文件系统(六)—文件系统mount过程 转载
https://blog.csdn.net/u012489236/article/details/124523247
前一章学习了虚拟文件系统组成的超级块、索引节点、目录项、文件四个结构体对象,那么就开始看内核是如何建立挂载点目录项与挂载文件系统的?我们接着下面图,学习整个mount的过程。
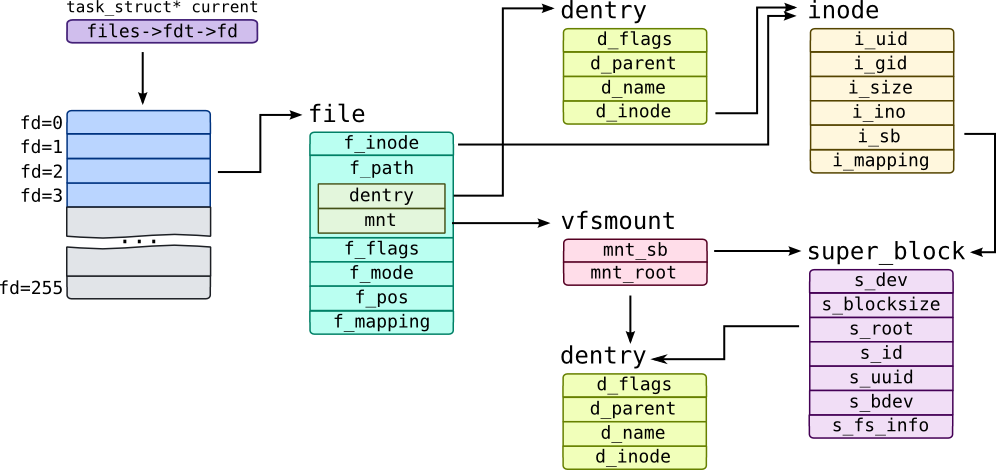
1 数据结构
虚拟文件系统通过目录项dentry实例组成的跟文件系统管理内核所有的文件,具体文件系统根目录需要关联到内核跟文件系统中某一目录项**(挂载点)**才能接入跟文件系统,如下图所示
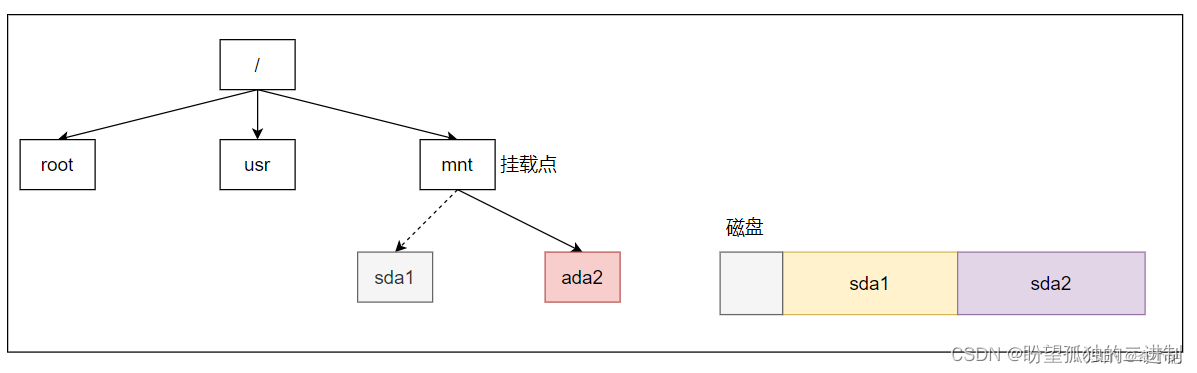
将磁盘分区sda1的文件系统根目录与跟文件系统中的/mnt目录项建立关联,称之为挂载,/mnt目录项称之为挂载点
根文件系统中的挂载点可以同时挂载多个文件系统,sda2在da1分区之后挂载,则分区sda2文件系统可见,分区sda1被引藏,当分区sda2文件系统被卸载时,分区sda1文件系统将自动可见
所以挂载操作是一个很复杂的过程,那么就需要为文件系统创建超级块,根目录项dentry和inode结构体实例,这些上一章中都已经介绍了,那么首选要建立挂载点目录项与挂载的文件系统根目录项之间的关联。
内核定义了一个mountpoint 结构体表示根文件系统中的挂载点,挂载点对应到跟文件系统中的一个dentry实例,定义了一个mount结构体表示一次挂载操作。定义如下(fs/mount.h):
struct mountpoint {
struct hlist_node m_hash; //散列链表节点成员,将实例链接到全局散列链表
struct dentry *m_dentry; // 指向挂载点 dentry 实例(根文件系统中目录项)
struct hlist_head m_list; // 链接 mount 实例
int m_count; // 挂载点挂载操作的次数
};
mountpoint 结构体成员简介如下,定义如下(fs/mount.h):
m_hash: 散列链表节点成员,将mountpoint实例添加到全局散列表mountpoint_hashtable
m_dentry: 指向挂载点dentry实例,根文件系统中的的目录项,不是挂载文件系统的根目录项
m_list: 挂载点挂载操作的Mount实例,链表头
m_count: 挂载点执行挂载操作的次数
mount结构体表示一次挂载操作,结构体定义在/fs/mount.h头文件:
struct mount {
struct hlist_node mnt_hash; //散列链表节点成员,将实例链入全局散列表
struct mount *mnt_parent; //父mount实例
struct dentry *mnt_mountpoint; //挂载点dentry实例指针(跟文件系统目录项)
struct vfsmount mnt; //vfsmount结构体实例,表示在vfs中的挂载信息
union {
struct rcu_head mnt_rcu;
struct llist_node mnt_llist;
};
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
struct mnt_pcp __percpu *mnt_pcp;
#else
int mnt_count;
int mnt_writers;
#endif
struct list_head mnt_mounts; // 子mount实例链表头
struct list_head mnt_child; // 链接兄弟mount实例
struct list_head mnt_instance; // 链入超级块中双链表,表头为sb->s_mounts
const char *mnt_devname; // 文件系统所在块设备文件名称,如:/dev/dsk/hda1
struct list_head mnt_list; // 将实例链接到挂载命名空间链表
struct list_head mnt_expire; // 用于特定于文件系统的过期链表
struct list_head mnt_share; // 用于共享挂载的循环链表
