debug mccl 02 —— 环境搭建及初步调试
发布时间:2024年01月06日
1, 搭建nccl 调试环境
下载 nccl 源代码
?git clone --recursive https://github.com/NVIDIA/nccl.git
只debug host代码,故将设备代码的编译标志改成 -O3
?
(base) hipper@hipper-G21:~/let_debug_nccl/nccl$ git diff
diff --git a/makefiles/common.mk b/makefiles/common.mk
index a037cf3..ee2aa8e 100644
--- a/makefiles/common.mk
+++ b/makefiles/common.mk
@@ -82,7 +82,8 @@ ifeq ($(DEBUG), 0)
NVCUFLAGS += -O3
CXXFLAGS += -O3 -g
else
-NVCUFLAGS += -O0 -G -g
+#NVCUFLAGS += -O0 -G -g
+NVCUFLAGS += -O3
CXXFLAGS += -O0 -g -ggdb3
endif修改后变成如下:
nccl$ vim makefiles/common.mk
ifeq ($(DEBUG), 0)
NVCUFLAGS += -O3
CXXFLAGS += -O3 -g
else
#NVCUFLAGS += -O0 -G -g
NVCUFLAGS += -O3
CXXFLAGS += -O0 -g -ggdb3
endif
构建 nccl shared library:
机器上是几张sm_85?的卡,故:
$ cd nccl
$ make -j src.build ?DEBUG=1 ? ?? ?NVCC_GENCODE="-gencode=arch=compute_80,code=sm_80"到此即可,不需要安装nccl,直接过来使用即可;
2, 创建调试APP
在nccl所在的目录中创建app文件夹:
$ mkdir app
$ cd app
$ vim sp_md_nccl.cpp
$ vim Makefilesp_md_nccl.cpp:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "nccl.h"
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#define CUDACHECK(cmd) do { \
cudaError_t err = cmd; \
if (err != cudaSuccess) { \
printf("Failed: Cuda error %s:%d '%s'\n", \
__FILE__,__LINE__,cudaGetErrorString(err)); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} \
} while(0)
#define NCCLCHECK(cmd) do { \
ncclResult_t res = cmd; \
if (res != ncclSuccess) { \
printf("Failed, NCCL error %s:%d '%s'\n", \
__FILE__,__LINE__,ncclGetErrorString(res)); \
exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
} \
} while(0)
void get_seed(long long &seed)
{
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
