【C++】模板类vector的简单实现
在C++的STL库中,vector是一个非常常用的容器,它提供了动态数组的功能。今天我们将一起来实现一个简化版的vector模板类,以便更好地理解它的原理和实现过程。
以下是简化版vector 类的主要实现:
1. 迭代器
vector 的迭代器是一个原生指针,定义如下:
typedef T value_type;
typedef value_type* pointer;
typedef value_type* iterator;
typedef value_type& reference;
typedef const T* const_iterator;
typedef const value_type& const_reference;
iterator begin() {
return _start;
}
iterator end() {
return _finish;
}
const_iterator begin() const {
return _start;
}
const_iterator end() const {
return _finish;
}
其中,iterator 和 const_iterator 分别表示可读写和只读的迭代器,pointer 和 reference 表示指向数据类型的指针和引用。
2.构造和析构
vector 支持默认构造、拷贝构造、赋值操作和析构函数。默认构造函数创建一个空的 vector,而拷贝构造函数将已有的 vector 复制到新的 vector 中。赋值操作符将一个 vector 赋值给另一个 vector。
析构函数会释放 vector 占用的内存空间,避免内存泄漏。
T* allocate_and_fill(size_t n, const T& value) {
T* ptr = new T[n]; // 在动态内存中分配 n 个 T 类型的对象空间
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ptr[i] = value; // 将每个对象初始化为 value
}
return ptr; // 返回指向分配的内存空间的指针
}
void fill_initialize(size_t n, const T& value) {
_start = allocate_and_fill(n, value);
_finish = _start + n;
_endofstorage = _finish;
}
//construct and destroy
vector() //默认构造
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstorage(nullptr)
{}
vector(size_t n, const T& value = T()) { //构造函数
fill_initialize(n, value);
}
vector(int n, const T& value = T()) { //构造函数,加一个int版本以免错误调用下面那个构造
fill_initialize(n, value);
}
template <class InputIterator>
vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {
while (first != last) {
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
vector(const vector<T>& v) { //拷贝构造
//_start = new T[v.capacity()];
//memcpy(_start, v._start, v.size() * sizeof(T)); //浅拷贝
//_finish = _start + v.size();
//_endofstorage = _start + v.capacity();
reserve(v.capacity());
for (const auto& e : v) {
push_back(e);
}
}
vector<T>& operator= (vector<T> v) {
swap(v);
return *this;
}
~vector() { //析构函数
if (_start){
delete[] _start;
_start = _finish = _endofstorage = nullptr;
}
}
3. 容量
vector 的容量包括 size 和 capacity。其中 size 表示当前 vector 中元素的个数,而 capacity 表示 vector 内部分配的存储空间的大小。reserve() 函数用于调整 vector 的空间大小,resize() 函数用于调整 vector 的大小。
//capacity
size_t size() const {
return _finish - _start;
}
size_t capacity() const {
return _endofstorage - _start;
}
void reserve(size_t n) {
if (capacity() < n) {
const size_t old_size = size();
T* tmp = new T[n];
if (_start) {
//memcpy(tmp, _start, n * sizeof(T)); //这是一种浅拷贝
for (size_t i = 0; i < old_size; i++) { //进行深拷贝
tmp[i] = _start[i];
}
delete[] _start; //1.调用析构函数 2.释放空间
}
_start = tmp;
_finish = _start + old_size;
_endofstorage = _start + n;
}
}
void resize(size_t new_size, const T& value = T()) {
if (new_size > size()) {
reserve(new_size);
while (_finish < _start + new_size) {
*_finish = value;
++_finish;
}
}
else {
_finish = _start + new_size;
}
}
4. 访问
vector 支持随机访问,可以使用下标操作符 [] 来访问 vector 中的元素。同时也提供了 begin() 和 end() 函数来获取迭代器访问 vector 中的元素。
//access
reference operator[](size_t n) {
return *(begin() + n);
}
const_reference operator[](size_t n) const {