struct list_head mnt_slave_list; // 从属挂载链表头
struct list_head mnt_slave; // 用于链入从属挂载链表
struct mount *mnt_master; // 指向包含从属挂载链表头的mount实例
struct mnt_namespace *mnt_ns; // 指向所属挂载命名空间
struct mountpoint *mnt_mp; // 挂载点结构体指针
union {
struct hlist_node mnt_mp_list; //将实例添加到挂载点的mount实例链表
struct hlist_node mnt_umount;
};
struct list_head mnt_umounting; /* list entry for umount propagation */
#ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY
struct fsnotify_mark_connector __rcu *mnt_fsnotify_marks;
__u32 mnt_fsnotify_mask;
#endif
int mnt_id; // ID标记
int mnt_group_id; // 组ID
int mnt_expiry_mark; // 标记挂载时否过期,true表示过期
struct hlist_head mnt_pins;
struct hlist_head mnt_stuck_children;
} __randomize_layout;
mount结构体实例在内核中组成父子的层次结构,同时由全局散列表管理,结构体中主要成员简介如下:
mnt_hash: 散列链表节点成员,将实例添加到全局散列表mount_hashtable
mnt_mountpoint:指向挂载点dentry实例
mnt_instance:双链表节点成员,将Mount实例链入超级块的双链表,链表头为sb→s_mounts
mnt_mp:挂载点mountpoint实例
mnt_mp_list:散列链表节点成员,将实例链接到挂载点mountpoint实例的mount实例链表
mnt_list:双链表节点成员,将mount实例链接到挂载命名空间mnt_namespace实例中的双链表
mnt:vfsmount结构体成员,用于建立Mount实例与挂载文件系统的关联
vfsmount结构体成员,用于建立mount实例与挂载文件系统之间的关联,结构体定义在头文件include/linux/mount.h:
struct vfsmount {
struct dentry *mnt_root; //指向挂载文件系统根目录项dentry实例
struct super_block *mnt_sb; //指向文件系统超级块实例
int mnt_flags; //内核内部使用的挂载标记
struct user_namespace *mnt_userns;
} __randomize_layout;
所以:
每一个挂载实例都对应一个vfsmount,vfsmount与待装载文件系统的root dentry,super_block关联
mount是vfsmount的封装,所有的mount链接成一张链表,mount代表待装载文件系统, 它的装载点指明了挂载到哪个dentry。可以为一个文件系统创建多个装载实例vfsmount,挂载到不同的挂载点上。图中的mount如果它的mnt_parent为它自身则为root mount,代表的是rootfs

2 挂载流程
对于 mount() 函数,source 是要挂载的设备名,target 是要挂载到哪,filesystemtype 就是文件系统类型名,而剩余的两个参数 flags 和 data 对应于传入的参数。
其中 flags 相应宏定义在 include/uapi/linux/fs.h 中,如 MS_RDONLY、MS_NOATIME 等,这些 flags 会在 VFS 层被解析使用。而 data 则是每个文件系统各自支持的挂载选项,可以通过 strace 查看最终调用 mount() 接口是调用的命令。
$ strace mount /dev/loop0 /mnt/foobar -o noquota,nodev
... ...
