netty线程调度定制
发布时间:2023年12月20日
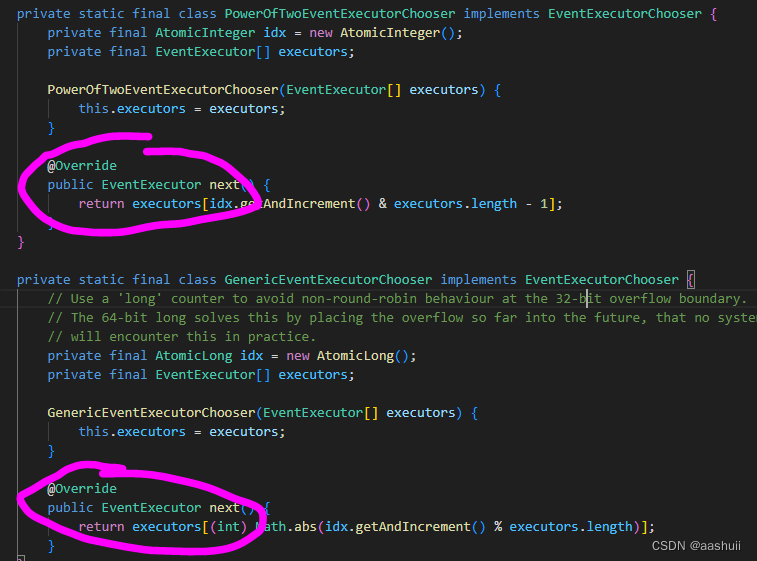
1、netty的线程调度问题
在netty的TCP调度中,线程的调度封装在NioEventLoopGroup中,线程执行则封装在NioEventLoop中。
线程调度规则封装在MultithreadEventExecutorGroup的next方法中,这个方法又封装了EventExecutorChooserFactory(实现在DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory)的next方法。
结果就是轮换着用线程。
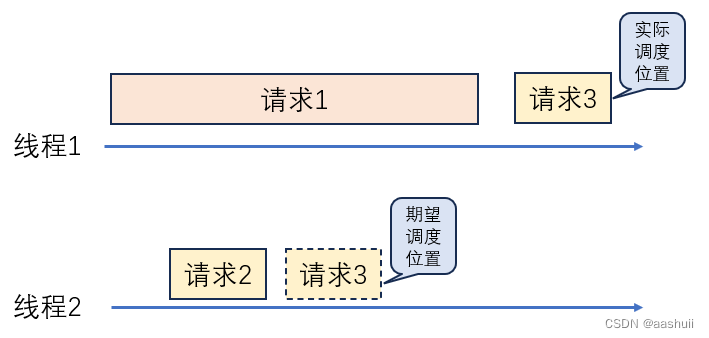
如果我们在2个线程上按顺序发送了三个http请求:请求1、请求2、请求3.
其中请求1耗时较长,请求2很快处理完成,我们就希望请求3能由线程2处理,而不是在请求1后面排队。但实际上netty把请求3分配给了线程1:
2、解决方法
为了解决请求被netty线程阻塞的问题,要么定制EventExecutorChooserFactory要么定制NioEventLoopGroup。由于定制EventExecutorChooserFactory入参较复杂,所以我们选择定制NioEventLoopGroup,定制的对象名为CustomEventLoopGroup,代码如下:
/*用来判断线程状态,有的请求响应耗时较长,netty默认的next实现是无脑轮换,
* 那么 有空闲线程也可能选择到正在执行任务的线程 导致原本可以快速返回的请求在慢请求后面等待
* 优先选择空闲线程 如果没有空闲线程则按照原来netty逻辑选择
* 但是客户端应该尽量不同业务使用不同的长连接 */
public class CustomEventLoopGroup extends NioEventLoopGroup {
static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(CustomEventLoopGroup.class);
public CustomEventLoopGroup(int nThreads, Executor executor) {
super(nThreads, executor);
}
@Override
public EventLoop next() {
EventLoop elNext = null;
EventLoop el = super.next();
elNext = el;
do {
if (elNext instanceof NioEventLoop nioEvent) {
logger.debug("pendingTasks: " + nioEvent.pendingTasks());
ThreadProperties threadInfo = nioEvent.threadProperties();
logger.debug("[" + threadInfo.id() + "] threadInfo.state: " + threadInfo.state());
if (threadInfo.state() == Thread.State.RUNNABLE) {
return elNext;
}
}
elNext = super.next();
if (elNext == null) {
return el;
}
if (elNext.equals(el)) {
return el;
}
} while (true);
}
}
服务器使用CustomEventLoopGroup代码如下:
public NettyServerHttp1(int portIn) {
port = portIn;
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = (ThreadPoolExecutor) Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new CustomEventLoopGroup(2, executor);
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024);
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG))
.childHandler(new NettyServerInitializer(null));
Channel ch = b.bind(port).sync().channel();
ch.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
logger.error("Server start err: " + e);
logger.error(e.getStackTrace());
} finally {
logger.info("Server Shutdown!");
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/aashuii/article/details/135109100
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!