return *(begin() + n);
}
5.修改
vector 支持在末尾添加元素(push_back()),删除末尾元素(pop_back()),插入元素(insert())和删除元素(erase())等操作。
//modify
void push_back(const T& x) {
if (_finish == _endofstorage) {
size_t newcapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
*_finish = x;
++_finish;
}
void pop_back() {
assert(size() > 0);
--_finish;
}
void swap(vector<T>& v) {
std::swap(_start, v._start);
std::swap(_finish, v._finish);
std::swap(_endofstorage, v._endofstorage);
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x) {
assert(pos >= _start && pos <= _finish);
if (_finish == _endofstorage) {
size_t len = pos - _start;//记录一下_start到pos的距离,以免迭代器失效
reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2);
pos = _start + len;
}
//memmove(pos + 1, pos, sizeof(T) * (_finish - pos)); //memove是浅拷贝覆盖
iterator end = _finish - 1;
while (end >= pos) {
(*end + 1) = *end;
--end;
}
*pos = x;
++_finish;
return pos;
}
void erase(iterator pos) {
assert(pos >= _start && pos < _finish);
iterator it = pos + 1;
while (it <= _finish) {
*(it - 1) = *it;
++it;
}
_finish--;
}
6.测试
五个测试函数 test_vector1() 至 test_vector5(),分别测试了 vector 的各种功能。
template <typename T>
void print_vector(const vector<T>& v) {
for (auto e : v) {
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
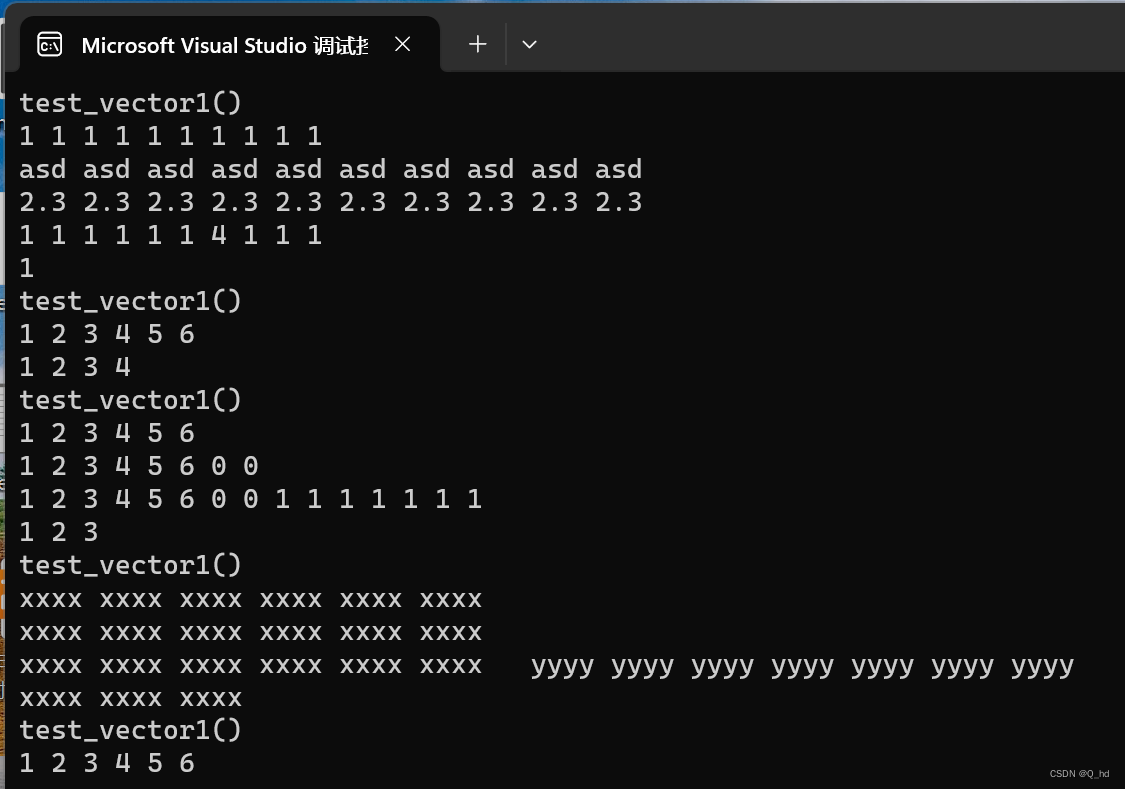
void test_vector1() {
cout << "test_vector1()" << endl;
vector<int> v1(10, 1);
vector<string> v2(10, "asd");
vector<double> v3(10, 2.3);
vector<int> v4 = v1;
print_vector(v1);
print_vector(v2);
print_vector(v3);
v4[6] = 4;
print_vector(v4);
cout << v1[6] << endl;
}
void test_vector2() {
cout << "test_vector1()" << endl;
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(2);
v1.push_back(3);
v1.push_back(4);
v1.push_back(5);
v1.push_back(6);
print_vector(v1);
v1.pop_back();
v1.pop_back();
print_vector(v1);
}
void test_vector3() {
cout << "test_vector1()" << endl;
vector<int> v;
v.reserve(10);
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
v.push_back(6);
for (auto e : v) {
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(8);
for (auto e : v) {
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(15, 1);
for (auto e : v) {
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(3);
for (auto e : v) {
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_vector4()
{
cout << "test_vector1()" << endl;
vector<string> v;
v.reserve(10);
v.push_back("xxxx");
v.push_back("xxxx");
v.push_back("xxxx");
v.push_back("xxxx");
v.push_back("xxxx");
v.push_back("xxxx");
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(8);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(15, "yyyy");
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(3);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_vector5()
{
cout << "test_vector1()" << endl;
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(2);
v1.push_back(3);
v1.push_back(4);
v1.push_back(5);
v1.push_back(6);
vector<int> v2(v1.begin(), v1.end());
for (auto e : v2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
