【vue3】-
发布时间:2024年01月02日
创建vue3工程
在终端输入以下命令,根据自己的需求做出相应的选择:
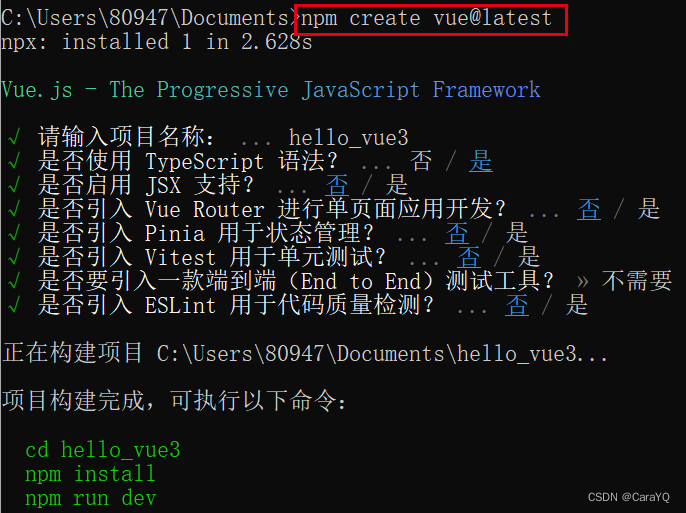
生成的项目文件作用:
extensions.json:插件
favicon.ico:页签图标
env.d.ts:ts不认识.css .html .txt .js……文件,这个文件里面指定的vite/client中就是让ts认识这些文件
index.html:入口文件
vite.config.ts:TS的配置文件
setup概述
setup()在beforecreate()前被执行
<template>
<h1>一个人的信息</h1>
<h2>姓名:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{age}}</h2>
<h2>性别:{{sex}}</h2>
<!-- vue2和vue3中的配置冲突时,以vue3为主 -->
<h2>a的值是:{{a}}</h2>
<button @click="sayHello">说话(Vue3所配置的——sayHello)</button>
<br>
<br>
<button @click="sayWelcome">说话(Vue2所配置的——sayWelcome)</button>
<br>
<br>
<button @click="test1">测试一下在Vue2的配置中去读取Vue3中的数据、方法</button>
<br>
<br>
<button @click="test2">测试一下在Vue3的setup配置中去读取Vue2中的数据、方法</button>
</template>
<script>
// import {h} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
//vue2的配置方法也可以用,vue3向下兼容
data() {
return {
sex:'男',
a:100
}
},
methods: {
sayWelcome(){
alert('欢迎来到尚硅谷学习')
},
//vue2中可以读取vue3中的配置
test1(){
console.log(this.sex)
console.log(this.name)
console.log(this.age)
console.log(this.sayHello)
}
},
//此处只是测试一下setup,暂时不考虑响应式的问题。
setup(){
//数据
let name = '张三'
let age = 18
let a = 200
//方法
function sayHello(){
alert(`我叫${name},我${age}岁了,你好啊!`)
}
function test2(){
console.log(name)
console.log(age)
console.log(sayHello)
//vue3中读不出来vue2的配置,建议这两个版本的配置不要混用
console.log(this.sex)
console.log(this.sayWelcome)
}
//返回一个对象(常用)
return {
name,
age,
sayHello,
test2,
a
}
//返回一个函数(渲染函数)
/*
渲染函数:要返回h函数的返回值
h('要把什么元素放到页面','标签体内容')
你模板中写的啥已经不重要了,页面展示以渲染函数为主
*/
// return ()=> h('h1','尚硅谷')
// 把你想展示的内容直接展示返回出去,你模板中写的啥已经不重要了,页面展示以渲染函数为主
// return ()=> '尚硅谷'
}
}
</script>
setup的语法糖
setup()每次都要返回一个对象才能让
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/CaraYQ/article/details/135342279
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- java大文件分块处理
- 《WebKit 技术内幕》之六(2): CSS解释器和样式布局
- 微信公众号多域名回调系统PHP源码,支持企业微信和消息事件转发,附安装教程
- 变分贝叶斯估计:Wishart分布
- 安卓RecyclerView组件实现分页展示数据效果
- 005、Softmax损失
- 农贸产品交易系统(JSP+java+springmvc+mysql+MyBatis)
- BUUCTF--ciscn_2019_s_31
- 力扣labuladong——一刷day75
- 蓝桥杯算法课【算法很美~位运算的妙用 2】学习记录