ThreadPoolExecutor中的keepAliveTime详解
一.keepAliveTime的概念:
keepAliveTime的单位是纳秒,即1s=1000000000ns,1秒等于10亿纳秒。
keepAliveTime是线程池中空闲线程等待工作的超时时间。
当线程池中线程数量大于corePoolSize(核心线程数量)或设置了allowCoreThreadTimeOut(是否允许空闲核心线程超时)时,线程会根据keepAliveTime的值进行活性检查,一旦超时便销毁线程。
否则,线程会永远等待新的工作。
? ? /**
? ? ?* Timeout in nanoseconds for idle threads waiting for work.
? ? ?* Threads use this timeout when there are more than corePoolSize
? ? ?* present or if allowCoreThreadTimeOut. Otherwise they wait
? ? ?* forever for new work.
? ? ?*/
? ? private volatile long keepAliveTime;
二. keepAliveTime的设置方法
1.通过构造函数设置
通过 keepAliveTime 、unit共同决定实际的 keepAliveTime值,最终会转化成纳秒单位。
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
2.通过setKeepAliveTime方法动态设置
重新设置线程池的keepAliveTime属性,如果发现将要设置的值比原来的keepAliveTime值要小(即减小keepAliveTime),则触发interruptIdleWorkers(),中断空闲线程。
