系列六、Springboot整合Spring Session
一、概述
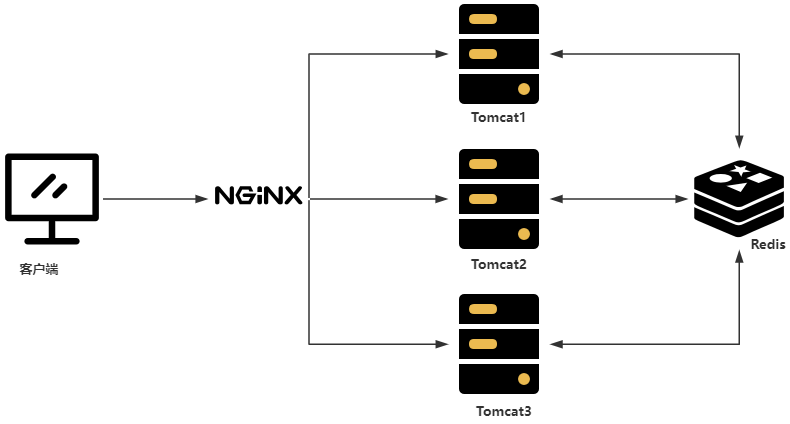
? ? ? ? 在互联网发展的起始阶段,一般使用的是单服务架构,由于只有一台服务器(Tomcat),所有的请求和响应都是基于这台服务器实现的,那么就不存在session共享的问题,但是在互联网发展的今天,基本上是分布式 + 微服务了,再使用传统的方案去处理session,显然是行不通的,先看一组简单的架构图:
? ? ? ? 在上述的架构中,会出现一些单服务中不存在的问题,例如客户端发送一个请求,经Nginx转发后请求落到Tomcat1上了,然后在Tomcat1的session中保存了一份数据,下次又来一个请求,经过Nginx转发之后请求落到Tomcat2上了,那么这个时候对于第二个请求来说,想从session中拿数据显示是无法拿到的。针对这种情况,Springboot也提供了对应的解决方案,即:Spring Session。所谓Spring Session其实也不是啥新鲜玩意儿,其实就是一个HttpSession,通过引入?spring-session-data-redis 和?spring-boot-starter-data-redis,以后所有关于session的操作,Spring Session都将使用Spring中的代理过滤器,将所有的Session操作拦截下来,自动地将Session中的数据同步到Redis中去,或者从Redis中取出数据然后响应给客户端,这对客户端是无感的,存数据不会再具体的存储到某一台服务器了,而是存到一个公共的地方,取数据也从公共的地方去取,这样就解决了微服务+分布式架构下session共享的问题,架构图如下:
二、案例代码
2.1、环境搭建
2.1.1、项目概览
2.1.2、pom
<dependencies>
<!-- springboot -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.session</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-session-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 工具 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
<version>1.18.30</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId>
<version>4.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.76</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.fastjson2</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson2</artifactId>
<version>2.0.37</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>20.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.citrus</groupId>
<artifactId>citrus-springext-all</artifactId>
<version>3.2.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.7.22</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>2.1.3、yml
spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.173.232
port: 6379
password: 123456
database: 0
server:
port: 80802.1.4、主启动
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/12/12 15:08
* @Description:
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootSessionApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootSessionApplication.class, args);
}
}2.1.5、MyRedisConfig
/**
* @Author : 一叶浮萍归大海
* @Date: 2023/12/12 15:08
* @Description:
*/
@Configuration
public class MyRedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
/**
* 解决RedisTemplate、StringRedisTemplate中文乱码问题
* @param connectionFactory
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(LettuceConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
/**
* 解决Spring Session中文乱码
* 思路:RedisHttpSessionConfiguration ===> createRedisTemplate ===>配置一个bean名为springSessionDefaultRedisSerializer的RedisSerializer
* 参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/dd1df913b1b2
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisSerializer<Object> springSessionDefaultRedisSerializer() {
GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer serializer = new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer();
return serializer;
}
}2.2、测试
2.2.1、说明
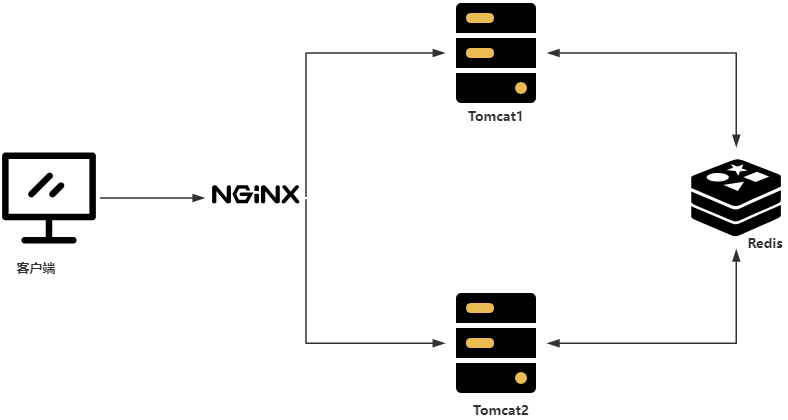
? ? ? ? 为了测试方便方便,我这边简易搞了一台Nginx+2个应用的模式来为大家演示Springboot整合Spring Session的大概流程,架构图如下:
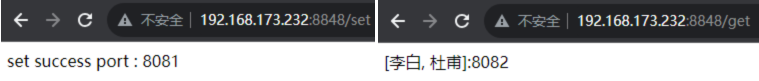
? ? ? ? 思路:通过Nginx转发,在Tomcat1中的session中存一个数据,然后从Tomcat2的session中看看能否拿到session中的数据,进而验证!
