Nginx location+Nginx rewrite(重写)(新版)
Nginx location+Nginx rewrite(重写)
一、location
1、常用的Nginx 正则表达式
^ :匹配输入字符串的起始位置
$ :匹配输入字符串的结束位置
* :匹配前面的字符零次或多次。如“ol*”能匹配“o”及“ol”、“oll”
+ :匹配前面的字符一次或多次。如“ol+”能匹配“ol”及“oll”、“olll”,但不能匹配“o”
? :匹配前面的字符零次或一次,例如“do(es)?”能匹配“do”或者“does”,”?”等效于”{0,1}”
. :匹配除“\n”之外的任何单个字符,若要匹配包括“\n”在内的任意字符,请使用诸如“[.\n]”之类的模式
\ :将后面接着的字符标记为一个特殊字符或一个原义字符或一个向后引用。如“\n”匹配一个换行符,而“\$”则匹配“$”
\d :匹配纯数字[0-9]
\s :空白符
\w :任意单词字符包括下划线[A-Za-z0-9_]
{n} :重复 n 次
{n,} :重复 n 次或更多次
{n,m} :重复 n 到 m 次
[] :定义匹配的字符范围
[c] :匹配单个字符 c
[a-z] :匹配 a-z 小写字母的任意一个
[a-zA-Z0-9] :匹配所有大小写字母或数字
() :表达式的开始和结束位置
| :或运算符
从功能看 rewrite 和 location 似乎有点像,都能实现跳转,主要区别在于 rewrite 是在同一域名内更改获取资源的路径,而 location 是对一类路径做控制访问或反向代理,还可以proxy_pass 到其他机器。
rewrite 对访问的域名或者域名内的URL路径地址重写
location 对访问的路径做访问控制或者代理转发
2、location的类型
location 大致可以分为三类:
精准匹配:location = / {…}
一般匹配:location / {…}
正则匹配:location ~ / {…}
3、location 的匹配规则
= :进行普通字符精确匹配,也就是完全匹配。
^~ :表示普通字符匹配。使用前缀匹配。如果匹配成功,则不再匹配其它 正则匹配location。
~ :区分大小写的匹配。
~* :不区分大小写的匹配。
!~ :区分大小写的匹配取非。
!~* :不区分大小写的匹配取非。
匹配规则:
首先看 优先级:精确= > 前缀^~ > 正则~,~*,!~,!~* > 一般前缀匹配 /XXXX > 通用匹配 /
在没有精准匹配的情况下,先看所有前缀匹配的长度,取最长匹配的location;
如果最长的前缀匹配带有 ^~ 则不再看其它正则匹配,直接使用^~的location匹配用户的访问路径并跳转页面;如果最长的前缀匹配是不带^~的,则会再看其它正则匹配
前缀匹配看长度,最长的优先匹配
正则匹配看上下顺序,由上往下依次匹配,当有匹配成功时候,停止匹配,按当前匹配规则处理请求
只有在精准、前缀、正则、一般 都没有匹配到的时候才会看通用匹配
4、location 优先级
首先精确匹配 =
其次前缀匹配 ^~
其次是按文件中顺序的正则匹配 ~或~*
然后匹配不带任何修饰符的一般前缀匹配
最后是交给 / 通用匹配
优先级总结:
(location = 完整路径) > (location ^~ 路径) > (location ~,~* 正则顺序) > (location 部分前缀路径) > (location /)
5、location 示例说明
(1)location = / {}
=为精确匹配 / ,主机名后面不能带任何字符串,比如访问 / 和 /data,则 / 匹配,/data 不匹配
再比如 location = /abc,则只匹配/abc ,/abc/或 /abcd不匹配。若 location /abc,则即匹配/abc 、/abcd/ 同时也匹配 /abc/。
(2)location / {}
因为所有的地址都以 / 开头,所以这条规则将匹配到所有请求 比如访问 / 和 /data, 则 / 匹配, /data 也匹配,
但后面前缀路径会和最长字符串优先匹配(最长匹配)
(3)location /documents/ {}
匹配任何以 /documents/ 开头的地址,匹配符合以后,还要继续往下搜索其它 location
只有其它 location后面的前缀路径没有匹配到时,才会采用这一条
(4)location /documents/abc {}
匹配任何以 /documents/abc 开头的地址,匹配符合以后,还要继续往下搜索其它 location
只有其它 location后面的前缀路径没有匹配到时,才会采用这一条
(5)location ^~ /images/ {}
匹配任何以 /images/ 开头的地址,匹配符合以后,停止往下搜索正则,采用这一条
(6)location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {}
匹配所有以 gif、jpg或jpeg 结尾的请求
然而,所有请求 /images/ 下的图片会被 location ^~ /images/ 处理,因为 ^~ 的优先级更高,所以到达不了这一条正则
(7)location /images/abc {}
最长字符匹配到 /images/abc,优先级最低,继续往下搜索其它 location,会发现 ^~ 和 ~ 存在
(8)location ~ /images/abc {}
匹配以/images/abc 开头的,优先级次之,只有去掉 location ^~ /images/ 才会采用这一条
(9)location /images/abc/1.html {}
匹配/images/abc/1.html 文件,如果和正则location ~ /images/abc/1.html 相比,正则优先级更高
5.1只修改网页路径
systemctl start nginx
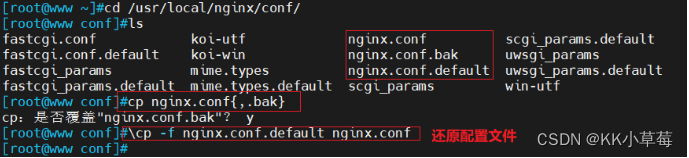
cp nginx.conf{,.bak}
\cp -f nginx.conf.default nginx.conf
#还原配置文件
#编写一个测试网页
cd /usr/local/nginx/html
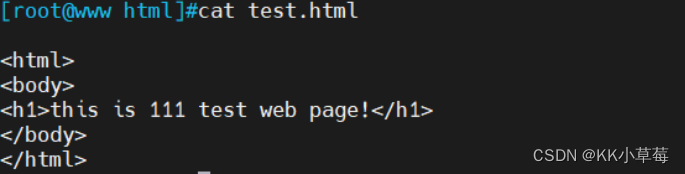
vim test.html
<html>
<body>
<h1>this is 111 test web page!</h1>
</body>
</html>
在浏览器访问
http://192.168.210.101/test.html
假如在nginx配置文件不做任何改动,要访问/abc/123/test.html这个路径的test.html页面,test.html应该放在哪个目录中?