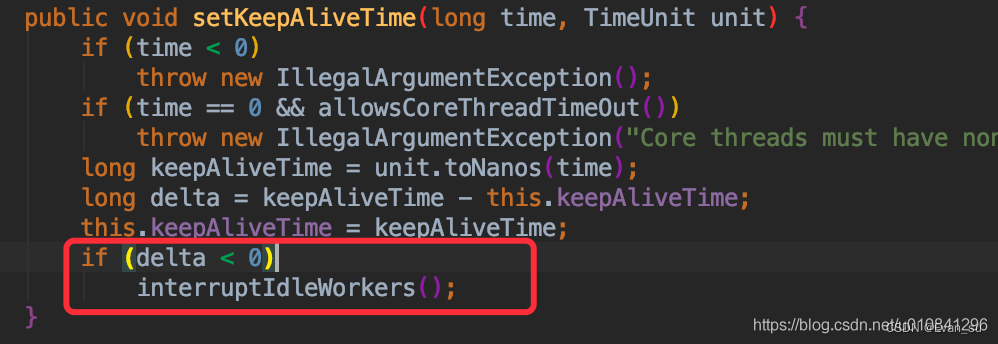
interruptIdleWorkers()是怎么中断线程的呢?
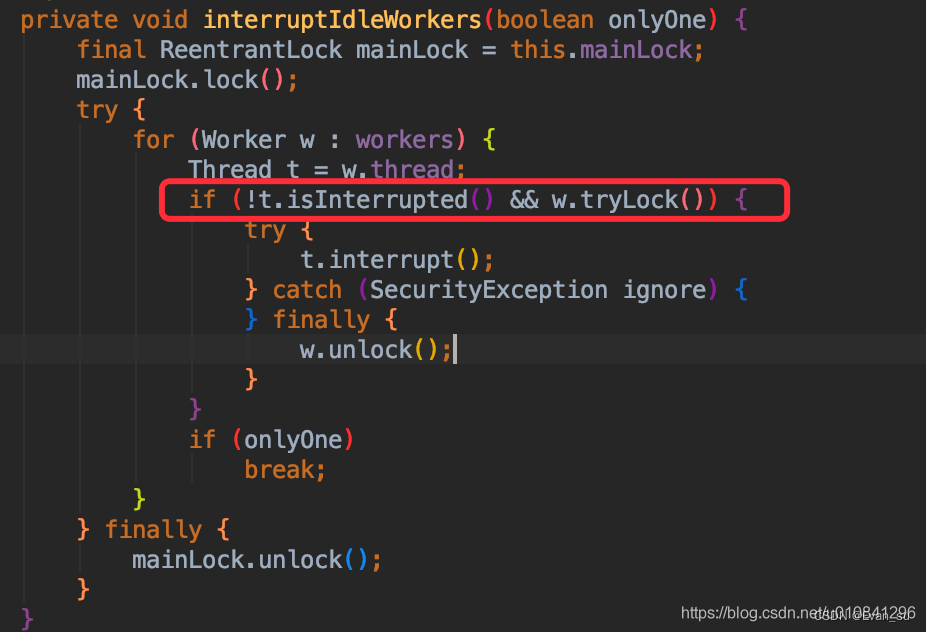
(1)interruptIdleWorkers先拿出所有的工作者进行遍历,判断工作者对应的线程是否已经中断。
(2)如果没有产生中断,则判断是否可以获得锁,如果能获得锁,则代表是空闲线程,然后中断该线程。
(3)至于线程的中断在什么时候会抛出中断异常,同学们可以自己找下资料,也可以参考下别人写的这篇文章Java并发之线程中断
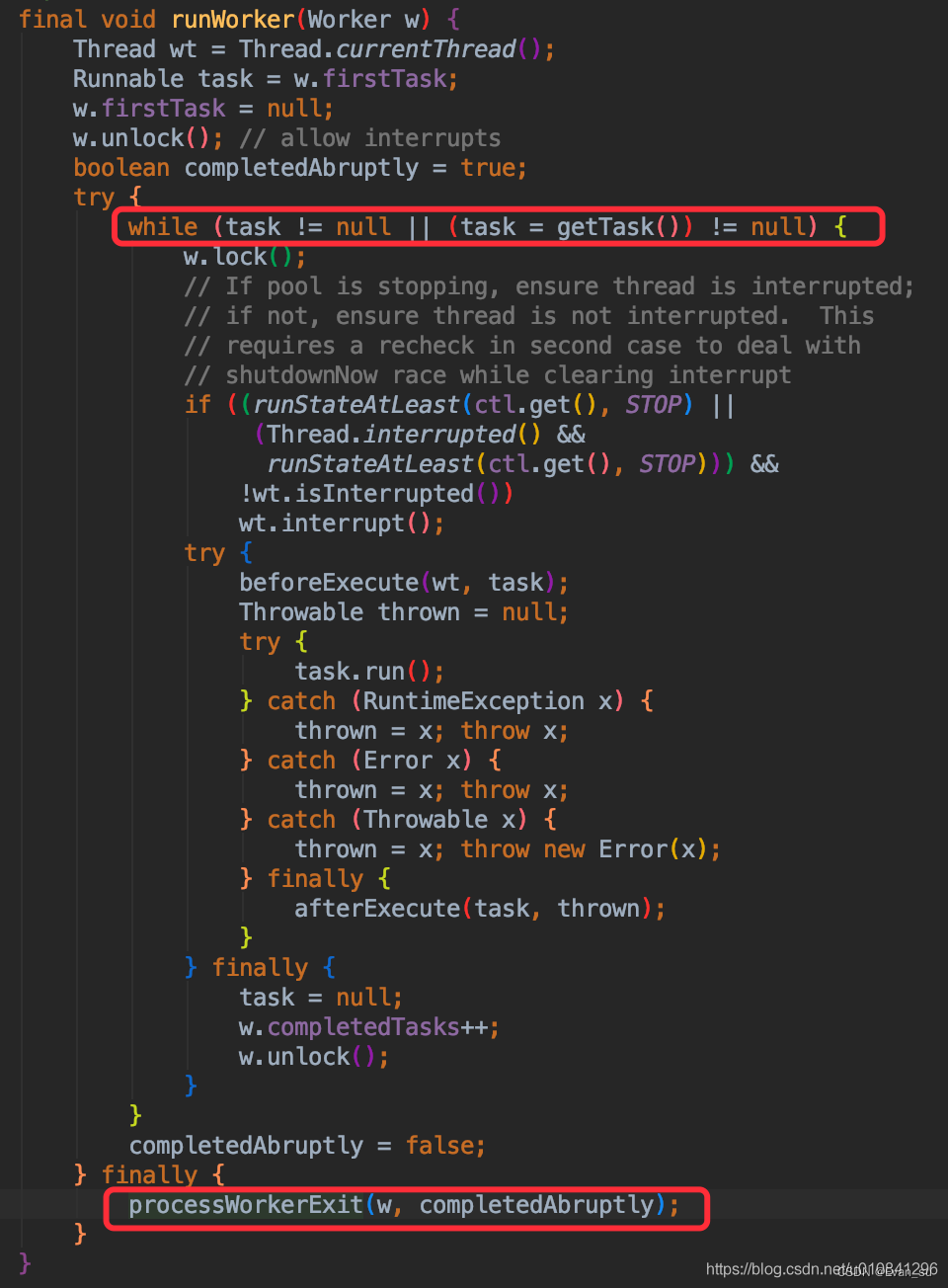
三.线程是如何根据keepAliveTime进行销毁的
线程池中的线程通过工作者(Worker)这个类进行包装,Worker通过 ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker() 这个方法进行自旋,从队列中获得task,并完成工作。
如果拿不到task(即firstTask == null 或 getTask() == null),则会退出自旋,进入finally代码块。finally中会调用processWorkerExit方法,注销当前Worker,实现worker的销毁。对keepAliveTime的使用,就在getTask()方法中,这个在后面讲解。
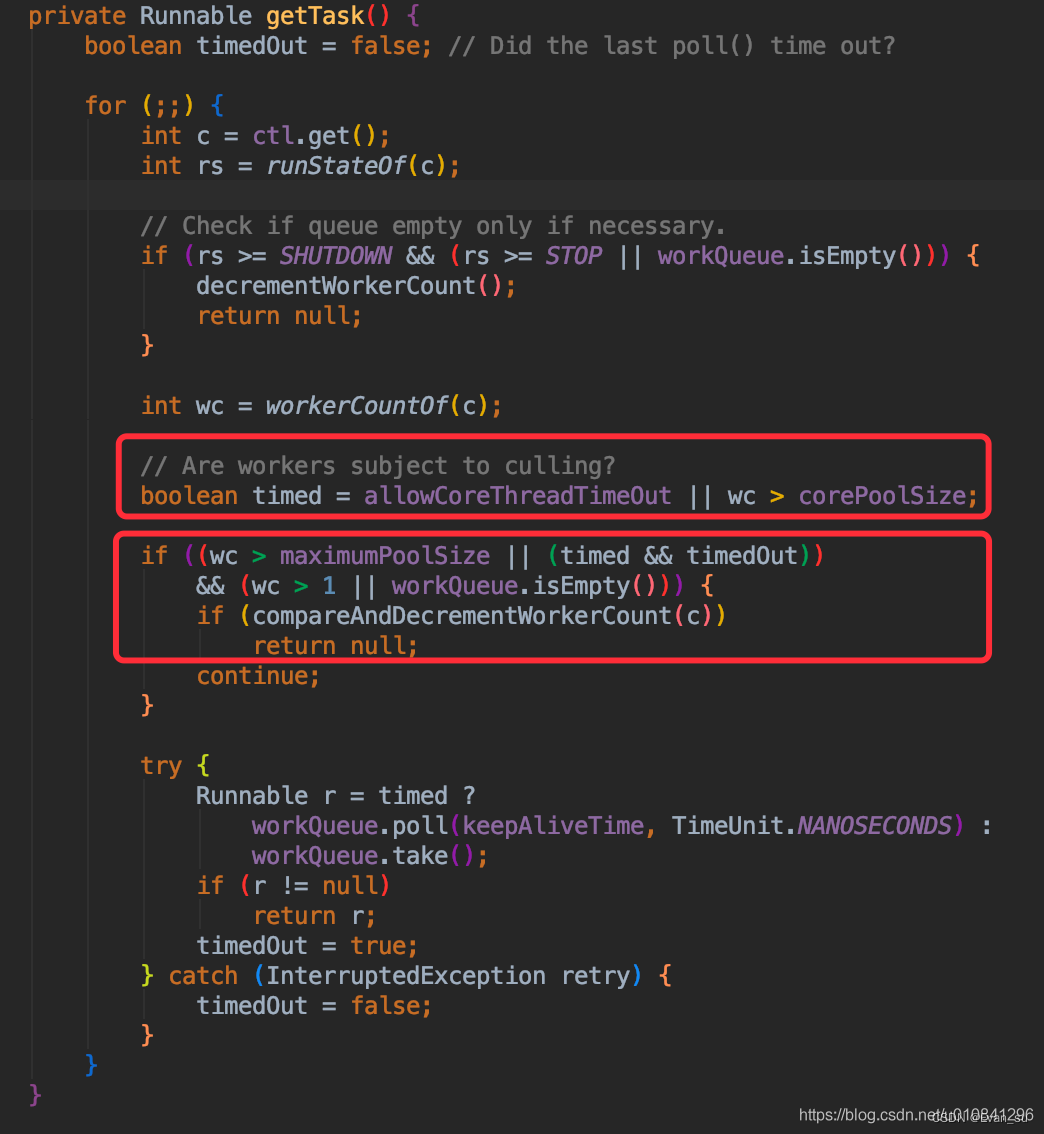
getTask 怎么使用 keepAliveTime