mount("/dev/loop0", "/mnt/foobar", "xfs", MS_MGC_VAL|MS_NODEV, "noquota") = 0
用户进程通过mount()系统调用挂载具体文件系统,内核mount函数入口为sys_mount(),实现在fs/namespace.c中。其中dev_name定义了块设备路径;di_name定义了挂载点目录;type定义了文件系统类型;flags挂载标志,data定义了一些挂载选项
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(mount, char __user *, dev_name, char __user *, dir_name,
char __user *, type, unsigned long, flags, void __user *, data)
{
int ret;
char *kernel_type;
char *kernel_dev;
void *options;
/* 拷贝文件系统类型名到内核空间 */
kernel_type = copy_mount_string(type);
ret = PTR_ERR(kernel_type);
if (IS_ERR(kernel_type))
goto out_type;
/* 拷贝块设备路径名到内核空间 */
kernel_dev = copy_mount_string(dev_name);
ret = PTR_ERR(kernel_dev);
if (IS_ERR(kernel_dev))
goto out_dev;
/* 拷贝挂载选项到内核空间 */
options = copy_mount_options(data);
ret = PTR_ERR(options);
if (IS_ERR(options))
goto out_data;
/* 挂载委托do_mount,最重要的接口实现 */
ret = do_mount(kernel_dev, dir_name, kernel_type, flags, options);
kfree(options);
out_data:
kfree(kernel_dev);
out_dev:
kfree(kernel_type);
out_type:
return ret;
}
在学习do_mount之前,先了解path结构体的定义,用于后面的挂载,结构体定义在include/linux/path头文件内
struct path {
/* 指向vfsmount实例,mount.mnt成员(挂载点所在文件系统的挂载信息) */
struct vfsmount *mnt;
/*指向挂载点dentry实例(根文件系统中目录项)*/
struct dentry *dentry;
};
do_mount函数在fs/namespace.c文件内实现,其实现代码如下:
long do_mount(const char *dev_name, const char __user *dir_name,
const char *type_page, unsigned long flags, void *data_page)
{
struct path path; //path结构体实例
int retval = 0;
int mnt_flags = 0; //挂载标记
//去掉标记参数中的魔数
if ((flags & MS_MGC_MSK) == MS_MGC_VAL)
flags &= ~MS_MGC_MSK;
/* 安全性检查 */
if (data_page)
((char *)data_page)[PAGE_SIZE - 1] = 0;
/* 1. 查找挂载点信息, 把挂载点解析成path内核结构,也就是路径解析过程 */
retval = user_path(dir_name, &path); //path保存挂载点目录项信息
if (retval)
return retval;
retval = security_sb_mount(dev_name, &path,
type_page, flags, data_page);
if (!retval && !may_mount())
retval = -EPERM;
if (!retval && (flags & MS_MANDLOCK) && !may_mandlock())
retval = -EPERM;
if (retval)
goto dput_out;
/* Default to relatime unless overriden */
if (!(flags & MS_NOATIME))
mnt_flags |= MNT_RELATIME;
/*挂载标记参数转成内核内部标记, 分割每个挂载点的挂载标志 */
if (flags & MS_NOSUID)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NOSUID;
if (flags & MS_NODEV)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NODEV;
if (flags & MS_NOEXEC)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NOEXEC;
if (flags & MS_NOATIME)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NOATIME;