cd /usr/local/nginx/html
#先在/usr/local/nginx/html目录下建一个abc/123文件
mkdir -p abc/123
#把html目录下的test.html文件移到html/abc/123目录下
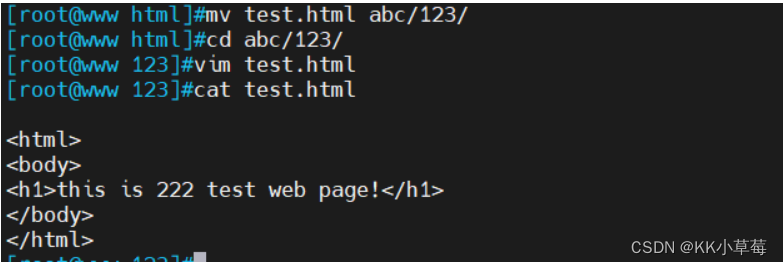
mv test.html abc/123/
#修改页面内容
vim test.html
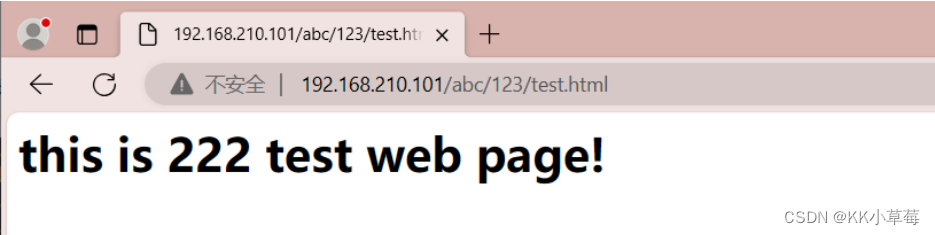
<h1>this is 222 test web page!</h1>
在浏览器访问
http://192.168.210.101/abc/123/test.html
5.2修改nginx配置文件和网页路径
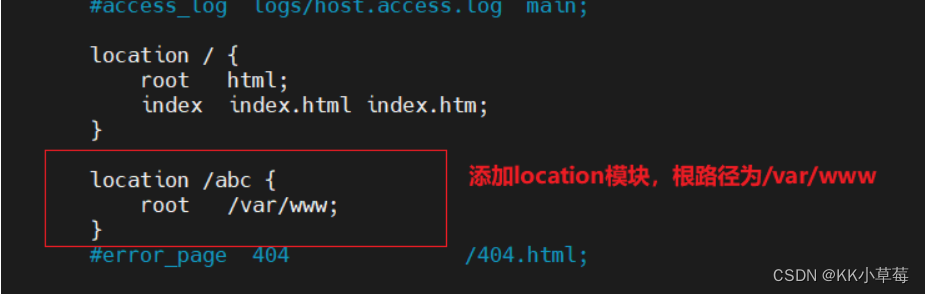
修改nginx配置文件,再访问test.html页面,test.html文件应该在哪个目录?
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server{
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /abc {
root /var/www;
}
}
systemctl restart nginx
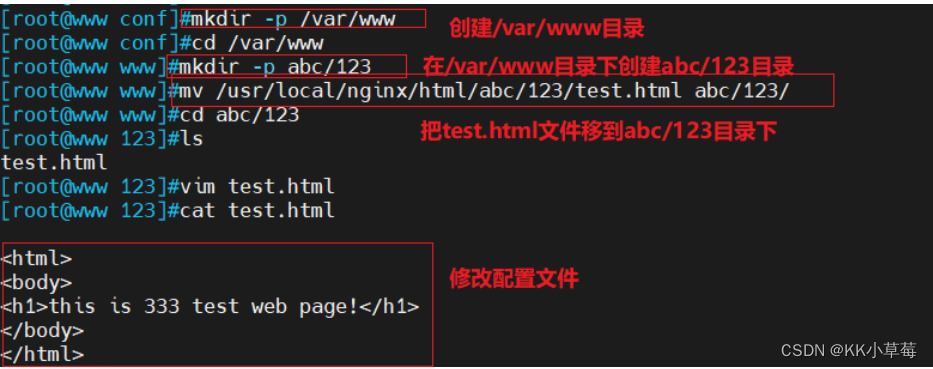
cd /usr/local/nginx/conf
#创建/var/www目录
mkdir -p /var/www
cd /var/www
#在/var/www目录下创建abc/123/目录
mkdir abc/123 -p
#把test.html文件移到abc/123/目录下
mv /usr/local/nginx/html/abc/123/test.html abc/123/
cd abc/123/
#修改test.html文件
vim test.html
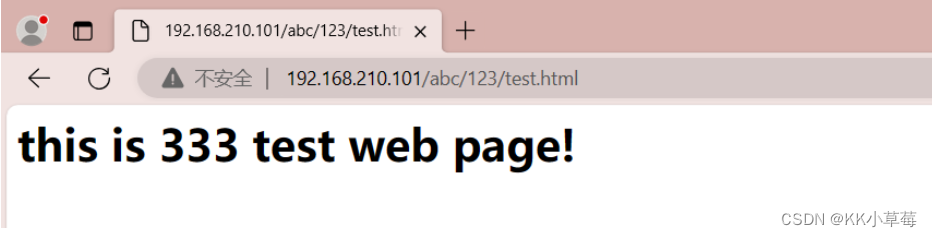
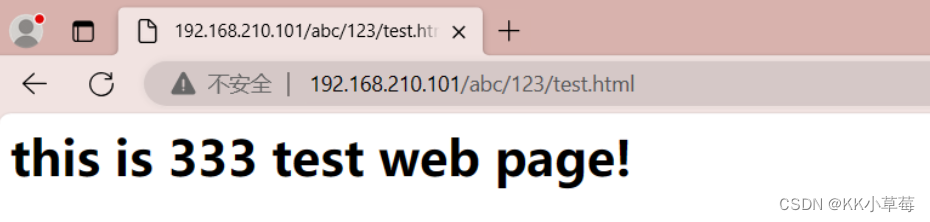
<h1>this is 333 test web page!</h1>
在浏览器访问
http://192.168.210.101/abc/123/test.html
5.3一般前缀
#一般前缀匹配,取最长匹配的location
#修改nginx配置文件
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server{
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /abc {
root /var/www;
}
location /abc/123 {
root /var/wyx;
}
}
systemctl restart nginx
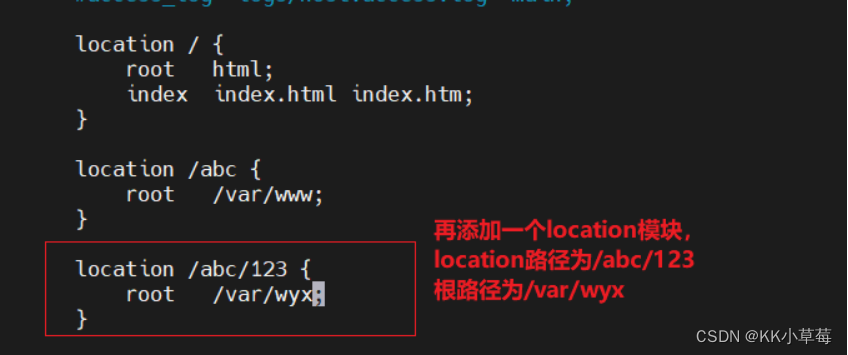
