Ansible中角色的使用
本章主要介绍ansible中角色的使用
- 了解什么是角色
- 独立地写一个角色
- 使用角色
- 系统自带角色的使用
1.1 了解角色
正常情况下,配置一个服务如 apache时,要做一系列的操作:安装、拷贝、启动服务等。如果要在不同的机器上重复配置此服务,需要重新执行这些操作
为了简化这些重复劳动,可以把安装、拷贝、启动服务等操作打包成一个整体,这个整体称为角色,如图

如果想在其他机器上安装并配置apache,只要调用此角色即可,这样就可以实现一次劳动、永久回报的效果
一个角色本质上就是一个文件夹,此文件夹名就是角色名,此文件夹中包含许多文件,有的是用于执行各种模块的文件,有的是用于拷贝到被管理主机的jinj2模板文件,有的是定义的变量文件
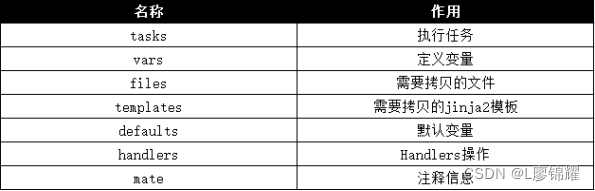
为了防止文件太多太乱,在此角色的文件夹中再创建一个个的子目录,用于存放不同的文件。例如,jinja2模板放在templates目录中,普通的文件放在files目录中,变量文件放在vars目录中,执行模块的各个task放在tasks目录中等。角色目录中每个子目录的作用总结如表
所有的角色都放在一个目录中等待被调用,默认目录为ansible.cfg所在目录的roles目录, 如果要修改路径可以在ansible.cfg中用roles path选项指定
本章实验都在demo5下操作,先把demo5目录创建出来并把 ansible.cfg 和hosts铂贝进去
[jin@rhel801 ~]$ cd demo5/
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ ls
ansible.cfg hosts
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$修改ansible.cfg,添加 roles path = ./roles
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ cat ansible.cfg
[defaults]
inventory = ./hosts
roles_path = ./roles
[privilege_escalation]
become=True
become_method=sudo
become_user=root
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$1.2 手把手创建一个角色
创建一个名称为apache的角色,命令如下
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ ansible-galaxy init roles/apache
- Role roles/apache was created successfully
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ ls roles/
apache
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$这里apache就是一个角色,看一下apache 中的内容
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ ls roles/apache/
defaults files handlers meta README.md tasks templates tests vars
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$里面有不少目录,如前面介绍的,这些目录分别用于存放不同的文件。回顾在 demo4目 录中写好的hand-1.yml的内容
[jin@rhel801 demo4]$ cat hand-1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
vars:
myport: 808
tasks:
- name: task1安装httpd
yum: name=httpd state=installed
- name: task2拷贝配置文件
template: src=httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: restart httpd1
- name: task3启动httpd服务
service: name=httpd state=restarted
handlers:
- name: restart httpd1
service: name=httpd state=restarted
- name: restart httpd2
service: name=httpd state=restarted
[jin@rhel801 demo4]$这个文件中包含了以下内容
(1)vars中是定义变量的
(2)tasks中的代码是正常要执行的
(3)handler中的代码是被触发才会执行的
(4)httpd.conf.j2是被引用的jinja2模板
下面把这个YAML文件中的内容拆分放在apache角色的不同目录中,把 tasks下的代码放在tasks目录中,把 handlers下的代码放在handlers目录中等
把 tasks的内容写入roles/apache/tasks/main.yml 中
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ cat roles/apache/tasks/main.yml
---
# tasks file for roles/apache
- name: task1安装httpd
yum: name=httpd state=installed
- name: task2拷贝配置文件
template: src=httpd.conf.j2 dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: restart httpd1
- name: task3启动httpd服务
service: name=httpd state=started
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$把 handlers 的内容写入roles/apache/handlers/main.yml 中,内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ cat roles/apache/handlers/main.yml
---
# handlers file for roles/apache
- name: restart httpd1
service: name=httpd state=restarted
- name: restart httpd2
service: name=httpd state=restarted
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$在roles/apache/tasks/main.yml 中,template模块拷贝的文件 http.conf.j2所在的目录是roles!apache/templates,所以先把需要的 httod.conf.i2拷贝到 roles/apache/templates中
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ cp ../demo4/httpd.conf.j2 roles/apache/templates/
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ ls roles/apache/templates/
httpd.conf.j2
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$把变量myport写入roles/apache/vars/main.yml中