完整代码
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace hd
{
template<class T>
class vector
{
public:
//vector 的迭代器是一个原生指针
typedef T value_type;
typedef value_type* pointer;
typedef value_type* iterator;
typedef value_type& reference;
typedef const T* const_iterator;
typedef const value_type& const_reference;
iterator begin() {
return _start;
}
iterator end() {
return _finish;
}
const_iterator begin() const {
return _start;
}
const_iterator end() const {
return _finish;
}
T* allocate_and_fill(size_t n, const T& value) {
T* ptr = new T[n]; // 在动态内存中分配 n 个 T 类型的对象空间
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ptr[i] = value; // 将每个对象初始化为 value
}
return ptr; // 返回指向分配的内存空间的指针
}
void fill_initialize(size_t n, const T& value) {
_start = allocate_and_fill(n, value);
_finish = _start + n;
_endofstorage = _finish;
}
//construct and destroy
vector() //默认构造
:_start(nullptr)
, _finish(nullptr)
, _endofstorage(nullptr)
{}
vector(size_t n, const T& value = T()) { //构造函数
fill_initialize(n, value);
}
vector(int n, const T& value = T()) { //构造函数,加一个int版本以免错误调用下面那个构造
fill_initialize(n, value);
}
template <class InputIterator>
vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) {
while (first != last) {
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
vector(const vector<T>& v) { //拷贝构造
//_start = new T[v.capacity()];
//memcpy(_start, v._start, v.size() * sizeof(T)); //浅拷贝
//_finish = _start + v.size();
//_endofstorage = _start + v.capacity();
reserve(v.capacity());
for (const auto& e : v) {
push_back(e);
}
}
vector<T>& operator= (vector<T> v) {
swap(v);
return *this;
}
~vector() { //析构函数
if (_start){
delete[] _start;
_start = _finish = _endofstorage = nullptr;
}
}
//capacity
size_t size() const {
return _finish - _start;
}
size_t capacity() const {
return _endofstorage - _start;
}
void reserve(size_t n) {
if (capacity() < n) {
const size_t old_size = size();
T* tmp = new T[n];
if (_start) {
//memcpy(tmp, _start, n * sizeof(T)); //这是一种浅拷贝
for (size_t i = 0; i < old_size; i++) { //进行深拷贝
tmp[i] = _start[i];
}
delete[] _start; //1.调用析构函数 2.释放空间
}
_start = tmp;
_finish = _start + old_size;
_endofstorage = _start + n;
}
}
void resize(size_t new_size, const T& value = T()) {
if (new_size > size()) {
reserve(new_size);
while (_finish < _start + new_size) {
*_finish = value;
++_finish;
}
}
else {
_finish = _start + new_size;
}
}
//access
reference operator[](size_t n) {
return *(begin() + n);
}
const_reference operator[](size_t n) const {
return *(begin() + n);
}
//modify
void push_back(const T& x) {
if (_finish == _endofstorage) {
size_t newcapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
*_finish = x;
++_finish;
}
void pop_back() {
assert(size() > 0);
--_finish;
}
void swap(vector<T>& v) {
std::swap(_start, v._start);
std::swap(_finish, v._finish);
std::swap(_endofstorage, v._endofstorage);
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x) {
assert(pos >= _start && pos <= _finish);
