【算法】串联所有单词的子串【滑动窗口】
题目
给定一个字符串 s 和一个字符串数组 words。 words 中所有字符串 长度相同。
s 中的 串联子串 是指一个包含 words 中所有字符串以任意顺序排列连接起来的子串。
例如,如果 words = ["ab","cd","ef"], 那么 "abcdef", "abefcd","cdabef", "cdefab","efabcd", 和 “efcdab” 都是串联子串。 “acdbef” 不是串联子串,因为他不是任何 words 排列的连接。
返回所有串联子串在 s 中的开始索引。你可以以 任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:s = "barfoothefoobarman", words = ["foo","bar"]
输出:[0,9]
解释:因为 words.length == 2 同时 words[i].length == 3,连接的子字符串的长度必须为 6。
子串 “barfoo” 开始位置是 0。它是 words 中以 [“bar”,“foo”] 顺序排列的连接。
子串 “foobar” 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 [“foo”,“bar”] 顺序排列的连接。
输出顺序无关紧要。返回 [9,0] 也是可以的。
示例 2:
输入:s = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword", words = ["word","good","best","word"]
输出:[]
解释:因为 words.length == 4 并且 words[i].length == 4,所以串联子串的长度必须为 16。
s 中没有子串长度为 16 并且等于 words 的任何顺序排列的连接。
所以我们返回一个空数组。
示例 3:
输入:s = "barfoofoobarthefoobarman", words = ["bar","foo","the"]
输出:[6,9,12]
解释:因为 words.length == 3 并且 words[i].length == 3,所以串联子串的长度必须为 9。
子串 “foobarthe” 开始位置是 6。它是 words 中以 [“foo”,“bar”,“the”] 顺序排列的连接。
子串 “barthefoo” 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 [“bar”,“the”,“foo”] 顺序排列的连接。
子串 “thefoobar” 开始位置是 12。它是 words 中以 [“the”,“foo”,“bar”] 顺序排列的连接。
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 104
1 <= words.length <= 5000
1 <= words[i].length <= 30
words[i] 和 s 由小写英文字母组成
Related Topics
哈希表
字符串
滑动窗口
题解
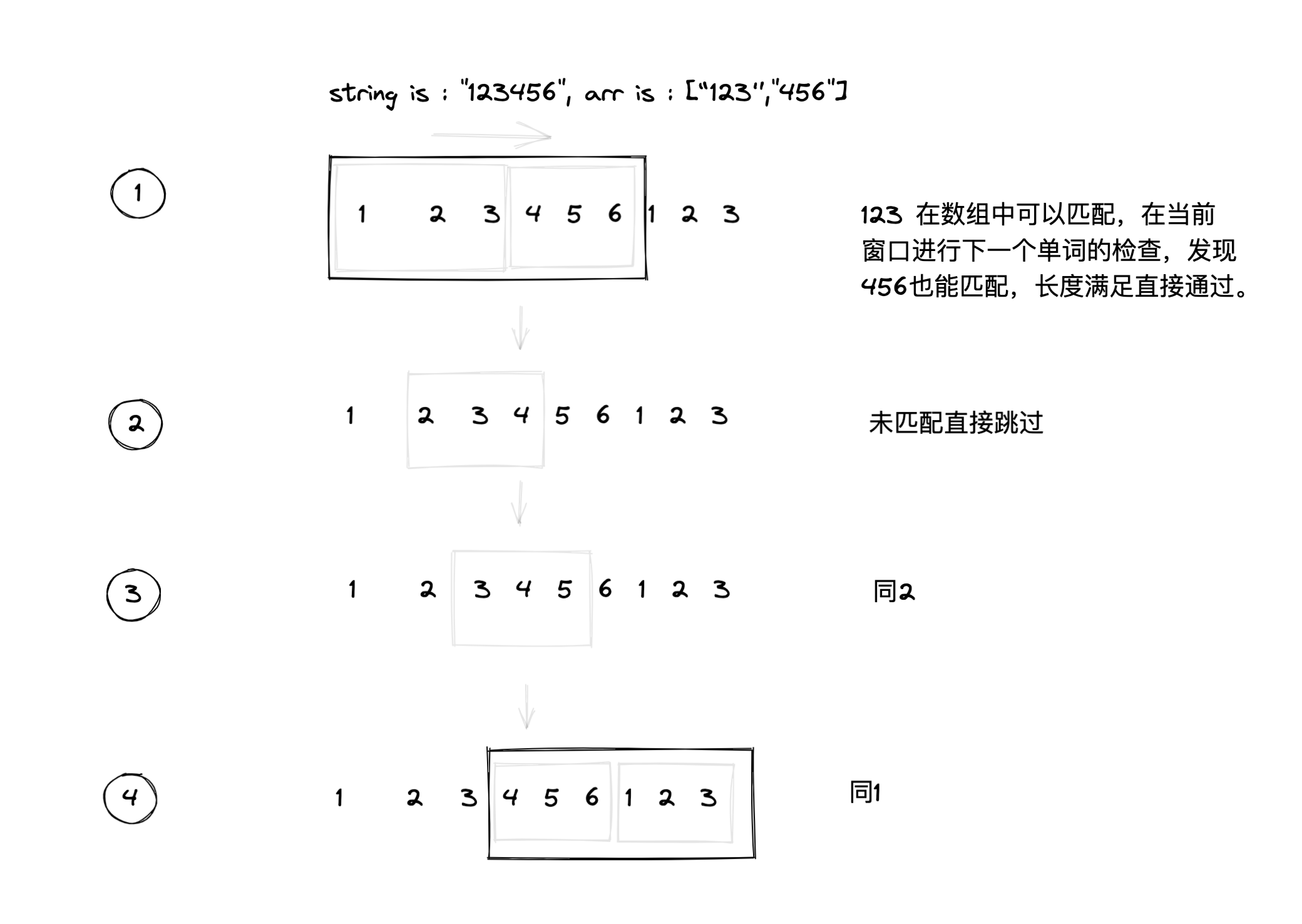
滑动窗口

实现代码
public List<Integer> findSubstring(String s, String[] words) {