seed = (long long)tv.tv_sec * 1000*1000 + tv.tv_usec;//only second and usecond;
printf("useconds:%lld\n", seed);
}
void init_vector(float* A, int n)
{
long long seed = 0;
get_seed(seed);
srand(seed);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
A[i] = (rand()%100)/100.0f;
}
}
void print_vector(float* A, float size)
{
for(int i=0; i<size; i++)
printf("%.2f ", A[i]);
printf("\n");
}
void vector_add_vector(float* sum, float* A, int n)
{
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
{
sum[i] += A[i];
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
ncclComm_t comms[4];
printf("ncclComm_t is a pointer type, sizeof(ncclComm_t)=%lu\n", sizeof(ncclComm_t));
//managing 4 devices
//int nDev = 4;
int nDev = 2;
//int size = 32*1024*1024;
int size = 16*16;
int devs[4] = { 0, 1, 2, 3 };
float** sendbuff_host = (float**)malloc(nDev * sizeof(float*));
float** recvbuff_host = (float**)malloc(nDev * sizeof(float*));
for(int dev=0; dev<nDev; dev++)
{
sendbuff_host[dev] = (float*)malloc(size*sizeof(float));
recvbuff_host[dev] = (float*)malloc(size*sizeof(float));
init_vector(sendbuff_host[dev], size);
init_vector(recvbuff_host[dev], size);
}
//sigma(sendbuff_host[i]); i = 0, 1, ..., nDev-1
float* result = (float*)malloc(size*sizeof(float));
memset(result, 0, size*sizeof(float));
for(int dev=0; dev<nDev; dev++)
{
vector_add_vector(result, sendbuff_host[dev], size);
printf("sendbuff_host[%d]=\n", dev);
print_vector(sendbuff_host[dev], size);
}
printf("result=\n");
print_vector(result, size);
//allocating and initializing device buffers
float** sendbuff = (float**)malloc(nDev * sizeof(float*));
float** recvbuff = (float**)malloc(nDev * sizeof(float*));
