Hive学习(13)lag和lead函数取偏移量
发布时间:2024年01月02日
hive里面lag函数
在数据处理和分析中,窗口函数是一种重要的技术,用于在数据集中执行聚合和分析操作。Hive作为一种大数据处理框架,也提供了窗口函数的支持。在Hive中,Lag函数是一种常用的窗口函数,可以用于计算前一行或前N行的值。
窗口函数简介
窗口函数是一种用于根据特定条件对数据进行分组和排序的函数,它可以在查询中使用。窗口函数配合分析函数一起使用,能够对数据进行更加灵活和高效的处理。
Hive中的窗口函数可以用于以下几种情况:
- 计算移动平均值或累积总和
- 计算每一行与前一行的差值
- 获取某一行相对于整个数据集的排序位置
- 对数据进行分组后,获取每个分组的排名
语法:
LAG(input[, offset[, default]]) OVER([PARTITION BY partition_expression, ...] ORDER BY sort_expression [, ...])
参数说明:
input:要获取的值所在的列或者表达式
offset:要获取的行之前的偏移量,默认为1
default:当没有前一行时,返回的默认值
场景1:
原数据如下,目标是客户取上次购买时间
| cust_no | purc_date |
|---|---|
| 300031 | 2022-01-01 |
| 300031 | 2022-01-02 |
| 300031 | 2022-01-03 |
| 300031 | 2022-01-04 |
| 300031 | 2022-01-05 |
| 300031 | 2022-01-06 |
代码如下:
lag(字段,向上取几行,取不到给默认值),lag函数是可以直接取指定行数,取不到默认为null;
可设置默认值,语法中【default】位置赋值默认值;
lead 同理,向下取行;
(lag设置默认值 ‘1970-01-01’ ,lead未设置;看下效果)
select cust_no,purc_date,
lag(purc_date,1,'1970-01-01') over (partition by cust_no order by purc_date) as time1,-- 上次购买时间(设置默认值)
lead(purc_date,1) over (partition by cust_no order by purc_date) as time2 -- 下次购买时间
from table_name a;
结果:
lag结果的首条记录的上次购买时间(已经是首条记录故没有上次购买时间),返回设置的默认值 ‘1970-01-01’;
lead结果的末条购买时间的下次购买时间为null
| 客户编号 | 购买时间 | 上次购买时间 | 下次购买时间 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 300031 | 2022-01-01 | 1970-01-01 | 2022-01-02 |
| 300031 | 2022-01-02 | 2022-01-01 | 2022-01-03 |
| 300031 | 2022-01-03 | 2022-01-02 | 2022-01-04 |
| 300031 | 2022-01-04 | 2022-01-03 | 2022-01-05 |
| 300031 | 2022-01-05 | 2022-01-04 | 2022-01-06 |
| 300031 | 2022-01-06 | 2022-01-05 | NULL |
补充:
--如有此业务场景,可计算本次距离上次间隔天数
datediff(purc_date,lag(purc_date,1,'1970-01-01') over (partition by cust_no order by purc_date))
场景2
简单看一下场景2,有问题可评论或私信讨论。
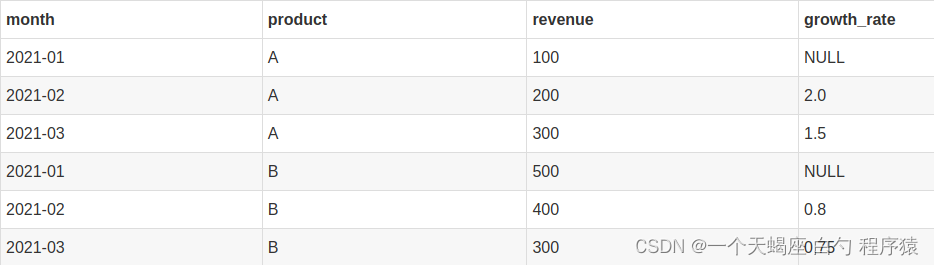
现在,我们希望计算每个产品的月度增长率,即当前月份的销售额与前一个月份的销售额之比。可以使用Lag函数来实现这个目标:
select
mth --月份
,product --产品代码
,revenue --收入金额
,(revenue / lag(revenue) over(partition by product order by mth)) as growth_rate --月度增长率
from
table_name
order by
product
,mth
结果:
产品A因未设置默认值,所以返回NULL;产品B同理
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/szdxltt/article/details/128615440
https://blog.51cto.com/u_16213418/7061149
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/Dreamy_zsy/article/details/135342668
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- easyexcel上传校验的方法封装
- Qt/C++中英输入法/嵌入式输入法/小数字面板/简繁切换/特殊字符/支持Qt456
- 看完这篇你就知道了!人气爆表的6款Sketch插件大揭秘!
- 【从浅到深的算法技巧】集合类数据类型的实现
- npm详细安装教程
- 【卡梅德生物】第二弹:慢病毒载体介绍
- [NAND Flash 6.6] NAND FLASH Multi Plane Program(写)操作_multi plane 为何能提高闪存速度
- 图文详解丨iOS App上架全流程及审核避坑指南
- 【云原生】springboot 整合 OpenTelemetry
- 突然又对 Go 感兴趣,GOPATH entry cannot start with shell metacharacter 错误