再次访问http://192.168.210.101/abc/123/test.html这个路径会匹配到哪一个?
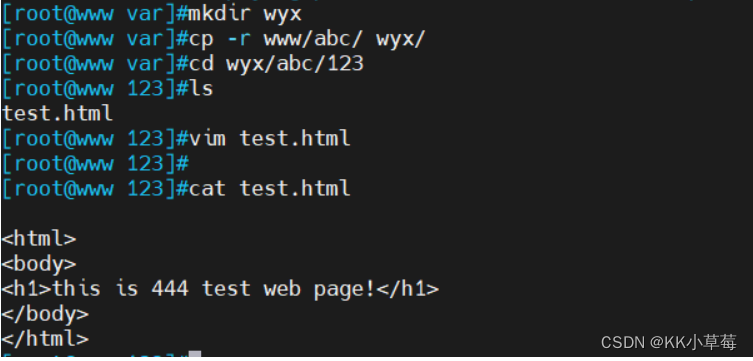
#在var目录下创建wyx文件
mkdir /var/wyx
cd /var/
#把/var/www/abc/复制到wyx目录下
cp -r www/abc/ wyx/
cd /wyx/abc/123/
#修改test.html文件
vim test.html
<h1>this is 444 test web page1</h1>
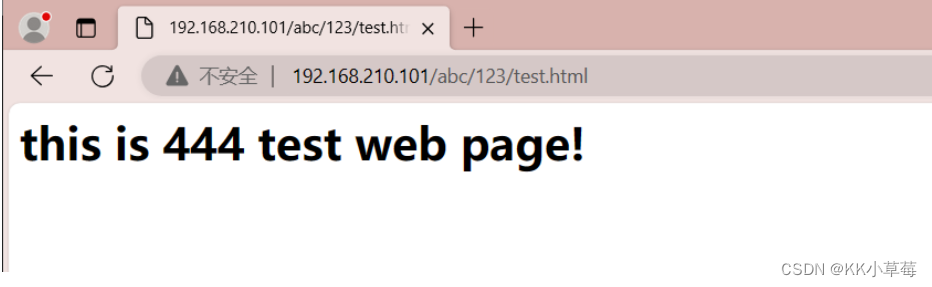
在浏览器访问
http://192.168.210.101/abc/123/test.html
5.4正则匹配
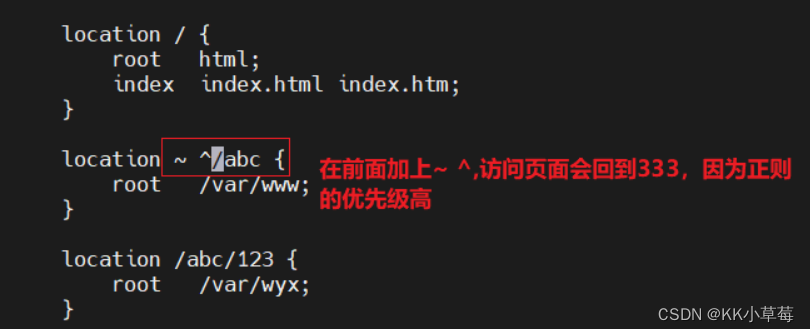
#正则匹配
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server{
location ~ ^/abc { #如果加上~ ^,访问页面会回到333页面,因为正则的优先级高
root /var/www;
}
}
systemctl restart nginx
在浏览器访问
http://192.168.210.101/abc/123/test.html
#正则匹配按顺序匹配
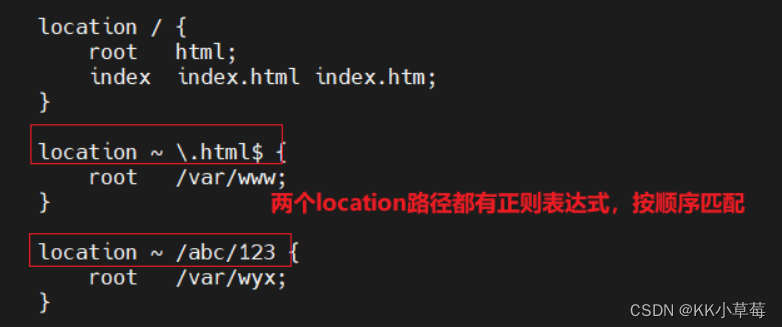
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server{
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#匹配以.html结尾的路径
location ~ \.html$ {
root /var/www;
}
location ~ /abc/123 {
root /var/wyx;
}
}
systemctl restart nginx
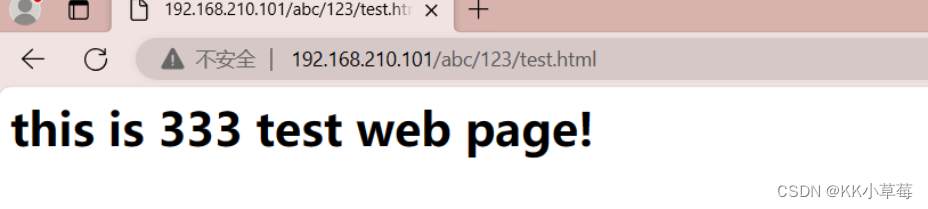
在浏览器访问http://192.168.210.101/abc/123/test.html
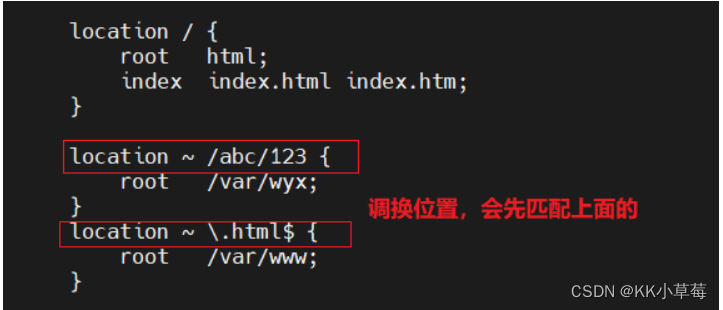
server{
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ /abc/123 {
root /var/wyx;
}
location ~ \.html$ {
root /var/www;
}
}
systemctl restart nginx
在浏览器访问http://192.168.210.101/abc/123/test.html
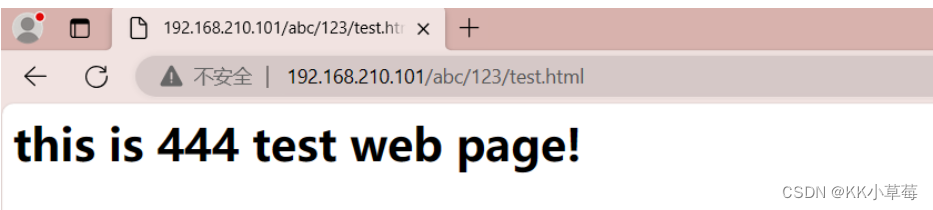
5.5前缀匹配
#前缀匹配