if (flags & MS_NODIRATIME)
mnt_flags |= MNT_NODIRATIME;
if (flags & MS_STRICTATIME)
mnt_flags &= ~(MNT_RELATIME | MNT_NOATIME);
if (flags & MS_RDONLY)
mnt_flags |= MNT_READONLY;
/* 默认的重新挂载时间是保存时间 */
if ((flags & MS_REMOUNT) &&
((flags & (MS_NOATIME | MS_NODIRATIME | MS_RELATIME |
MS_STRICTATIME)) == 0)) {
mnt_flags &= ~MNT_ATIME_MASK;
mnt_flags |= path.mnt->mnt_flags & MNT_ATIME_MASK;
}
flags &= ~(MS_NOSUID | MS_NOEXEC | MS_NODEV | MS_ACTIVE | MS_BORN |
MS_NOATIME | MS_NODIRATIME | MS_RELATIME| MS_KERNMOUNT |
MS_STRICTATIME | MS_NOREMOTELOCK | MS_SUBMOUNT);
if (flags & MS_REMOUNT) // 修改已经挂载文件系统的选项
retval = do_remount(&path, flags & ~MS_REMOUNT, mnt_flags,
data_page);
else if (flags & MS_BIND) // 通过环回接口挂载一个文件系统
retval = do_loopback(&path, dev_name, flags & MS_REC);
else if (flags & (MS_SHARED | MS_PRIVATE | MS_SLAVE | MS_UNBINDABLE))
retval = do_change_type(&path, flags); // 处理共享、从属和不可绑定挂载操作
else if (flags & MS_MOVE) //移动一个已经挂载的文件系统
retval = do_move_mount(&path, dev_name);
else // 执行新的挂载操作
retval = do_new_mount(&path, type_page, flags, mnt_flags,
dev_name, data_page);
dput_out:
path_put(&path);
return retval;
}
从以上代码可见,大部分用于flags的标志位的判断和设置。在do_mount()函数中,将挂在分成了5种情况:
(1)如果是重新挂载:将调用do_remount()执行挂载操作。
(2)如果是MS_BIND标志:则调用do_loopback()函数。
(3)如果是MS_SHARED | MS_PRIVATE | MS_SLAVE | MS_UNBINDABLE标志:则调用do_change_type()函数。
(4)如果是MS_MOVE:则调用do_move_mount()函数。
(5)如果都不是以上四种挂载情况,那么就会调用do_new_mount()函数创建新的挂载。
这里我们以执行新的挂载操作do_new_mount()函数为例,介绍挂载操作的实现。do_new_mount()函数定义在fs/namespace.c文件内,代码如下:
static int do_new_mount(struct path *path, const char *fstype, int flags,
int mnt_flags, const char *name, void *data)
{
struct file_system_type *type; //文件系统类型
struct vfsmount *mnt;
int err;
if (!fstype)
return -EINVAL;
type = get_fs_type(fstype); //由名称查找file_system_type实例
if (!type)
return -ENODEV;
/* 1 内核挂载函数 */
mnt = vfs_kern_mount(type, flags, name, data);
if (!IS_ERR(mnt) && (type->fs_flags & FS_HAS_SUBTYPE) &&
!mnt->mnt_sb->s_subtype)
mnt = fs_set_subtype(mnt, fstype);
put_filesystem(type);
if (IS_ERR(mnt))
return PTR_ERR(mnt);
if (mount_too_revealing(mnt, &mnt_flags)) {
mntput(mnt);
return -EPERM;
}
/* 2 关联挂载点 */
err = do_add_mount(real_mount(mnt), path, mnt_flags);
if (err)
mntput(mnt);
return err;
}
do_new_mount()函数主要完成以下工作
由文件系统类型名称查找file_system_type实例
然后调用vfs_kern_mount()函数执行内核挂载操作,主要完成创建超级块super_block、根目录项dentry和inode结构体实例(由文件系统类型挂载函数完成),创建mount结构体实例并建立各结构体实例之间的关联
