*/
protected abstract void doFilterInternal(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws ServletException, IOException;通过request中的属性Key:alreadyFilteredAttributeName是否已设置,判断是否已经执行;未执行则执行该过滤器逻辑,已执行则跳过,继续执行过滤链;
同时执行内部过滤逻辑委托给了抽象方法doFilterInternal,并交由子类来具体实现;
3.2.5?AdviceFilter
AdviceFilter继承自OncePerRequestFilter,并实现了抽象方法doFilterInternal,具体过滤逻辑如下:
/**
* Actually implements the chain execution logic, utilizing
* {@link #preHandle(javax.servlet.ServletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse) pre},
* {@link #postHandle(javax.servlet.ServletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse) post}, and
* {@link #afterCompletion(javax.servlet.ServletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse, Exception) after}
* advice hooks.
*
* @param request the incoming ServletRequest
* @param response the outgoing ServletResponse
* @param chain the filter chain to execute
* @throws ServletException if a servlet-related error occurs
* @throws IOException if an IO error occurs
*/
public void doFilterInternal(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
Exception exception = null;
try {
boolean continueChain = preHandle(request, response);
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Invoked preHandle method. Continuing chain?: [" + continueChain + "]");
}
if (continueChain) {
executeChain(request, response, chain);
}
postHandle(request, response);
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Successfully invoked postHandle method");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
exception = e;
} finally {
cleanup(request, response, exception);
}
}
protected void executeChain(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws Exception {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
protected boolean preHandle(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception {
return true;
}
protected void postHandle(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception {
}
public void afterCompletion(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Exception exception) throws Exception {
}如上,AdviceFilter引入了扩展方法,并给出了默认空实现,也可交由子类进行方法覆盖:
preHandle:控制后续过滤链是否继续执行还是直接跳过
postHandle:handle后处理
afterCompletion:过滤链执行完成后的处理
这些扩展点实现了类似Aop模式的嵌入逻辑,并交由子类按需灵活实现;
3.2.6?PathMatchingFilter
继承AdviceFilter,实现了preHandle方法,执行url路径匹配,这里的appliedPaths即为url访问控制过滤器配置的url,路径匹配的条件下才执行过滤逻辑;
protected boolean preHandle(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (this.appliedPaths == null || this.appliedPaths.isEmpty()) {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("appliedPaths property is null or empty. This Filter will passthrough immediately.");
}
return true;
}
for (String path : this.appliedPaths.keySet()) {
// If the path does match, then pass on to the subclass implementation for specific checks
//(first match 'wins'):
if (pathsMatch(path, request)) {
log.trace("Current requestURI matches pattern '{}'. Determining filter chain execution...", path);
Object config = this.appliedPaths.get(path);
return isFilterChainContinued(request, response, path, config);
}
}
//no path matched, allow the request to go through:
return true;
}?isFilterChainContinued方法实现如下,内部判断过滤器是否开启,如果已开启,引入了新的扩展方法onPreHandle来判断是否执行该过滤链:
private boolean isFilterChainContinued(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
String path, Object pathConfig) throws Exception {
if (isEnabled(request, response, path, pathConfig)) { //isEnabled check added in 1.2
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Filter '{}' is enabled for the current request under path '{}' with config [{}]. " +
"Delegating to subclass implementation for 'onPreHandle' check.",
new Object[]{getName(), path, pathConfig});
}
//The filter is enabled for this specific request, so delegate to subclass implementations
//so they can decide if the request should continue through the chain or not:
return onPreHandle(request, response, pathConfig);
}
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Filter '{}' is disabled for the current request under path '{}' with config [{}]. " +
"The next element in the FilterChain will be called immediately.",
new Object[]{getName(), path, pathConfig});
}
//This filter is disabled for this specific request,
//return 'true' immediately to indicate that the filter will not process the request
//and let the request/response to continue through the filter chain:
return true;
} protected boolean onPreHandle(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) throws Exception {
return true;
}onPreHandle方法默认返回true,表示继续执行后续过滤链,并可交由子类进行覆盖实现;?