2.2.2、修改nginx.conf配置信息并启动
? ? ? ? 如果对Nginx使用不熟悉的小伙伴,可以参考我之前写的 Nginx系列文章,这里就不再赘述啦!nginx.conf中增加内容如下:
# Spring Session共享
upstream sessionShareServer{
?? ?server 127.0.0.1:8081 weight=1;
?? ?server 127.0.0.1:8082 weight=1;
}
server {
? ? listen ? ? ? 8848;
? ? server_name ?localhost;
? ? location / {
?? ??? ?proxy_pass?? ?http://sessionShareServer;
?? ??? ?proxy_redirect default;
? ? ? ??
? ? }
}配置解释:
????????upstream模块:
? ? ? ? ????????upstream:表示配置上游服务器
????????????????sessionShareServer:给上游服务器起一个名字(自定义)
????????????????server 127.0.0.1:8081:?配置的是一个个单独服务的地址,待会儿我们会将本地jar包上传至Linux服务器,然后分别以8081和8082端口启动
? ? ? ? ????????weight:权重,表示当请求过来时,如何分配请求
? ? ? ? server模块:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? listen 8848:监听的端口
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? server_name:服务的名称
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? location / :表示拦截所有以 http://192.168.173.232:8848/打头的请求
????????????????proxy_pass:表示请求转发的地址,地址为上边的上游服务器
????????????????proxy_redirect:表示设置当发生重定向请求时,nginx 自动修正响应头数据(默认是 Tomcat 返回重定向,此时重定向的地址是 Tomcat 的地址,我们需要将之修改使之成为 Nginx 的地址)? ? ? ??
2.2.3、编译 & 打包 & 将打包的jar包上传至 linux的/applications目录
2.2.4、启动服务
nohup java -jar springboot2x16-session-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8081 &
nohup java -jar springboot2x16-session-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8082?&
指令解释:
? ? ? ? nohup:表示当终端关闭时,Spring Boot应用不要停止运行;
? ? ? ? &:表示让Spring Boot应用在后台启动;
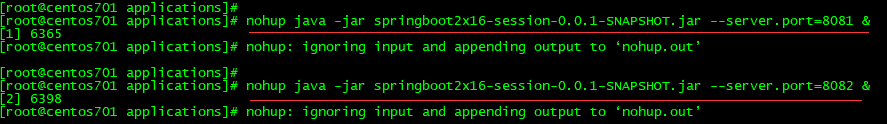
2.2.5、后台启动日志
????????日志文件在/applications/nohup.out中,如果启动过程中报错的话,可以在这里查看原因。

2.2.6、set & get
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 前端基础知识:html表格
- 数据结构--稀疏矩阵及Java实现
- Windows 10中的驱动程序与device guard的兼容性
- 人工智能与自动驾驶:智能出行时代的未来之路
- 养猫家庭怎么挑选宠物空气净化器?猫用空气净化器推荐来了!
- 专为Mac用户设计的思维导图软件MindNode 2023 for Mac助您激发创意!
- Leetcode 455 分发饼干
- 观察者模式
- nodejs终止子进程,终止命令行进程
- R302 指纹识别模块的应用及指标