最后调用关联挂载点函数do_add_mount()建立mount和挂载点mountpoint实例、挂载点dentry实例之间的关联,并将mount实例插入全局散列链表头部,挂载操作完成。
下文将详细介绍内核挂载函数和关联挂载点函数的实现如下
struct vfsmount *
vfs_kern_mount(struct file_system_type *type, int flags, const char *name, void *data)
{
struct mount *mnt;
struct dentry *root;
if (!type)
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
/* 1. 从slab缓存分配mount实例,分配ID号,并初始化各成员 */
mnt = alloc_vfsmnt(name);
if (!mnt)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
/* 2 内核发起的挂载操作 */
if (flags & MS_KERNMOUNT)
mnt->mnt.mnt_flags = MNT_INTERNAL;
/* 3 调用文件系统类型定义的挂载函数 */
root = mount_fs(type, flags, name, data);
if (IS_ERR(root)) {
mnt_free_id(mnt);
free_vfsmnt(mnt);
return ERR_CAST(root);
}
/* 建立mount实例与super_block、dentry实例之间的关联 */
mnt->mnt.mnt_root = root; //指向挂载文件系统根目录项dentry实例
mnt->mnt.mnt_sb = root->d_sb; //指向超级块实例
mnt->mnt_mountpoint = mnt->mnt.mnt_root; //设为挂载文件系统根目录dentry实例
mnt->mnt_parent = mnt; //父mount实例指向自身
lock_mount_hash();
list_add_tail(&mnt->mnt_instance, &root->d_sb->s_mounts); //插入超级块中链表的末尾
unlock_mount_hash();
return &mnt->mnt; //返回mount实例mnt成员指针,vfsmount结构体成员
}
ount实例mnt.mnt_root和mnt_mountpoint成员都指向挂载文件系统根目录项dentry实例,mnt_mountpoint成员在关联挂载点时将重新赋值,指向内核根文件系统中挂载点dentry实例。
vfs_kern_mount()函数创建的数据结构实例组织关系如下图所示:
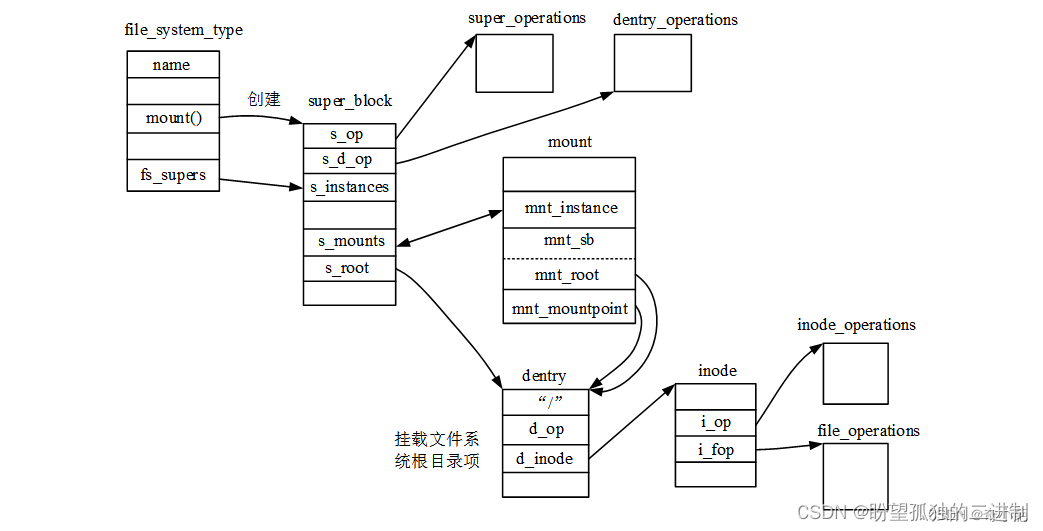
vfs_kern_mount()函数内调用mount_fs()函数,此函数又调用文件系统类型定义的mount()函数,创建文件系统超级块super_block、根目录项dentry和inode结构体实例,返回挂载文件系统根目录项dentry实例指针。函数定义如下(fs/super.c)
struct dentry *
mount_fs(struct file_system_type *type, int flags, const char *name, void *data)
{
struct dentry *root; //返回值,挂载文件系统根目录项的dentry实例指针
struct super_block *sb;
char *secdata = NULL;
int error = -ENOMEM;
if (data && !(type->fs_flags & FS_BINARY_MOUNTDATA)) {
secdata = alloc_secdata();
if (!secdata)
goto out;
error = security_sb_copy_data(data, secdata);
if (error)
goto out_free_secdata;
}
/* 1. 调用文件系统类型挂载函数,创建各数据结构体实例 */
root = type->mount(type, flags, name, data);
if (IS_ERR(root)) {
error = PTR_ERR(root);
goto out_free_secdata;
}
sb = root->d_sb; /* 文件系统超级块指针 */
BUG_ON(!sb);
WARN_ON(!sb->s_bdi);
sb->s_flags |= MS_BORN;
error = security_sb_kern_mount(sb, flags, secdata);
if (error)
goto out_sb;
/*
* filesystems should never set s_maxbytes larger than MAX_LFS_FILESIZE
* but s_maxbytes was an unsigned long long for many releases. Throw
* this warning for a little while to try and catch filesystems that
* violate this rule.