3.3 内置过滤器解析
3.3.1?AnonymousFilter
AnonymousFilter,枚举名称为“anno”,表示不对url进行拦截,直接放行,其具体类图如下:
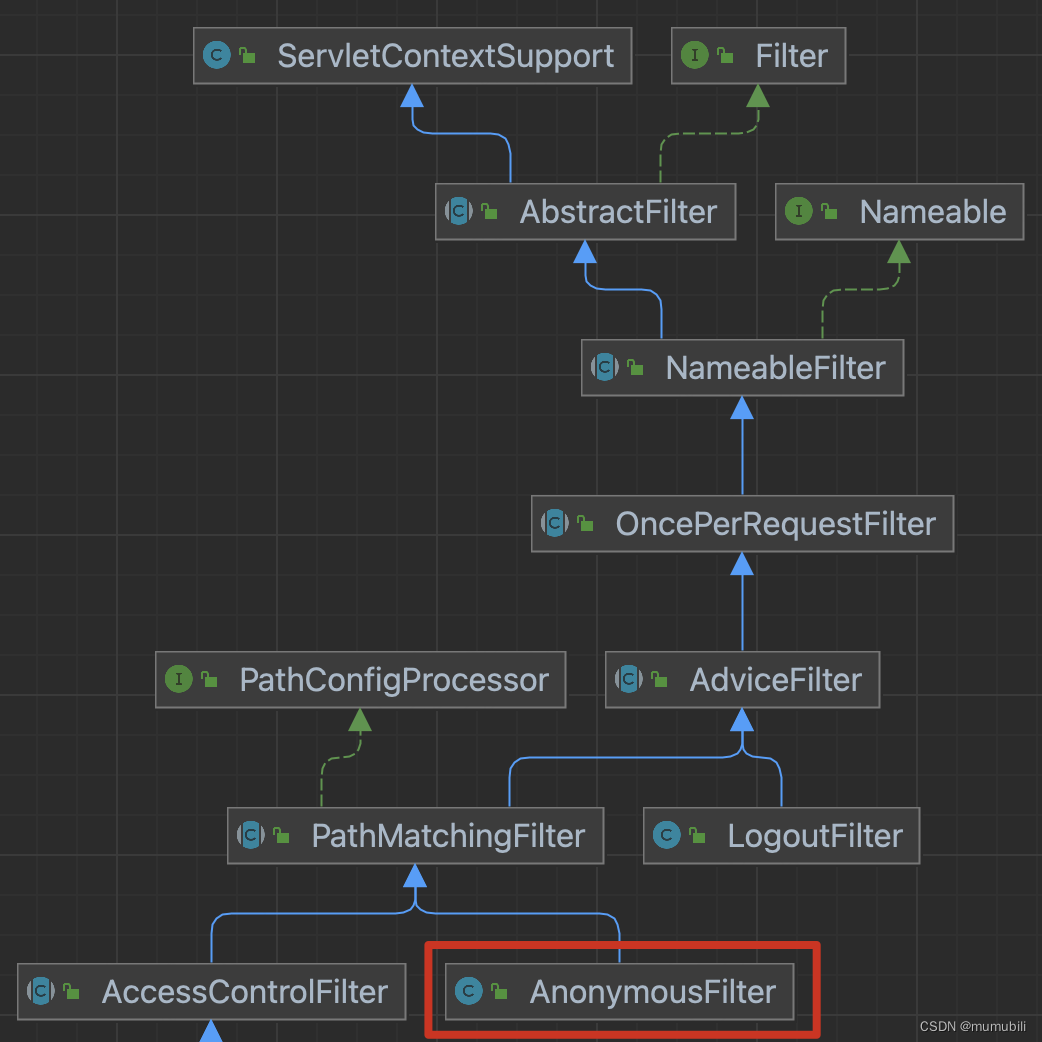
AnonymousFilter类定义非常简单,它继承自PathMatchingFilter,同时覆盖了扩展方法onPreHandle,并固定返回true,表示继续执行后续过滤链,直接放行;
AnonymousFilter类定义如下:
public class AnonymousFilter extends PathMatchingFilter {
/**
* Always returns <code>true</code> allowing unchecked access to the underlying path or resource.
*
* @return <code>true</code> always, allowing unchecked access to the underlying path or resource.