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ cat roles/apache/vars/main.yml
---
# vars file for roles/apache
myport: 8080
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$这里把myport的值改为8080,原来的值为808,会使httpd.conf.j2中的端口发生变化,从而会触发handler
也可以不在roles/apache/vars/main.yml中定义变量,而是在playbook 中定义myport变量,如果在角色的vars 和 playbook 中都定义了myport变量,且变量的值不同,则角色的vars中定义的变量生效
面查看apache这个角色的结构
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ tree roles/apache/
roles/apache/
├── defaults
│?? └── main.yml
├── files
├── handlers
│?? └── main.yml
├── meta
│?? └── main.yml
├── README.md
├── tasks
│?? └── main.yml
├── templates
│?? └── httpd.conf.j2
├── tests
│?? ├── inventory
│?? └── test.yml
└── vars
└── main.yml
8 directories, 9 files
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ 这样apache这个角色我们就算是最终写好了
1.3 使用角色
角色写好之后,只要在playbook中直接调用即可,在playbook中的roles下调用,调用的语法如下
1 roles:
2 ‐ name: 名称1
3 role: rolesname1
4 ‐ name: 名称2
5 role: rolesname2
或
1 roles:
2 ‐ role: rolesname1
3 ‐ role: rolesname2下面写一个名称为test-role1.yml的 playbook,里面调用apache这个角色
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ cat test-role1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
roles:
- role: apache
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$运行此playbook
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ ansible-playbook test-role1.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [apache : task1安装httpd] ***************************************************
changed: [rhel802]
TASK [apache : task2拷贝配置文件] ****************************************************
changed: [rhel802]
TASK [apache : task3启动httpd服务] *************************************************
changed: [rhel802]
RUNNING HANDLER [apache : restart httpd1] **************************************
changed: [rhel802]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=5 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$这里是运行test-rolel vam1之后的完整结果,可以看到运行的结果与前面运行的结果一样。变量可以在角色的defaults. vars中定义,也可以在nlavbook中定义,优先级的顺序是: 角色的vars中定义的变量→playbook中定义的变量→角色的defaults 中定义的变量
所以,如果同一个变量同时在这三个地方被定义了,则角色的vars中定义的变量生效。先把在roles/apache/vars/main.yml中定义变量myport 的那行注释掉,这个变量将在 playbook中定义,如下所示
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ cat roles/apache/vars/main.yml
---
# vars file for roles/apache
#myport: 8080
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$修改test-tole1.yml的内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ cat test-role1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
vars:
myport: 8080
roles:
- role: apache
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ 运行此playbook
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ ansible-playbook test-role1.yml
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [apache : task1安装httpd] ***************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [apache : task2拷贝配置文件] ****************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
TASK [apache : task3启动httpd服务] *************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=4 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$到rhel802上验证 httpd 开启的端口是多少
[root@rhel802 jin]# netstat -ntulp | grep httpd
tcp6 0 0 :::8080 :::* LISTEN 5911/httpd
[root@rhel802 jin]#可以看到。httpd现在使用的端口是8080
1.4 系统自带的角色
除我们自己创建的角色外,系统中也包含了一些内置的角色
在rhel802上切换到root 用户,然后安装软件包rhel-system-roles.noarch,命令如下
[root@rhel801 ~]# yum -y install rhel-system-roles.noarch
正在更新 Subscription Management 软件仓库。
无法读取客户身份
本系统尚未在权利服务器中注册。可使用 subscription-manager 进行注册。
...输出信息...
已安装:
python3-jmespath-0.9.0-11.el8.noarch python3-netaddr-0.7.19-8.el8.noarch
rhel-system-roles-1.7.3-2.el8.noarch
完毕!