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server{
location ~ ^/abc {
root /var/www;
}
#加上^~,访问页面又会回到444页面,因为前缀^~的优先级大于正则~
location ^~ /abc/123 {
root /var/wyx;
}
}
systemctl restart nginx
在浏览器访问http://192.168.210.101/abc/123/test.html
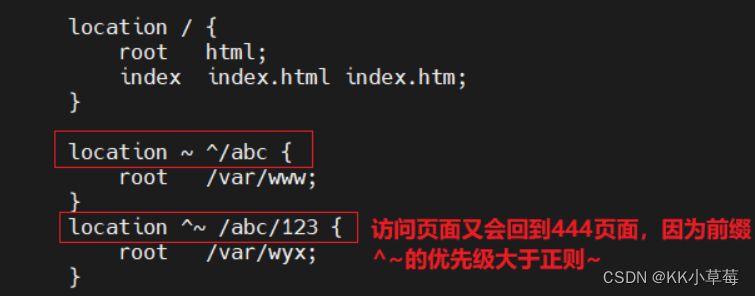

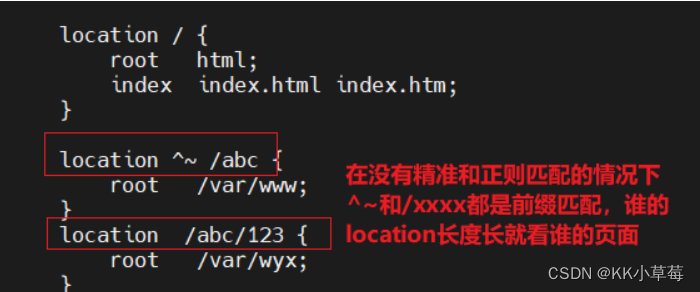
#在没有精准和正则匹配的情况下,^~和/XXXX都是前缀匹配,谁的长度长就看谁的页面
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server{
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location ^~ /abc {
root /var/www;
}
#/abc/123的长度长,所以还是匹配444页面
location /abc/123 {
root /var/wyx;
}
}
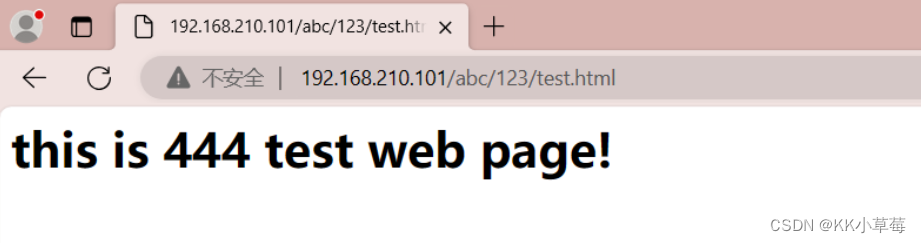
在浏览器访问http://192.168.210.101/abc/123/test.html
5.6精准匹配
#精准匹配
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server{
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~ ^/abc {
root /var/www;
}
location ^~ /abc/123 {
root /var/wyx;
}
#精准匹配优先级最高
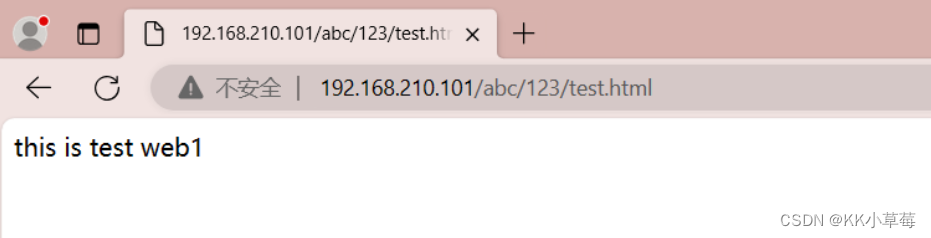
location = /abc/123/test.html {
root html;
}
}
systemctl restart nginx
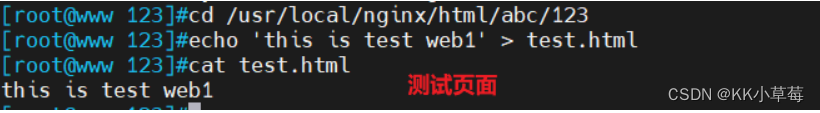
#编写精准匹配的测试页面
cd /usr/local/nginx/html/abc/123
echo 'this is test web1' > test.html
在浏览器访问http://192.168.210.101/abc/123/test.html
5.7通用匹配
#通用匹配
#编写通用匹配测试页面
cd /usr/local/nginx/html
mkdir data
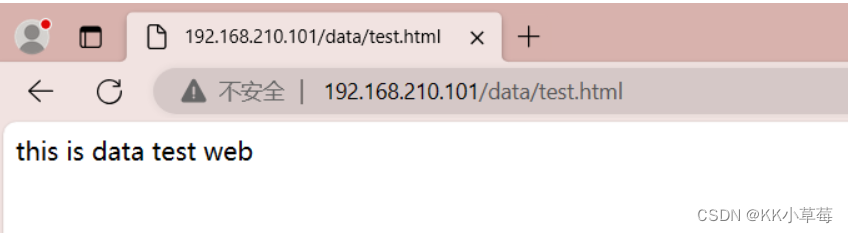
echo 'this is data test web' > data/test.html
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