*/
@Override
protected boolean onPreHandle(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) {
// Always return true since we allow access to anyone
return true;
}
}3.3.2?FormAuthenticationFilter
FormAuthenticationFilter过滤器继承层次结构如下:

这里也是继承自PathMatchingFilter,下面对继承结构中的其它几个类进行具体分析;
3.3.2.1?AccessControlFilter
访问控制过滤器,内部覆盖实现了onPreHandle方法,允许放行(即返回true)的条件是:
- 已认证通过,比如用户已登录;
- 未认证通过时,也即访问拒绝后,依据访问拒绝后的操作结果来判断是否继续执行后续过滤链,比如访问拒绝后会执行用户登录,如果登录成功,则继续执行后续过滤链
/**
* Returns <code>true</code> if
* {@link #isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest,ServletResponse,Object) isAccessAllowed(Request,Response,Object)},
* otherwise returns the result of
* {@link #onAccessDenied(ServletRequest,ServletResponse,Object) onAccessDenied(Request,Response,Object)}.
*
* @return <code>true</code> if
* {@link #isAccessAllowed(javax.servlet.ServletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse, Object) isAccessAllowed},
* otherwise returns the result of
* {@link #onAccessDenied(javax.servlet.ServletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse) onAccessDenied}.
* @throws Exception if an error occurs.
*/
public boolean onPreHandle(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) throws Exception {
return isAccessAllowed(request, response, mappedValue) || onAccessDenied(request, response, mappedValue);
}同时,AccessControlFilter又引入了新的扩展方法交由子类灵活实现,如下:
/**
* Returns <code>true</code> if the request is allowed to proceed through the filter normally, or <code>false</code>
* if the request should be handled by the
* {@link #onAccessDenied(ServletRequest,ServletResponse,Object) onAccessDenied(request,response,mappedValue)}
* method instead.
*
* @param request the incoming <code>ServletRequest</code>
* @param response the outgoing <code>ServletResponse</code>
* @param mappedValue the filter-specific config value mapped to this filter in the URL rules mappings.
* @return <code>true</code> if the request should proceed through the filter normally, <code>false</code> if the
* request should be processed by this filter's
* {@link #onAccessDenied(ServletRequest,ServletResponse,Object)} method instead.
* @throws Exception if an error occurs during processing.
*/
protected abstract boolean isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) throws Exception;
/**
* Processes requests where the subject was denied access as determined by the
* {@link #isAccessAllowed(javax.servlet.ServletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse, Object) isAccessAllowed}
* method, retaining the {@code mappedValue} that was used during configuration.
* <p/>
* This method immediately delegates to {@link #onAccessDenied(ServletRequest,ServletResponse)} as a
* convenience in that most post-denial behavior does not need the mapped config again.
*
* @param request the incoming <code>ServletRequest</code>
* @param response the outgoing <code>ServletResponse</code>
* @param mappedValue the config specified for the filter in the matching request's filter chain.
* @return <code>true</code> if the request should continue to be processed; false if the subclass will
* handle/render the response directly.
* @throws Exception if there is an error processing the request.
* @since 1.0
*/
protected boolean onAccessDenied(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) throws Exception {
return onAccessDenied(request, response);
}
/**
* Processes requests where the subject was denied access as determined by the
* {@link #isAccessAllowed(javax.servlet.ServletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse, Object) isAccessAllowed}
* method.
*
* @param request the incoming <code>ServletRequest</code>
* @param response the outgoing <code>ServletResponse</code>
* @return <code>true</code> if the request should continue to be processed; false if the subclass will
* handle/render the response directly.
* @throws Exception if there is an error processing the request.
*/
protected abstract boolean onAccessDenied(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception;
3.3.2.2?AuthenticationFilter
AuthenticationFilter实现了isAccessAllowed方法,判断当前登录用户是否已认证通过:
/**
* Determines whether the current subject is authenticated.
* <p/>
* The default implementation {@link #getSubject(javax.servlet.ServletRequest, javax.servlet.ServletResponse) acquires}
* the currently executing Subject and then returns
* {@link org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject#isAuthenticated() subject.isAuthenticated()};
*
* @return true if the subject is authenticated; false if the subject is unauthenticated
*/
protected boolean isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) {
Subject subject = getSubject(request, response);
return subject.isAuthenticated();
}3.3.2.3 AuthenticatingFilter
覆盖实现了isAccessAllowed方法,判断是否允许访问,允许访问的条件包括:
- 用户已认证
- 非登录url且url路径配置中包括“permissive”,表示允许放行
/**
* Determines whether the current subject should be allowed to make the current request.
* <p/>
* The default implementation returns <code>true</code> if the user is authenticated. Will also return
* <code>true</code> if the {@link #isLoginRequest} returns false and the "permissive" flag is set.