*/
WARN((sb->s_maxbytes < 0), "%s set sb->s_maxbytes to "
"negative value (%lld)\n", type->name, sb->s_maxbytes);
up_write(&sb->s_umount);
free_secdata(secdata);
return root; //返回挂载文件系统根目录项dentry实例指针
out_sb:
dput(root);
deactivate_locked_super(sb);
out_free_secdata:
free_secdata(secdata);
out:
return ERR_PTR(error);
}
例如,ext4文件系统类型实例定义如下(/fs/ext2/super.c):
static struct file_system_type ext4_fs_type = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = "ext4",
.mount = ext4_mount, //挂载时调用 用于读取创建超级块实例
.kill_sb = kill_block_super, //卸载时调用 用于释放超级块
.fs_flags = FS_REQUIRES_DEV, //文件系统标志为 请求块设备,文件系统在块设备上
};
MODULE_ALIAS_FS("ext4");
文件系统类型挂载函数ext4_mount()调用了通用的mount_bdev()函数,定义如下(/fs/ext4/super.c):
static struct dentry *ext4_mount(struct file_system_type *fs_type, int flags,
const char *dev_name, void *data)
{
return mount_bdev(fs_type, flags, dev_name, data, ext4_fill_super);
}
函数内直接调用通用的mount_bdev()函数,需要注意的是最后一个参数ext4_fill_super是一个函数指针,mount_bdev()函数内会调用此函数完成超级块实例的填充和初始化,包括dentry和inode实例的创建
ext4_fill_super的一个函数指针作为参数传递给get_sb_bdev。该函数用于填充一个超级块对象,如果内存中没有适当的超级块对象,数据就必须从硬盘读取。
mount_bdev是个公用的函数,一般磁盘文件系统会使用它来根据具体文件系统的fill_super方法来读取磁盘上的超级块并在创建内存超级块。
我们来看下mount_bdev的实现,它执行完成之后会创建vfs的三大数据结构 super_block、根inode和根dentry
struct dentry *mount_bdev(struct file_system_type *fs_type,
int flags, const char *dev_name, void *data,
int (*fill_super)(struct super_block *, void *, int))
{
struct block_device *bdev;
struct super_block *s;
fmode_t mode = FMODE_READ | FMODE_EXCL;
int error = 0;
if (!(flags & MS_RDONLY))
mode |= FMODE_WRITE;
/* 通过要挂载的块设备路径名 获得它的块设备描述符block_device
(会涉及到路径名查找和通过设备号在bdev文件系统查找block_device,
block_device是添加块设备到系统时创建的) */
bdev = blkdev_get_by_path(dev_name, mode, fs_type);
if (IS_ERR(bdev))
return ERR_CAST(bdev);
/*
* once the super is inserted into the list by sget, s_umount
* will protect the lockfs code from trying to start a snapshot
* while we are mounting
*/
mutex_lock(&bdev->bd_fsfreeze_mutex);
if (bdev->bd_fsfreeze_count > 0) {
mutex_unlock(&bdev->bd_fsfreeze_mutex);
error = -EBUSY;
goto error_bdev;
}
/* 查找或创建vfs的超级 */
s = sget(fs_type, test_bdev_super, set_bdev_super, flags | MS_NOSEC,
bdev);
mutex_unlock(&bdev->bd_fsfreeze_mutex);
if (IS_ERR(s))
goto error_s;
/*超级块的根dentry是否被赋值*/
if (s->s_root) {
if ((flags ^ s->s_flags) & MS_RDONLY) {
deactivate_locked_super(s);
error = -EBUSY;
goto error_bdev;
}
/*
* s_umount nests inside bd_mutex during
* __invalidate_device(). blkdev_put() acquires
* bd_mutex and can't be called under s_umount. Drop
* s_umount temporarily. This is safe as we're
* holding an active reference.