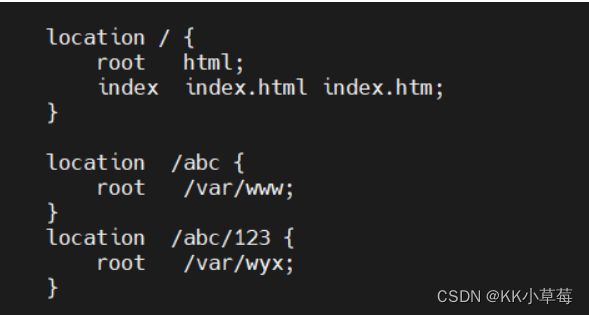
server{
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /abc {
root /var/www;
}
location /abc/123 {
root /var/wyx;
}
}
systemctl restart nginx
在浏览器中访问http://192.168.210.101/data/test.html
二、rewrite地址重写
rewrite功能就是,使用nginx提供的全局变量或自己设置的变量,结合正则表达式和标记位实现URL重写以及重定向。
比如:更换域名后需要保持旧的域名能跳转到新的域名上、某网页发生改变需要跳转到新的页面、网站防盗链等等需求。
rewrite只能放在server{},location{},if{}中,并且默认只能对域名后边的除去传递的参数外的字符串起作用,
例如 http://www.kgc.com/abc/bbs/index.php?a=1&b=2 只对/abc/bbs/index.php重写。
1、rewrite跳转实现
①Nginx:通过ngx_http_rewrite_module 模块支持URL重写、支持if条件判断,但不支持else
②跳转:从一个 location跳转到另一个location,循环最多可以执行10次,超过后nginx将返回500错误
③PCRE支持:perl兼容正则表达式的语法规则匹配
④重写模块 set 指令:创建新的变量并设其值
2、rewrite 执行顺序
(1) 执行 server 块里面的 rewrite 指令。
(2) 执行 location 匹配。
(3) 执行选定的 location 中的 rewrite 指令。
3、rewrite语法格式
语法格式:rewrite <regex> <replacement> [flag];
regex :表示正则匹配规则。
replacement :表示跳转后的内容。
flag :表示 rewrite 支持的 flag 标记。
###flag标记说明###
last :本条规则匹配完成后,不终止重写后的url匹配,一般用在 server 和 if 中。
break :本条规则匹配完成即终止,终止重写后的url匹配,一般使用在 location 中。
redirect :返回302临时重定向,浏览器地址会显示跳转后的URL地址。
permanent :返回301永久重定向,浏览器地址栏会显示跳转后的URL地址。
4、rewrite实例
4.1 基于域名的跳转
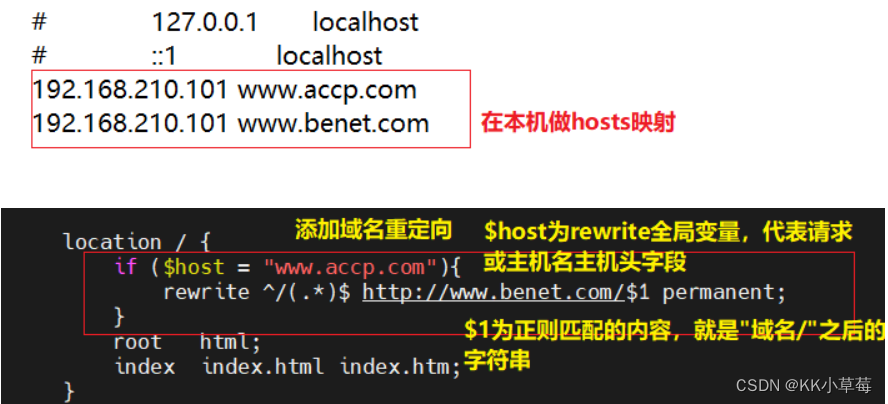
现在公司旧域名www.kgc.com有业务需求变更,需要使用新域名www.benet.com代替,但是旧域名不能废除,需要跳转到新域名上,而且后面的参数保持不变。
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