cudaStream_t* s = (cudaStream_t*)malloc(sizeof(cudaStream_t)*nDev);
for (int i = 0; i < nDev; ++i) {
CUDACHECK(cudaSetDevice(i));
CUDACHECK(cudaMalloc(sendbuff + i, size * sizeof(float)));
CUDACHECK(cudaMalloc(recvbuff + i, size * sizeof(float)));
CUDACHECK(cudaMemcpy(sendbuff[i], sendbuff_host[i], size*sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));
CUDACHECK(cudaMemcpy(recvbuff[i], recvbuff_host[i], size*sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));
CUDACHECK(cudaStreamCreate(s+i));
}
//initializing NCCL
NCCLCHECK(ncclCommInitAll(comms, nDev, devs));
//calling NCCL communication API. Group API is required when using
//multiple devices per thread
NCCLCHECK(ncclGroupStart());
printf("blocked ncclAllReduce will be calleded\n");
fflush(stdout);
for (int i = 0; i < nDev; ++i)
NCCLCHECK(ncclAllReduce((const void*)sendbuff[i], (void*)recvbuff[i], size, ncclFloat, ncclSum, comms[i], s[i]));
printf("blocked ncclAllReduce is calleded nDev =%d\n", nDev);
fflush(stdout);
NCCLCHECK(ncclGroupEnd());
//synchronizing on CUDA streams to wait for completion of NCCL operation
for (int i = 0; i < nDev; ++i) {
CUDACHECK(cudaSetDevice(i));
CUDACHECK(cudaStreamSynchronize(s[i]));
}
for (int i = 0; i < nDev; ++i) {
CUDACHECK(cudaSetDevice(i));
CUDACHECK(cudaMemcpy(recvbuff_host[i], recvbuff[i], size*sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost));
}
for (int i = 0; i < nDev; ++i) {
CUDACHECK(cudaSetDevice(i));
CUDACHECK(cudaStreamSynchronize(s[i]));
}
for(int i=0; i<nDev; i++) {
printf("recvbuff_dev2host[%d]=\n", i);
print_vector(recvbuff_host[i], size);
}
//free device buffers
for (int i = 0; i < nDev; ++i) {
CUDACHECK(cudaSetDevice(i));
CUDACHECK(cudaFree(sendbuff[i]));
