Ubuntu 磁盘管理DF命令用法
Linux磁盘空间管理是系统运维中的核心环节,它直接影响到系统的稳定运行、数据的安全性和业务的连续性。
通过实施有效的磁盘空间管理策略,系统管理员可以确保系统的高效运作,满足不断变化的业务需求,并为用户提供可靠的服务。
因此,对Linux磁盘空间管理的重视和精通对于任何企业的IT运营都属于核心业务。
DF命令用法
Linux df命令用于显示文件系统的磁盘空间使用情况。以下是一些常用的df命令参数:
-
-a或--all: 显示所有文件系统,包括未挂载的和已被挂载多次的文件系统。 -
-h或--human-readable: 以人类可读的格式(如K、M、G)显示磁盘空间大小。 -
-H或--si: 类似于-h,但使用1000而不是1024作为基数来计算单位(例如,1MB = 1,000,000字节而不是1,048,576字节)。 -
-k或--kilobytes: 使用千字节(KB)作为块大小单位。 -
-m或--megabytes: 使用兆字节(MB)作为块大小单位。 -
-g或--gigabytes: 使用千兆字节(GB)作为块大小单位。 -
-l或--local: 只显示本地文件系统。 -
-i或--inodes: 显示每个文件系统的inode使用信息。 -
-T或--type=TYPE: 只显示指定类型的文件系统,例如"ext4"、"tmpfs"等。 -
-x或--exclude-type=TYPE: 排除指定类型的文件系统。 -
-t或--type=TYPE: 只显示指定类型的文件系统。 -
-B或--block-size=SIZE: 指定块大小,例如-BM表示块大小为1,048,576字节。 -
FILE: 如果指定文件名,df将只显示包含该文件的文件系统的信息。 -
--output=FIELD_LIST: 自定义输出字段列表,例如--output=target,fstype,size,used,avail. -
--help: 显示帮助信息。 -
--version: 显示df命令的版本信息。
这些参数可以根据需要组合使用,例如,要以人类可读的格式查看所有文件系统的磁盘空间使用情况,包括 inode 使用信息,可以使用以下命令:
df -ahi
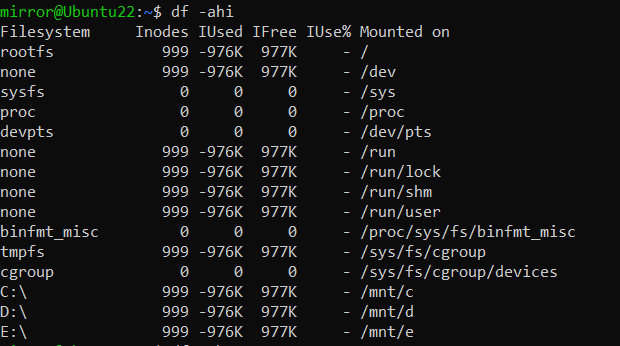
请注意,不同的Linux发行版可能会有一些细微的差异,部分参数可能在某些版本中不可用。所以,在实际环境中,我们通常会先查看当前版本信息。
接下来我们会对DF命令参数进行实际演示:
- df命令参数
-a
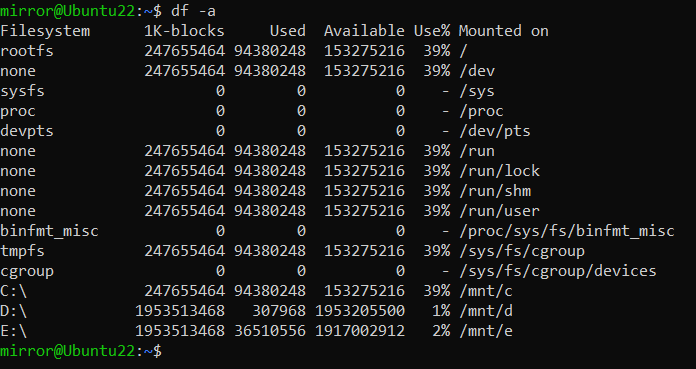
显示所有文件系统,包括未挂载的和已被挂载多次的文件系统。-a参数的可视性其实不是很好,因为默认也是用的千字节,大家根据自己的情况选择合适的方式。
df -a
- df命令参数
-h
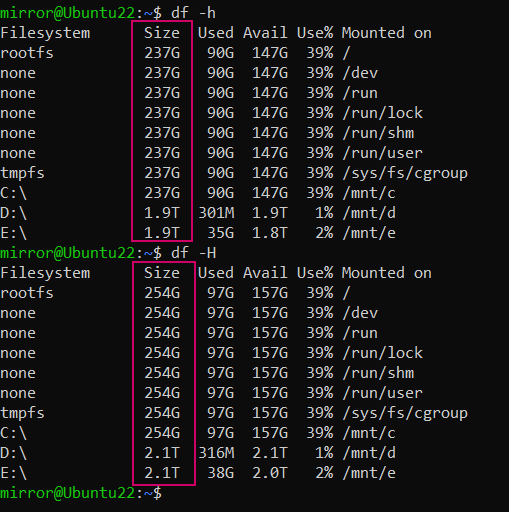
-h参数的效果好一些,其看来很直观,也是我们常见的大小表达方式。
df -h
mirror@Ubuntu22:~$ df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
rootfs 237G 91G 147G 39% /
none 237G 91G 147G 39% /dev
none 237G 91G 147G 39% /run
none 237G 91G 147G 39% /run/lock
none 237G 91G 147G 39% /run/shm
none 237G 91G 147G 39% /run/user
tmpfs 237G 91G 147G 39% /sys/fs/cgroup
C:\ 237G 91G 147G 39% /mnt/c
D:\ 1.9T 301M 1.9T 1% /mnt/d
E:\ 1.9T 35G 1.8T 2% /mnt/e
mirror@Ubuntu22:~$
- df命令参数
-H
-H参数使用1000而不是1024作为基数来计算单位(例如,1MB = 1,000,000字节而不是1,048,576字节),所以,实际显示出来的Size栏位数值要更大一些。
df -H
- df命令参数
-k
使用千字节(KB)作为块大小单位来显示文件系统大小。
df -k
mirror@Ubuntu22:~$ df -k
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
rootfs 247655464 94374736 153280728 39% /