*
* @return <code>true</code> if request should be allowed access
*/
@Override
protected boolean isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) {
return super.isAccessAllowed(request, response, mappedValue) ||
(!isLoginRequest(request, response) && isPermissive(mappedValue));
}
/**
* Returns <code>true</code> if the mappedValue contains the {@link #PERMISSIVE} qualifier.
*
* @return <code>true</code> if this filter should be permissive
*/
protected boolean isPermissive(Object mappedValue) {
if(mappedValue != null) {
String[] values = (String[]) mappedValue;
return Arrays.binarySearch(values, PERMISSIVE) >= 0;
}
return false;
}3.3.2.4?FormAuthenticationFilter处理逻辑
上述涉及的父类解析完毕,我们看下FormAuthenticationFilter本身的主要实现逻辑;
FormAuthenticationFilter覆盖了AccessControlFilter类提供的扩展方法onAccessDenied,执行访问拒绝后的后续操作,具体实现如下:
可以看到这里主要包含了2个代码分支:
- 如果提交url是登录url且是登录提交,则会执行具体的登录操作
- 如果不是登录url,又因为之前还未认证通过,则重定向到登录页面,引导用户登录
protected boolean onAccessDenied(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (isLoginRequest(request, response)) {
if (isLoginSubmission(request, response)) {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Login submission detected. Attempting to execute login.");
}
return executeLogin(request, response);
} else {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Login page view.");
}
//allow them to see the login page ;)
return true;
}
} else {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Attempting to access a path which requires authentication. Forwarding to the " +
"Authentication url [" + getLoginUrl() + "]");
}
saveRequestAndRedirectToLogin(request, response);
return false;
}
}executeLogin方法实现了具体的登录操作,获取当面登录用户,然后执行登录login;
protected boolean executeLogin(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception {
AuthenticationToken token = createToken(request, response);
if (token == null) {
String msg = "createToken method implementation returned null. A valid non-null AuthenticationToken " +
"must be created in order to execute a login attempt.";
throw new IllegalStateException(msg);
}
try {
Subject subject = getSubject(request, response);
subject.login(token);
return onLoginSuccess(token, subject, request, response);
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
return onLoginFailure(token, e, request, response);