CUDACHECK(cudaFree(recvbuff[i]));
}
//finalizing NCCL
for(int i = 0; i < nDev; ++i)
ncclCommDestroy(comms[i]);
printf("Success \n");
return 0;
}
Makefile:
INC := -I /usr/local/cuda/include -I ../nccl/build/include
LD_FLAGS := -L ../nccl/build/lib -lnccl -L /usr/local/cuda/lib64 -lcudart
EXE := singleProc_multiDev_nccl
all: $(EXE)
%: %.cpp
g++ -g -ggdb3 $< -o $@ $(INC) $(LD_FLAGS)
.PHONY: clean
clean:
-rm -rf $(EXE)export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=../nccl/build/lib
3, 开始调试
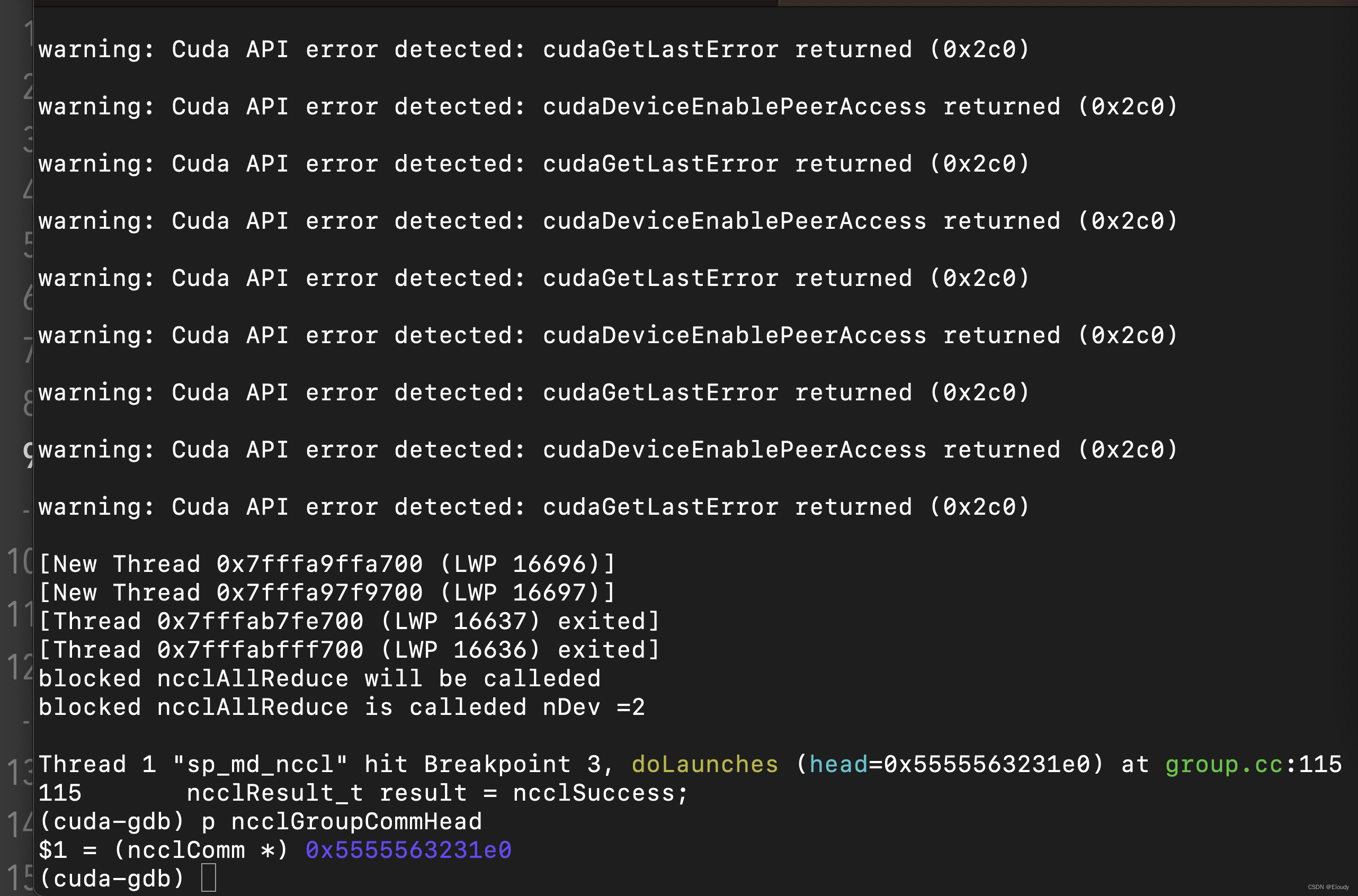
$ cuda-gdb sp_md_nccl
(cuda-gdb) start
(cuda-gdb) rbreak doLauches
(cuda-gdb) c
(cuda-gdb) p ncclGroupCommHead->tasks.collQueue.head->op 初步实现了可debug的效果:
现在想要搞清楚在程序调用 ncclAllReduce(..., ncclSum, ?... ) 后,是如何映射到 cudaLaunchKernel调用到了正确的 cuda kernel 函数的。
在doLaunches函数中,作如下debug动作:
查看 doLaunches(ncclComm*) 的函数参数,即,gropu.cc中的变量:ncclGroupCommHead的某个成员的成员的值:op
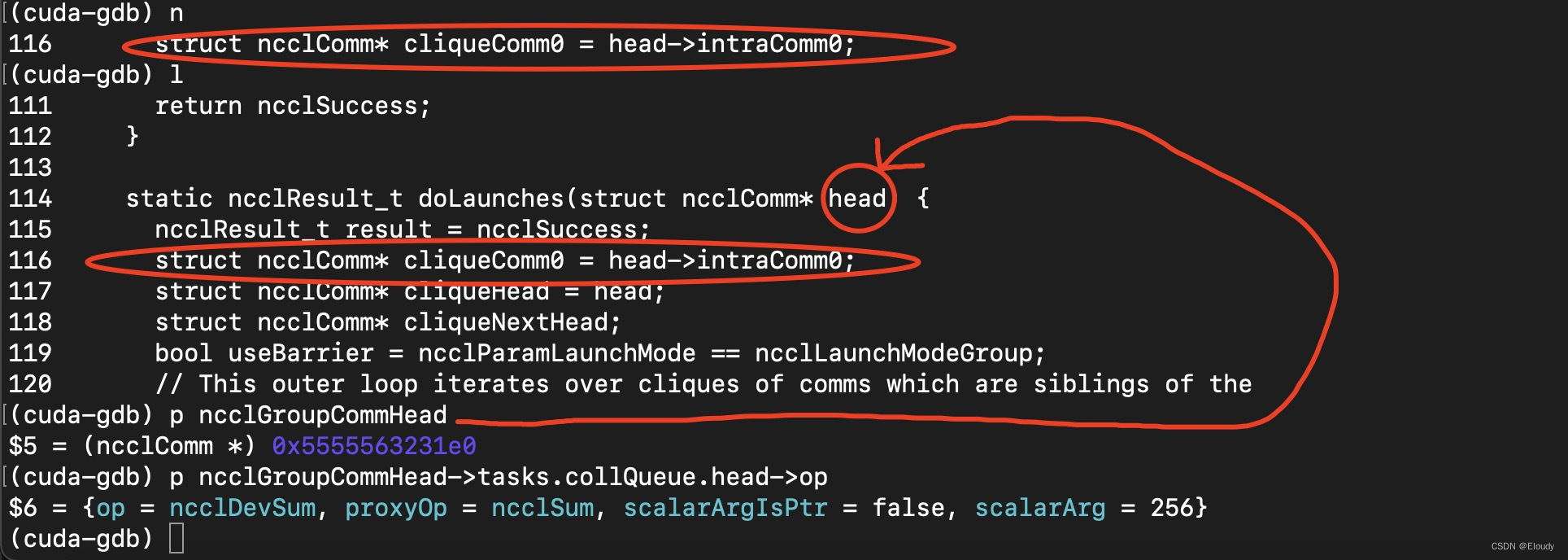
其结果如下:
(cuda-gdb) p ncclGroupCommHead
$5 = (ncclComm *) 0x5555563231e0
(cuda-gdb) p ncclGroupCommHead->tasks.collQueue.head->op
$6 = {op = ncclDevSum, proxyOp = ncclSum, scalarArgIsPtr = false, scalarArg = 256}
(cuda-gdb) 不过这依然只停留在了 ncclSum的这个枚举类型上,还没锁定对应的cudaKernel。
接下来继续努力 ...
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/eloudy/article/details/135430680
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- CSS 画三角形
- ForecastPFN: Synthetically-Trained Zero-Shot Forecasting
- Linux常用159个命令详细汇总,快码住~
- 第五章 程序控制结构
- 【考研数学】10早鸟课 导数的计算
- 连接progressql报错Cannot load JDBC driver class ‘org.postgresql.Driver‘,亲测有效!!!
- DeciLM-7B:突破极限,高效率、高精准度的70亿参数AI模型
- MySQL-多表查询
- MYSQL 深入探索系列六 SQL执行计划
- 解锁小程序UI设计的奥秘:必须知晓的相关事项