none 247655464 94374736 153280728 39% /dev
none 247655464 94374736 153280728 39% /run
none 247655464 94374736 153280728 39% /run/lock
none 247655464 94374736 153280728 39% /run/shm
none 247655464 94374736 153280728 39% /run/user
tmpfs 247655464 94374736 153280728 39% /sys/fs/cgroup
C:\ 247655464 94374736 153280728 39% /mnt/c
D:\ 1953513468 307968 1953205500 1% /mnt/d
E:\ 1953513468 36510556 1917002912 2% /mnt/e
- df命令参数
-m
使用兆字节(MB)作为块大小单位来显示文件系统大小。
df -m
mirror@Ubuntu22:~$ df -m
Filesystem 1M-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
rootfs 241852 92163 149689 39% /
none 241852 92163 149689 39% /dev
none 241852 92163 149689 39% /run
none 241852 92163 149689 39% /run/lock
none 241852 92163 149689 39% /run/shm
none 241852 92163 149689 39% /run/user
tmpfs 241852 92163 149689 39% /sys/fs/cgroup
C:\ 241852 92163 149689 39% /mnt/c
D:\ 1907728 301 1907428 1% /mnt/d
E:\ 1907728 35655 1872074 2% /mnt/e
- df命令参数
-l
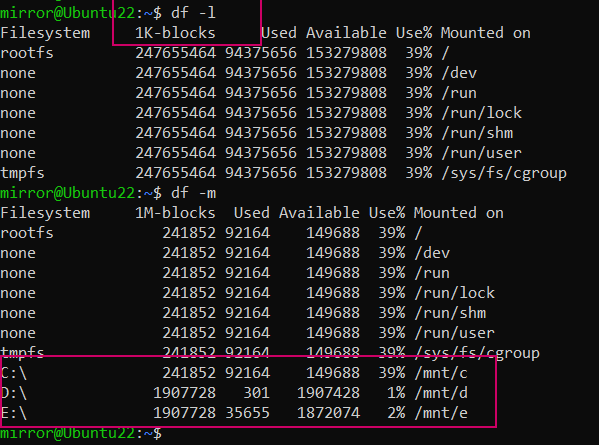
-l参数只显示本地的文件系统,不会显示网络挂载的部分。
df -l
用df -l 和df -m 比较久比较明显:
- df命令参数
-i
显示每个文件系统的inode使用信息。
df -i
mirror@Ubuntu22:~$ df -i
Filesystem Inodes IUsed IFree IUse% Mounted on
rootfs 999 -999001 1000000 - /
none 999 -999001 1000000 - /dev
none 999 -999001 1000000 - /run
none 999 -999001 1000000 - /run/lock
none 999 -999001 1000000 - /run/shm
none 999 -999001 1000000 - /run/user
tmpfs 999 -999001 1000000 - /sys/fs/cgroup
C:\ 999 -999001 1000000 - /mnt/c
D:\ 999 -999001 1000000 - /mnt/d
E:\ 999 -999001 1000000 - /mnt/e
- df命令参数
-T
直接用-T可以查看所有的文件系统类型,以下为只显示tmpfs文件类型,用--type=tmpfs来过滤
df -T
我们的演示主机有wslfs、tmpfs、drvfs三种文件系统
mirror@Ubuntu22:~$ df -T
Filesystem Type 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
rootfs wslfs 247655464 94378312 153277152 39% /
none tmpfs 247655464 94378312 153277152 39% /dev
none tmpfs 247655464 94378312 153277152 39% /run
none tmpfs 247655464 94378312 153277152 39% /run/lock
none tmpfs 247655464 94378312 153277152 39% /run/shm
none tmpfs 247655464 94378312 153277152 39% /run/user