}
}登录成功,会重定向到成功页面,并不再执行后续过滤链;
登录失败,设置登录失败属性,用户可以继续登录;
protected boolean onLoginSuccess(AuthenticationToken token, Subject subject,
ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception {
issueSuccessRedirect(request, response);
//we handled the success redirect directly, prevent the chain from continuing:
return false;
}
protected boolean onLoginFailure(AuthenticationToken token, AuthenticationException e,
ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug( "Authentication exception", e );
}
setFailureAttribute(request, e);
//login failed, let request continue back to the login page:
return true;
}
protected void setFailureAttribute(ServletRequest request, AuthenticationException ae) {
String className = ae.getClass().getName();
request.setAttribute(getFailureKeyAttribute(), className);
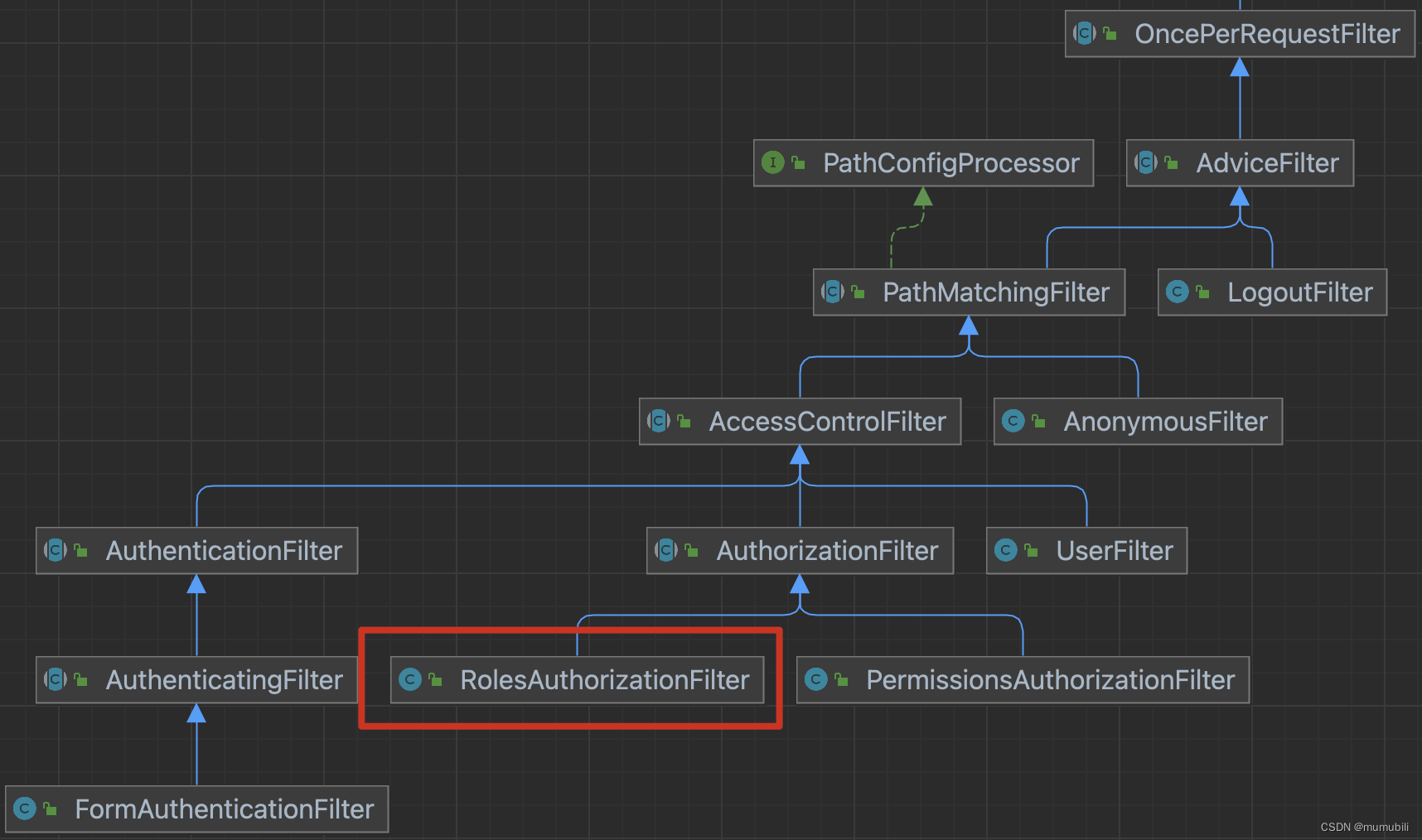
}3.3.3?RolesAuthorizationFilter
RolesAuthorizationFilter类继承层次结构如下,继承了AuthorizationFilter抽象类,进一步继承了AccessControlFilter,下面首先看下AuthorizationFilter的实现;
3.3.3.1?AuthorizationFilter
AuthorizationFilter内部覆盖了onAccessDenied方法,如下:
protected boolean onAccessDenied(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws IOException {
Subject subject = getSubject(request, response);
// If the subject isn't identified, redirect to login URL
if (subject.getPrincipal() == null) {
saveRequestAndRedirectToLogin(request, response);
} else {
// If subject is known but not authorized, redirect to the unauthorized URL if there is one
// If no unauthorized URL is specified, just return an unauthorized HTTP status code
String unauthorizedUrl = getUnauthorizedUrl();
//SHIRO-142 - ensure that redirect _or_ error code occurs - both cannot happen due to response commit:
if (StringUtils.hasText(unauthorizedUrl)) {
WebUtils.issueRedirect(request, response, unauthorizedUrl);
} else {
WebUtils.toHttp(response).sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
}
}
return false;
}在没有访问控制权限的情况下,会重定向到无权限的页面,提示用户无访问权限,并返回false终止后续过滤链的执行;
?3.3.3.2?RolesAuthorizationFilter处理逻辑
内部实现覆盖了isAccessAllowed方法,如下:
主要逻辑是判断当前登录用户是否具有配置的角色(Role),配置角色支持使用注解RequiresRoles进行定义;
/**
* Filter that allows access if the current user has the roles specified by the mapped value, or denies access
* if the user does not have all of the roles specified.