*/
up_write(&s->s_umount);
blkdev_put(bdev, mode);
down_write(&s->s_umount);
} else { //没有赋值说明时新创建的sb
s->s_mode = mode;
snprintf(s->s_id, sizeof(s->s_id), "%pg", bdev);
sb_set_blocksize(s, block_size(bdev)); // 根据块设备描述符设置文件系统块大小
/* 调用传递的具体文件系统的填充超级块方法读取填充超级块等 如ext4_fill_super */
error = fill_super(s, data, flags & MS_SILENT ? 1 : 0);
if (error) {
deactivate_locked_super(s);
goto error;
}
s->s_flags |= MS_ACTIVE;
bdev->bd_super = s; //块设备bd_super指向sb
}
//返回文件系统的根dentry
return dget(s->s_root);
error_s:
error = PTR_ERR(s);
error_bdev:
blkdev_put(bdev, mode);
error:
return ERR_PTR(error);
}
对于ext4_fill_super主要的工作,如下:
1.读取磁盘上的超级块;
2.填充并关联vfs超级块;
3.读取块组描述符;
4.读取磁盘根inode并建立vfs 根inode;
5.创建根dentry关联到根inode。
综上所述,内核挂载函数的主要工作包括:
一、调用文件系统类型定义的挂载函数,创建(或查找)超级块super_block、根目录项dentry和inode结构体实例,对数据结构实例进行初始化,并建立实例之间的关联。
二、创建表示挂载操作的mount结构体实例,并建立其与超级块super_block实例和根目录项dentry实例之间的关联。
接下来的工作就是通过mount实例建立挂载点dentry实例与挂载文件系统根目录项dentry实例之间的关联,并将mount实例添加到全局散列链表头部。以便将挂载的文件系统导入内核根文件系统,使之对用户进程可见。
static int do_add_mount(struct mount *newmnt, struct path *path, int mnt_flags)
{
struct mountpoint *mp;
struct mount *parent;
int err;
mnt_flags &= ~MNT_INTERNAL_FLAGS;
/* 1 创建mountpoint实例,并建立与挂载点dentry关联 */
mp = lock_mount(path);
if (IS_ERR(mp))
return PTR_ERR(mp);
/* 2 vfsmount指针转mount实例指针,父mount实例 */
parent = real_mount(path->mnt);
err = -EINVAL;
if (unlikely(!check_mnt(parent))) {
/* that's acceptable only for automounts done in private ns */
if (!(mnt_flags & MNT_SHRINKABLE))
goto unlock;
/* ... and for those we'd better have mountpoint still alive */
if (!parent->mnt_ns)
goto unlock;
}
/* 3 避免同一文件系统重复挂载到同一挂载点 */
err = -EBUSY;
if (path->mnt->mnt_sb == newmnt->mnt.mnt_sb &&
path->mnt->mnt_root == path->dentry)
goto unlock;
err = -EINVAL;
if (d_is_symlink(newmnt->mnt.mnt_root))
goto unlock;
/* 4 建立mount与mountpoint、挂载点dentry实例关联,并插入散列表*/
newmnt->mnt.mnt_flags = mnt_flags;
err = graft_tree(newmnt, parent, mp);
unlock:
unlock_mount(mp);
return err;
}
(1)调用lock_mount(path)函数创建(或查找)挂载点mountpoint实例,建立其与挂载点dentry实例的关联,设置挂载点dentry实例DCACHE_MOUNTED标记位(d_set_mounted(dentry)),并将mountpoint实例添加到全局散列表。
(2)调用graft_tree()函数,建立mount实例与mountpoint、挂载点dentry实例之间的关联,并将mount实例插入到全局散列链表的头部,以及加入到内核mount实例的层次(父子关系)结构中。
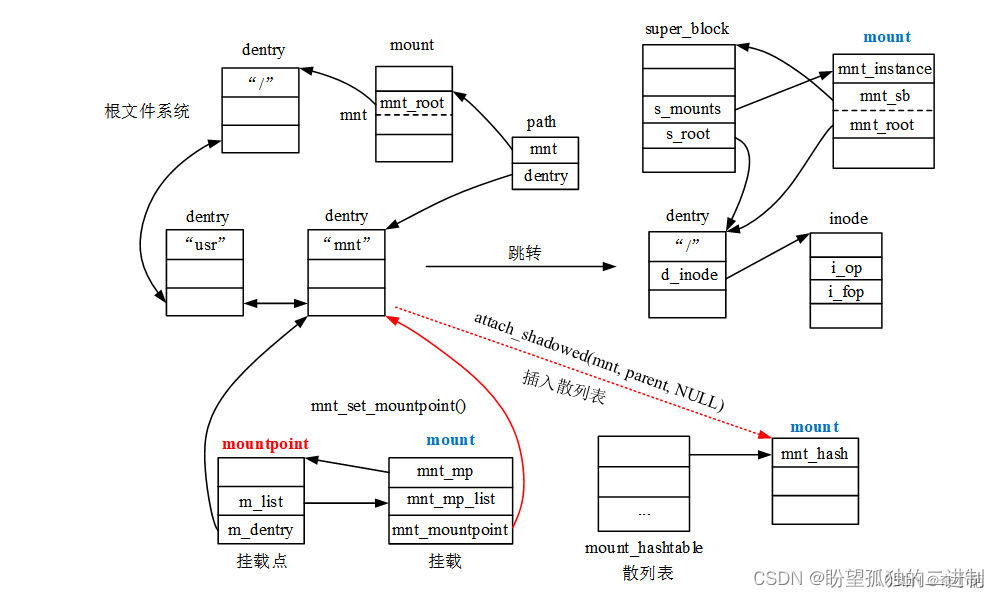
do_add_mount()函数调用关系如下图所示:

do_new_mount()函数执行完内核挂载函数vfs_kern_mount()之后,接下来的工作就是通过mount实例建立挂载点dentry实例与挂载文件系统根目录项dentry实例之间的关联,并将mount实例添加到全局散列链表头部。以便将挂载的文件系统导入内核根文件系统,使之对用户进程可见。
do_add_mount()函数创建的数据结构实例及组织关系如下图所示:
内核的整个Mount过程如下:
SYSCALL_DEFINE5(mount...) //namespace.c
do_mount()
user_path()
do_remount()
do_loopback()
do_change_type()