location / {
#添加域名重定向
if ($host = "www.accp.com"){ #$host为rewrite全局变量,代表请求主机头字段或主机名
rewrite ^/(.*)$ http://www.benet.com/$1 permanent; #$1为正则匹配的内容,即“域名/”之后的字符串
}
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
#在本机添加域名解析
192.168.210.101 www.accp.com
192.168.210.101 www.benet.com
systemctl restart nginx
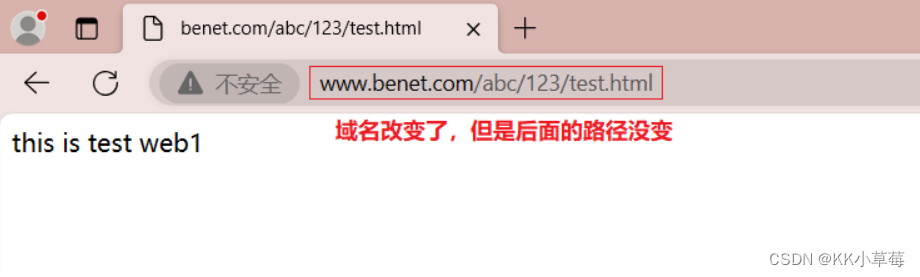
浏览器输入模拟访问 http://www.accp.com/abc/123/test.html
.html(虽然这个请求内容是不存在的)
会跳转到www.benet.com/abc/123/test.html,查看元素可以看到返回301,实现了永久重定向跳转,而且域名后的参数也正常跳转。
4.2基于客户端 IP 访问跳转
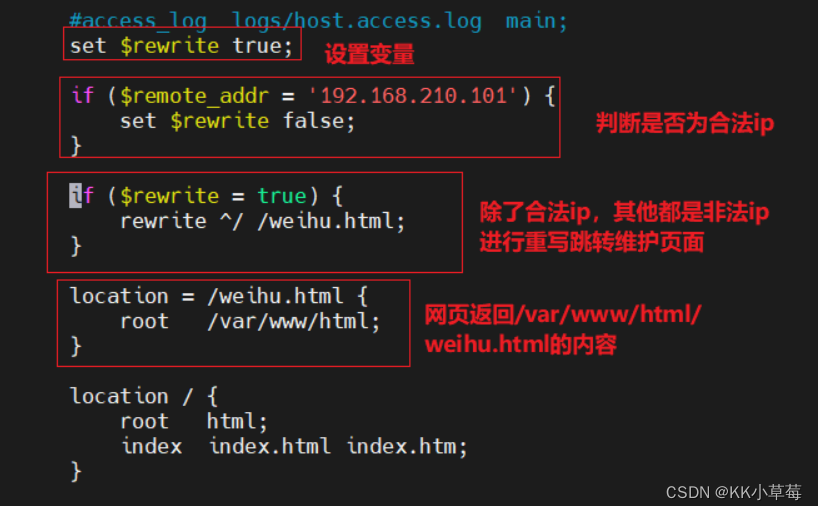
今天公司业务新版本上线,要求所有 IP 访问任何内容都显示一个固定维护页面,只有公司 IP :192.168.210.101访问正常。
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
#设置是否合法的IP标记
set $rewrite true; #设置变量$rewrite,变量值为boole值true
#判断是否为合法IP
if ($remote_addr = "192.168.210.101"){
#当客户端IP为192.168.210.101时,将变量值设为false,不进行重写
set $rewrite false;
}
#所有主机可以访问
#if ($remote_addr = "192.168.210.1"){
# set $rewrite false;
#}
#除了合法IP,其它都是非法IP,进行重写跳转维护页面
if ($rewrite = true){
#当变量值为true时,进行重写
rewrite ^/ /weihu.html;
#将域名后边的路径重写成/weihu.html后转发,例如www.kgc.com/weihu.html
}
location = /weihu.html {
root /var/www/html;
#网页返回/var/www/html/weihu.html的内容
}
#创建/var/www/html/
mkdir -p /var/www/html/
#编写测试页面
echo '<h1>We are maintaining now!</h1>' > /var/www/html/weihu.html
#在本机做域名解析
echo '192.168.210.101 www.accp.com www.benet.com' > /etc/hosts