*
* @since 0.9
*/
public class RolesAuthorizationFilter extends AuthorizationFilter {
//TODO - complete JavaDoc
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked"})
public boolean isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) throws IOException {
Subject subject = getSubject(request, response);
String[] rolesArray = (String[]) mappedValue;
if (rolesArray == null || rolesArray.length == 0) {
//no roles specified, so nothing to check - allow access.
return true;
}
Set<String> roles = CollectionUtils.asSet(rolesArray);
return subject.hasAllRoles(roles);
}
}3.3.4?PermissionsAuthorizationFilter
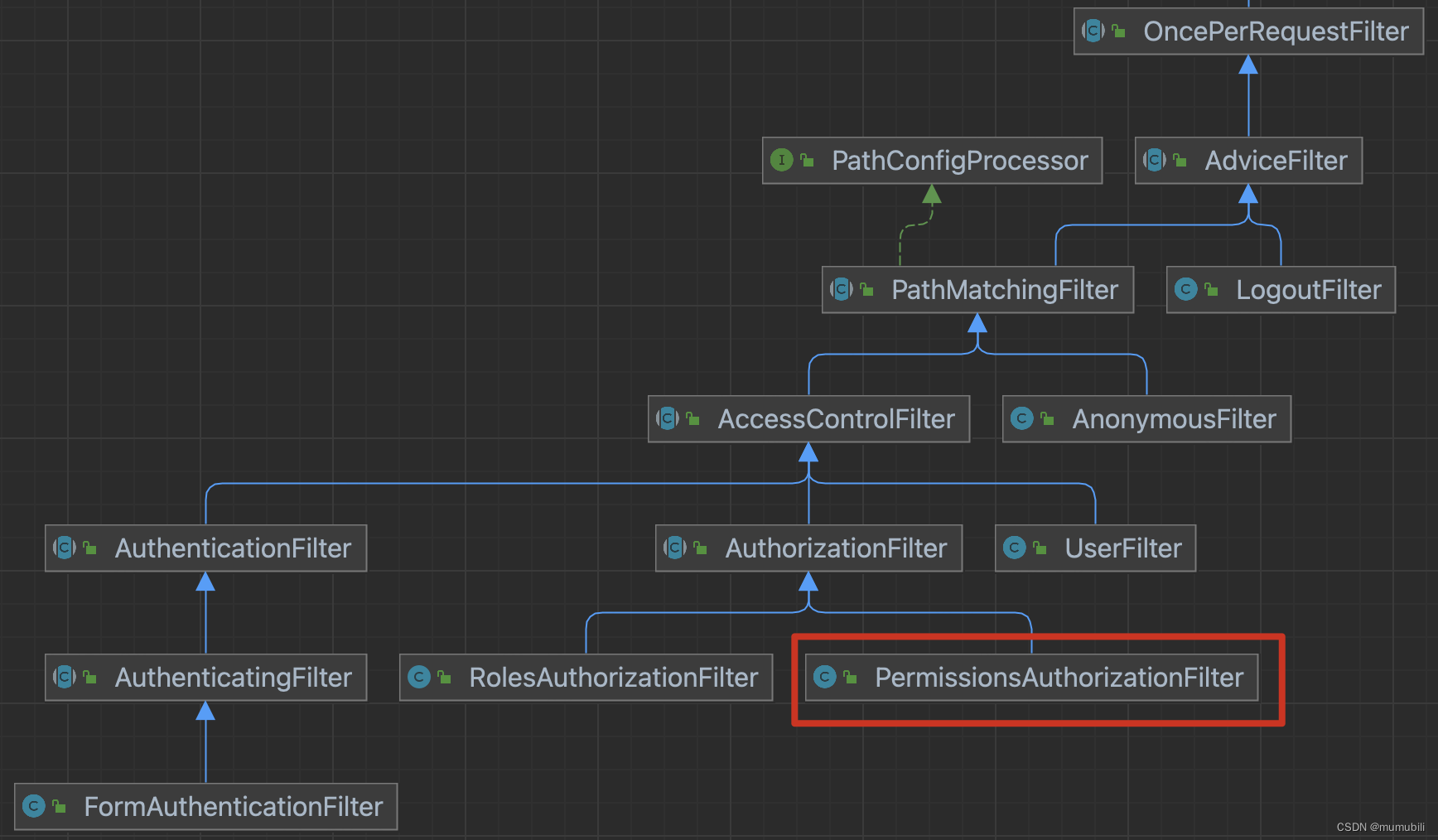
PermissionsAuthorizationFilter和RolesAuthorizationFilter一样,同样继承AuthorizationFilter类,且覆盖实现了isAccessAllowed方法,如下:
校验用户是否有指定权限,支持注解RequiresPermissions进行权限配置;
/**
* Filter that allows access if the current user has the roles specified by the mapped value, or denies access
* if the user does not have all of the roles specified.
