java并发编程
发布时间:2024年01月14日
一、java线程
1.三种创建线程的方式
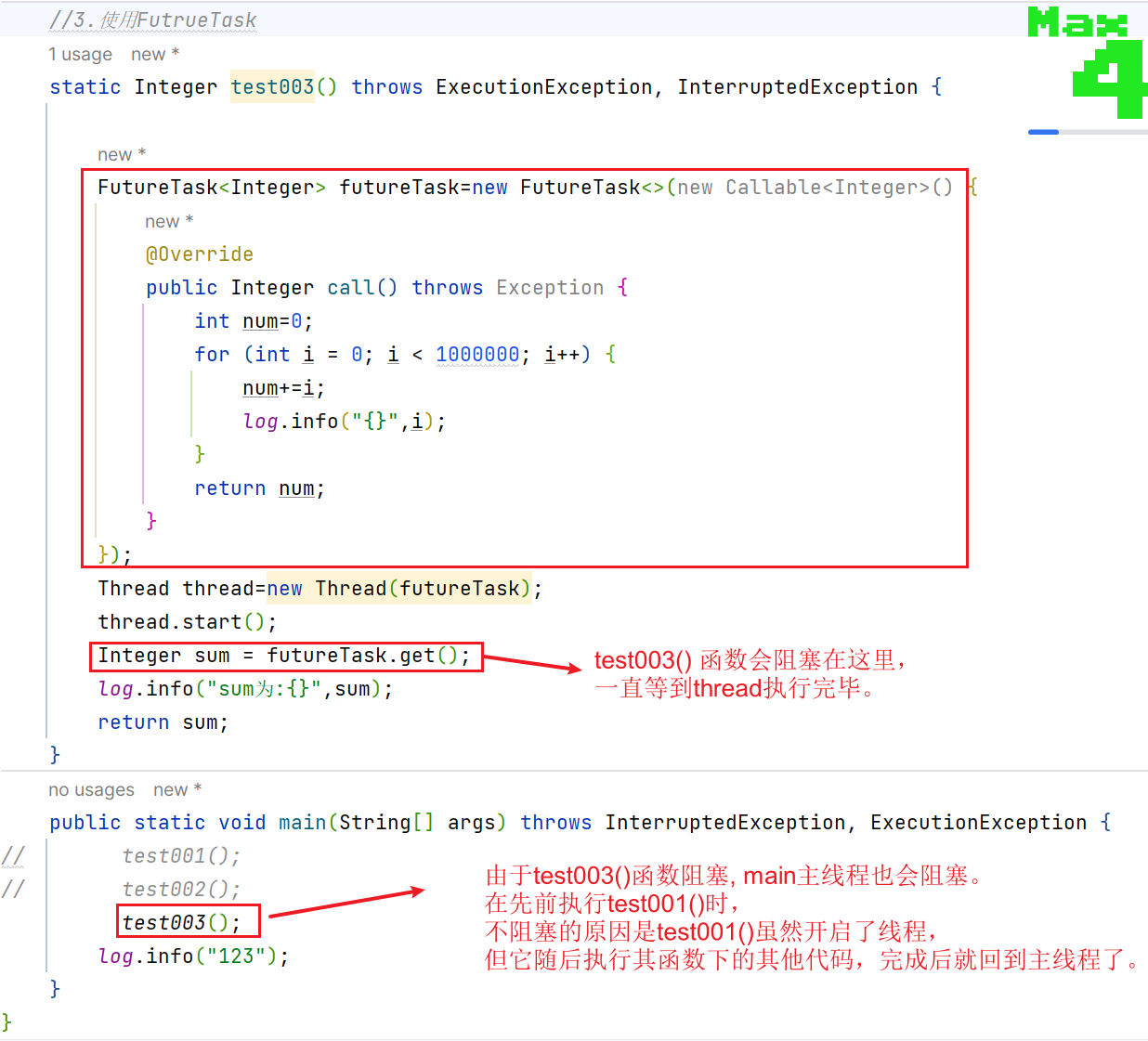
Integer sum = futureTask.get(); 会等待其对应的线程执行完 ,即阻塞 再获得结果。
所以我在测试时,出现一个小插曲
@Slf4j
public class ThreeWays {
//1.自定义MyThread进行继承Thread
static void test001(){
Thread thread = new MyThread();
thread.setName("t1");
thread.start();
}
//2.实现Runnable接口
static void test002(){
Thread thread=new Thread(()-> {
for (int i = 0; i <1000 ; i++) {
log.info("{}",i);
}
});
thread.setName("t2");
thread.start();
}
//3.实现
static Integer test003() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask=new FutureTask<>(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
int num=0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
num+=i;
log.info("{}",i);
}
return num;
}
});
Thread thread=new Thread(futureTask);
thread.start();
Integer sum = futureTask.get();
log.info("sum为:{}",sum);
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
// test001();
// test002();
test003();
log.info("123");
}
}
2. Thread跟Runable的关系
当使用Runable作为参数时 ,即 new Thread( runnable )
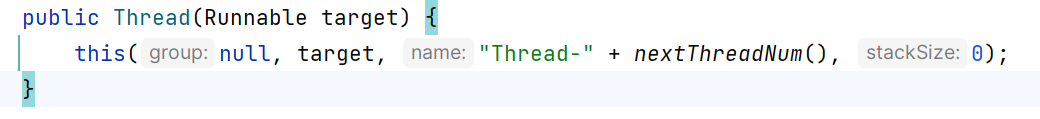
把runnable 赋给 target
![]()
再运行时,去判断,究竟是否调用 targert.run()

2.linux查看线程信息
文章来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_64071349/article/details/135585821
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。 如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系我的编程经验分享网邮箱:chenni525@qq.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!
最新文章
- Python教程
- 深入理解 MySQL 中的 HAVING 关键字和聚合函数
- Qt之QChar编码(1)
- MyBatis入门基础篇
- 用Python脚本实现FFmpeg批量转换
- 2024在视频号开店怎么样?平台现状如下,有电商经验者优先!
- 在系统性学习Linux系统之前,你需要了解一下这些东西
- 【MySQL】 字符集排序规则(字符集校验规则)命名格式
- Composer之 找不到扩展类
- K8S POD
- 适用于 Windows 的 12 款最佳 PDF 编辑器
- 遥感图像分割系统:融合空间金字塔池化(FocalModulation)改进YOLOv8
- 三菱PLC限幅器功能块(内嵌ST代码)
- Grafana(三)Grafana 免密登录-隐藏导航栏-主题变换
- 2.1-学成在线内容管理之课程查询