List<Integer> lists = new ArrayList<>(); // 结果集列表先初始化
int wordsLen = words[0].length(); // 单词长度
int count = words.length * wordsLen; // 单词需要组成的字符串的总长度,后面要根据这个去判断是否完成一次窗口的移动
int left = 0, right = 0; // 窗口的左边位置和右边位置
// 这里必须是map,因为words数组中可能会有多个相同的单词,所以当存在多个相同的单词的时候必须要计数,后面判断的时候必须判断存在之后对map的值进行-1
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// 将数组转换成数组
Arrays.stream(words).forEach(key -> {
Integer integer = map.get(key);
if (integer == null) {
map.put(key, 1);
} else {
// 同个key存在多个value就++
map.put(key, ++integer);
}
});
while (right < s.length()) { // 循环出口
HashMap<String, Integer> copyMap = new HashMap<>(map); // 因为每次循环都要判断数组中所有的单词是否耗尽,所以必须每次从原始的map copy一份新的map,保证每次都可以重新分配数组中的所有单词
int start = left; // 当前窗口起始位置
while (start < left + count) {
right = start + wordsLen;
if (right > s.length()) {
break;
}
// 截取窗口字符串
String substring = s.substring(start, right);
// 获取map中的字符串,如果有 value --,没有直接break,当前窗口不存在
Integer integer = copyMap.get(substring);
if (integer != null && integer > 0) {
copyMap.put(substring, --integer);
start += wordsLen; // 在当前窗口内继续查找下个单词是否能够匹配
if (right - left == count) {
lists.add(left);
break;
}
} else {
break;
}
}
left ++; // 窗口靠右移动
}
return lists;
}
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- React Native实现升级等级进度条-代码示例
- 闪动文字gif怎么制作?一个常用gif制作网站分享
- Redis 实现全局唯一ID
- git: fork仓库后的同步操作
- gem5学习(11):将缓存添加到配置脚本中——Adding cache to the configuration script
- 使用Go语言实现RESTful API
- SL3062替代 RT6361 降压IC 60V降12V 5V 3.3V低功耗芯片
- 50个超强的Pytorch操作 ! ! !
- 大模型训练营Day2 homework
- 不忘初心,聚焦安全 —— 一名码龄15年的老程序员2023总结