[root@rhel801 ~]#安装好这个软件包之后,在/usr/share/ansible/roles目录中会有许多角色,如图
[jin@rhel801 ~]$ ls /usr/share/ansible/roles/
linux-system-roles.certificate rhel-system-roles.certificate
linux-system-roles.crypto_policies rhel-system-roles.crypto_policies
linux-system-roles.ha_cluster rhel-system-roles.ha_cluster
linux-system-roles.kdump rhel-system-roles.kdump
linux-system-roles.kernel_settings rhel-system-roles.kernel_settings
linux-system-roles.logging rhel-system-roles.logging
linux-system-roles.metrics rhel-system-roles.metrics
linux-system-roles.nbde_client rhel-system-roles.nbde_client
linux-system-roles.nbde_server rhel-system-roles.nbde_server
linux-system-roles.network rhel-system-roles.network
linux-system-roles.postfix rhel-system-roles.postfix
linux-system-roles.selinux rhel-system-roles.selinux
linux-system-roles.ssh rhel-system-roles.ssh
linux-system-roles.sshd rhel-system-roles.sshd
linux-system-roles.storage rhel-system-roles.storage
linux-system-roles.timesync rhel-system-roles.timesync
linux-system-roles.tlog rhel-system-roles.tlog
linux-system-roles.vpn rhel-system-roles.vpn
[jin@rhel801 ~]$下面演示rhel-system-roles.selinux这个角色,使用lduan用户把rhel-system-roles.selinux拷贝到demo5下的roles目录中
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ cp -r /usr/share/ansible/roles/rhel-system-roles.selinux/ roles/
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ ls roles/
apache rhel-system-roles.selinux
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$前面在讲解handlers时,为httpd 配置了其他端口808,但是因为SELinux的问题,我们把 SELinux关闭了
[root@rhel802 jin]# getenforce
Permissive
[root@rhel802 jin]#可以看到,rhel802上 SELinux的模式是Permissive。下面我们利用角色rhel-system-roles.selinux把 rhel802上 SELinux的模式改为 Enforcing
查看角色rhel-system-roles.selinux中默认的变量
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ cat roles/rhel-system-roles.selinux/defaults/main.yml
---
selinux_state: null
selinux_policy: null其中第一个变量是selinux state,这个变量用于指定SELinux的模式,默认值设置为了null。可以在playbook中定义这个变量,覆盖这个默认的变量值
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ cat test-roles.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
vars:
selinux_state: enforcing
roles:
- role: rhel-system-roles.selinux
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$运行此playbook
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ ansible-playbook test-roles.yml
[WARNING]: Found variable using reserved name: roles
PLAY [rhel802] *****************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *********************************************************
ok: [rhel802]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
rhel802 : ok=1 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$到 rhel802上查看验证,命令如下
[root@rhel802 ~]# getenforce
Enforcing
[root@rhel802 ~]#1.5 修改端口上下文
在介绍handler 时,可以通过变量myport随意修改端口。但是端口上下文不对,httpd是启动不起来的,所以当初把 rhel802上的 SELinux 临时关闭了
下面介绍如何使用角色rhel-system-roles.selinux修改端口上下文
查看角色 rhel-system-roles.selinux中默认的变量
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ cat roles/rhel-system-roles.selinux/defaults/main.yml
---
selinux_state: null
selinux_policy: null
# Set up empty lists for SELinux changes.
selinux_booleans: []
selinux_fcontexts: []
selinux_logins: []
selinux_ports: []
selinux_restore_dirs: []
# Purging local modifications is disabled by default.
selinux_all_purge: no
selinux_booleans_purge: no
selinux_fcontexts_purge: no
selinux_ports_purge: no
selinux_logins_purge: no
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$这里变量selinux_ports是一个列表,里面的元素需要定义多个变量,但是变量名是什么我们现在还不清楚
用vim 编辑器打开roles/rhel-system-roles.selinux/tasks/main.yml,大概第116行是用于定义端口上下文的
114 - name: Set an SELinux label on a port
115 seport:
116 ports: "{{ item.ports }}"
117 proto: "{{ item.proto | default('tcp') }}"
118 setype: "{{ item.setype }}"
119 state: "{{ item.state | default('present') }}"
120 with_items: "{{ selinux_ports }}"
这里只截取了部分代码,可以看到循环列表selinux ports中的4个变量。其中 proto和 state有默认值,ports和setvpe没有默认值,所以我们在定义列表selinux ports时,至少要在列表的元素中定义ports和 setype这两个变量
修改test-role1.yml的内容如下
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ cat test-role1.yml
---
- hosts: rhel802
vars:
myport: 808
selinux_ports:
- ports: "{{myport}}"
setype: http_port_t
roles:
- role: apache
- role: rhel-system-roles.selinux
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$这里定义了一个变量myport的值为808,然后定义了一个列表selinux_ports。这个列表 中只有一个元素,元素中有两个变量ports和 setype。其中 ports这个变量引用myport 的 值,记得要用双引号引起来,setype的值被设置为了http_port_t
运行此 playbook
[jin@rhel801 demo5]$ ansible-playbook test-role1.yml 然后到rhel802上检查httpd所使用的端口
[root@rhel802 ~]# netstat -antp | grep httpd
tcp6 0 0 :::808 :::* LISTEN 3029/httpd
[root@rhel802 ~]#可以看到,httpd此时使用的端口是808
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 运维大模型探索之 Text2PromQL 问答机器人
- 阿里云环境搭建
- <JavaEE> TCP 的通信机制(六) -- 异常情况处理 和 总结
- Pandas实战100例 | 案例 2: 数据探索 - 查看和理解数据
- 【Proteus仿真】【Arduino单片机】汽车尾灯控制设计
- 系分笔记计算机系统之分区分页分段存储
- SpringBoot 单元测试用例怎么写
- 代码随想录算法训练营第四十三天 | 1049. 最后一块石头的重量 II、494. 目标和、474.一和零
- python_将二维列表写入excel
- 紧跟国际潮流,勇探未知领域