【C语言题解】 | 144. 二叉树的前序遍历
发布时间:2024年01月09日
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
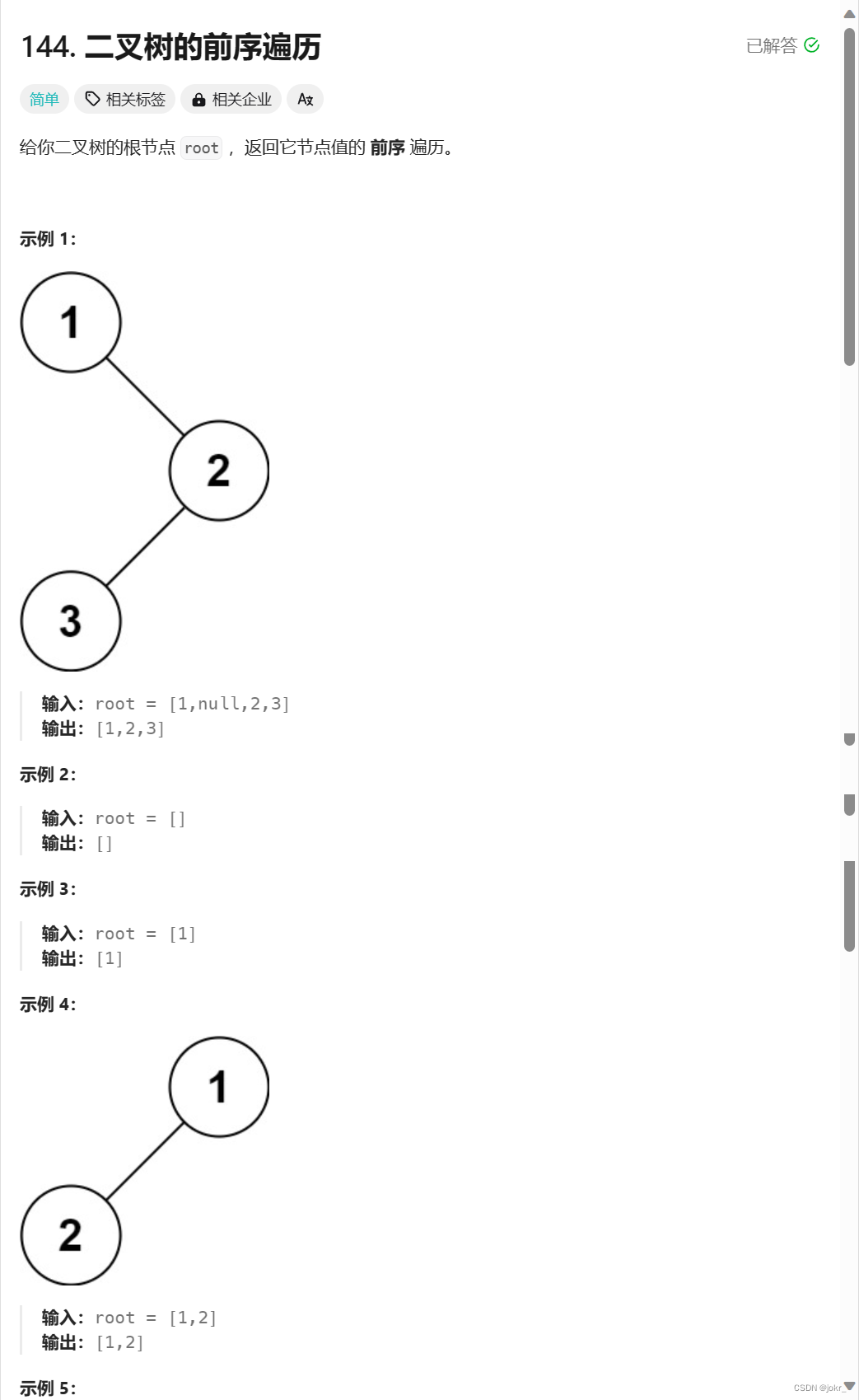
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
函数原型:
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) {
首先先观察一下这个函数原型,TreeNode* root 为形参,传入根节点,int* returnSize为形参,在函数调用时用于返回改题目所求数组的长度,因为由于C语言的局限,只能返回一个参数,所以采用这种通过传入指针的形参,来改变函数外部实参的方法。
题目要求给一个二叉树的根节点,返回其前序遍历的数组。
首先先计算二叉树的节点个数,用于后续的数组空间申请。
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
然后先序遍历,写入数组:
因为根据上述代码,求得节点个数为n,则该数组一共有n个空间,控制写入数组的下标需要传入int* ,因为若直接传入int,形参的改变不影响实参的改变。
void preorder (struct TreeNode* root, int* a,int* pi)
{
if(root == NULL)
return ;
a[(*pi)++] = root->val;
preorder(root->left,a,pi);
preorder(root->right,a,pi);
}
使用malloc函数构建数组,返回数组。
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) {
int n = TreeSize(root);
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
*returnSize = n;
int* i = 0;
preorder(root,a,&i);
return a;
}
代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
void preorder (struct TreeNode* root, int* a,int* pi)
{
if(root == NULL)
return ;
a[(*pi)++] = root->val;
preorder(root->left,a,pi);
preorder(root->right,a,pi);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) {
int n = TreeSize(root);
int* a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
*returnSize = n;
int* i = 0;
preorder(root,a,&i);
return a;
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/jokr_/article/details/135460801
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 一文读懂算法中的时间复杂度和空间复杂度,O(1)、O(logn)、O(n)、O(n^2)、O(2^n) 附举例说明,常见的时间复杂度,空间复杂度
- 企业计算机服务器中了halo勒索病毒如何解密,halo勒索病毒恢复流程
- 记录Oracle Exadata X8M-2 存储服务器告警灯亮的处理过程(/SYS/MB/P0&PCIE7)
- 微信可以定时发送朋友圈吗?朋友圈怎么停止发表?
- Python 基础(一):入门必备知识_python基础知识
- 目标检测应用场景—数据集【NO.21】火灾检测数据集
- MD5算法的简述
- 55 回溯算法解黄金矿工问题
- vivado 指定相对位置
- 从零开始怎么做好产品宣传册