do_move_mount()
do_new_mount()
struct file_system_type *type
struct vfs_mount *mnt
mnt = vfs_kern_mount()
struct mount * mnt
mnt = alloc_vfsmnt()
root = mount_fs()
struct super_block *sb
root = type->mount() //回调file_system_type的mount方法
sb = root ->d_sb
security_sb_kern_mount()
up_write()
init mnt
list_add_tail(&mnt->mnt_instance, &root->d_sb->s_mounts)
do_add_mount(real_mount(mnt),path,mnt_flags)
ext4_mnt() //ext4
mount_bdev(...ext4_fill_super)
struct block_device *bdev
struct super_block *s
bdev = blkdev_get_by_path()
s = sget(...test_bdev_super,set_bdev_super...) //find or create a superblock
alloc_super()
kzalloc()
init_waitqueue_head()
s->s_bdi = &noop_backing_dev_info
...other initialization of s
set() //set_bdev_super()
s->s_bdev = data;
s->s_dev = s->s_bdev->bd_dev;
s->s_bdi = &bdev_get_queue(s->s_bdev)->backing_dev_info;
bdev->bd_disk->queue;
list_add_tail(...&super_blocks)
hlist_add_head()
get_filesystem()
__module_get()
sb_set_blocksize()
fill_super() //ext4_fill_super()
struct ext4_sb_info *sbi
sbi = kzalloc()
... init sbi...
ext4_msg()
setup_timer()
sb->s_op = &ext4_sops
sb->s_export_op = &ext4_export_ops
sb->s_xattr = ext4_xattr_handlers
sb->s_root = d_make_root()
ext4_setup_super()
ext4_ext_init()
ext4_mb_init()
sbi->s_kobj.kset = ext4_kset
init_completion()
kobject_init_and_add(&sbi->s_kobj, &ext4_ktype...)
s->s_flags|=MS_ACTIVE
bdev->bd_super = s
dget()
3 总结
对于内核的Mount流程,内核定义了一个Mountpoint结构体表示跟文件系统中的一个挂载点,挂载点对应跟文件系统中的一个dentry实例,用户通过mount系统调用实现文件系统的挂载,其主要流程为:
-
执行内核的挂载函数vfs_kern_mount:该函数主要是创建文件系统超级块super_block、根目录项dentry和inode结构体实例,并创建表示本次挂载操作的mount结构体实例,mount实例添加到超级块实例s_mounts成员链表中,并与挂载文件系统根目录项dentry建立关联

-
关联挂载点do_add_mount:创建挂载点mountpoint结构体实例,并添加到全局散列表,mountpoint实例关联到挂载点dentry实例(跟文件系统中目录项),并将挂载mount实例添加到Mountpoint实例链表和全局散列表中,建立mount实例与挂载断点dentry之间的关联,一个挂载点可以有多个挂载,因此Mountpoint实例包含一个挂载mount实例的链表

执行完这两步,通过mount实例建立了挂载点dentry实例和挂载文件系统根目录项dentry实例之间的联系。

当内核打开文件搜索路径到达挂载点时(挂载点dentry实例设置DCACHE_MOUNTED标记位),将调用函数lookup_mnt(path),在mount实例全局散列表中查找第一个关联到挂载点dentry实例的mount实例,搜索路径随后进入mount实例关联的挂载文件系统根目录项。
4 参考文档
https://blog.51cto.com/u_15127540/3543420
linux内核解析
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「奇小葩」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u012489236/article/details/124523247
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 发格Fagor 8055i /A, 8055i /B, 8055i /C / 8055i机床数据采集与机床配置
- 字正腔圆,万国同音,coqui-ai TTS跨语种语音克隆,钢铁侠讲16国语言(Python3.10)
- 零停机升级Postgres
- [Java并发基础] 共享内存
- 山羊目标检测数据集VOC格式290张
- 如何解决跨域问题
- DOCKER安装MYSQL8.2.0版本
- 二维和三维联合进行圆孔空间定位
- css 实现满屏升空的气球动画
- 2023海内外零知识证明学习资料汇总(一)(故事中的零知识证明篇)