tmpfs tmpfs 247655464 94378312 153277152 39% /sys/fs/cgroup
C:\ drvfs 247655464 94378312 153277152 39% /mnt/c
D:\ drvfs 1953513468 307968 1953205500 1% /mnt/d
E:\ drvfs 1953513468 36510556 1917002912 2% /mnt/e
过滤一下tmpfs的文件系统类型
df -T --type=tmpfs
mirror@Ubuntu22:~$ df -T --type=tmpfs
Filesystem Type 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
none tmpfs 247655464 94379132 153276332 39% /dev
none tmpfs 247655464 94379132 153276332 39% /run
none tmpfs 247655464 94379132 153276332 39% /run/lock
none tmpfs 247655464 94379132 153276332 39% /run/shm
none tmpfs 247655464 94379132 153276332 39% /run/user
tmpfs tmpfs 247655464 94379132 153276332 39% /sys/fs/cgroup
mirror@Ubuntu22:~$
- df命令参数
-x
-x参数用来排除指定类型的文件系统
df -x tmpfs
或者
df --exclude-type=tmpfs
mirror@Ubuntu22:~$ df --exclude-type=tmpfs
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
rootfs 247655464 94371068 153284396 39% /
C:\ 247655464 94371068 153284396 39% /mnt/c
D:\ 1953513468 307968 1953205500 1% /mnt/d
E:\ 1953513468 36510556 1917002912 2% /mnt/e
- df命令参数
-t
只显示指定类型的文件系统。方法如下:
df -t tmpfs
或者
df --type=tmpfs
mirror@Ubuntu22:~$ df -t tmpfs
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
none 247655464 94367632 153287832 39% /dev
none 247655464 94367632 153287832 39% /run
none 247655464 94367632 153287832 39% /run/lock
none 247655464 94367632 153287832 39% /run/shm
none 247655464 94367632 153287832 39% /run/user
tmpfs 247655464 94367632 153287832 39% /sys/fs/cgroup
mirror@Ubuntu22:~$
- df命令参数
-B
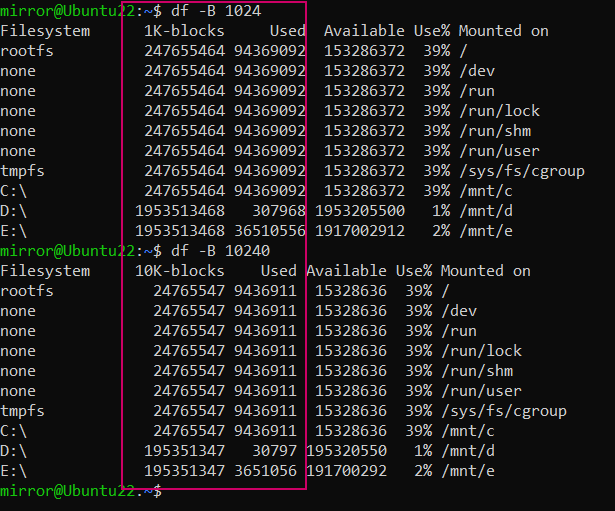
指定块大小,用df -B 1024和df -B 10240比较会直观一些
- 查看指定文件大小
df -h file /etc
- 输出自定义的字段列表
例如我们要查看/etc目录 used的字段信息,请参考如下命令:
df -h file /etc --output=used
以上希望帮助大家掌握df命令的常用方法。
推荐阅读
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- Java实现大学计算机课程管理平台 JAVA+Vue+SpringBoot+MySQL
- HTML--表单
- MySQL 一个线程(或事务)在更新表时,另一个线程能否读取这个表
- C++入门学习(七)整型
- 报名软考需要满足哪些条件?
- 实战:使用Spring Boot监控SQL执行
- 数据结构-数据结构导论
- x-cmd pkg | usql - SQL 数据库的通用交互界面
- APP出海:洞察移动应用海内外市场的差异与应对策略
- 洛谷P3084 [USACO13OPEN] Photo G