*
* @since 0.9
*/
public class RolesAuthorizationFilter extends AuthorizationFilter {
//TODO - complete JavaDoc
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked"})
public boolean isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) throws IOException {
Subject subject = getSubject(request, response);
String[] rolesArray = (String[]) mappedValue;
if (rolesArray == null || rolesArray.length == 0) {
//no roles specified, so nothing to check - allow access.
return true;
}
Set<String> roles = CollectionUtils.asSet(rolesArray);
return subject.hasAllRoles(roles);
}
}3.3.5?LogoutFilter
登录过滤器LogoutFilter,继承层次结构如下:
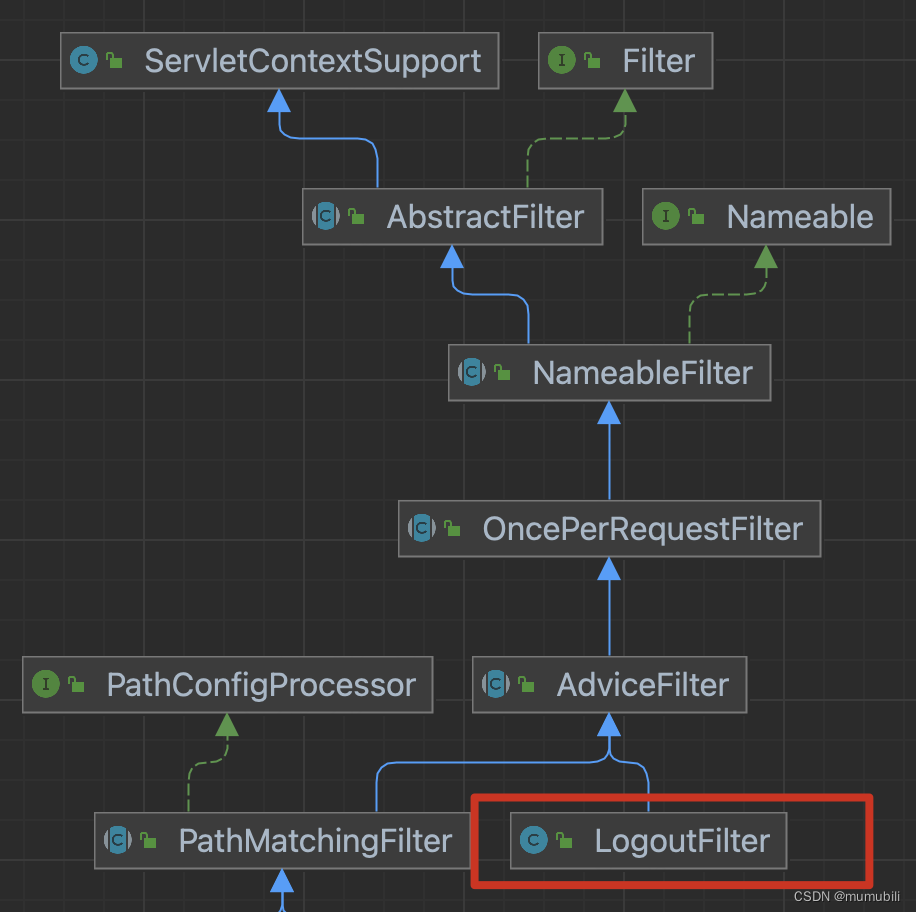
其也是继承自AdviceFilter,并覆盖实现了preHandle方法,如下:
@Override
protected boolean preHandle(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response) throws Exception {
Subject subject = getSubject(request, response);
// Check if POST only logout is enabled
if (isPostOnlyLogout()) {
// check if the current request's method is a POST, if not redirect
if (!WebUtils.toHttp(request).getMethod().toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH).equals("POST")) {
return onLogoutRequestNotAPost(request, response);
}
}
String redirectUrl = getRedirectUrl(request, response, subject);
//try/catch added for SHIRO-298:
try {
subject.logout();
} catch (SessionException ise) {
log.debug("Encountered session exception during logout. This can generally safely be ignored.", ise);
}
issueRedirect(request, response, redirectUrl);
return false;
}如上内部实现获取了当前登录用户,并执行用户登出操作,并引导跳转到重定向url;
这里logout的具体实现以及上面用户登录、角色控制、权限控制的具体操作,都是委托SecurityManager安全管理器来完成的,由于篇幅较长,不再展开说明,待后续再单独进行深入分析;
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!