nginx -t
systemctl restart nginx
再开一台主机
vim /etc/hosts
192.168.210.101 www.accp.com
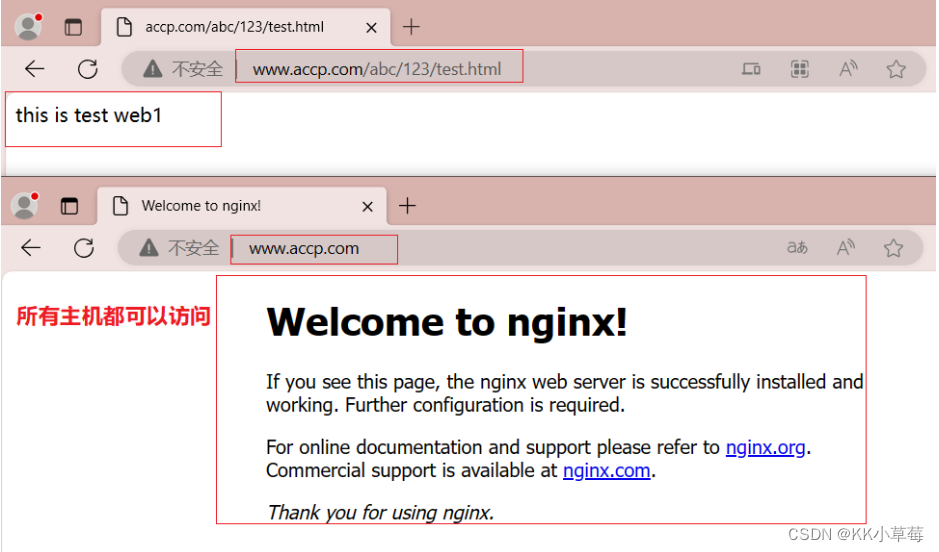
在内置浏览器测试:http://www.accp.com

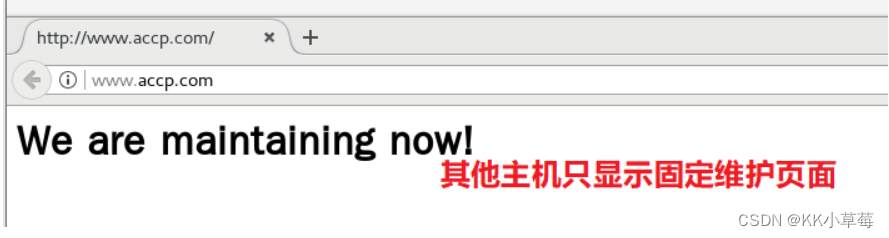
本机访问:curl http://www.accp.com
curl http://www.accp.com/abc/123/test.html
只有 IP 为 192.168.210.101 能正常访问,其它地址都是维护页面
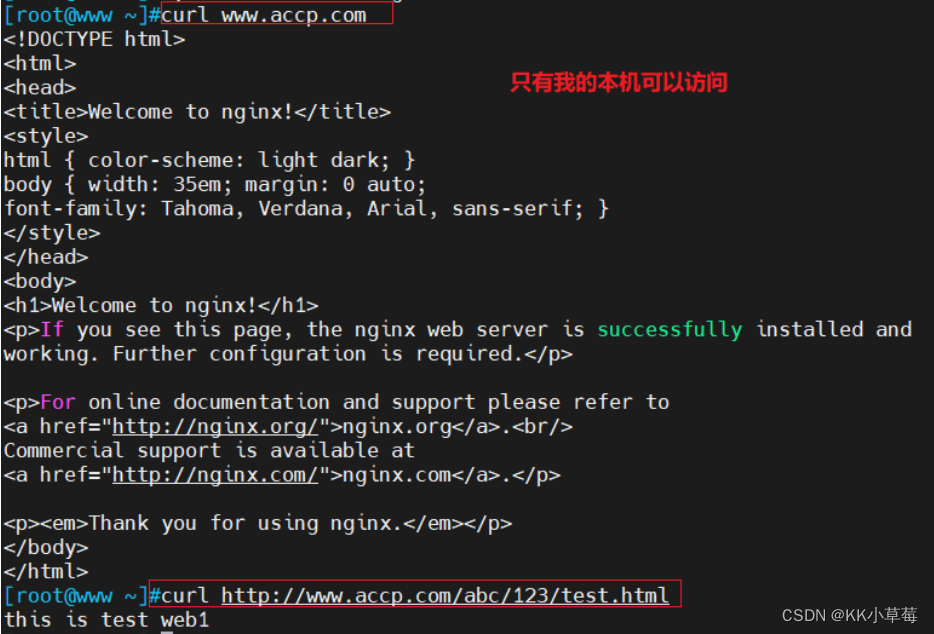
server {
set $rewrite true;
if ($remote_addr = "192.168.210.101"){
set $rewrite false;
}
#所有主机可以访问
if ($remote_addr = "192.168.210.1"){
set $rewrite false;
}
if ($rewrite = true){
rewrite ^/ /weihu.html;
}
4.3基于旧域名跳转到新域名后面加目录
现在访问的是 http://nba.accp.com/jordan/test.html,现在需要将这个域名下面的访问都跳转到http://www.accp.com/nba/jordan/test.html
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
#添加
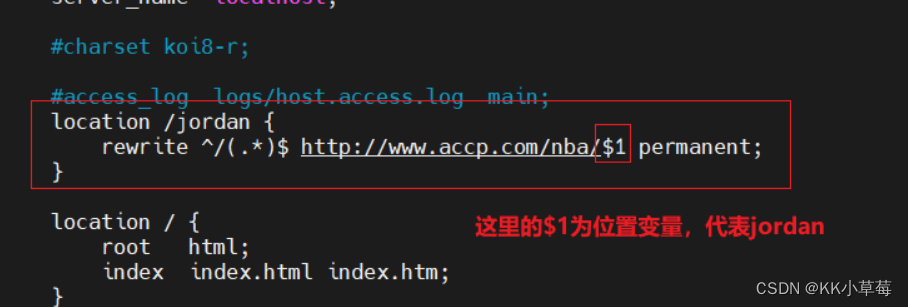
location /jordan {
rewrite ^/(.*)$ http://www.accp.com/nba/$1 permanent; #这里的$1为位置变量,代表/jordan
}
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
nginx -t
systemctl restart nginx
#在本地添加hosts域名解析
192.168.210.101 nba.accp.com
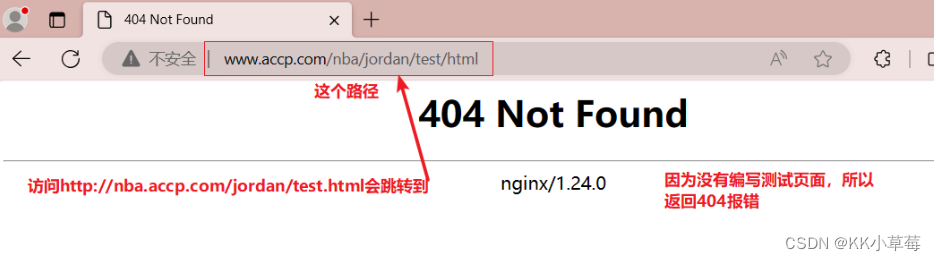
在浏览器访问 http://nba.accp.com/jordan/test.html会跳转到http://www.accp.com/jordan/test/html
4.4基于参数匹配的跳转
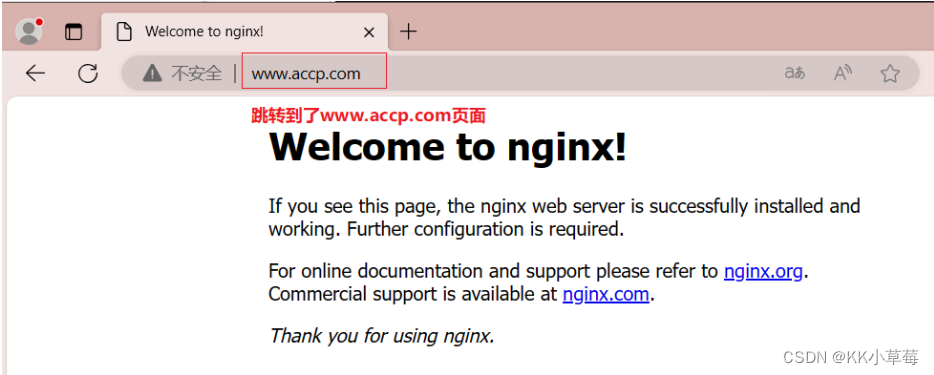
现在访问http://www.accp.com/100-(100|200)-100.html 跳转到http://www.accp.com页面。
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