if (_finish == _endofstorage) {
size_t len = pos - _start;//记录一下_start到pos的距离,以免迭代器失效
reserve(capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2);
pos = _start + len;
}
//memmove(pos + 1, pos, sizeof(T) * (_finish - pos)); //memove是浅拷贝覆盖
iterator end = _finish - 1;
while (end >= pos) {
(*end + 1) = *end;
--end;
}
*pos = x;
++_finish;
return pos;
}
void erase(iterator pos) {
assert(pos >= _start && pos < _finish);
iterator it = pos + 1;
while (it <= _finish) {
*(it - 1) = *it;
++it;
}
_finish--;
}
private:
iterator _start; //指向数据块的开始
iterator _finish; //指向有效数据的尾
iterator _endofstorage; //指向存储容量的尾
};
template <typename T>
void print_vector(const vector<T>& v) {
for (auto e : v) {
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_vector1() {
cout << "test_vector1()" << endl;
vector<int> v1(10, 1);
vector<string> v2(10, "asd");
vector<double> v3(10, 2.3);
vector<int> v4 = v1;
print_vector(v1);
print_vector(v2);
print_vector(v3);
v4[6] = 4;
print_vector(v4);
cout << v1[6] << endl;
}
void test_vector2() {
cout << "test_vector1()" << endl;
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(2);
v1.push_back(3);
v1.push_back(4);
v1.push_back(5);
v1.push_back(6);
print_vector(v1);
v1.pop_back();
v1.pop_back();
print_vector(v1);
}
void test_vector3() {
cout << "test_vector1()" << endl;
vector<int> v;
v.reserve(10);
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5);
v.push_back(6);
for (auto e : v) {
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(8);
for (auto e : v) {
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(15, 1);
for (auto e : v) {
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(3);
for (auto e : v) {
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_vector4()
{
cout << "test_vector1()" << endl;
vector<string> v;
v.reserve(10);
v.push_back("xxxx");
v.push_back("xxxx");
v.push_back("xxxx");
v.push_back("xxxx");
v.push_back("xxxx");
v.push_back("xxxx");
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(8);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(15, "yyyy");
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v.resize(3);
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_vector5()
{
cout << "test_vector1()" << endl;
vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(2);
v1.push_back(3);
v1.push_back(4);
v1.push_back(5);
v1.push_back(6);
vector<int> v2(v1.begin(), v1.end());
for (auto e : v2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
总结:
通过以上的实现和测试,我们可以看到,我们的简化版vector类能够成功地实现动态数组的功能,并且具备了基本的操作和容器相关的函数。当然,这只是一个简化版的实现,与STL库中的vector相比还有很多功能和细节需要进一步完善。
希望本文能够帮助你更好地理解和使用vector容器。如果您对这篇博客内容有任何疑问或建议,欢迎在下方留言进行讨论。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Upload-lab(pass1~2)
- 13年Android老码农精心总结《Android全套进阶学习资料》帮助大龄程序员突破内卷
- re:Invent 产品体验与感受分享:Amazon ElastiCache Serverless 缓存的即时扩展
- 亚马逊多店铺运营:如何有效降低账号关联风险?
- 【Java 设计模式】设计原则之里氏替换原则
- 编程语言的分类
- 企业泛域名https证书哪里申请比较好
- 被遗忘在角落的RPA,成了提升AI Agent执行能力的天选神器
- 2024年广东省安全员C证第四批(专职安全生产管理人员)证模拟考试题库及广东省安全员C证第四批(专职安全生产管理人员)理论考试试题
- vue3 环境变量