(1)首先也是一个自旋,当allowCoreThreadTimeout(运行空闲核心线程超时) 或 wc>corePoolSize(当前线程数量大于核心线程数量) 时,timed会标识为true,表示需要进行超时判断。
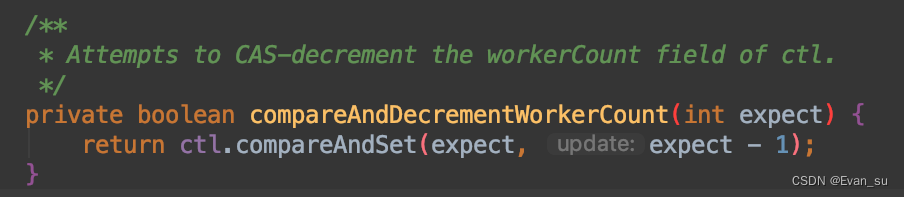
(2)当wc(当前工作者数量)大于 最大线程数 或 空闲线程的空闲时间大于keepAliveTime(timed && timeout),以及wc>1或(workQueue)任务队列为空时,会进入compareAndDecrementWorkerCount方法,对wc的值减1。
(3)当compareAndDecrementWorkerCount方法返回true时,则getTask方法会返回null,终止getTask方法的自旋。这时候回到runWorker方法,就会进入到processWorkerExit方法,进行销毁worker。
compareAndDecrementWorkerCount中操作的是ctl属性:
(1)ctl是中心控制器,一个AtomicInteger类型的整数,通过数字的二进制编码的位进行分段,不同的二进制位段表示有不同的含义。
(2)在ctl中,低29为表示线程池的容量,即线程池最大容量为 536870911 = 000 11111111111111111111111111111。
/**
* The main pool control state, ctl, is an atomic integer packing
* two conceptual fields
* workerCount, indicating the effective number of threads
* runState, indicating whether running, shutting down etc
*/
private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0));
// COUNT_BITS = 29
private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3;
// CAPACITY = 536870911 = 000 11111111111111111111111111111
private static final int CAPACITY = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1;
private static int workerCountOf(int c) {
return c & CAPACITY;
}
ThreadPoolExecutor中的keepAliveTime详解-CSDN博客
ThreadPoolExecutor中的keepAliveTime到底是什么意思?-CSDN博客
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 说一说文件转换服务的系统设计
- spark on yarn安装部署
- 惯性动作捕捉技术,驱动数字人助力企业晚会活动主持
- 共享购模式:引领未来消费潮流
- 【合阳新起点公益】“关爱留守儿童 守护牙齿健康”牙膏发放活动
- 【BI】FineBI功能学习路径-20231211
- 利用亚马逊API:一键获取全球商品详细信息
- SpringBoot Starter机制 ——自动化配置
- 4S店汽车行业万能通用小程序源码系统:功能强大,集合汽车在线展示+在线预约+贷款计算器......附带完整的搭建教程
- 前端 -- 基础 综合案例 一 圣诞老人网页的静态实现