location ~ ^/100-(100|200)-100.html$ {
rewrite ^/ http://www.accp.com permanent;
}
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.html;
}
}
nginx -t
systemctl restart nginx
使用浏览器访问 http://www.accp.com/100-200-100.html 或 http://www.accp.com/100-100-100.html 跳转到http://www.accp.com页面。
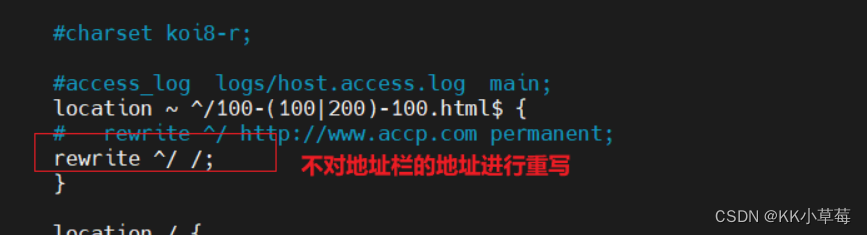
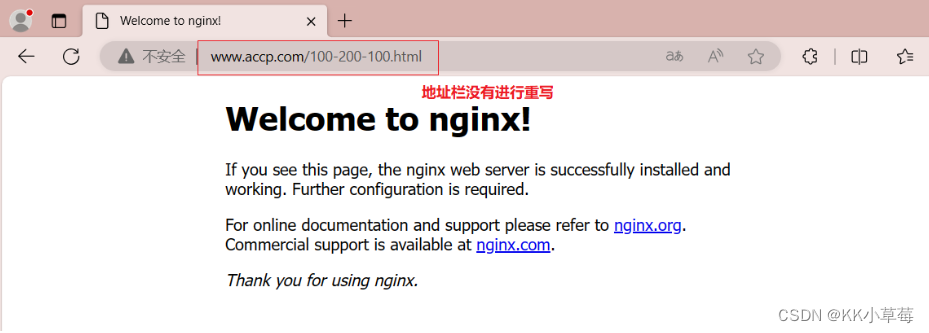
#不把地址栏的地址进行重写
server {
location ~ ^/100-(100|200)-100.html$ {
#rewrite ^/ http://www.accp.com permanent;
rewrite ^/ /;
}
nginx -t
systemctl restart nginx
使用浏览器访问 http://www.accp.com/100-200-100.html
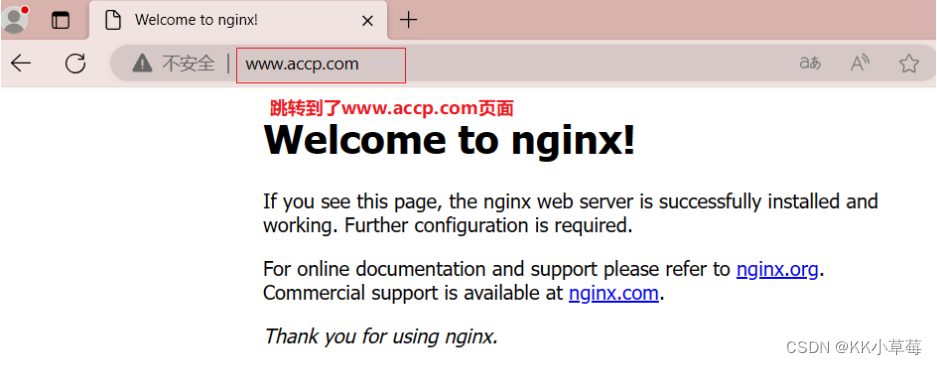
4.5基于目录下所有 php 结尾的文件跳转
要求访问 http://www.accp.com/discuz/XXX.php 跳转到http://www.accp.com。
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
location ~ ^/discuz/.*\.php$ {
rewrite ^/ http://www.accp.com permanent;
}
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
nginx -t
systemctl restart nginx
浏览器访问 http://www.accp.com/discuz/index.php 跳转到http://www.accp.com页面。
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 2023年全国职业院校技能大赛软件测试赛题—单元测试卷④
- 查看自己超算账号上剩余储存空间教程
- Sepolia 和 Holesky 测试网对比
- C++从零基础到入门(2)—— (if、switch、for、while语句)
- Harmony全局应用生命周期 EntryAbility.ts 讲解
- Vue学习笔记10--路由1(概念、基本使用、多级路由)
- 列出系统硬件信息的lshw
- 使用git工具把项目文件上传到github 的操作
- PSoc62?开发板之ADC读取电压
- JVM内存结构